*NURSING > ATI > Rasmussen College: NURSING ATI pharm ATI pr copy (2) Questions and Answers,100% CORRECT (All)
Rasmussen College: NURSING ATI pharm ATI pr copy (2) Questions and Answers,100% CORRECT
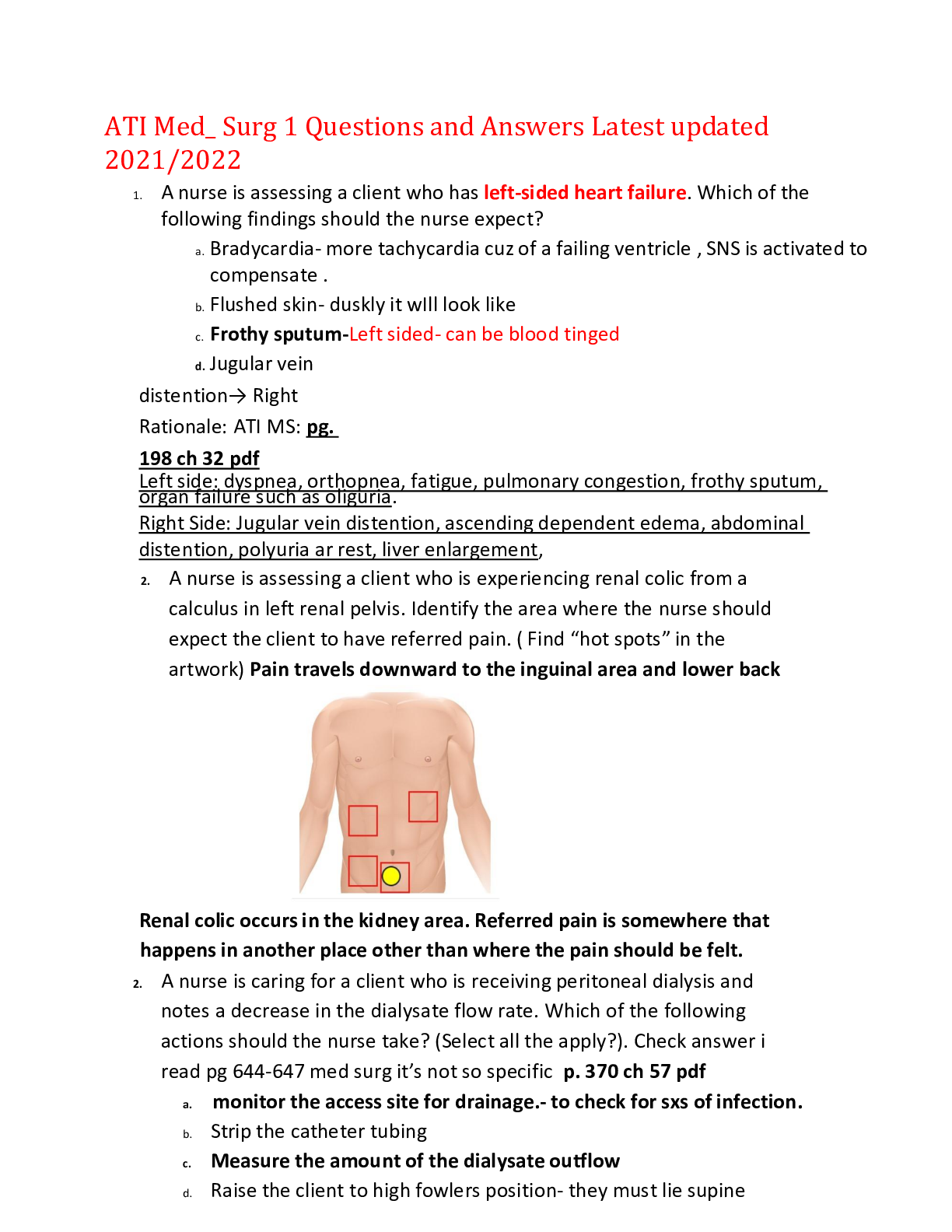
Document Content and Description Below
Rasmussen College: NURSING ATI pharm ATI pr copy (2) Questions and Answers 1. A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving IV therapy. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as... a manifestation of fluid volume excess? 1. Decreased bowel sounds 2. Distended neck veins 3. Bilateral muscle weakness 4. Thready pulse 2. A nurse is caring for a client who has hyponatremia and is receiving an infusion of a prescribed hypertonic solution. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the treatment is effective? a. Absent Chvostek’s sign b. Improved cognition c. Decreased vomiting d. Cardiac arrhythmias absent 3. A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for a nitroglycerin transdermal patch. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? a. “Discontinue the patch if you experience a headache.” b. “Apply a new patch if you have chest pain.” c. “Cover the patch with dry gauze when taking a shower.” d. “Remove the patch prior to going to bed.” 4. A nurse is reviewing the lab results of a client who has a prescription for sodium polystyrene sulfonate every 6 hours. Which of the following should the nurse report to the provider? a. Creatinine 0.72 mg/dL b. Sodium 138 mEq/L c. Magnesium 2 mEq/L d. Potassium 5.2 mEq/L 5. A nurse is caring for a client who has tuberculosis and is taking isoniazid and rifampin. Which of the following outcomes indicates that the client is adhering to the medication regimen? a. The client has a negative sputum culture. b. The client tests negative for HIV. c. The client has a positive purified protein derivative test. d. The client’s liver function test results are within the expected reference range. 6. A nurse is caring for a client who develops an anaphylactic reaction to IV administration. After assessing the client’s respiratory status and stopping the medication infusion, which of the following actions should the nurse take next? a. Replace the infusion with 0.9% sodium chloride b. Give diphenhydramine IM c. Elevate the client’s legs and feet d. Administer epinephrine IM 7. A nurse is caring for a client who is taking sertraline and reports a desire to begin taking supplements. Which of the following supplements should the nurse advise the client to avoid? a. St John’s Wort b. Ginger root c. Black cohosh d. Coenzyme Q10 8. A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure and a new prescription for lisinopril. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse monitor when administering lisinopril? a. Bradycardia b. Hypokalemia c. Tinnitus d. Hypotension 9. A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving heparin continuous IV. The client has an aPPT of 90 seconds. They should monitor the client for which of the following changes in their vital signs? a. Decreased temperature b. Increased pulse rate Page 193 in ATI book says monitor for hemorrhage which would be tachycardia and hypotension c. Decreased respiratory rate d. Increased blood pressure I think this is right - Rosie 10. A nurse is preparing to administer medication to a client and discovers a medication error. The nurse should recognize which of the following staff members is responsible for completing an incident report? a. The quality improvement committee b. The nurse who identifies the error c. The nurse who caused the error Found this in ATI Med Administration 1 Skills -Bailey d. The charge nurse 11. A nurse is planning care for a client who is receiving morphine via continuous epidural infusion. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following? a. Pruritus b. Cough c. Tachypnea d. Gastric bleeding 12. A nurse is preparing to administer digoxin orally to a client. Identify the sequence of steps the nurse should take. (Move steps into the box on the right, placing them in order of performance. Use all the steps.) D, A, C, B, E Bailey has no idea… ADBCE a. Remove the medication from the dispensing system b. Compare the client’s wristband to the medication administration record c. Open the medication package d. Obtain the client’s apical heart rate e. Document administration of the medication 13. A nurse is reviewing the medical record of an adult client who has a fever and a prescription for acetaminophen. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as a contraindication for receiving this medication? a. Alcohol use disorder - contraindicated in alcohol use-Rosie b. Chronic kidney disease You would want to avoid in Liver Disease-Rosie c. Hepatitis B vaccine with the last week d. Diabetes mellitus 14. A home health nurse is visiting a client who has heart failure and a prescription for furosemide. The nurse identifies that the client has gained 2.5 kg (5 lb.) since the last visit 2 days ago. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? a. Encourage the client to dangle the legs while sitting in a chair b. Teach the client about foods low in sodium c. Determine medication adherence by the client d. Notify the provider of the client’s weight gain 15. A nurse is preparing to administer the initial dose of penicillin G IM to a client. The nurse should monitor for which of the following as an indication of an allergic reaction following the injection? a. Urticaria b. Bradycardia c. Pallor d. Dyspepsia 16. A nurse is teaching a client who has angina about a new prescription for sublingual nitroglycerin tablets. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? a. “Discard any tablets you do not use every 6 months.” b. “Take one tablet each morning 30 minutes prior to eating.” c. “Keep the tablets at room temperature in their original glass bottle.” d. “Place the tablet between your cheek and gum to dissolve.” 17. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for theophylline, a sustained-release capsule. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. “I can take my medication in the morning with my coffee.” b. “I may sprinkle the medication in applesauce.” c. “I should limit my fluid intake while on this medication.” d. “I will need to have blood levels drawn.” 17. A nurse is mixing regular insulin and NPH insulin in the same syringe prior to administering it to the client who has diabetes mellitus which of the following actions should the nurse take first? a. Withdraw the regular insulin from the vial b. Withdraw the NPH insulin from the vial c. Inject air into the NPH vial d. Inject air into the regular insulin vial C… because[Clear before cloudy] so push air into cloudy insulin first (nph), remove no drug, move to clear insulin, push remaining air, then w/draw dose, go back to cloudy and remove drug equal to amount of initial air injected.. NPH:cloudy Regular: clear.. ally 19. A nurse is preparing to administer subcutaneous heparin to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Massage the site after administering the medication b. Use a 21-gauge needle for the injection c. Aspirate before injecting the medication d. Insert the needle at least 5 cm (2 in) from the umbilicus 20. A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for amoxicillin. Which of the following findings indicates the client is experiencing an allergic reaction? a. Nausea b. Cardiac dysrhythmia c. Laryngeal edema d. Insomnia 21. A nurse is teaching a newly licensed nurse about medication reconciliation. The nurse should instruct the newly licensed nurse to perform medication reconciliation for which of the following? a. A client who has a referral for social services b. A client who is transdermal (transferal?) to radiology c. A client who is transferal to a step-down unit d. A client who has a consultation for physical therapy 22. A nurse is reviewing the lab values of a client who is taking atorvastatin. Which of the following lab values indicates the treatment has been effective? a. BUN 15 mg/dL b. Blood glucose 90 mg/dL c. Urine specific gravity 1.020 d. LDL 120 mg/dL 23. A nurse is receiving a medication prescription by telephone from a provider. The provider states, “Administer 6 milligrams of morphine IV push every 3 hours as needed for acute pain.” How should the nurse transcribe the prescription in the client’s medical record? a. Morphine 6 mg IV push every 3 hr PRN acute pain b. MSO 6 mg IV push every 3 hr acute pain c. MS 6 mg IV push every 3 hr PRN acute pain d. Morphine 6.0 mg IV push every 3 hr PRN acute pain 24. A nurse is assessing a client’s IV infusion site and notes that the site is cool and edematous. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Slow the IV infusion rate b. Initiate a new IV distal to the initial site c. Maintain the extremity below the level of the heart d. Apply a warm, moist compress 25. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for clozapine. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching? a. “Diarrhea is a common adverse effect of this medication.” b. “Ringing in the ears is an expected adverse effect of this medication.” c. “Notify the provider if you develop a fever while taking this medication.” 26. A nurse is teaching a client about oral contraceptives. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Abdominal pain is an expected adverse effect of oral contraceptives b. It can take up to 1 year to become pregnant after stopping an oral contraceptive c. Some herbal supplements can decrease the effectiveness of an oral contraceptive d. A pelvic examination is needed prior to starting an oral contraceptive 27. A nurse is planning to administer medication to an older adult client who has dysphagia. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? a. Tilt the client’s head back when administering the medications b. Mix the medications with a semisolid food for the client c. Administer more than one pill to the client at a time d. Place the medications on the back of the client’s tongue 28. A nurse is providing teaching to a client about the administration of omeprazole. Which of the following should the nurse include? a. “You cannot take this medication with an antacid.” I think this is right because you have to wait 2 hours before taking an antacid - Rosie b. “You should reduce your intake of calcium while taking this medication.” c. “You should take this medication before meals.” d. “You can take a second dose if symptoms persist up to 2 hours after the first dose.” 29. A nurse is assessing for allergies with a client who is scheduled to receive the influenza vaccine. Which of the following allergies should the nurse report to the provider as a possible contraindication to receiving the vaccine? a. Eggs b. Shellfish c. Peanuts d. Milk 30. A nurse is caring for a client who has a new diagnosis of benign prostate hypertrophy and a prescription for doxazosin. The client tells the nurse, “I do not take this medication. I would prefer natural therapy.” Which of the following supplements should the nurse suggest the client discuss with the provider? a. Black cohosh b. Garlic c. Feverfew d. Saw Palmetto 31. A nurse is caring for a client who is taking digoxin to treat heart failure. Which of the following predisposes this client to developing digoxin toxicity? a. Taking a high ceiling diuretic b. Having a 10-year history of COPD c. Having a prolapsed mitral valve d. Taking an HMG CoA reductase inhibitor 32. A nurse is administering naloxone to a client who has developed an adverse reaction to morphine. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a therapeutic effect of naloxone? a. Decrease nausea b. Increased pain relief c. Decreased blood pressure d. Increased respiratory rate 33. A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has sinusitis and a new prescription for cefuroxime. Which of the following client information is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? a. The client has a BUN of 18 mg/dL b. The client takes an aspirin daily c. The client has a history of a severe penicillin allergy d. The client reports a history of nausea with cefuroxime 34. A nurse is assessing a client who has hypermagnesemia. Which of the following medications should the nurse prepare to administer? a. Protamine sulfate b. Acetylcysteine c. Calcium gluconate d. Flumazenil 35. A nurse is assessing a client following the administration of ondansetron (Zofran). Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the ondansetron has been effective? a. Client reports a decrease in pain b. Client reports a decrease in nausea c. Client reports a decrease in coughing d. Client reports a decrease in diarrhea 35. A nurse manager is planning an in-service about pain management with opioids for a client who has cancer. Which of the following information should the nurse manager include? a. IM administration is recommended if PO opioids are ineffective b. Respiratory depression decreases as opioid tolerance develops c. Meperidine is the opioid of choice for treating chronic pain d. Withhold PRN medication for the client who is receiving opioids every 6 hr 37. A nurse is reviewing the list of current medications for a client who is to start a prescription for carbamazepine. The nurse should identify which of the following medications interacts with carbamazepine? a. Nicotine transdermal system b. Diphenhydramine c. Estrogen-progestin combination d. Beclomethasone 38. A nurse is caring for a client who has a respiratory infection and is receiving an antibiotic. Which of the following medications puts the client at risk for developing hearing loss? a. Rifampin b. Ciprofloxacin c. Penicillin G d. Gentamicin 39. A nurse is teaching a guardian of a school-age child who has a prescription for fluticasone metered dose inhaler. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? SATA a. Soak inhaler in water after use b. Have your child take one inhalation as needed for shortness of breath c. Shake the device prior to administration d. A space will make it easier to use the device e. Rinse your child’s mouth following administration 40. A nurse is preparing to administer potassium chloride elixir 20mEq/day PO to divide equally every 12 hours. Available is 6.7mEq/5ml. How many ml should the nurse administer per dose? Round to nearest tenth _7.5 mL 41. A nurse is instructing a client who has a new prescription for a daily dose of lovastatin extended release. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? a. You will need liver function tests before beginning therapy b. Avoid consuming dairy products while taking this medication c. You may crush the medication and mix it with applesauce d. You should take the medication in the morning 42. A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving peripheral IV infusion and notes infiltration fluid into the tissue surrounding the insertion site. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Flush the IV catheter b. Apply pressure to the IV site c. Elevate the extremity d. Slow the infusion rate 43. A Nurse is preparing to administer 4,000 units of heparin subcutaneously to a client with deep vein thrombosis. Available is heparin 10,000 units. How many ml of heparin should the nurse administer? Round to nearest tenth 0.4 mL 44. A nurse is caring for a client who is in shock and is receiving an infusion of albumin. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? a. Oxygen saturation 96% b. PaCO2 30 mm Hg c. Increase in BP d. Decreased protein 45. A nurse is discussing adverse reactions to pain medications in older adult clients with a newly licensed nurse. Which of the following findings should the nurse include as risk factors for an adverse drug reaction? SATA B,E...found on quizlet-Rosie a. Polypharmacy b. Increased rate of absorption c. Decreased percentage of body fat- unlighted this one- Bailey d. Multiple health problems e. Decreased renal function From ATI book page 46- Older adults: decreased gastric motility and emptying time, resulting in a slower rate of absorption, decreased kidney function and glomerular filtration rate, decreased body water, increased body fat, and decreased lean body mass. Other factors affecting med therapy: Multiple or severe illnesses, polypharmacy: The practice of taking several meds… So I dk if the answers are different because it’s asking about opioids specifically but just thought I’d throw this out there. 46. A nurse is reviewing the laboratory data of a client prior to administering IV tobramycin. Which of the following lab values should the nurse report to the provider? a. Sodium 137mEq/L b. Hct 43% c. Hgb 15g/dL d. Creatinine 2.5mg/dL 47. A nurse is preparing to administer enoxaparin to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Apply firm pressure to the injection site following administration b. Administer the medication into the clients muscle c. Expel air bubble from syringe prior to injection d. Insert the syringe needle halfway in the client’s skin 48. A nurse is reviewing a client’s 0800 laboratory values at 1100. The nurse notes that the client received heparin at 1000. Which of the following lab values warrants an incident report? a. aPTT 90 seconds b. Hgb 16 g/dL c. INR 1.6 d. WBC 6,000/mm3 49. A nurse is caring for a client who has breast cancer and reports pain 1 hr administration of prescribed morphine 10mg IV. Which of the following medications should the nurse expect to administer? a. Naloxone IV b. Morphine tablet c. Lidocaine patch d. Fentanyl transmucosal 50. A nurse is assessing a client who reports taking over the counter antacids. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as a manifestation of hypercalcemia? a. Constipation- ally, ati ebook pg 222 b. Decreased urine output c. Positive trousseau’s sign This sign happens w/ hypOcalcemia I thought? d. Headache 51. N/A 52. A nurse is caring for a client who is to receive potassium replacement. The provider’s prescription reads: “Potassium chloride 30mEq in 0.9% sodium chloride 100ml IV over 30min” which of the following reasons should the nurse clarify this prescription with the provider? a. Potassium chloride should be diluted in dextrose 5% in water b. The potassium infusion rate is too rapid c. Another formulation of potassium should be given IV d. The client should be treated by giving potassium by IV bolus 53. A nurse is monitoring lab values for a client who has chronic heart failure and is receiving digoxin. Which of the following values should the nurse report to the provider? a. Sodium 138mEq/dL b. Magnesium 1.5mEq/dL c. BUN level 10mg/dL d. Potassium 2.9 mEq/L 54. N/A 55. A client who has active tuberculosis and is taking rifampin reports that his urine and sweat have developed a red tinge. