These are all from the test bank for the textbook.
What causes the rapid change in the resting membrane potential to initiate an action potential?
a. Potassium gates open, and potassium rushes into the cell, changing t
...
These are all from the test bank for the textbook.
What causes the rapid change in the resting membrane potential to initiate an action potential?
a. Potassium gates open, and potassium rushes into the cell, changing the membrane potential from
negative to positive.
b. Sodium gates open, and sodium rushes into the cell, changing the membrane potential from negative
to positive.
c. Sodium gates close, allowing potassium into the cell to change the membrane potential from positive
to negative.
d. Potassium gates close, allowing sodium into the cell to change the membrane potential from positive
to negative.
What is a consequence of leakage of lysosomal enzymes during chemical injury?
a. Enzymatic digestion of the nucleus and nucleolus occurs, halting DNA synthesis.
b. Influx of potassium ions into the mitochondria occurs, halting the ATP production.
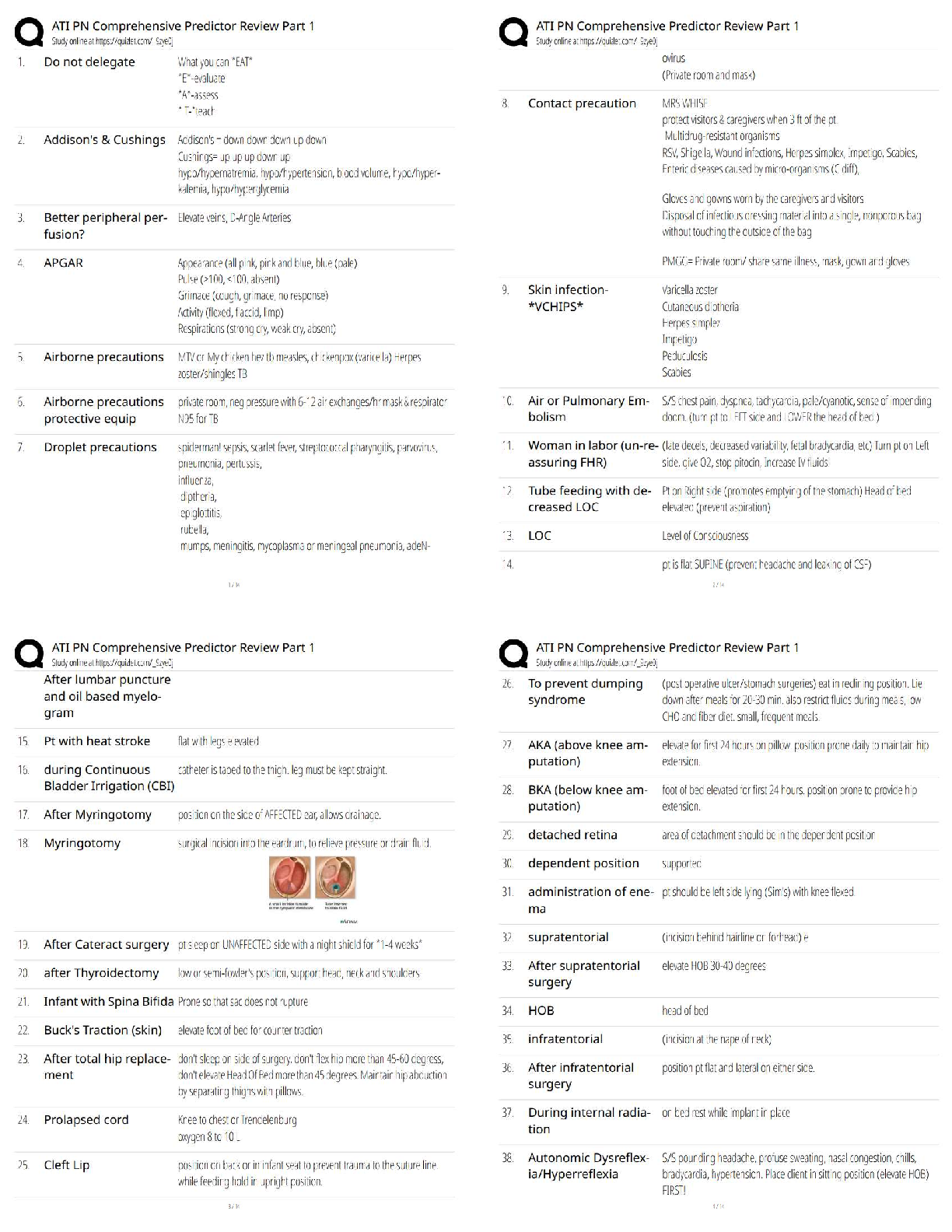
c. Edema of the Golgi body occurs, preventing the transport of proteins out of the cell.
