Financial Accounting > EXAM > ACCOUNTING 2021 CPA Final Exam - 79 Questions and Answers, Graded A (All)
ACCOUNTING 2021 CPA Final Exam - 79 Questions and Answers, Graded A
Document Content and Description Below
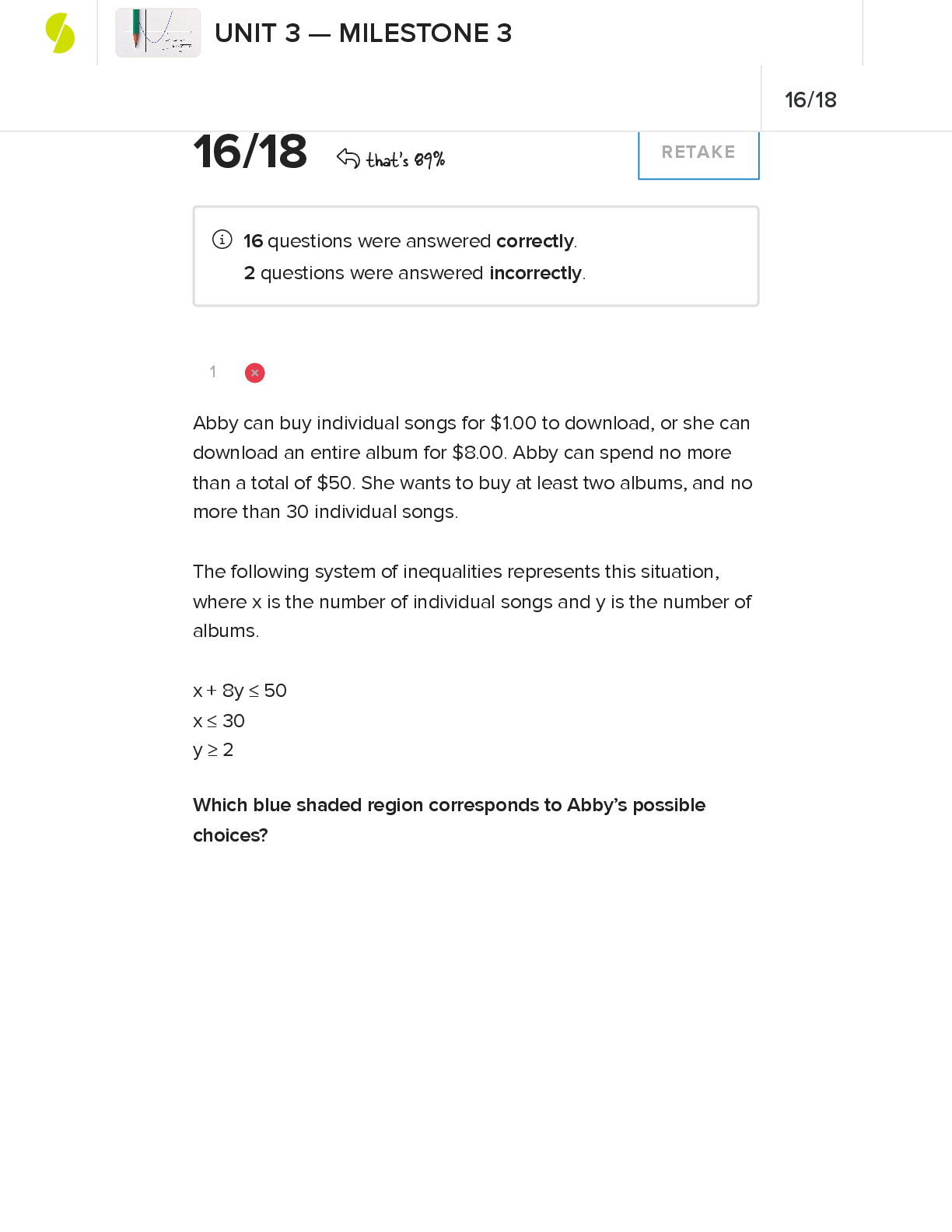
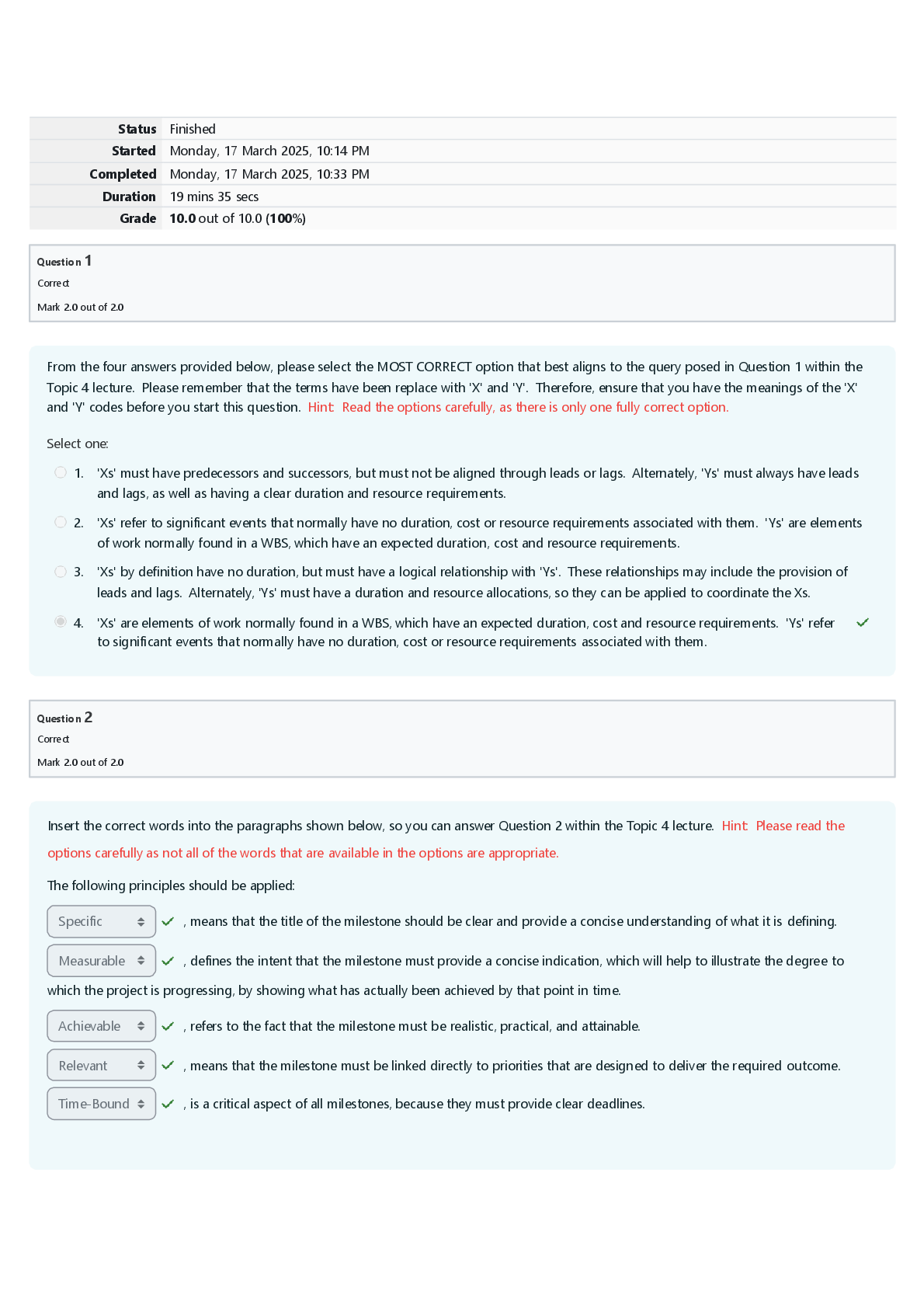
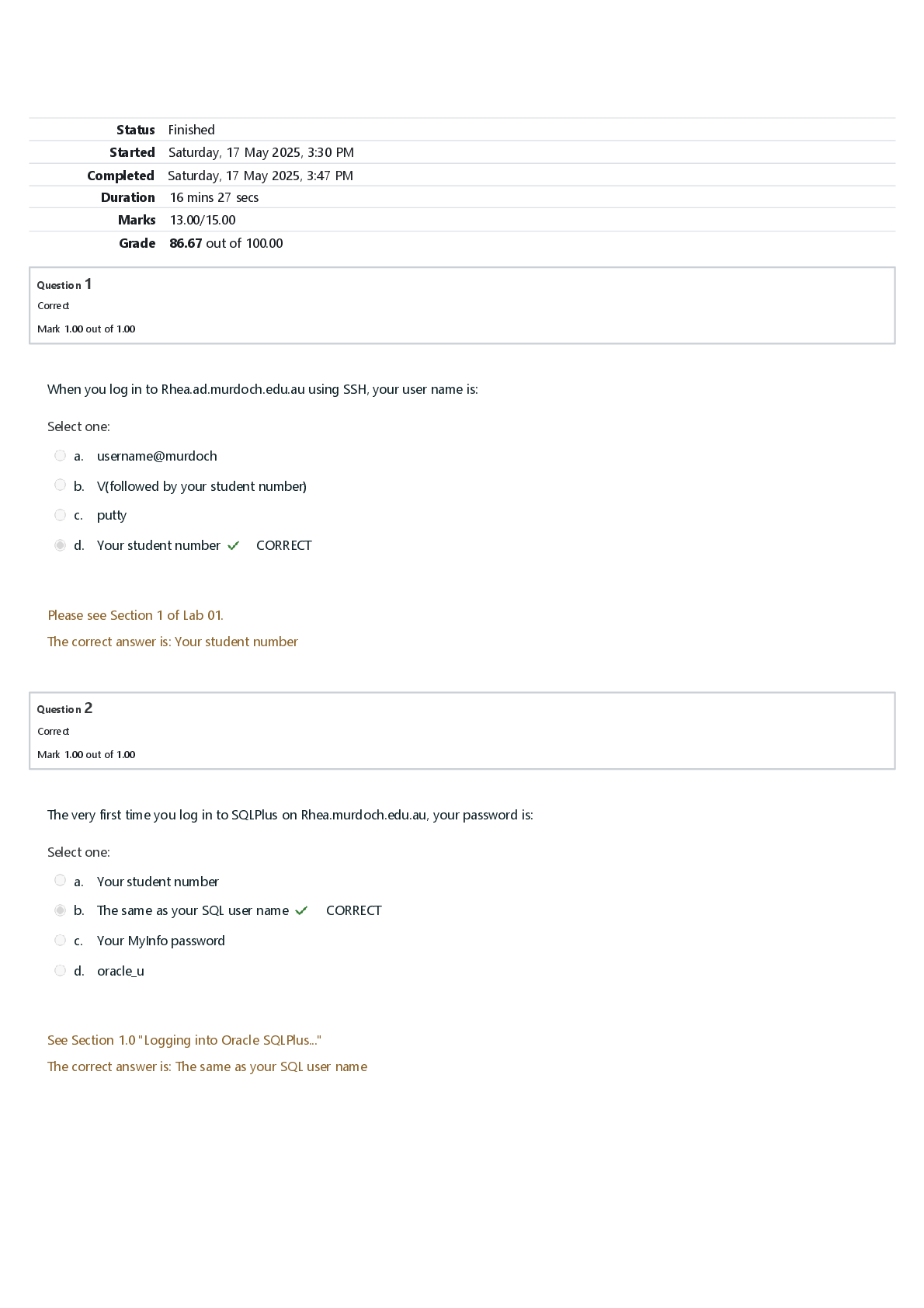
CPA Final Exam 1. Which of the following is the list of the basic financial statements? A. Balance sheet, income statement, statement of changes in retained earnings B. Statement of financial pos... ition, income statement, and statement of changes in retained earnings C. Balance sheet, statement of financial position, income statement, and statement of changes in retained earnings D. Balance sheet, income statement, and statement of cash flows (Chapter 1, pg. 2) 2. Which of the following is NOT true? The objectives of financial reporting are to provide