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? a. Check client liver function test results b. Instruct the client to increase his fluid intake c. Document this as an expected finding d. Prepare the client for dialysis 55. A nurse accidently administers the medication metformin instead of metoprolol to a client. Which action should the nurse take? a. Monitor the clients thyroid function levels b. Collect the clients uric acid level c. Obtain the client HDL level d. Check client’s glucose level 57. A nurse is administering 4mg hydromorphone to a client by mouth every 4 hr, the medication is provided as hydromorphone 8mg per tablet. Which of the following actions is appropriate for the nurse to take? a. Return the remaining medication to the facility’s pharmacy b. Store the remaining half of the pill in the automated medication dispensing system c. Place the remaining half of the pill in the unit dose package d. Dispose of the remaining medication while another nurse observes 58. A nurse is caring for a 4yr child following an orthopedic procedure. When assessing the child for pain. Which of the following pain scales should the nurse use? a. FACES b. Numeric c. CRIES d. Word graphic 59. A nurse is planning care for a client who requires treatment for high cholesterol. Which of the following prescriptions should the nurse expect to administer? a. Colchicine b. Cimetidine c. Colesevelam d. Chlorpromazine 60. A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure. The nurse administered furosemide 60mg IV bolus 30min earlier. For which of the following findings should the nurse notify the provider? a. Potassium 3.8mEq/L b. Client reports dizziness upon standing c. Client reports difficulty hearing d. BUN 15mg/dL 61. A nurse is planning teaching for a client who is trying to quit smoking. Which of the following instructions about nicotine replacement options should the nurse include? a. Change the nicotine patch every other day b. Do not drink beverages while sucking a nicotine lozenge c. Chew nicotine gum for 10min before spitting it out d. Administer 2 sprays of nicotine spray in each nostril with each dose 62. A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for total parenteral nutrition (TPN). Which of the following routes of administration should the nurse use? a. Subcutaneous b. Intravenous- possibly intraosseous was the option if so I think it’s central venous c. Central venous access device d. Midline catheter 63. A nurse is preparing to administer filgrastim 5mcg/kg/day subcutaneous to a client who weighs 143lb. How many mcg should the nurse administer? (round to whole number) _325 mcg 64. A nurse is preparing to initiate IV therapy for a client. Which of the following sites should the nurse use to place the peripheral IV catheter? a. Nondominant dorsal venous arch b. Dominant dorsal vein c. Nondominant forearm basilic vein d. Dominant antecubital vein 65. A nurse is assessing a client who is taking an osmotic laxative which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication of fluid volume deficit? a. Nausea b. Weight gain c. Headache d. Oliguria 66. A nurse is reviewing the lab results of a client who is taking amitriptyline which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the provider? a. Total bilirubin 1.5 mg/dL b. Potassium 4.2 mEq/L c. Hct 44% d. WBC count 5,000/mm3 67. N/A 68. A nurse is caring for a client who is taking lithium and reports starting a new exercise program. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following electrolyte imbalances? a. Hypocalcemia b. Hypokalemia c. Hyponatremia d. Hypomagnesemia 69. A nurse is assessing a client after administering phenytoin IV bolus for seizure. Which of the following should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of this medication? a. Hypoglycemia b. Bradycardia c. Red man syndrome d. Hypotension 70. A nurse is consulting a formulary about a client’s new prescription for raloxifene. The nurse should identify that this medication is used to treat which of the following conditions? a. Osteoporosis b. Hypothyroidism c. Urinary tract infection d. Deep vein thrombosis Extra stuff just in case Found this on CourseHero it had both sets of questions so I dk if this is another possible version? 1. A nurse is providing discharge dietary teaching to a client who has something and is taking theophylline and to provide general instructions the nurse should include? 1. Avoid caffeinated beverages 2. Take the medication with meals 3. Restrict milk products 4. Limit sodium intake 2. The nurse is mixing regular insulin and NPH into a syringe for a client who has diabetes mellitus. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? a. Withdrawal NPH from the vial b. Inject air into the NPH vial c. Inject air into the regular vial d. Withdrawal regular insulin from the vial 3. A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription of Alendronate for osteoporosis. What instructions should the nurse include? a. Take the medication immediately after breakfast b. Take the medication with an antacid c. Sit upright for at least 30 mins after taking the medication d. Drink orange juice with the medication 4. A nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative following a thyroidectomy and is receiving morphine for pain. Which of the following findings should the nurse recognize as an adverse effect of morphine? a. Bladder distention b. Productive cough c. Gastrointestinal bleeding d. Decrease deep tendon reflexes 5. A nurse is teaching a client who has pernicious anemia to self-administer cyanocobalamin. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Use nasal decongestant 15 mins before the medication if you have a stuffy nose b. Lie down for 1 hour after administering the medication c. Administer the medication into one nostril once per week d. Plan to self-administer this medication for the next 6 months 6. A nurse is teaching a newly licensed nurse about medication reconciliation. The nurse should instruct the newly licensed nurse for medication reconciliation for which of the following clients? a. Client who is transported to radiology b. A client who has a consultation for …. c. A client who has a referral for social services d. A client who has been transferred to a step-down unit 7. A nurse is assessing a client who is to receive a dinoprostone gel to stimulate cervical ripening. Which of the following is the nurse’s priority? a. Back pain b. Flushing c. Nausea d. Uterine tachysystole 8. A nurse is performing a return demonstration of an enoxaparin administration. Which of the following client actions indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. Messages the site to enhance absorption b. Injections the medication into a muscle c. Administers the medication into the abdomen d. Aspirates the medication after injection 9. A nurse is assessing a client who has been taking digoxin and …… which of the following findings to the nurse indicates this client has developed digoxin toxicity? a. Ringing in the ears b. Hyperkalemia c. Blurred vision d. Hypertension 9. A nurse is caring for a client who received neostigmine 1 hour ago and is experiencing muscarinic response. Which if the following manifestations should the nurse expect? a. Headache b. Excessive salivation c. Fever d. Myoclonic seizure 11. A nurse in the emergency department is reviewing a medication record for a client who reports vomiting blood. The nurse should anticipate the provider will discontinue which of the following medications? a. NPH insulin b. Clopidogrel c. Furosemide d. Pantoprazole 12. A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving clindamycin. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of this medication? a. Agitation b. Report of blurred vision c. Hypertension d. Watery diarrhea 13. A nurse is teaching a client who is to start taking Cromolyn. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Cromolyn should take effect within 5 mins b. Cromolyn should dilate the bronchioles c. Cromolyn can be used after exercise d. Cromolyn is a long-term management medication 14. A nurse is reviewing the medications of a client that is experiencing orthostatic hypotension. The nurse should identify this finding as an adverse effect of which of the following medications? a. Imipramine b. Levothyroxine c. Montelukast d. Omeprazole 15. A nurse is reviewing a client’s medical history before administering a new prescription of atropine. Which of the following client conditions is contraindicated? a. Glaucoma 15. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for carbamazepine for the treatment of seizures. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? a. Insomnia b. Blurred vision c. Tachypnea d. Metallic taste 17. Math problem: a nurse is preparing to administer 4000 units of heparin available is 10,000 units = 0.4 18. A nurse is caring for a client who reports that his current pain medication is no longer relieving her pain. Which of the following medications requires the nurse to obtain a written rather than a verbal prescription from the provider? a. Fentanyl 19. A charge nurse is observing a newly licensed nurse provide care to a group of clients. Which of the following actions by the newly licensed nurse requires the charge nurse to complete an incident report? a. A client who has a lithium level of 1.8 receives her morning dose 20. A nurse is caring for a client who has an alcohol use disorder and is experiencing withdrawals. Which of the following interventions is a priority at this time? a. Encourage participation in a 12-step program b. Implement seizure precautions 21. A nurse is planning care for a group of clients. Which of the following client's medications should be monitored by the nurse for hearing loss related to a medication interaction? a. Furosemide and Amikacin 22. A nurse is caring for a client who has major depression and a new prescription for citalopram. Which of the following adverse effects is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? a. Insomnia b. Bruxism - Bruxism occurs in < 1 % of patients with citalopram. This should be addressed but is not an immediate health concern. c. Confusion d. Weight loss 23. A nurse is caring for a client who requires a re-insertion of a short peripheral venous catheter. In which of the following locations should the nurse place the catheter? a. A vein on the client’s wrist 24. A nurse is assessing a client who is in labor and is receiving epidural anesthesia. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as the priority? a. Hypotension 25. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a prescription for omeprazole. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Long term use increases risk of fractures 26. A nurse is reviewing a client’s laboratory results before administering furosemide 40 mg IV bolus. For which of the following values should the nurse withhold the medication and contact the provider? a. Potassium 2.5 mEq/L 27. The nurse is assessing a client who takes glipizide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Which of the following findings indicates effectiveness of the medication? a. Hba1c 6.5% 28. A nurse in the emergency department is caring for a client who reports a severe headache. The client's blood pressure is 280/160 mm hg. the nurse should plan to administer which of the following medications? a. Nitroprusside 29. A nurse is teaching the parent of a toddler who is to begin taking ferrous fumarate. Which of the following statements by the parent indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I will rinse my child's mouth with water after she takes the medicine 30. A nurse is caring for a client who is to start therapy with lovastatin. the nurse should prepare the client for which of the following diagnostic assessments? a. Liver function test 31. A nurse is developing a teaching plan for an older adult client who has a new prescription for insulin glargine. Which of the following expected outcomes should the nurse include in the plan? a. The client will wear his reading glasses when drawing insulin glargine 32. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving a continuous IV infusion of magnesium sulfate for preterm labor. the nurse should discontinue the infusion and prepare to administer calcium gluconate if the client demonstrates which of the following findings? (Select all that apply) a. Absence of deep-tendon reflexes b. Urine output 80 mL/hr- not true… don’t know other options c. Decreased LOC d. Decreased RR if that’s an option 33. A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin patches. the nurse should identify which of the following statements as an indication that the client understands the teaching? a. I will rotate application site to avoid skin irritation 34. A nurse in a provider's office is preparing to teach a middle adult client who has a new diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and an HbA1c of 6.5%. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to teach the client about first? a. Metformin 35. A nurse is teaching a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis about management of medication for the disease. Which of the following statements is appropriate for the nurse to make? a. You will need to take two or more medications to treat your disease 36. A nurse is planning care for a client who has a prescription for erythromycin lactobionate IV bolus. Which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? a. Monitor for hearing loss 37. A nurse is obtaining a medication history from a client who has gout and is prescribed probenecid. the nurse should notify the provider that the client is taking which of the following over-the counter medications? a. Salicylic acid (Aspirin) 38. A nurse is teaching a client who has HIV and a new prescription for efavirenz. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Notify provider for the appearance of a skin rash- Can lead to Stevens- Johnson Syndrome 39. A nurse is evaluating a client who has tuberculosis and has been taking rifampin for 1 month. Which of the following laboratory tests should the nurse review to evaluate for an adverse effect of this medication? a. ALT 40. A nurse is teaching a client who has multiple allergies about using an epinephrine auto- injector. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? a. Administer the medication through clothing if necessary 41. for ferrous gluconate. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I should stay upright for 15 minutes after taking this medication. 42. A nurse is preparing to administer methylprednisolone sodium succinate 80 mg IV bolus. the nurse reconstitutes the 125 mg in the vial in powder form to 2 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? a. 1.3 43. A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure. The nurse administered furosemide 60 mg IV bolus 30 min earlier. for which of the following findings should the nurse notify the provider? a. Client reports difficulty hearing 44. A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking pioglitazone. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects? a. Orthostatic hypotension- I don’t think this is accurate b. From the book s/e: fluid retention monitor for edema, weight gain, heart failure. Monitor cholesterol levels, liver function tests 45. A nurse is wanting to report an infusion reaction for a client who is receiving a dose via IV of amphotericin B. Which are the following findings that indicate to the nurse that the patient is experiencing an acute infusion reaction? a. Fever 46. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for paroxetine. the nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? a. Drowsiness - Nausea, drowsiness, dizziness, trouble sleeping, loss of appetite, weakness, dry mouth, sweating, blurred vision, and yawning may occur. If any of these effects persist or worsen, tell your doctor or pharmacist promptly. 47. A client who has Graves' disease is prescribed methimazole. Which of the following effects should the nurse expect to see after the client has taken the medication for 2 months? a. Increased sleeping- pretty sure this is correct b. Indications of effectiveness: weight gain, absence of hyperthyroidism signs like: anxiety, tachycardia, palpitations, increased appetite, abdominal cramping, heat intolerance, fever, sweating, weight loss) 48. A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for ergotamine to treat vascular headaches. The nurse should inform the client that which of the following is a potential adverse effect of this medication? a. Muscle pain 49. A nurse is reviewing a client's 0800 laboratory values at 1100. the nurse notes that the client received heparin at 1000. Which of the following laboratory values warrants an incident report? a. aPtt 90 50. A nurse is administering medications to a client. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to administer by a parenteral route? a. Fondaparinux- not sure they are given via prefilled syringe it does say they can be given sub q or IV but that’s talking about anticoagulants in general like heparin 51. A nurse is assessing a client who takes levothyroxine for hypothyroidism. the nurse should identify that which of the following findings indicates the need for an increase in dosage? Select all that apply a. Heart rate 46 b. Cold intolerance c. Impaired short-term memory d. Signs of hypothyroidism- depression, weight gain, bradycardia, anorexia, cold intolerance, dry skin, menorrhagia. 52. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for warfarin about potential interactions with over the counter products. which of the following products should the nurse instruct the client to avoid? a. Naproxen 53. A nurse is teaching a client who is to begin cyclophosphamide therapy to treat cancer. Which of the following adverse effects of this medication should the nurse include in the teaching? a. Leukopenia 54. A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who is receiving vancomycin daily. the nurse should review which of the following laboratory results prior to administering the next dose? a. Creatinine level 55. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for phenelzine. which of the following foods should the nurse instruct the client to avoid? a. Cheddar cheese 56. A nurse is preparing to administer nitroglycerin topical ointment to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? a. Measure dosage on medication applicator paper 57. A nurse is caring for a client who is taking azathioprine to treat rheumatoid arthritis. which of the following laboratory values indicates an adverse effect of this medication? a. WBC 3000 58. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for phenelzine. the nurse instructs the client to avoid which of the following foods? a. smoked salmon 59. A nurse is reviewing the laboratory data of a client who is receiving filgrastim. which of the following laboratory values should the nurse monitor to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment? a. WBC count 60. A nurse is planning to administer medications to a client who weighs 198 lb. he prescription reads, "filgrastim 5mcg/kg, subcutaneous, daily". available is filgrastim 300 mcg/mL. how many ml should the nurse plan to give with each dose? a. 1.5 61. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin. which of the following client statements indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. I will call 911 if pain is not relieved after taking the medication 62. A nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who is receiving warfarin. Which of the following statements is appropriate to make? a. Avoid eating large amounts of cabbage and broccoli 63. A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has sinusitis and a new prescription for cefuroxime. Which of the following client information is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? a. A client with a history of severe Penicillin allergy 64. A nurse recently administered filgrastim intravenously to a client who has cancer and is receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy. For which of the following data, discovered after the medication was administered, should the nurse file an incident report.? a. Vial sat out for 2 hours at room temperature before administration- not sure, google says can sit out in room temp 24 hours not in sunlight. ATI says use each vial for one dose and don’t reinsert needle 65. A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving heparin therapy for deep-vein thrombosis. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the therapy is effective? a. Platelets within the expected range- unsure about this heparin is an anticoagulant so shouldn’t affect platelets, maybe it’s the best option I dk, it can cause low platelets as an adverse effect 66. A nurse receives a prescription to give tobramycin to a client daily. Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the provider? a. Serum creatinine 2.5 67. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin sublingual. which of the following client responses indicates an understanding of the teaching? a. Keep tablets in dark container at room temperature 68. A nurse is reviewing a client's medical record before administering acetaminophen 650 mg PO every 6 hr. Which of the following findings indicates a need for the nurse to notify the provider? a. History of alcohol use disorder- Avoid use in clients with severe liver impairment or disease, kidney impairment, chronic alcohol use disorder, malnutrition. 