d. Shift of calcium out of the plasma membrane occurs, destroying the cytoskeleton.
In hypoxic injury, sodium enters the cell and causes swelling because:
a. The cell membrane permeability increases for sodium during periods of hypoxia.
b. ATP is insufficient to maintain the pump that keeps sodium out of the cell.
c. The lactic acid produced by the hypoxia binds with sodium in the cell.
d. Sodium cannot be transported to the cell membrane during hypoxia.
What mechanisms occur in the liver cells as a result of lipid accumulation?
a. Accumulation of lipids that obstruct the common bile duct, preventing flow of bile
from the liver to the gallbladder
b. Increased synthesis of triglycerides from fatty acids and decreased synthesis of apoproteins
c. Increased binding of lipids with apoproteins to form lipoproteins
d. Increased conversion of fatty acids to phospholipids
During an IgE-mediated hypersensitivity reaction, the degranulation of mast cells is a result of which
receptor action?
a. Histamine bound to H2
b. Chemotactic factor binding to the receptor
c. Epinephrine bound to mast cells
d. Acetylcholine bound to mast cells
What is the mechanism that results in type II hypersensitivity reactions?
a. Antibodies coat mast cells by binding to receptors that signal its degranulation, followed by a
discharge of preformed mediators.
b. Antibodies bind to soluble antigens that were released into body fluids, and the immune complexes
are then deposited in the tissues.
c. Cytotoxic T lymphocytes or lymphokine-producing helper T 1 cells directly attack and destroy cellular
targets.
d. Antibodies bind to the antigens on the cell surface
Type III hypersensitivity reactions are a result of which of the following?
a. Antibodies coating mast cells by binding to receptors that signal its degranulation, followed by the
discharge of preformed mediators
b. Antibodies binding to soluble antigens that were released into body fluids and the immune complexes
being deposited in the tissues
c. Tc cells or lymphokine-producing Th1 cells directly attacking and destroying cellular targets
d. Antibodies binding to the antigen on the cell surface.
Tissue damage caused by the deposition of circulating immune complexes containing an antibody
against the host DNA is the cause of which disease?
a. Hemolytic anemia
b. Pernicious anemia
c. Systemic lupus erythematosus
d. Myasthenia gravis
Why does tissue damage occurs in acute rejection after organ transplantation?
a. Th1 cells release cytokines that activate infiltrating macrophages, and cytotoxic T cells directly attack
the endothelial cells of the transplanted tissue.
b. Circulating immune complexes are deposited in the endothelial cells of transplanted tissue, where the
complement cascade lyses tissue.
c. Receptors on natural killer cells recognize antigens on the cell surface of transplanted tissue, which
releases lysosomal enzymes that destroy tissue.
d. Antibodies coat the surface of transplanted tissue to which mast cells bind and liberate preformed
chemical mediators that destroy tissue.