69. A nurse is preparing to administer the initial dose of penicillin G IM to a client. The nurse should monitor for which of the following as an indication of an allergic reaction following the injection? a. Urticaria 70. A nurse is assessing a client who has been taking lithium for one year. Which of the following client reports is the nurse's priority? a. Mild thirst A nurse is assessing a client who takes glipizide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Which of the following findings indicates effectiveness of the medication? HbA1c A nurse is caring for a client who has hyponatremia and is receiving an infusion of a prescribed hypertonic solution. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the treatment is effective? Improved cognition A nurse is preparing to administer medication to a client and discovers a medication error. The nurse should recognize that which of the following staff members is responsible for completing an incident report? The nurse who made the error ideally within 24 hours A nurse is providing teaching to a client about the administration of omeprazole. Which of the following should the nurse include? "You cannot take this medication with an antacid." A nurse is caring for a client who has a new diagnosis of benign prostate hypertrophy and a prescription for doxazosin. The client tells the nurse. "I do not take this medication. I would prefer a natural therapy." Which of the following supplements should the nurse suggest the client discuss with the provider? Saw palmetto A nurse is administering naloxone to a client who has developed an adverse reaction to morphine. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a therapeutic effect of naloxone? Increased respiratory rate A nurse is assessing a client who has hypermagnesemia. Which of the following medications should the nurse prepare to administer? Calcium gluconate A nurse is discussing adverse reactions to pain medications in older adult clients with a newly licensed nurse. Which of the following findings should the nurse include as risk factors for an adverse drug reaction? (SATA) a. Polypharmacy c. Decreased percentage of body fat- ATI says increased body fat so don’t think C is correct d. Multiple health problems e. Decreased renal function A nurse is reviewing a client's 0800 laboratory values at 1100. The nurse notes that the client received heparin at 1000. Which of the following laboratory values warrants an incident report? ePTT 90 seconds A nurse accidentally administers the medication metformin instead of metoprolol to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Check the client's glucose level A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure. The nurse administered furosemide 60 mg IV bolus 30 min earlier. For which of the following findings should the nurse notify the provider? The client reports difficulty hearing A nurse is assessing a client who is taking an osmotic laxative which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication of fluid volume deficit? Oliguria A nurse is caring for a client who is taking lithium and reports starting a new exercise program. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following electrolyte imbalances? Hyponatremia A nurse is teaching a client who has pernicious anemia to self administer cyanocobalamin. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? Administer the medication into one nostril once per week A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for carbamazepine for the treatment of seizures. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? Blurred vision A nurse is caring for a client who has major depression and a new prescription for citalopram. which of the following adverse effects is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? Confusion A nurse is teaching a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis about management of medication for the disease. which of the following statements is appropriate for the nurse to make? You will need to take two or more medication to treat your disease A nurse is planning care for a client who has a prescription for erythromycin lactobionate IV bolus. which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? Monitor for hearing loss For ferrous gluconate. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? I should stay upright or 15 minutes after taking this medication A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking pioglitazone. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects? Orthostatic hypotension- don’t think this is right, can cause fluid retention A nurse is wanting to report a n infusion reaction for a client who is receiving a dose via IV of amphotericin B. which is the following findings that indicate to the nurse that the patient is experiencing an acute infusion reaction? Fever A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for paroxetine. the nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? Drowsiness A client who has Graves' disease is prescribed methimazole. Which of the following effects should the nurse expect to see after the client has taken, he medication for 2 months? Increased sleeping A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin sublingual. which of the following client responses indicates an understanding of the teaching? keep tablets in dark container at room temperature A nurse is preparing to administer the initial dose of penicillin G IM to a client. The nurse should monitor for which of the following as an indication of an allergic reaction following the injection? Urticaria A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking pioglitazone. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects? Orthostatic hypotension A nurse is assessing a client who takes glipizide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Which of the following findings indicates effectiveness of the medication? Hgba1c 6.5% A nurse is reviewing a client's medical record before administering acetaminophen 650 mg PO every 6 hr. Which of the following findings indicates a need for the nurse to notify the provider? History of alcohol use disorder A client who has Graves' disease is prescribed methimazole. Which of the following effects should the nurse expect to see after the client has taken he medication for 2 months? increased sleeping A nurse is teaching a client who is to begin cyclophosphamide therapy to treat cancer. Which of the following adverse effects of this medication should the nurse include in the teaching? leukopenia A nurse receives a prescription to give tobramycin to a client daily. Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the provider? serum creatinine 2.5 A nurse is teaching a client who has a prescription for ferrous gluconate. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? I should stay upright for 15 minutes after taking this medication. A nurse is teaching a client who has multiple allergies about using an epinephrine auto-injector. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? admin meds through clothing if necessary A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving heparin therapy for deep-vein thrombosis. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the therapy is effective? platelets within the expected range a nurse is caring for a client who has major depression and a new prescription for citalopram. which of the following adverse effects is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? confusion or bruxism a nurse is caring for a client who require a re-insertion of a short peripheral venous catheter. in which of the following locations should the nurse place the catheter? a vein on the clients wrist a nurse is providing discharge dietary teaching to a client who has a new prescription for theophylline. which of the following instructions should the nurse include? avoid caffeinated beverages a nurse is caring for a client who received neostigmine 1 hr ago and is experiencing a muscarinic response. which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect? excessive salivation a nurse is caring for a client who is taking azathioprine to treat rheumatoid arthritis. which of the following laboratory values indicates an adverse effect of this medication? WBC 3000 a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin sublingual. which of the following client responses indicates an understanding of the teaching? keep tablets in dark container at room temperature a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for paroxetine. the nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? drowsiness or Peripheral edema a nurse is caring for a client who is to start therapy with lovastatin. the nurse should prepare the client for which of the following diagnostic assessments? liver function test a nurse is planning care for a client who has a prescription for erythromycin lactobionate IV bolus. which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? monitor for hearing loss a nurse is reviewing a client's 0800 laboratory. the nurse notes that the client received heparin at 1000. which of the following laboratory values warrants an incident report. aptt 90 a nurse is caring for a client who is receiving IV amphotericin B. which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an acute infusion reaction? fever a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for carbamazepine for the treatment of seizures. the nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? blurred vision a nurse is planning care for a group of clients. which of the following client's medications should be monitored by the nurse for hearing loss related to a medication interaction? furosemide and amikacin a nurse recently administered filgrastim intravenously to a client who has cancer and is receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy. for which of the following data, discovered after the medication was administered, should the nurse file an incident report.? vile sat out for 2 hours at room temp before administration a nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for ergotamine to treat vascular headaches. The nurse should inform the client that which of the following is a potential adverse effect of this medication? muscle pain a nurse is teaching a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis about management of medication for the disease. which of the following statements is appropriate for the nurse to make? you will need to take two or more medication to treat your disease A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving intravenous therapy. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a manifestation of fluid volume excess? Distended neck veins A nurse is caring for a client who has hyponatremia and is receiving an infusion of a prescribed hypertonic solution. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the treatment is effective?Improved cognition A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for a nitroglycerin transdermal patch. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? "Remove the patch prior to going to bed." A nurse is reviewing he laboratory results of a client who has a prescription for sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) every 6 hr. which of the following should the nurse report to the provider? Potassium 5.2 mEq/L A nurse is caring for a client who has tuberculosis and is taking isoniazid and rifampin. Which of the following outcomes indicates that the client is adhering to the medication regimen? The client has a negative sputum culture A client is caring for a client who develops an anaphylactic reaction to IV administration. After assessing the client's respiratory status and stopping the medication infusion. Which of the following actions should the nurse take next? Administer epinephrine IM A nurse is caring for a client who is taking sertraline and reports a desire to begin taking supplements. Which of the following supplements should the nurse advise the client to avoid? St. John's Wort A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure and a new prescription for lisinopril. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse monitor when administering lisinopril? Hypotension A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving heparin IV continuous IV. The client has an PPT of 90 seconds. They should monitor the client for which of the following changes in their vital signs? Increased blood pressure A nurse is preparing to administer medication to a client and discovers a medication error. The nurse should recognize that which of the following staff members is responsible for completing an incident report? The nurse who identifies the error A nurse is planning care for a client who is receiving morphine via continuous epidural infusion. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following? Pruritus A nurse is preparing to administer digoxin orally to a client. Idenfy the sequence of steps the nurse should take. (Move the steps into the box on the right, placing them in the order of performance. Use all the steps.) a. Obtain the client's apical heart rate b. Remove the medication from the dispensing system c. Open the medication package d. Compare the client's wristband to the medication administration record e. Document administration of the medication A home health nurse is visiting a client who has heart failure and a prescription for furosemide. The nurse identifies that the client has gained 2.5 kg (5 lb.) since the last visit 2 days ago. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? Determine medication adherence by the client A nurse is preparing to administer the initial dose of penicillin G IM to a client. The nurse should monitor for which of the following as an indication of an allergic reaction following the injection? a. Urt Urticaria A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for theophylline, a sustained-released capsule. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? "I can take my medication in the morning with my coffee." A nurse is mixing regular insulin and NPH insulin in the same syringe prior to administering it to client who has diabetes mellitus following actions should the nurse take first? Inject air into the regular insulin vial A nurse is preparing to administer subcutaneous heparin to a client. Which of the following should the nurse take? Insert the needle at least 5 cm (2 in) from the umbilicus A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for amoxicillin. Which of the following findings indicates the client is experiencing an allergic reaction? Cardiac dysrhythmia A nurse is teaching a newly licensed nurse about medication reconciliation. The nurse should instruct the newly licensed nurse to perform medication reconciliation for which of the following? A client who is transferal to a step-down unit A nurse is reviewing the laboratory values of a client who is taking atorvastatin. Which of the following laboratory values indicates the treatment has been effective? LDL 120 mg/dL A nurse is receiving a medication prescription by telephone from a provider. The provider states, "Administer 6 milligrams of morphine IV push every 3 hours as needed for acute pain." How should the nurse transcribe the prescription in the client's medical record? Morphine 6 mg IV push every 3 hr PRN acute pain A nurse is assessing a client's IV infusion site and notes that the site is cool and edematous. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Apply a warm, moist compress A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for clozapine. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching? "Notify your provider if you develop a fever while taking this medication." A nurse is planning to administer medication to an older adult client who has dysphagia. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? Mix the medications with a semisolid food for the client A nurse is providing teaching to a client about the administration of omeprazole. Which of the following should the nurse include? "You cannot take this medication with an antacid." A nurse is assessing for allergies with a client who is scheduled to receive the influenza vaccine. Which of the following allergies should the nurse report to the provider as a possible contraindication to receiving the vaccine? Eggs A nurse is caring for a client who has a new diagnosis of benign prostate hypertrophy and a prescription for doxazosin. The client tells the nurse. "I do not take this medication. I would prefer a natural therapy." Which of the following supplements should the nurse suggest the client discuss with the provider? Saw palmetto A nurse is caring for a client who is taking digoxin to treat heart failure. Which of the following predisposes this client to developing digoxin toxicity? Taking a high ceiling diuretic A nurse is administering naloxone to a client who has developed an adverse reaction to morphine. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a therapeutic effect of naloxone? Increased respiratory rate A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has sinusitis and a new prescription for cefuroxime. Which of the following client information is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? The client has a history of a severe penicillin allergy A nurse is assessing a client who has hypermagnesemia. Which of the following medications should the nurse prepare to administer? Calcium gluconate A nurse is reviewing the list of current medication for a client who is to start prescription for carbamazepine. The nurse should identify that which of the following medications interacts with carbamazepine? Estrogen-progestin combination A nurse is teaching a guardian of a school-age child who has a new prescription for a fluticasone metered-dose inhaler. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? (SATA) c. "Shake the device prior to administration." d. "A spacer will make it easier to use the device." e. "Rinse your child's mouth following administration." A nurse is preparing to administer potassium chloride elixir 20 mEq/day PO to divide equally 12 hr. available is 6.7 mEq/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trialing zero.) 7.5 mL A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving a peripheral IV infusion and notes infiltration of fluid into the tissue surrounding the insertion site. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Elevate the extremity A nurse us caring for a client who is in shock and is receiving an infusion of albumin. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? Increase in BP A nurse is discussing adverse reactions to pain medications in older adult clients with a newly licensed nurse. Which of the following findings should the nurse include as risk factors for an adverse drug reaction? (SATA) a. Polypharmacy c. Decreased percentage of body fat d. Multiple health problems e. Decreased renal function A nurse is reviewing the laboratory data of a client prior to administering IV tobramycin. Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the provider? Creatinine 2.5 mg/dL A nurse is preparing to administer enoxaparin to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Apply firm pressure to the injection site following administration A nurse is reviewing a client's 0800 laboratory values at 1100. The nurse notes that the client received heparin at 1000. Which of the following laboratory values warrants an incident report? ePTT 90 seconds A nurse is caring for a client who has breast cancer and reports pain. 1 hr after administration of prescribed morphine 10 mg IV. Which of the following medications should the nurse expect to administer? Lidocaine patch A nurse is caring for a client who is to receive potassium replacement. The provider's prescription reads. "Potassium chloride 30 mEq in 0.9% sodium chloride 100 mL IV over 30 min." which of the following reasons should the nurse clarify this prescription with the provider. The potassium infusion rate is too rapid A nurse is monitoring laboratory values for a client who has chronic heart failure and is receiving digoxin. Which of the following values should the nurse report to the provider? Potassium 2.9 mEq/L A client who has active tuberculosis and is taking rifampin reports that his urine and sweat have developed a red tinge. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Document this as an expected finding A nurse accidentally administers the medication metformin instead of metoprolol to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Check the client's glucose level A nurse is administering 4 mg of hydromorphone to a client by mouth every 4 hr. the medication is provided as hydromorphone 8 mg per tablets. Which of the following actions is appropriate for the nurse to take? Dispose of the remaining medication while another nurse observes A nurse is caring for 4-year-old child following an orthopedic procedure. When assessing the child for pain. Which of the following pain scales should the nurse use? FACES A nurse is planning care for a client who requires treatment for high cholesterol. Which of the following prescriptions should the nurse expect to administer? Colerain A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure. The nurse administered furosemide 60 mg IV bolus 30 min earlier. For which of the following findings should the nurse notify the provider? The client reports difficulty hearing A nurse is planning teaching for a client who is trying to quit smoking. Which of the following instructions about nicotine replacement options should the nurse include? Do not drink beverages while sucking on a nicotine lozenge A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for total parental nutrition (TPN). Which of the following routes of administration should the nurse use? Intravenous A nurse is preparing to initiate IV therapy for a client. Which of the following sites should the nurse use to place the peripheral IV catheter? Nondominant dorsal venous arch A nurse is assessing a client who is taking an osmotic laxative which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication of fluid volume deficit? Oliguria A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client who is taking amitriptyline which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the provider? Total bilirubin 1.5 mg/dL A nurse is caring for a client who is taking lithium and reports starting a new exercise program. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following electrolyte imbalances? Hyponatremia A nurse is assessing a client after administering phenytoin IV bolus for a seizure. Which of the following should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of this medication? Bradycardia A nurse is consulting a formulary about a client's new prescription for raloxifene. The nurse should identify that this medication is used to treat which of the following conditions? Osteoporosis ***A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription of Alendronate for osteoporosis. What instructions should the nurse include?*** Sit upright for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication A nurse is teaching a client who has pernicious anemia to self administer cyanocobalamin. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? Administer the medication into one nostril once per week A nurse is teaching a newly license nurse about medication reconciliation. The nurse should instruct the newly license nurse for medication conciliation for which of the following clients? A client who has been transferred to a step down unit. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for carbamazepine for the treatment of seizures. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? Blurred vision A nurse is caring for a client who has major depression and a new prescription for citalopram. which of the following adverse effects is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? Confusion A nurse is assessing a client who is in labor and is receiving epidural anesthesia. which of the following findings should the nurse identify as the priority? Hypotension A nurse is reviewing a client's laboratory results before administering furosemide 40 mg IV bolus. For which of the following values should the nurse withhold the medication and contact the provider? Potassium 2.5 mEq/L A nurse is teaching a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis about management of medication for the disease. which of the following statements is appropriate for the nurse to make? You will need to take two or more medication to treat your disease ***A nurse is planning care for a client who has a prescription for erythromycin lactobionate IV bolus. which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care?*** Monitor for hearing loss ***For ferrous gluconate. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?*** I should stay upright or 15 minutes after taking this medication A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking pioglitazone. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects? Orthostatic hypotension A nurse is wanting to report a n infusion reaction for a client who is receiving a dose via IV of amphotericin B. which is the following findings that indicate to the nurse that the patient is experiencing an acute infusion reaction? Fever A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for paroxetine. the nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? Drowsiness A client who has Graves' disease is prescribed methimazole. Which of the following effects should the nurse expect to see after the client has taken, he medication for 2 months? Increased sleeping ***A nurse is reviewing a client's 0800 laboratory values at 1100. the nurse notes that the client received heparin at 1000. which of the following laboratory values warrants an incident report? *** aPtt 90 A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has sinusitis and a new prescription for cefuroxime. which of the following client information is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? A client with a history of severe Penicillin allergy A nurse recently administered filgrastim intravenously to a client who has cancer and is receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy. for which of the following data, discovered after the medication was administered, should the nurse file an incident report.? Vile sat out for 2 hours at room temperature before administration ***A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin sublingual. which of the following client responses indicates an understanding of the teaching? *** keep tablets in dark container at room temperature A nurse is preparing to administer the initial dose of penicillin G IM to a client. The nurse should monitor for which of the following as an indication of an allergic reaction following the injection? Urticaria A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving intravenous therapy. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a manifestation of fluid volume excess? Distended neck veins A nurse is caring for a client who has hyponatremia and is receiving an infusion of a prescribed hypertonic solution. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the treatment is effective?Improved cognition A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for a nitroglycerin transdermal patch. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? "Remove the patch prior to going to bed." A nurse is reviewing he laboratory results of a client who has a prescription for sodium polystyrene sulfonate (Kayexalate) every 6 hr. which of the following should the nurse report to the provider? Potassium 5.2 mEq/L A nurse is caring for a client who has tuberculosis and is taking isoniazid and rifampin. Which of the following outcomes indicates that the client is adhering to the medication regimen? The client has a negative sputum culture A client is caring for a client who develops an anaphylactic reaction to IV administration. After assessing the client's respiratory status and stopping the medication infusion. Which of the following actions should the nurse take next? Administer epinephrine IM A nurse is caring for a client who is taking sertraline and reports a desire to begin taking supplements. Which of the following supplements should the nurse advise the client to avoid? St. John's Wort A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure and a new prescription for lisinopril. For which of the following adverse effects should the nurse monitor when administering lisinopril? Hypotension A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving heparin IV continuous IV. The client has an PPT of 90 seconds. They should monitor the client for which of the following changes in their vital signs? Increased blood pressure A nurse is preparing to administer medication to a client and discovers a medication error. The nurse should recognize that which of the following staff members is responsible for completing an incident report? The nurse who identifies the error A nurse is planning care for a client who is receiving morphine via continuous epidural infusion. The nurse should monitor the client for which of the following? Pruritus A nurse is preparing to administer digoxin orally to a client. Idenfy the sequence of steps the nurse should take. (Move the steps into the box on the right, placing them in the order of performance. Use all the steps.) a. Obtain the client's apical heart rate b. Remove the medication from the dispensing system c. Open the medication package d. Compare the client's wristband to the medication administration record e. Document administration of the medication A home health nurse is visiting a client who has heart failure and a prescription for furosemide. The nurse identifies that the client has gained 2.5 kg (5 lb.) since the last visit 2 days ago. Which of the following actions should the nurse take first? Determine medication adherence by the client A nurse is preparing to administer the initial dose of penicillin G IM to a client. The nurse should monitor for which of the following as an indication of an allergic reaction following the injection? a. Urt Urticaria A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for theophylline, a sustained-released capsule. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? "I can take my medication in the morning with my coffee." A nurse is mixing regular insulin and NPH insulin in the same syringe prior to administering it to client who has diabetes mellitus following actions should the nurse take first? Inject air into the regular insulin vial A nurse is preparing to administer subcutaneous heparin to a client. Which of the following should the nurse take? Insert the needle at least 5 cm (2 in) from the umbilicus A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for amoxicillin. Which of the following findings indicates the client is experiencing an allergic reaction? Cardiac dysrhythmia A nurse is teaching a newly licensed nurse about medication reconciliation. The nurse should instruct the newly licensed nurse to perform medication reconciliation for which of the following? A client who is transferal to a step-down unit A nurse is reviewing the laboratory values of a client who is taking atorvastatin. Which of the following laboratory values indicates the treatment has been effective? LDL 120 mg/dL A nurse is receiving a medication prescription by telephone from a provider. The provider states, "Administer 6 milligrams of morphine IV push every 3 hours as needed for acute pain." How should the nurse transcribe the prescription in the client's medical record? Morphine 6 mg IV push every 3 hr PRN acute pain A nurse is assessing a client's IV infusion site and notes that the site is cool and edematous. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Apply a warm, moist compress A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for clozapine. Which of the following statements should the nurse include in the teaching? "Notify your provider if you develop a fever while taking this medication." A nurse is planning to administer medication to an older adult client who has dysphagia. Which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? Mix the medications with a semisolid food for the client A nurse is providing teaching to a client about the administration of omeprazole. Which of the following should the nurse include? "You cannot take this medication with an antacid." A nurse is assessing for allergies with a client who is scheduled to receive the influenza vaccine. Which of the following allergies should the nurse report to the provider as a possible contraindication to receiving the vaccine? Eggs A nurse is caring for a client who has a new diagnosis of benign prostate hypertrophy and a prescription for doxazosin. The client tells the nurse. "I do not take this medication. I would prefer a natural therapy." Which of the following supplements should the nurse suggest the client discuss with the provider? Saw palmetto A nurse is caring for a client who is taking digoxin to treat heart failure. Which of the following predisposes this client to developing digoxin toxicity? Taking a high ceiling diuretic A nurse is administering naloxone to a client who has developed an adverse reaction to morphine. The nurse should identify which of the following findings as a therapeutic effect of naloxone? Increased respiratory rate A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has sinusitis and a new prescription for cefuroxime. Which of the following client information is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? The client has a history of a severe penicillin allergy A nurse is assessing a client who has hypermagnesemia. Which of the following medications should the nurse prepare to administer? Calcium gluconate A nurse is reviewing the list of current medication for a client who is to start prescription for carbamazepine. The nurse should identify that which of the following medications interacts with carbamazepine? Estrogen-progestin combination A nurse is teaching a guardian of a school-age child who has a new prescription for a fluticasone metered-dose inhaler. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? (SATA) c. "Shake the device prior to administration." d. "A spacer will make it easier to use the device." e. "Rinse your child's mouth following administration." A nurse is preparing to administer potassium chloride elixir 20 mEq/day PO to divide equally 12 hr. available is 6.7 mEq/5 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer per dose? (Round the answer to the nearest tenth. Use a leading zero if it applies. Do not use a trialing zero.) 7.5 mL A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving a peripheral IV infusion and notes infiltration of fluid into the tissue surrounding the insertion site. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Elevate the extremity A nurse us caring for a client who is in shock and is receiving an infusion of albumin. Which of the following findings should the nurse expect? Increase in BP A nurse is discussing adverse reactions to pain medications in older adult clients with a newly licensed nurse. Which of the following findings should the nurse include as risk factors for an adverse drug reaction? (SATA) a. Polypharmacy c. Decreased percentage of body fat d. Multiple health problems e. Decreased renal function A nurse is reviewing the laboratory data of a client prior to administering IV tobramycin. Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the provider? Creatinine 2.5 mg/dL A nurse is preparing to administer enoxaparin to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Apply firm pressure to the injection site following administration A nurse is reviewing a client's 0800 laboratory values at 1100. The nurse notes that the client received heparin at 1000. Which of the following laboratory values warrants an incident report? ePTT 90 seconds A nurse is caring for a client who has breast cancer and reports pain. 1 hr after administration of prescribed morphine 10 mg IV. Which of the following medications should the nurse expect to administer? Lidocaine patch A nurse is caring for a client who is to receive potassium replacement. The provider's prescription reads. "Potassium chloride 30 mEq in 0.9% sodium chloride 100 mL IV over 30 min." which of the following reasons should the nurse clarify this prescription with the provider. The potassium infusion rate is too rapid A nurse is monitoring laboratory values for a client who has chronic heart failure and is receiving digoxin. Which of the following values should the nurse report to the provider? Potassium 2.9 mEq/L A client who has active tuberculosis and is taking rifampin reports that his urine and sweat have developed a red tinge. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Document this as an expected finding A nurse accidentally administers the medication metformin instead of metoprolol to a client. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? Check the client's glucose level A nurse is administering 4 mg of hydromorphone to a client by mouth every 4 hr. the medication is provided as hydromorphone 8 mg per tablets. Which of the following actions is appropriate for the nurse to take? Dispose of the remaining medication while another nurse observes A nurse is caring for 4-year-old child following an orthopedic procedure. When assessing the child for pain. Which of the following pain scales should the nurse use? FACES A nurse is planning care for a client who requires treatment for high cholesterol. Which of the following prescriptions should the nurse expect to administer? Colerain A nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure. The nurse administered furosemide 60 mg IV bolus 30 min earlier. For which of the following findings should the nurse notify the provider? The client reports difficulty hearing A nurse is planning teaching for a client who is trying to quit smoking. Which of the following instructions about nicotine replacement options should the nurse include? Do not drink beverages while sucking on a nicotine lozenge A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for total parental nutrition (TPN). Which of the following routes of administration should the nurse use? Intravenous A nurse is preparing to initiate IV therapy for a client. Which of the following sites should the nurse use to place the peripheral IV catheter? Nondominant dorsal venous arch A nurse is assessing a client who is taking an osmotic laxative which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication of fluid volume deficit? Oliguria A nurse is reviewing the laboratory results of a client who is taking amitriptyline which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the provider? Total bilirubin 1.5 mg/dL A nurse is caring for a client who is taking lithium and reports starting a new exercise program. The nurse should assess the client for which of the following electrolyte imbalances? Hyponatremia A nurse is assessing a client after administering phenytoin IV bolus for a seizure. Which of the following should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of this medication? Bradycardia A nurse is consulting a formulary about a client's new prescription for raloxifene. The nurse should identify that this medication is used to treat which of the following conditions? Osteoporosis ***A nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription of Alendronate for osteoporosis. What instructions should the nurse include?*** Sit upright for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication A nurse is teaching a client who has pernicious anemia to self administer cyanocobalamin. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? Administer the medication into one nostril once per week A nurse is teaching a newly license nurse about medication reconciliation. The nurse should instruct the newly license nurse for medication conciliation for which of the following clients? A client who has been transferred to a step down unit. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for carbamazepine for the treatment of seizures. The nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? Blurred vision A nurse is caring for a client who has major depression and a new prescription for citalopram. which of the following adverse effects is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? Confusion A nurse is assessing a client who is in labor and is receiving epidural anesthesia. which of the following findings should the nurse identify as the priority? Hypotension A nurse is reviewing a client's laboratory results before administering furosemide 40 mg IV bolus. For which of the following values should the nurse withhold the medication and contact the provider? Potassium 2.5 mEq/L A nurse is teaching a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis about management of medication for the disease. which of the following statements is appropriate for the nurse to make? You will need to take two or more medication to treat your disease ***A nurse is planning care for a client who has a prescription for erythromycin lactobionate IV bolus. which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care?*** Monitor for hearing loss ***For ferrous gluconate. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching?*** I should stay upright or 15 minutes after taking this medication A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking pioglitazone. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects? Orthostatic hypotension A nurse is wanting to report a n infusion reaction for a client who is receiving a dose via IV of amphotericin B. which is the following findings that indicate to the nurse that the patient is experiencing an acute infusion reaction? Fever A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for paroxetine. the nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? Drowsiness A client who has Graves' disease is prescribed methimazole. Which of the following effects should the nurse expect to see after the client has taken, he medication for 2 months? Increased sleeping ***A nurse is reviewing a client's 0800 laboratory values at 1100. the nurse notes that the client received heparin at 1000. which of the following laboratory values warrants an incident report? *** aPtt 90 A nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has sinusitis and a new prescription for cefuroxime. which of the following client information is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? A client with a history of severe Penicillin allergy A nurse recently administered filgrastim intravenously to a client who has cancer and is receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy. for which of the following data, discovered after the medication was administered, should the nurse file an incident report.? Vile sat out for 2 hours at room temperature before administration ***A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin sublingual. which of the following client responses indicates an understanding of the teaching? *** keep tablets in dark container at room temperature A nurse is preparing to administer the initial dose of penicillin G IM to a client. The nurse should monitor for which of the following as an indication of an allergic reaction following the injection? Urticaria Lido w/epi- epi slows absorption of lido Hydroxychloroquine, malaria drug- adverse= retinopathy Sumatriptan- do not give history of ischemic heart disease Varicella- not ok w/gelatin allergy Flu vaccine not ok if egg allergy Tobramycin therapeutic range: 5mcg-10mcg/ ml Pharm ATI Study Doc Notes from question bank on ATI: Chlorothiazide causes hypokalemia Thyroid levels: TSH 0.3-5mcg/mL will be higher in hypothyroidism. T3: 70-205ng/dL under 50 years and 40-180ng/dL over 50 T4: 4-12mcg/dL under 60, 5-11mcg/dL over 60 Thyroxine-binding globulin 1.7-3.6 mg/dL Levothyroxine- tx hypothyroidism, can be crushed Methimazole- tx hyperthyroidism Somatropin- growth hormone for client w/ growth hormone deficiency in anterior pituitary gland Propylthiouracil- tx hyperthyroidism, 2 line meds, black thyroid production Infusion pump: change every 1-3 days, short acting insulin, move 1in away from old site Lispro- rapid acting insulin onset of 15 minutes, give food within 15 min Short acting or combination insulin- onset of 30-60 min Increase fluids when using PCA pump, continue to ambulate patient even on PCA PO morphine takes 60-90 minutes to peak Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy: Propylthiouracil in first trimester Methimazole during second and third trimester Liothyronine is for hypothyroidism Misoprostol is contraindicated with past c-section Oxytocin is contraindicated for clients with active genital herpes Vitamin deficiencies: Vitamin K- bleeding, vitamin D-irregular bone formations in kids like rickets or osteomalacia in adults, vitamin E-abnormal movements or ataxia, vitamin A blurred vision, night blindness, vitamin A can cause damage to the bones by decreasing absorption of vitamin D At risk for vitamin D deficiency- obesity, pregnancy, dark-pigmented skin, older adults Hydrocortisone for adrenal insufficiency: take in the morning unless altered sleep pattern, carry supply of pills in case unexpected stress, increase dosage during stressful times or illness Omeprazole for ulcers, dont use longer than 1-2 months, increases risk of getting pneumonia, report severe diarrhea, take once daily before meal, less effective if taken with food Furosemide: potassium sparing diuretic, don’t take with NSAIDs, increases risk of ototoxicity when taken with streptomycin Heparin- aPTT 60-80 seconds, if higher reduce infusion rate and assess for bleeding, protamine sulfate for severe overdose, can increase potassium levels, and cause thrombocytopenia so check platelet count (normal 150-400 thous). Given subQ in abdomen using 25 gauge or smaller Fondaparinux- anticoagulant Bivalirudin- IV anticoagulant Hepatotoxic drugs: dantrolene- given to treat muscle spasticity, malignant hyperthermia, cerebral palsy. Isoniazid treats TB. Methotrexate a non-biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug can also cause immunosuppression. Chenodiol to treat gallstones, LFTs required during tx, usually used for 2 years, can cause diarrhea, pregnancy risk cat X. Gemfibrozil- lowers triglycerides. Ranitidine- tx gastric ulcer Diltiazem- Calcium channel blocker, anti arrhythmic used during cardioversion to that arterial fibrillation, contraindication: hypotension, bradycardia Amoldipine and Nifedipine are CCB used to treat HTN and angina, not for arrhythmias Lidocaine is an antidysrhythmic med used to treat ventricular dysrhythmias Lactulose reduces ammonia levels Fludrocortisone adverse affect of hypokalemia due to excessive sodium and water retention, other s/e are HTN, weight gain, increased appetite and nausea Thyrotoxicosis: can results of too much levothyroxine, s/e: chest pain, tachycardia, insomnia, tremors, hyperthermia, heat intolerance, and diaphoresis Clopidogrel- antiplatelet med that inhibits aggression of platelets to prevent thrombotic events like MI, ischemic stroke, and peripheral vascular disease. Contraindication- Hx of intracranial bleeding ie: hemorrhagic stroke Imipenem- antibiotic that can cause seizures Cephalosporins can increase risk of bleeding Penicillin G IM can cause sensory dysfunction if injected into peripheral nerve Aminoglycosides can cause ototoxicity which can manifest as tinnitus and deafness. Can affect liver and spleen, can cause twitching or flaccid paralysis Hydrochlorithiazide- diuretic that causes potassium excretion, used for diabetes insipidus Isoniazid- Tx for TB, no alcohol, take on empty stomach, hepatotoxic, avoids antacids, monitor AST, report jaundice, nausea, dark urine Anticoagulants like warfarin dont dissolve clots, they prevent clots therefore reducing risk of having a stroke Chlordiazepoxide- long-acting oral benzo, first line med for acute alcohol withdraw Acamprosate- used to maintain abstinence with alcohol disorder Naltrexone- decreases cravings for alcohol Disulfiram- helps avoid alcohol use Prednisone- used for severe rheumatoid arthritis, can cause gastric ulceration not immunosuppression. Used short-term, if long term monitor for osteoporosis and stress fractures Prenisone- tx asthma, if used long term take med on alternate days to decrease adverse effects like suppression on the adrenal gland, don’t stop suddenly, take with food can cause GI distress and ulcers DTAP- given to young children either in deltoid of mediolateral thigh, not a live virus, first one given at 2 months old then 4 months then 6 months then 15-18 months then 4-6 years old, five injections given IM Memantine is excreted through kidneys, check creatinine clearance level, used for Alzheimer’s Nitro patch- worn 12-14 hours then removed at night, rotate every few days to hairless areas, headache is common s/e Alosetron used to treat IBS with diarrhea, client must sign agreement before using, has potentially fatal affects associated w/ constipation and bowel obstruction, stop taking if diarrhea is not controlled after 1 month, report tachydysrhythmias Beta blocker contraindication: asthma, because it causes bronchospasm Oral contraceptives inhibit ovulation, causes thickening of endometrial lining, decreases follicular stimulating hormone, thicken cervical mucus Dinoprostone vaginal insert pouch- lie on back for at least two hours, if using gel use catheter and lay down for 30 min, pouch releases med slowly and is removed after 12 hours or with active labor, gel can require 2-3 doses during 12 hours timeframe Bleomycin- treat cancer can cause severe lung injury priority to check pulmonary function, thrombocytopenia, decreased kidney function, weight gain, and peripheral edema Doxazosin used to treat BPH can cause hypotension, dizziness, h/a, depression, drowsiness Acarbose- treat T2D, most symptoms are GI related like diarrhea, abdominal distention, cramping, sleepiness, h/a, anemia because it can decrease absorption of iron, take with food 3x/day, can be used alone or with other meds like insulin MAOIs like phenelzine avoid foods that contain tyramine Amytriptyline- treat depression can cause sedation, dry mouth urinary retention, blurred vision, constipation, weight gain Don’t take St. Johns wort with antidepressants, can cause serotonin syndrome Spironolactone- potassium sparing diuretic, can cause gynecomastia, impotence, irregular menses, and hirsutism in women Giving IV injection slowly helps reduce risk of toxicity Tetracycline- take on empty stomach, avoid or limit dairy products, don’t take with iron or antacids Ginkgo biloba- herbal supplement to decrease platelet aggregation, and increase cognitive function in older adults, can improve leg pain of peripheral arterial disorders, don’t take with other anti platelets like NSAIDs or clopidogrel Feverfew is used to prevent migraines and can decrease platelet aggregation Echinacea- used to strengthen immune system and treat infections and colds Garlic can lower cholesterol and triglyceride levels and decrease platelet aggregation, if taking garlic there is increased risk of bleeding Ginger- alleviate nausea and vomiting Saw palmetto- taken for urinary health promotion like for BPH Corticosteroids can delay wound healing like prednisone Nifedipine can cause dermatitis and urticaria Chlopromazine- tx schizophrenia, adverse affects: parkinsonism can cause dermatitis and eczema, Amantadine- an antiparkinsonian med used to treat extrapyramidal manifestations Bupropion- atypical antidepressant Phenelzine- MAOI antidepressant Hydroxyzine- antihistamine tx mild to moderate anxiety Cyclosporine- taken to reduce organ rejection, for the rest of their life, immunosuppressive, can cause higher BP and require antihypertensive meds Metoprolol- treat HTN, can mask symptoms of hypoglycemia in diabetics, can cause weight gain Clozapine- tx schizophrenia, can cause agranulocytosis- life threatening, WBCs are severely decreased. Myocarditis: potentially fatal effect occurs within 30 days of starting med, look out for chest pain, palpitations, tachycardia, dyspnea, tachypnea, fever, peripheral edema, unexplained fatigue. Normal neutrophil count is 2500-8000/mm^3, also can cause hyperglycemia, dyslipidemia, elevated triglycerides. Normal triglycerides: 35-160 Normal cholesterol less than 200 Clomiphene- tx infertility, promotes follicular maturation, successful tx would show progressive follicular enlargement followed by conversion of the follicle to a corpus luteum after ovulation Warfarin- prevent thrombosis, delayed onset given long-term, steroids can interfere, INR 2-3 if too high give vitamin K, INR drawn daily first five days and then 2x weekly for next 1-2 weeks, carry medical alert, Antitussives suppress cough reflex Ipratropium- tx COPD bronchospasms not for asthma Tiotropium- Long acting inhaled corticosteroid for COPD not asthma Budesonide- tx asthma, inhaled corticosteroid to decrease inflammation, for severe forms of asthma to prevent attack Acetycysteine- tx chronic bronchitis, cough productively before tx TB tx- isoniazid and rifampin used together Ethambutol- given for TB that’s drug resistant, adverse effect: loss of red/green color discrimination, peripheral neuropathy, Rifampin- tx TB, expected effects: red-tinged urine, saliva and tears. Decreased visual acuity is bad, stop med Lithium- adverse effects: tinnitus, blurred vision, dry mouth, interacts with most NSAIDs like ibuprofen but not aspirin Digoxin- tx dysrhythmias, slows AV conduction and prolongs PR interval, adverse effects: n/v, abdominal discomfort, fatigue, and visual disturbances can indicate toxicity. Menopause- estrogen and progestin given short term to control urogenital atrophy and other symptoms of menopause Tobramycin- expected peak levels 5-10mcg/mL Amlodipine- tx HTN, s/e: dizziness, palpitations, peripheral edema, flushing, h/a Clonidine- tx HTN, avoid driving until reaction to med is known, can cause drowsiness, weakness, sedation, don’t stop suddenly due to HTN crisis, dry mouth and constipation are expected at first Methotrexate- chemo and immunosuppressant, can cause: thrombocytopenia, kidney injury, bone marrow suppression (monitor hemoglobin), liver damage. Monitor AST, BUN, platelets, and hemoglobin Oral contraceptive- contraindication would be liver disease Clopidogrel- antithrombotic med inhibits platelet aggregation, used to prevent stenosis, MIs, and strokes. Monitor for bleeding: coffee ground emesis, black tarry stools, ecchymosis. S/e: dizziness, h/a, HTN, diarrhea Lisnopril- ACE inhibitor, can cause angioedema: swelling of the tongue, lips or pharynx. Can cause hyperkalemia, persistent, dry cough, flushing, pruritus, rashes Captopril- ACE, can cause hypotension, dizziness, change positions slowly, can cause severe neutropenia so report sore throat and fever. Take 1 hour before or 2 hours after meals, don’t take NSAIDs. Can affect urinary system causing dysuria, urinary frequency, and changes in amount. Enlapril- ACE, can cause hypotension and postural hypotension, decrease in Hgb and Hct, can cause kidney failure, hyperkalemia Tetracycline antibiotics- doxycycline, can cause photosensitivity, diarrhea, interfere with color vision Aminoglycosides- antibiotics (-mycins), adverse effect ototoxicity Needle sizes for IM- 1.5 inches for normal BMI, if obese possibly 2.5-3 inches Simvastatin- tx hyperlipidemia, serious adverse effect is muscle injury which can progress to myositis, report any onset of muscle pain or tenderness immediately. Other s/e: constipation, flatulence, h/a. NO GRAPEFRUIT Gemfibrozil- lowers triglycerides by decreasing livers uptake of fatty acids, can cause liver toxicity so monitor liver function Dobutamine hydrochloride- vasopressor that improves cardiac output and hemodynamic status, improves hypotension and increases heart rate Alendronate sodium- used with osteoporosis, take with full glass of water on empty stomach, sit upright after taking, s/e: esophageal irrigation, musculoskeletal pain, femur fractures, osteonecrosis of the jaw Alendronate- tx post menopause, take on empty stomach, sit upright for 30 min, take with full glass of water Etidronate- don’t take with antacids or vitamins that contain mineral supplements Sodium phosphate- can cause excess fluid loss as a result of cleansing the bowel of stool, at risk for electrolyte imbalance, ingest 20 tabs with clear liquid in the evening and 20 tabs the next day Flu vaccine- contraindication allergy to eggs Varicella vaccine- contraindication allergy to gelatin, neomycin Bethanechol- tx urinary retention, can cause excessive salivation, hypotension, bradycardia, bronchoconstriction Chronic use of salicylates like aspirin can lead to ototoxicity Diltiazem- anti arrhythmic reduces ventricular rate in atrial fibrillation Atropine- anti arrhythmia agent given to accelerate HR to treat sinus bradycardia and heart block Epinephrine and vasopressin- vasopressor given to treat cardiac arrest and asystole Varenicline- used for smoking cessation, can develop neuropsychiatric effects that can progress to depression and suicide. Other s/e: n/v, altered sense of taste, skin rash Methotrexate- tx rheumatoid arthritis, given within 3 months of diagnosis to prevent or delay joint degeneration, glucocorticoids are given during flare ups Pioglitazone- used with T2D, increases cellular response to insulin, peaks 2-4 hours Alprazolam- bento, taper off slowly if used long term, when stopping can experience insomnia, muscle twitches, convulsions, paranoia, delirium if stopped too quickly, Hormone injection therapy- given subq, will grow 1-3 inches, will last 4-6 years, given 6-7 times each week Pharmacokinetics with older adult- excretion of medication is reduced, absorption is reduced, liver metabolizes slower, can increase concentration of water-soluble meds Lipid soluble meds- meds cross the client’s membranes that separate the med from the blood Bismuth subsalicylate- for peptic ulcer disease, can assist by eliminating bacteria H pylori Meds for PUD- they can increase prostaglandins, increase blood flow to the stomach, increase bicarbonate Pegloticase- tx gout, can take NSAIDs during flare ups, given if allopurinol is not working, given IV, adverse effects: anaphylaxis, can give client antihistamine before and reduce rate of IV if necessary Allopurinol- tx gout, can cause renal injury so increase fluids 2L/day, dose begins at 100mg daily, taken once daily Zafirlukast- leukotriene receptor antagonist for asthma, not given with theophylline it can suppress metabolism of theophylline which can lead to toxicity. Theophylline- bronchodilator, signs of toxicity: CNS stimulation like tremors, seizures, diarrhea, restless, irritable, tachycardia. Don’t take with leukotriene modifier like zileuton which impairs the metabolism and can cause toxicity with theophylline Comolyn- mast cell stabilizer that decrease inflammation of airways Insulin glulisine- rapid acting, onset of 15 minutes Regular insulin- onset 30-60 minutes NPH insulin- onset of 1-2 hours Glargine- long acting, give once per day, should be clear, don’t mix with any other insulins Alteplase- given for MI, adverse affect is bleeding, used to treat clot formation by dissolving clots Erythromycin- antibiotic, report persistent diarrhea to provider, can take antacids with it but not with azithromycin Telavancin- check client for pruritus, flushing, rash, urticaria, tachycardia, hypotension, could mean IV is given too rapidly. Adverse effect: foamy urine, hypotension “red man syndrome” Salmetrol- tx asthma, long-term use increases risk of asthma related death, give with inhaled corticosteroid Budesonide- tx asthma or Crohn’s, corticosteroid, decreases inflammation, suppresses immune system, inhibit actions of prostaglandins and leukotrienes. Can increase blood glucose, causes sodium and water