Oncogenes are genes that are capable of:
a. Undergoing mutation that directs the synthesis of proteins to accelerate the rate of tissue proliferation
b. Directing synthesis of proteins to regulate growth and to provide necessary replacement of tissue
c. Encoding proteins that negatively regulate the synthesis of proteins to slow or halt the replacement of
tissue
d. Undergoing mutation that directs malignant tissue toward blood vessels and lymph nodes for
metastasis
After the baroreceptor reflex is stimulated, the resulting impulse is transmitted from the carotid artery
by which sequence of events?
a. Vagus nerve to the medulla to increase parasympathetic activity and to decrease sympathetic activity
b. Glossopharyngeal cranial nerve through the vagus nerve to the medulla to increase sympathetic
activity and to decrease parasympathetic activity
c. Glossopharyngeal cranial nerve through the vagus nerve to the medulla to increase parasympathetic
activity and to decrease sympathetic activity
d. Glossopharyngeal cranial nerve through the vagus nerve to the hypothalamus to increase
parasympathetic activity and to decrease sympathetic activity.
Regarding the endothelium, what is the difference between healthy vessel walls and those that
promote clot formation?
a. Inflammation and roughening of the endothelium of the artery are present.
b. Hypertrophy and vasoconstriction of the endothelium of the artery are present.
c. Excessive clot formation and lipid accumulation in the endothelium of the artery are present.
d. Evidence of age-related changes that weaken the endothelium of the artery are present.
What is the expected electrocardiogram (ECG) pattern when a thrombus in a coronary artery
permanently lodges in the vessel and the infarction extends through the myocardium from the
endocardium to the epicardium?
a. Prolonged QT interval
b. ST elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI)
c. ST depression myocardial infarction (STDMI)
d. Non-ST elevation myocardial infarction (non-STEMI)
A patient reports sudden onset of severe chest pain that radiates to the back and worsens with
respiratory movement and when lying down. These clinical manifestations describe:
a. Myocardial infarction (MI)
b. Pericardial effusion
c. Restrictive pericarditis b. Pericardial effusion
d. Acute pericarditis
Respirations that are characterized by alternating periods of deep and shallow breathing are a result
of which respiratory mechanism?
a. Decreased blood flow to the medulla oblongata
b. Increased partial pressure of arterial carbon dioxide (PaCO2), decreased pH, and decreased partial
pressure of arterial oxygen (PaO2)
c. Stimulation of stretch or J-receptors
d. Fatigue of the intercostal muscles and diaphragm
Which cytokines activated in childhood asthma produce an allergic response?
a. Interleukin (IL)–1, IL-2, and interferon-alpha (IFN-α)
b. IL-8, IL-12, and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-α)
c. IL-4, IL-10, and colony-stimulating factor (CSF)
d. IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13
Which statement accurately describes childhood asthma?
a. An obstructive airway disease characterized by reversible airflow obstruction, bronchial
hyperreactivity, and inflammation
b. A pulmonary disease characterized by severe hypoxemia, decreased pulmonary compliance, and
diffuse densities on chest x-ray imaging
c. A pulmonary disorder involving an abnormal expression of a protein, producing viscous mucus that
lines the airways, pancreas, sweat ducts, and vas deferens
d. An obstructive airway disease characterized by atelectasis and increased pulmonary resistance as a
result of a surfactant deficiency
Which statement best describes cystic fibrosis?
a. Obstructive airway disease characterized by reversible airflow obstruction, bronchial hyperreactivity,
and inflammation
b. Respiratory disease characterized by severe hypoxemia, decreased pulmonary compliance, and diffuse
densities on chest x-ray imaging
c. Pulmonary disorder involving an abnormal expression of a protein-producing viscous mucus that
obstructs the airways, pancreas, sweat ducts, and vas deferens
d. Pulmonary disorder characterized by atelectasis and increased pulmonary
What are the abnormalities in cytokines found in children with cystic fibrosis (CF)?
a. Deficit of interleukin (IL)–1 and an excess of IL-4, IL-12, and interferon-alpha (IFN-α)
b. Deficit of IL-6 and an excess of IL-2, IL-8, and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF)
c. Deficit of IL-10 and an excess of IL-1, IL-8, and TNF-α
d. Deficit of IL-3 and an excess of IL-14, IL-24, and colony-stimulating factor (CSF)
Examination of the throat in a child demonstrating signs and symptoms of acute epiglottitis may
contribute to which life-threatening complication?
a. Retropharyngeal abscess
b. Laryngospasms
[Show More]














.png)