retention and potassium loss, can cause hypokalemia and gastric ulcers Ranitidine- tx gastric ulcer, GERD, less effective in people who smoke, not affected by food, take antacids 1 hour after, dizziness is adverse effect report to the provider Levonorgestrel-releasing IUD- spotting between cycles is an adverse effect, vaginitis is a common adverse effect for a vaginal ring not IUD Nifedipine- given to stop premature labor, can cause hyperglycemia and hypotension if client is hypovolemic Epoetin alfa- tx chronic kidney failure, can cause HTN, monitor BP before and during med Filgrastim- increases neutrophil production, given to reduce risk of infection in clients receiving chemo or got bone marrow transplant. Can cause anemia Gabapentin- tx neuropathic pain that is sharp and darting, can decrease cramping, aching, and burning pain Etidronate- can help reduce cancer related bone pain Sulfasalazine- tx ulcerative colitis and RA, can cause jaundice and yellow/orange urine notify provider if those happen. It can cause bloody diarrhea, stomatitis, h/a, peripheral neuropathy. Check CBC before giving med can cause bone marrow suppression Naproxen- NSAID, increase risk of nephrotoxicity when taken with streptomycin Amphotericin B- anti fungal agent, increase risk of nephrotoxicity when taken with streptomycin Mineralcorticoids- tx Addisons disease, maintain electrolyte and fluid balance, high levels of aldosterone increase risk of cardiac dysrhythmias Glucocorticoids- enhance carb, fat and protein metabolism, take with calcium supplement, avoid NSAIDs Scopolamine patches- tx motion sickness, apply patch behind ear, replace every 72 hours, apply one patch at a time Mucolytic agents- can irritate airways causing brochospasm while producing a cough and thinning mucus secretions Omeprazole and other PPIs- report severe diarrhea, associated with C-diff infection, take before meal in the morning, can cause deficiency in magnesium Fentanyl patch- given to a client who is opined tolerant, client with severe persistent pain Terbutaline- tocolytic, can experience tachycardia, if HR is over 120 medication needs to be stopped, can experience hyperglycemia Gentamicin- adverse effects: proteinuria which is manifestation of nephrotoxicity, monitor for oliguria and hematuria, can cause hypokalemia, impaired hearing, if given through eye drops can cause eye photosensitivity, redness, itching, and excess tearing Estradiol cream- has fewer side effects than oral estrogen, intravaginal estrogen used 1-3 times per week, decreases risk of postmenopausal bone lose Alosetron- tx IBS with diarrhea contact provider if constipated, initial dosage is 0.5mg twice daily, increased after a month to 1mg if still not working med will be stopped Zidovudine- tx AIDS, can cause severe anemia and neutropenia from bone marrow suppression causing hematologic toxicity, monitor hemoglobin other adverse effects: n/v, decreased appetite, anxiety Sirolimus- avoid grapefruit Famotidine- adverse effect thrombocytopenia so look out for bleeding Epoetin alfa- stimulates production of RBC, adverse effects- HTN, clot formation IVIG- IV immune globulin, can’t get live vaccine for at least three months Ticarclillin-clavulanate- check BUN and creatinine, doesn’t matter if allergic to amionglycosides High dose ibuprofen with CF can slow progression of pulmonary damage by suppressing the inflammatory response. Meripidine- opined analgesic, not indicated for cancer pain, it can cause severe toxic effects when given more than a few doses, doses range of 50mg every 3-4 hours max 600mg/day Enteric coating- helps prevent stomach pain Fentanyl transdermal patch- can’t drink grapefruit juice, takes up to 24 hours to reach maximum effect, can still cause constipation, avoid direct heat on patch Allopurinol- used for chronic gout not used in tx for acute flare up, give NSAID like naproxen Sumatriptan- tx for cluster headaches, adverse effect: chest pressure and heavy arms, HTN, alterations in vision. Contraindication- cardia diseases Cyclopegia- aka paralysis of accommodation focusing for near vision is impaired which causes blurred vision, happens after atropine is administered Risedronate- tx osteoporosis, drink full glass of water with med, remain upright for 30 min, take on empty stomach, take in the morning 30 min before breakfast Clozapine- tx schizophrenia, temperature will be indicator of adverse effect. Antipsychotics cause depletion of WBCs Hydroxycholoquine- tx rheumatoid arthritis, adverse effect: retinopathy look out for vision changes Methotrexate- tx RA, causes immunosuppression can cause mouth sores, GI ulcers Minocycline- tx RA, antibiotic, adverse effect: dizzy Leftunomide- tx RA, hepatotoxic, report liver failure signs Glucocorticoid adrenal replacement- tx Addisons, adverse effect: inhibit bone growth, osteoporosis, weight gain, HTN, restlessness, agitation, anxiety Spinal anesthesia- hypotension is adverse effect, rarely get headaches if they do remain flat in bed, can cause urinary retention Lidocaine toxicity- sign is bradycardia Infliximab- Tumor necrosis factor antibody med, reduces RA manifestations can cause immunosuppression Morphine- Given IV bolus, respiratory depression can occur 7 min after given, peaks at 20 minutes, don’t give if resp rate below 12, give slowly over 4-5 minutes Brimonidine- tx open angle glaucoma, alpha 2 adrenergic agonist, decreases intraocular pressure Angiogenesis inhibitors- tx macular degeneration, block growth of new optic blood vessels Mydriasis- dilation of the pupil Vasopressin- tx diabetes insipidus, contraindication renal impairment: low creatinine clearance below 87mL/min Desmopressin- tx diabetes insipidus, headaches are indicator of adverse effect of water intoxication because med can cause fluid retention Clients with diabetes insipidus- can have frequent thirst due to lack of ADH, norturia and excessive urination, at risk of dehydration body will compensate by increasing heart rate which can cause palpitations. Giving pressin can stop these manifestations Simvastatin- used for tx of clients who have had an MI Furosemide- loop diuretic tx pulmonary edema and congestive heart failure Sildenafil- tx erectile dysfunction, greatly intensifies nitroglycerin-induced vasodilation causing life threatening hypotension Don’t take cyclosporine with tacrolimus, space apart 24 hours when switching, taking together increases risk of nephrotoxicity Nitroglycerin topical ointment- apply with a dose-measuring applicator, cover ointment with plastic wrap, use gloves, avoid rubbing or massaging Alendronate- tx Paget’s disease of the bone, ambulate client to a chair before giving med, want them sitting upright to prevent esophagitis, keep up 30 mint after, give before breakfast, give with water Hydroxyzine- anticholinergic dry mouth is common, sometimes used to treat anxiety, has antiemetic properties Fluticasone- long term use can cause adrenal insufficiency look for anorexia, weakness, nausea, hypotension, hypoglycemia Methotrexate- tx RA, delays progression of the disease and delay joint damage or deformity Brompheniramine- tx allergies, first gen antihistamine causes anticholinergic effects like dry mouth, can experience GI issues like nausea, vomiting, loss of appetite, diarrhea, constipation, can cause CNS effects like dizziness, confusion, fatigue, urinary retention, palpitations Rotavirus vaccine- given at 8 weeks, not given if vomiting, diarrhea, or hx of intussusception which is where part of the intestines telescopes into adjacent part, also don’t give to infants that have uncorrected GI congenital malformation Interferon beta-1a- tx multiple sclerosis, adverse effect flu-like symptoms like general body and muscle aches Dimethyl fumarate- tx multiple sclerosis, can cause GI discomfort Teriflunomide- tx multiple sclerosis, disease modifying med can cause hair loss of alopecia Natalizumab- tx multiple sclerosis, disease modifying med, can cause UTIs Raloxifene- tx osteoporosis, clients have increases risk for thromboembolic events like DVTs, pulmonary embolism, stroke so monitor for those like sudden onset of dyspnea, contraindication for clients with DVTs Teriparatide- tx osteoporosis, increases bone formation, adverse effects: arthralgia, muscle pain in lower extremities, headaches Denosumab- tx osteoporosis, decreases bone resorption, monitor for bladder infections Zoledronate- tx osteoporosis, inhibiting osteoclasts, can cause osteonecrosis of the jaw which can result in localized bone death and decreased bone strength Vincristine sulfate- tx acute lymphocytic leukemia, adverse effects: neurotoxicity, monitor for paresthesia, other effects are alopecia, stomatitis, constipation Grave’s Disease: hyperthyroidism, have difficulty focusing, restlessness, mani-type behaviors, insomnia, increased appetite, weight loss, increased GI motility, Propylthiouracil: tx Grave’s (hyperthyroidism), thyroid hormone antagonist decreases T4 hormone, reducing manifestations. Adverse effect: decrease in WBC or myelosuppression, can cause severe liver injury, report dark urine and jaundice, lab tests to check liver function, taken multiple times a day. Rash is a common reaction it doesn’t indicate allergy, likely to cause drowsiness Give subQ injections outside the 5cm (2in) range of umbilicus, above the iliac crest. Fluoxetine (SSRI): tx depression, can cause muscle twitching, sexual dysfunction, abnormal dreaming, sedation, delusions, hallucinations, psychosis, agitation, euphoria. Ranitidine: tx gastric ulcers, take with or without food, report yellowing of skin, take full course don’t stop when stomach pain is gone Metoclopramide: increases gastric motility by reducing n/v and prevents nausea has many CNS effects, dizziness, fatigue, sedation, tardive dyskinesia. Contraindicated with intestinal obstruction or perforatio. Use caution with HTN Neuroleptic Malignant Syndrome: high fever, diaphoresis, respiratory distress, and hypo or hypertension Cholinergic crisis: caused by too much cholinesterase inhibitor like neostigmine. Give an anticholinergic like atropine Protamine: heparin antagonist given if aPTT is greater than 70 seconds Potassium iodide: thyroid hormone antagonist given with tx of radioactive iodine exposure Filgrastim: stimulates bone marrow to make WBCs, given to chemo clients Hypokalemia: presence of U-waves, ST depression Hyperkalemia: tall tented-T waves, widened QRS complex Ischemia: ST elevation Acetylcysteine: antidote for acetaminophen toxicity Benzotropine: anticholinergic tx adverse effects of Parkinson’s by reducing rigidity and tremors Physotigmine: antidote for antimuscarinic poisoning from meds like atropine, scopolamine, some antihistamines, phenothiazines, and tricyclic antidepressants Metoprolol- Beta blocker, weight client daily, check apical pulse before giving, adverse effects: orthostatic hypotension, bradycardia. Don’t give is HR below 60 ARB’s- Sartans Sodium polystyrene sulfonate- tx hyperkalemia, monitor for constipation, lasts 24 hours in fridge, hole other oral meds for 6 hr before and after Mannitol- osmotic diuretic, decreases intraocular pressure. Adverse effects: increased intracranial pressure, seizures, confusion, h/a, can precipitate heart failure, pulmonary edema, if hear crackles stop medication Isotretinoin- tx severe nodulocystic ance vulgaris, has teratogenic effects give pregnancy tests, 2 before starting and one for every refill. Aspartate aminotransferase levels taken before staring, 1 month after starting, and periodically Donepezil- tx Alzheimer’s, adverse effects: Dyspnea, dizziness, diarrhea, dyspepsia Neostigmine- tx myasthenia gravis, adverse effects: mitosis which is pupillary constriction causing difficult with visual accommodation, increased salivation, urinary urgency, bradycardia Myasthenia gravis- breakdown in communication between nerves and muscles causing weakness and rapid fatigue of voluntary muscles H2 receptor antagonists like famotidine- treat ulcers by decreasing stomach acid Antacids like aluminum hydroxide- neutralize acids and prevent pepsin formation Capnography level- when back to baseline indicates the gas exchange is adequate After endoscopy client can go home once capnography returns to baseline, gag reflex return, and state of arousal is at preprocedure level Monitor for passing flatus after general anesthesia Oxybutynin- tx urinary incontinence, anticholinergic causes dry mouth, blurred vision, dry eyes, prolonged QT interval, palpitations, HTN, tachycardia Flumazenil- antidote for benzos Ergotamine- tx migraines by vasoconstriction dilated cerebral blood vessels, take one tablet at onset of migraine every 30 min, max of 3 tabs per 24 hours. Can cause ergotism which causes peripheral gangrene due to vasoconstriction and ischemia. If overused can become addicted, not safe for pregnancy, notify provider if tingling in fingers or toes, or if experiencing withdrawal signs like restlessness, h/a, n/v Tamoxifen- tx breast cancer, common causes hot flashes, can effect vaginal discharge, uterine cancer, n/v, chest pain, flushing, clots Bupropion- helps quit smoking, atypical antidepressant with stimulant properties causing agitation, tremors, mania, insomnia. Can cause bradykinesia, changes in vision and hearing. Methylprednisolone- tx multiple sclerosis, monitor blood glucose, avoid sick people, grapefruit can increase effects of med. Take with food or milk, increase intake of potassium Cyclobenzaprine- tx muscle spasms, taper off med to prevent abstinence syndrome or rebound insomnia. Causes anticholinergic effects Tizanidine- tx spasms, use with caution in clients with liver issues like hepatitis, med can cause liver damage, can cause urinary rhinitis Acetazolamide- tx open-angle glaucoma, report paresthesia like tingling in extremities, can cause: diarrhea, weight loss, polyuria Ciproflaxin- contraindication tendonitis, can cause achilles rupture Alcohol Treatments: Chlordiazepoxide- tx acute alcohol withdraw, prevents delirium tremens Propranolol- decreases cravings during withdraw Acamprosate- helps maintain abstinence by decreasing anxiety Atenolol or other beta-adrenergic blocker minimizes autonomic things like sweating Naltrexone- pure oppio antagonist given to decrease cravings for alcohol and block pleasurable effects Parenteral thiamine- given to a client with hx of alcohol use disorder and has ataxia, altered LOC, and nystagmus is exhibiting Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome due to thiamine deficiency Celecoxib- tx rheumatoid arthritis, NSAID Adalimumab- tx moderate to severe RA, monoclonal antibody, used when patents haven’t responded to other medications Abatacept- tx RA for patients that haven’t responded well to other meds, T-cell activation inhibitor acts by reducing T-calls, interferon gamma, and interleukins Hypercalcemia is an indication of vit D toxicity Disadvantage of inhaled glucocorticoid and a LABA combined is the dosages are fixed and can’t be adjusted Amitriptyline- tx depression, can cause orthostatic hypotension get up slowly, given 3x daily until therapeutic dose achieved and then entire dose is taken at bedtime, cause cause sedative effects, has anticholinergic effects causing constipation, dry mouth, urinary retention, and blurred vision. Can cause tachycardia and ECG changes, which puts older adult at risk for cardio effects so perform ECG before starting therapy in older adult Medication reconciliation- nurse does it whenever patient is transferred, provide the client and next provider with a list of meds that client will take after discharge. Don’t give handwritten, don’t include meds the client received at the care facility Selegiline- tx depression and mild Parkinson’s, notify provider is drowsy, can indicate serotonin syndrome. Adverse effects: bruising, diarrhea. Spinal anesthesia- if client dizzy with low BP place them in a head down position at 10-15 degrees Epinephrine- given for cardiac arrest, anaphylaxis, control of superficial bleeding, and delay of local anesthetic absorption Lidocaine- given for ventricular dysrhythmias Atropine- given for bradycardia, increases heart rate Diphenoxylate-atropine: tx opiod to tx diarrhea, adverse effects: drowsy, dry mouth, bronchial plugging causing asthma like symptoms Acetaminophen- can be given for pain to a client with peptic ulcer disease because it doesn’t affect blood coagulation and doesn’t increase risk of GI bleeding Aspirin- NSAID, antipyretic that suppressed platelet aggregatio, can be used to as prophylactic therapy for ischemic stroke, transient ischemic attack, chronic stable angina, and coronary stenting, if used long term can lead to ototoxicity, not given to children who have a viral infection like chicken pox or flu due to risk of getting Reye’s Syndrome which is a condition that causes confusion, swelling in the brain, and liver damage Reye’s Syndrome- early symptoms diarrhea, rapid breathing, vomiting, severe fatigue. Emergency tx if confusion, seizures, and loc Phenytoin- tx seizures, if stopped can cause status epileptics, adverse effect: cardiac dysrhythmias, hypotension if given too quickly, gastric discomfort for oral phenytoin reduced by taking with food, bradycardia, gingival hyperplasia, alter cognitive function, n/v. Should not exceed 50mg/ min. Therapeutic range: 10-20 mcg/mL Tobramycin- therapeutic levels 5-10mcg/mL Lamotrigine- tx seizures, Risk of Stevens Johnson syndrome or tonic epidermal necrolysis, which are reactions that occur 2-8 weeks after starting. Report rash to provider ASAP. Adverse effects: diplopia, dizzy, h/a Lactulose- laxative tx cirrhosis, tx is effective if there is a decrease in serum ammonia, works by decreasing ammonia levels by enhancing intestinal secretion of ammonia, an increase in AST indicate liver is worsening, a decrease in ALT means liver is improving but lactulose doesn’t directly effect that lab value, an increase in PT means liver is worsening. Liver is directly r/t clotting factors and ability to form a clot Iron dextran IV- administer small test dose five minutes before, can cause anaphylaxis, monitor client for hypotension and other anaphylaxis reactions, give dose slowly IV bolus over at least 1 min, IV infusion over 10-15 min Deferoxamine- antidote for iron toxicity Cyanocobalamin or vit B12- given for megaloblastic anemia Urine specific gravity- increase over 1.030 indicate dehydration Tardive dyskinesia- caused by antipsychotics, signs: repetitive involuntary movements Adenosine- tx atrial tachycardia, has short half life around 10 sec, can cause dyspnea due to bronchoconstriction, can give feeling of warmth and flushing of the face Quinidine- anti-dysrhythmic, can cause cinchonism: tinnitus, h/a, vertigo, and visual disturbances Baclofen- tx spasms, don’t stop taking suddenly can cause visual hallucinations, paranoia, and seizures. Adverse effects: urinary retention, constipation, orthostatic hypotension, take with milk or food. Report to provider if urinary frequency occurs. Use caution in males with BPH Cefotetan- antibiotic that affects vit K levels which can cause bleeding and epistaxis, and diarrhea. Second-get cephalosporin so doesn’t manifest disorientation Methadone- tx opioid withdrawal Methylnaltrexone- opioid antagonist can tx opined induced constipation Naloxone- tx opioid overdose Clarify orders for enteric coated meds through an NG tube like aspirin, they should not be crushed Detrimental inhibitory interaction- when meds are taken together and interfere with therapeutic effects like albuterol and propranolol Potentiative interaction- 2 meds taken together to increase or prolong therapeutic effects Increased adverse reaction- when detrimental potential interactions worsen adverse effects like warfarin and aspirin Toxicity-reducing inhibitory interaction- reduce effects or block action of another with a beneficial interaction to reduce toxicity like naloxone with opioid overdose Pancreatic enzyme replacement- given to CF clients, indication of therapeutic response is 1-2 bowel movements/ day, weight gain. Adverse effect of high doses would be abdominal distention Levodopa- tx Parkinson’s, can take months for full effect, don’t eat high-protein foods, given for more severe symptoms. Adverse effect: vivid dreams Cromolyn sodium- antihisamine (mast cell stabilizer), given for chronic asthma, takes weeks for full effect, given via nebulizer Verapamil- tx HTN and angina, calcium channel blocker, dilates arteries and decreases after load Isosorbide- nitrate, tx heart failure, don’t take with sildenafil, causes vasodilation so change positions slowly d/t orthostatic hypotension, take no later than 7pm, never double dose of med even if missed one Sildenafil- tx erectile dysfunction, don’t take with nitrates, use caution with liver disease, renal failure, and older adults. Contraindicated with nonartheritic ischemic optic neuropathy Fexofenadine- tx allergies, question if standard tabs are given to child below 12 years, don’t take with orange juice, 30mg 2x/ day is good for 7 year old Dexamethasone- glucocorticoid that decreases inflammation, immunosuppression, increases BG levels, can cause fluid retention Ezetimibe- tx hyperlipidemia, blacks absorption of cholesterol in intestinal tract. Adverse effects: myopathy, hepatitis, pancreatitis, thrombocytopenia, gallstones. Notify if jaundice Gemfibrozil- fibrate, can raise cholesterol content of bile and increase risk of gallstones, don’t take with ezetimibe. Pentazocine- agonist-antagonist opined given to relieve pain Butorphanol- opioid given to relieve pain Dinoprostone- med used to stimulate contractions and control hemorrhaging Aminophylline- systemic methylxanthine that decreases smooth muscle contraction, dilating bronchioles Hep A vaccine- normal for child to lose appetite for a few days Enoxaparin- low molecular weight heparin used to prevent a DVT Ticagrelor- anti platelet med prevents thrombotic events in clients who have acute coronary syndrome Psyllium- tx chronic constipation, increase fiber and dietary bulk in diet, mis with water and drink another full glass of liquid after, don’t use if abdominal pain, n/v, or fever occurs Phenazopyridine- tx pain for UTI, can change urine and other body fluids orange Tamoxifen- anti-estrogen med used to tx breast cancer, also used to prevent breast cancer XR- extended release can’t be crushed SL- sublingually, don’t crush or chew Amphetamine/dextroamphetamine- tx ADHD, report palpitations to the provider, med can cause: restlessness, take medication during the day, insomnia, appetite suppression causing weight loss. Eliminate caffeine from diet Zolpidem- tx helps sleep, can cause dizziness and daytime drowsiness, and confusion in older adults Niacin- tx reduce cholesterol levels or correct a deficiency Parenteral pyridoxine- tx vit B6 deficiency. Signs of vit B deficiency: peripheral neuritis and neuropathy Riboflavin- tx vit B2 deficiency. Signs: sore throat and cracks at corner of mouth, later signs: painful cracks in the lips, inflamed tongue, itchy dermatitis of scrotum or vulva Superinfection- can develop from fungal overgrowth due to antibiotic effects, monitor for oral candidiasis, soreness of mouth, and swollen tongue Amphotericin B- tx severe fungal infections, can cause nephrotoxicity. Monitor clients creatinine every 3-4 days and increase fluids, other adverse effects: hypokalemia, hypotension, diarrhea Zileuton- leukotriene modifier, can affect the liver so monitor ALT levels Linezolid- tx staph infection, adverse effects: nausea, h/d, insomnia. Report to provider if client develops paresthesias it is rare but can cause irreversible peripheral neuropathy and reversible optic neuropathy Etanercept- tx RA, is at risk for infections while taking like TB, test for latent TB, check results of last purified protein derivative (PPD) test, given injection, can cause liver injury so check LFTs Omalizumab- tx asthma, reduces immunoglobulin E molecules on mast cells, limiting ability of allergens to trigger immune mediators that cause bronchospasm Quizlet stuff: Nurse in a provider's office is preparing to teach a middle adult client who has a new diagnosis of metabolic syndrome and an HbA1c of 6.5%. Which of the following medications should the nurse plan to teach the client about first? metformin A nurse is reviewing a client's laboratory results before administering furosemide 40 mg IV bolus. For which of the following values should the nurse withhold the medication and contact the provider? Potassium 2.5 mEq/L A nurse is preparing to administer the initial dose of penicillin G IM to a client. The nurse should monitor for which of the following as an indication of an allergic reaction following the injection? Urticaria A nurse is caring for a client who has diabetes mellitus and is taking pioglitazone. The nurse should plan to monitor the client for which of the following adverse effects? Orthostatic hypotension A nurse is assessing a client who takes glipizide for the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Which of the following findings indicates effectiveness of the medication? Hgba1c 6.5% A nurse is reviewing a client's medical record before administering acetaminophen 650 mg PO every 6 hr. Which of the following findings indicates a need for the nurse to notify the provider? History of alcohol use disorder A nurse is assessing a client who has been taking lithium for one year. Which of the following client reports is the nurse's priority? mild thirst A client who has Graves' disease is prescribed methimazole. Which of the following effects should the nurse expect to see after the client has taken he medication for 2 months? increased sleeping A nurse is preparing to administer 4,000 units of heparin subcutaneously to a client who has deep-vein thrombosis. Available is heparin 10,000 units/mL. How many mL of heparin should the nurse administer? 0.4 A nurse is teaching a client who is to begin cyclophosphamide therapy to treat cancer. Which of the following adverse effects of this medication should the nurse include in the teaching? leukopenia A nurse is teaching a client who has HIV and a new prescription for efavirenz. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? notify provider for the appearance of a skin rash. A nurse is assessing client who has been taking digoxin for about a month. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an indication that this client has developed digoxin toxicity? blurred vision A nurse receives a prescription to give tobramycin to a client daily. Which of the following laboratory values should the nurse report to the provider? serum creatinine 2.5 a nurse is caring for a client who has alcohol use disorder and is experiencing withdrawal. Which of the following interventions is the priority at this time? implement seizure precautions A nurse is reviewing a client's medical history before administering a new prescription for atropine. Which of the following client conditions is contraindicated? glaucoma A nurse is teaching a client who has a prescription for ferrous gluconate. Which of the following statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? I should stay upright for 15 minutes after taking this medication. A nurse is teaching a client who has multiple allergies about using an epinephrine auto-injector. Which of the following instructions should the nurse include? admin meds through clothing if necessary A nurse is assessing a client who is receiving heparin therapy for deep-vein thrombosis. Which of the following findings should indicate to the nurse that the therapy is effective? platelets within the expected range a charge nurse is observing a newly licensed nurse provide care to a group of clients. Which of the following action by the newly licensed nurse requires the charge nurse to complete an incident report? a client who has a lithium level of 1.8 receives her morning dose a nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative following a thyroidectomy and is receiving morphine for pain. which of the following findings should the nurse recognize as an adverse effect of morphine? bladder distention a nurse is teaching a client who is to start taking cromolyn. which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? Cromolyn is a long term management medication a nurse is preparing to administer methylprednisolone sodium succinate 80 mg IV bolus. the nurse reconstitutes the 125 mg in the vial in powder form to 2 mL. How many mL should the nurse administer? 1.3 a nurse is caring for a client who has major depression and a new prescription for citalopram. which of the following adverse effects is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? confusion or bruxism a nurse is mixing regular insulin and mph insulin in the same syringe prior to administering it to a client who has diabetes mellitus. which of the following actions should the nurse take first? inject air into NPH a nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin patches. the nurse should identify which of the following statements as an indication that the client understands the teaching? I will rotate application site to avoid skin irritation a nurse is caring for a client who require a re-insertion of a short peripheral venous catheter. in which of the following locations should the nurse place the catheter? a vein on the clients wrist a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for phenlzine. which of the following foods should the nurse instruct the client to avoid? cheese a nurse is providing discharge dietary teaching to a client who has a new prescription for theophylline. which of the following instructions should the nurse include? avoid caffeinated beverages a nurse is caring for a client who received neostigmine 1 hr ago and is experiencing a muscarinic response. which of the following manifestations should the nurse expect? excessive salivation a nurse is caring for a client who is taking azathioprine to treat rheumatoid arthritis. which of the following laboratory values indicates an adverse effect of this medication? WBC 3000 a nurse is assessing a client who received dinoprostone gel to stimulate cervical ripening. which of the following findings is the nurse's priority ? uterine tachysystole a nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who is receiving vancomycin daily. the nurse should review which of the following laboratory results prior to administering the next dose. creatinine level a nurse is teaching the parent of a toddler who is to begin taking ferrous fumarate. which of the following statements by the parent indicates an understanding of the teaching? I will rinse my child's mouth with water after she takes the medicine a nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for alendronate to treat osteoporosis. which of the following instructions should the nurse include? sit upright for at least 30 minutes after taking the medication. a nurse in the emergency department is reviewing a medication record for a client who reports vomiting blood. the nurse should anticipate that the provider will discontinue which of the following medications? clopidogrel a nurse is caring for a client who reports that his current pain medication is no longer relieving her pain. which of the following medications requires the nurse to obtain a written rather than a verbal prescription from the provider? fentanyl a nurse eis preparing to administer nitroglycerin topical ointment to a client. which of the following actions should the nurse plan to take? measure dosag on medication applicator paper a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin sublingual. which of the following client responses indicates an understanding of the teaching? keep tablets in dark container at room temperature a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a prescription for omeprazole. which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? long term use increases risk of fractures a nurse is assessing client who is in labor and is receiving epidural anesthesia. which of the following findings should the nurse identify as the priority ? hypotension a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for paroxetine. the nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? drowsiness or Peripheral edema a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for pheneizine. the nurse instruct the client to avoid which of the following foods? smoked salmon a nurse is caring for a client who is receiving a continuous IV infusion of magnesium sulfate for preterm labor. the nurse should discontinue the infusion and prepare to administer claim gluconate if the client demonstrate which of the following findings? absence of deep-tendon reflexes, urine output 80 mL/hr, decreased LOC a nurse is caring for a client who has heart failure. the nurse administered furosemide 60 mg IV bolus 30 min earlier. for which of the following findings should the nurse notify the provider? client reports difficulty hearing a nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who has sinusitis and a new prescription for cefuroxime. which of the following client information is the priority for the nurse to report to the provider? a client with a Hx of severe PCN allergy a nurse is teaching a newly licensed nurse about medication reconciliation. the nurse should instruct the newly licensed nurse to perform medications reconciliation for which of the following clients? a client who is transferred to a step down unit a nurse is caring for a client who is to start therapy with lovastatin. the nurse should prepare the client for which of the following diagnostic assessments?a nu liver function test a nurse is planning care for a client who has a prescription for erythromycin lactobionate IV bolus. which of the following actions should the nurse include in the plan of care? monitor for hearing loss a nurse is teaching a client who has pernicious anemia to self-administer nasal canocobalamin. which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching? administer medication into one nostril, once a week a nurse is administering medications to a client. which of the following medications should the nurse plan to administer by a parental route. fondapriux a nurse is providing discharge teaching to a client who is receiving warfarin. which of the following statements is appropriate avoid eating large amounts of greens a nurse is reviewing a client's 0800 laboratory. the nurse notes that the client received heparin at 1000. which of the following laboratory values warrants an incident report. aptt 90 a nurse is obtaining a medication history from a client who has gout and is prescribed probenecid. the nurse should notify the provider that the client is taking which of the following over-the counter medications? salicylic acid a nurse is caring for a client who is receiving IV amphotericin B. which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an acute infusion reaction? fever a nurse in the emergency department is caring for a client who reports a severe headache. the client's blood pressure is 280/160 mm hg. the nurse should plan to administer which of the following medications? nitroprusside a nurse is developing a teaching plan for an older adult client who has anew prescription for insulin glargine. which of the following expected outcomes should the nurse include in the plan? the client will wear his reading glasses when drawing insulin glargine a nurse is assessing a client who takes levothyroxine for hypothyroidism. the nurse should identify that which of the following findings indicates the need for an increase in dosage? heart rate 46, cold intolerance, impaired short term memory a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for carbamazepine for the treatment of seizures. the nurse should instruct the client to monitor for which of the following adverse effects? blurred vision a nurse is planning to administer medications to a client who weighs 198 lb. he prescription reads, "filgrastim 5mcg/kg, subcutaneous, daily". available is filgrastim 300 mcg/mL. how many ml should the nurse plan to give with each dose? 1.5 a nurse is planning care for a group of clients. which of the following client's medications should be monitored by the nurse for hearing loss related to a medication interaction? furosemide and amikacin a nurse is reviewing the medications of a client who is experiencing orthostatic hypotension. the nurse should identify this finding as an adverse effect of which of the following medications? imipramine a nurse is evaluating a client who has tuberculosis and has been taking rifampin for 1 month. which of the following laboratory tests should the nurse review to evaluate for an adverse effect of this medication? ALT a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for warfarin about potential interactions with over the counter products. which of the following products should the nurse instruct the client to avoid? naproxen a nurse recently administered filgrastim intravenously to a client who has cancer and is receiving cytotoxic chemotherapy. for which of the following data, discovered after the medication was administered, should the nurse file an incident report.? vile sat out for 2 hours at room temp before administration a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for nitroglycerin. which of the following client statements indicates an understanding of the teaching? I will call 911 if pain is not relieved after taking the medication a nurse is assessing a client who is receiving clindamycin. Which of the following findings should the nurse identify as an adverse effect of this medication? watery diarrhea a nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for ergotamine to treat vascular headaches. The nurse should inform the client that which of the following is a potential adverse effect of this medication? muscle pain a nurse is teaching a client who has active pulmonary tuberculosis about management of medication for the disease. which of the following statements is appropriate for the nurse to make? you will need to take two or more medication to treat your disease a nurse is reviewing the laboratory data of a client who is receiving filgrastim. which of the following laboratory values should the nurse monitor to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment? WBC count a nurse is evaluating a client who is performing a return demonstration of enoxaparin administration. which of the following client actions indicates an understanding of the teaching? administers injection into abdomen a nurse is caring for a client who is receiving morphine, what assessment is priority RR a nurse is assessing a client who has been using beclomethasone for 2 weeks to manage her asthma, what is the priority to report to the provider bronchospasms a nurse is caring for a client who has prescription for terazosin, the nurse should identify that this medication is indicated for which of the following disorders? hypertension BPH a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for beclomethasone inhaler to use with an albuterol inhaler for asthma maintenance, what should the nurse instruct? you should gargle with water after each use of this inhaler a nurse is preparing to administer topotecan IV, which of the following meds should the nurse expect to administer to control the adverse effects granisetron (antiemetic to prevent n/v) for clients receiving chemo a nurse is planning a staff education session on AE of meds, what info should the nurse discuss about anticholinergic adverse effects? blurred vision tachycardia constipation a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for guaifenesin, what info regarding the action of guaifenesin should the nurse include in the teaching? guaifenesin increases cough production a nurse is preparing to administer verapamil to a client who is 2 days postmyocardial infarction. the nurse should monitor the client for which of the following outcomes as therapeutic response to the medication? decreased anginal pain a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for levothyroxine, which statement indicates understanding of the teaching? "i might not realize the full effect of the medication for several weeks" take on empty stomach with glass of water, first thing in the morning 30-60min prior to breakfast a nurse is assessing a client who has HF is taking digoxin. the nurse should monitor the client for which of the following manifestations as an indication of digoxin toxicity to report to the provider? vomiting (n/v, anorexia, blurred vision) a nurse is providing teaching for a pt with a prescription for oral metronidazole, what is the priority teaching point? you should report a rash to your provider (fatal disorder Stevens-Johnson syndrome) a nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who has a new prescription for codeine for cough suppression, what is the priority instruction? move slowly when standing from a lying down position (r/f orthostatic hypotension) a nurse is reviewing the medical record of a client who received his medications 1 hour ago, the pt reports chest pain, this can be an AE of what med? albuterol (beta2agonist, controls bronchospasm for asthma--can cause tremors, chest pain, tachycardia, dysrhythmias) a nurse is teaching a pt who has a new prescription for brimonidine to treat open-angle glaucoma, what indicates an understanding of the instructions? i can expect to feel some irritation when i put these drops in my eyes a nurse is caring for a female client who has osteoporosis and a new prescription for raloxifene, what should the nurse assess prior to initiating therapy? pregnancy status (risk category X) a nurse is teaching a pt to use TD nitroglycerin patches to treat angina pectoris, what instructions should she include? apply a new patch every morning (effects begin 30-60 min after application and last 14 hours) a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has a new prescription for allopurinol to treat gout, what should the nurse include? increase your fluid intake a nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for alprazolam to treat an anxiety disorder, what should the nurse include? avoid taking this med with GFJ (take with food to reduce gastric distress) a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has hypertension and a new prescription for clonidine twice daily, the client understands when he says i will stop drinking a glass of red wine at night (avoid due to the additive CNS effects) a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a neuropathic pain and a new prescription for amitriptyline once per day, what should the nurse include? increase fluids while on this med (urine turns blue/green, sedation is an AE) a nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for vancomycin 1g IV intermittent infusion over 30min every 12 hours, what should the nurse take? contact the provider for prescription clarification (administer over 60min or more to reduce risk of infusion reaction--hypotension, flushing) a nurse is providing teaching to a male client who has a new prescription for folic acid, the client tells the nurse he heard that the medication is prescribed for women during pregnancy, what statements should the nurse make? folic acid is important for the building of blood cells for adults and children (tx megaloblastic and macrocytic anemias) a nurse is caring for a client who has HIV-1 and is starting therapy with ritonavir and zidovudine. the client asks why she has to take both medications, which explanation should the nurse provide? taking the 2 meds together keeps you from becoming resistant to either of them a nurse in the PACU is caring for a client who has received GA and has a manifestations of malignant hyperthermia, the nurse should expect to administer which of the following meds? dantrolene a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for oxybutynin, what statements by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? i need to avoid jogging on warm days (suppression of sweating by the anticholinergic effects by oxybutynin can result in hyperthermia) a nurse is reviewing the lab findings for a client who is taking zidovudine to treat HIV, which should the nurse report to the provider neutrophil count 650/mm3 (normal is 1500-8000) a nurse is assessing a client who is receiving gemfibrozil, the nurse should identify what finding as an AE of this med? muscle tenderness (--> myopathy, rhabdomyolysis) a nurse is caring for a pt with T2D and began therapy with metformin 2 days ago the client reports experiencing n/d, what should the nurse say your symptoms are common AE of metformin and should decrease with time (GI manifestations at onset of therapy) a nurse is caring for 4 clients who have peptic ulcer disease, the nurse should recognize that misoprostol is contraindicated for which of the following clients? a client who might be pregnant (category X, can cause spontaneous abortion) a nurse is in the ICU and caring for a pt with sudden onset of sustained SVT, what med should the nurse prepare? adenosine (decreases electrical conduction through the AV node) a nurse is assessing a pt who has open angle glaucoma and a new prescription for timolol, the nurse should monitor for what AE hypoglycemia a nurse is caring for a client who has varicella zoster, what med should the nurse administer acyclovir a nurse is caring for a client who has recurrent lower UTIs which of the following meds should the nurse expect to administer? nitrofuratoin ab for lower recurrent UTIs a nurse is teaching a pt who is starting subq leuprolide for treatment of prostate cancer. what info should the nurse include? increase calcium intake (can cause bone loss) a nurse in ICU is monitoring a pt who has cardiogenic shock and is receiving a continuous IV infusion of dopamine. what requires an immediate intervention by the nurse? infiltration of the peripheral IV a nurse is caring for a pt who has a new diagnosis of adrenal insufficiency. which of the following prescriptions should the nurse anticipate? fludrocortisone (mineralcorticoid replacement med used to treat adrenal insufficiency, monitor for hypertension and edema) a nurse is providing discharge teaching to a pt who is starting to use an albuterol inhaler, what statement indicates understanding? i should take this medication 15 minutes before exercising a nurse is teaching a pt who has ED and starting to take tadalafil, what statement by the pt indicates and understanding of the teaching? this medication can decrease my BP a nurse is providing a teaching to a pt who is starting to take sulfasalazine for the treatment of ulcerative colitis, which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching this med can cause your urine and skin to turn orange and can stain contact lenses a nurse is teaching a pt who is taking methyldopa for the tx of htn, what info should the nurse include? the med can cause dizziness a nurse is caring for a pt who has hypertension and nephropathy due to T2D, the nurse should expect to administer what med to slow the progression of nephropathy? losartan (angiotensin II receptor blocker) a nurse is assessing a pt who is taking ondansetron, what is a therapeutic effect? suppressed emesis a nurse is administering bumetanide to a pt who has ascites, the nurse should monitor for what as an expected therapeutic effect of this med increased urinary output (loop diuretic) a nurse is teaching a client who has a seizure disorder and is starting to take phenytoin, what statement should indicate understanding? i will have my blood checked to monitor the med levels (10-20) a nurse is providing teaching to the parents of a child who is starting to take liquid ferrous sulfate, what info should the nurse include in the teaching monitor your child for constipation a nurse is caring for a pt with hyperlipidemia, a new prescription for colesevelam, the nurse should monitor what as an AE of colesevelam? constipation (and dyspepsia) the nurse is providing teaching to a female pt for ciprofloxacin, what statement indicates understanding of the teaching i should wear protective clothing when I go outdoors (and sunscreen to prevent sunburn bc r/f photosensitivity) 1 puff MDI, 2 puff albuterol, what is the correct order have pt take one puff of albuterol pt rests for one min take 2nd puff of albuterol have pt rest for 5 min have pt take one puff of fluticasone a nurse is teaching a pt who will start methimazole for hyperthyroidism, what indicates understanding? i will contact the provider if my throat becomes sore (potential for agranulocytosis, notify provider immediately if fever, sore throat, or other indications of infection) a nurse is taching a pt who has prostate cancer and a new prescription for leuprolide, explain how it treats prostate cancer decreases the production of testosterone (initial increase, then desensitization and decrease in testosterone production) a nurse is caring for apt with difficulty voiding following surgery, nurse notes a palpable bladder distention, what med should the nurse administer bethanechol (for nonobstructive urinary retention) a nurse is preparing to admin meds to a client who has type 1 diabetes mellitus, the client receives multiple oral meds, takes lispro insulin, he is starting to take pramlintide, what actions should the nurse take? monitor for hypoglycemia for 3 hours after pramlintide administration (take before meals along with lispro insulin) a nurse is caring for a pt who has HIV and a prescription for delavirdine, the nurse should monitor the pt for what manifestations as an AE of the med rash (steven-Johnson sndrome) a nurse is reviewing the health history of a pt who has migraine headaches and asks about a prescription for sumatriptan, the nurse should identify what as a contraindication for the med coronary artery disease (can cause coronary vasospasm, ECG changes, hypertension) a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has angina and a new prescription for sublingual nitroglycerin tablets, what info should the nurse include store unused tablets at room temp (take one tablet every 5 mins, up to 3 tablets until pain resolves, call 911 after 1st tablet) a nurse is caring for a client who has a systemic fugal infection and is receiving IV amphotericin B deoxycholate, during previous infusions the pt developed a fever and chills, what should the nurse take administer diphenhydramine prior to administration (admin an antipyretic, corticosteroid, antihistamine, or antiemetic prior to to minimize the effects) a nurse is providing discharge instructions to a pt who has a prescription for omeprazole for the tx of GERD, what statement by the client indicates an understanding of the teaching? the med reduces stomach acid (suppressing production of gastric acid, reduces baseline acid level and blocks production of all stimulated acid production within 2 hours of an oral dose) a nurse is caring for a pt who has a prescription for HCTZ for the initial tx of hypertension, what should the nurse recognize as the action of this med? HCTZ decreases the reabsorption of sodium and water in the distal renal tubule a nurse is teaching a client who is starting to take benzonatate, which of the following statements by the pt indicates understanding? i should not drive while taking this medication (AE is sedation and dizziness) a nurse is caring for a pt who reports using the herbal med garlic along with his prescribed warfarin, the nurse should identify what is a potential AE of taking both of these products concurrently? increased ecchymosis (antiplatelet effects can increase bleeding) a nurse is reviewing lab data for a pt who is taking niacin to correct plama lipid levels, what lab findings should inidcate the nurse an AE of this therapy? elevated ALT (AE hepatotoxicity: incr ALT, AST, LDH) a nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for metoclopramide, what outcomes should the nurse use to evaluate the effectiveness of this med? reduced nausea a nurse is teaching a client who has a new prescription for isoniazid to tx TB, what info should the nurse include? you will have frequent sputum tests to monitor the effectiveness of this medication (sputum species every 2-4 weeks to monitor the effectiveness, 3 negative tests, continue for 6-12 mo) a nurse is assessing a client after administering paclitaxel for the tx of ovarian cancer, the nurse should identify what findings as a priority bradycardia (r/f 3rd deg HB, and MI) a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has RA and is starting to take hydroxychloroquine, what indicates understanding? i will need to have a baseline eye exam before starting this med (and every 6months , can cause possible retinal damage that can eventually lead to blindness) a charge nurse is orienting a newly licensed nurse to the unit-dose med system, what info should the nurse include? the pharmacist restocks the med drawer every day a nurse is caring for a client who has an infection and is starting to take gentamicin, what lab test should the nurse monitor to detect an AE of the med? creatinine (Cr, BUN, U.O.) a nurse is assessing a pt who has DI and is starting intranasal desmopressin, what can indicate to the nurse that the med is effective? the client's urine output is 1.256ml/24 hours a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is starting to take finasteride for the treatment of male pattern baldness, what indicates understanding the med can increase my risk for impotence a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who is starting to take aspirin, instruct the pt to monitor for what AE black, tarry stools (r/f bleeding) a nurse is reviewing the med history of a pt who has MG and is asking about starting neostigmine, the nurse should identify what pt condition as a ptoential contraindication to cholinesterase inhibitor therapy peptic ulcer disease (r/f erosion and perforation) a nurse is caring for a pt who has chemo induced anemia, the nurse should expect to administer which of the following meds to treat the anemia epoetin alfa a nurse is administering timolol to a pt being treated for open-angle glaucoma, after administration the nurse should monitor what AE blurred vision, bradycardia, conjuntivitis a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has a prescription for buspirone, what info should the nurse include in the teaching expect to have a full response from buspirone after 3-4 weeks a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a duodenal ulcer and is starting to take sucralfate, what instruction should the nurse include in the teaching? increase fluid intake while taking med (incr fluid and dietary fiber to prevent constipation) a nurse is caring for an OA client who is confirmed positive for HIV and will begin med therapy, what instruction should the nurse give the client you will be prescribed more than one medication to fight the virus your medication plan can also include an antibiotic medication you will need to take the medication for the rest of your life a nurse is assessing a pt who is in preterm labor and is receiving mg sulfate via continuous IV infusion, what findings should the nurse identify as the priority deep tendon reflexes 1+ (indicates depressed CNS and possible mg sulf toxicity) a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has a new prescription for calcitonin, what statements by the client indicates an understanding of the meds AE the med can cause nausea a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has osteoporosis and is starting to take oral ibandronate, what instruction should the nurse include? take one tablet of med on the same date each month (maintain med level) a nurse is completing an admission assessment for a client who has been taking st. john's wort, the nurse should identify that which of the following meds can interact with St. John's wort? citalopram (causing serotonin syndrome when combined with antidepressants, dec effect of BC, warfarin, cyclosporine, digoxin, CCB, steroids, HIV PI, and some chemo agents) a nurse is teaching the partner of a pt who has DM how to manage episodes of sever hypoglycemia, when the pt is unresponsive, what action should the nurse instruct the pt to do first? administer glucagon IM to the client a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has a new prescription for ranitidine for the tx of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. the nurse should explain to the client that ranitidine treats ulcers by which of the following actions? it reduces gastric acid production (H2 antagonist) a nurse is caring for a pt who has a prescription for ipratropium inhaler to control COPD bronchospasm, the nurse should monitor the client for which of the following manifestations as an AE of the med xerostoma (anticholinergic) a nurse in the PACU is caring for a pt who has received GA and has a manifestation of malignant hyperthermia, the nurse should expect to administer what med? dantrolene a nurse is caring for a pt who is receiving a continuous IV of heparin, the nurse should expect to administer which of the following meds if the client experiences a heparin overdose? protamine sulfate a nurse is preparing to administer IV mannitol to a client, the nurse should monitor the client for which of the following manifestations as an expected outcome of this med reduced intracranial pressure a nurse is preparing to initiate a peripheral IV line on an OA client who has dehydration. which of the following actions should the nurse take? (SATA) apply traction to the skin when inserting the catheter cleanse the insertion site with antiseptic swabs a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has fibromyalgia and a new prescription for pregabalin. which of the following instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? you should notify your provider if you experience blurred vision (dizziness, difficulty with coordination, n, ha) a nurse is caring for a client who has HF and a prescription for acetazolamide. prior to administration of the first dose, the nurse should ask the client if she has allergy to what meds? sulfa-based meds a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has a new prescription for oral extended release potassium chloride tablets, what instructions should the nurse include in the teaching? do not crush this medication a nurse is caring for a female client who has a new prescription for alosetron, what therapeutic effects should the nurse expect in this pt? a decrease in the frequency of defecation a nurse is discussing AE with a pt who has non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and it is starting to take methotrexate, what should the nurse provide? methotrexate can increase the risk for bleeding a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has PD and has a new prescription for levodopa/carbidopa, what should the nurse include in the teaching you should move slowly when you want to stand up a nurse is planning care for a client who has neutropenia, what meds should the nurse anticipate administering? filgrastim (leukopoietic growth factor) a nurse is teaching a pt who has a new prescription for nitrofurantoin, what info should the nurse include in the teaching? you should stop taking the med if you develop a cough (pulmonary reactions) a nurse is providing teaching to a pt who has a new prescription for montelukast, what statement by the pt indicates understanding i will take the med every day to control my exercise-induced asthma a nurse is preparing to administer a 2nd unit of PRBCs to a pt who is experiencing hemorrhagic shock, the nurse should monitor for the manifestations of what as circulatory overload? dyspnea acetylcysteine is prescribed for what med acetaminophen overdose a nurse is providing teaching to a client who has T2D, and is starting to take immediate release exenatide, what statement is an understanding of the teaching i will take this med 1 hour before morning and evening meals [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 131 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$24.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 22, 2022
Number of pages
131
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 22, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
99