information A. That is useful to those making investment and credit decisions. B. To internal managers in planning, controlling, and making a variety of management decisions. (Chapter 1, pg. 2) C. That is helpful to current and potential investors and creditors in assessing the amount, timing, and uncertainty of future cash flows. D. That discloses economic resources, claims to those resources, and the changes therein. 3 Which of the following is the typical way to date an income statement? A. For the year ended December 31, 20XX (Chapter 1, pg. 2) B. At December 31, 20XX C. As of December 31, 20XX D. During the period 20X4 -20XX 4 What organizations must present a statement of cash flows? A. Only Publicly held business enterprises (Chapter 1.8, pg. 38) B. Only Privately held business enterprises C. Business enterprises only D. All business enterprises and not-for-profit organizations 5 Which of the following financial statements includes investing, operating activities, and financial activities? A. Statement of cash flows ( Chapter 1, Page 18) B. Balance sheet C. Income statement D. Statement of shareholders’ equity 6 What is the purpose of a statement of cash flows? A. To evaluate a firm’s liquidity, solvency, and financial flexibility ( Chapter 1, Page 18) B. To evaluate a firm’s economic resources and obligations C. To determine a firm’s components of income from operations D. To determine whether insiders have sold or purchased the firm’s stock 7 Which of the following is NOT a condition for reporting a segment? A. Revenue is 10% or more of total corporate revenue. B. Operating profit is 10% or more of total corporate operating profit. C. Identifiable assets are 10% or more of total corporate assets. D. Foreign operations provide 3% or more of total corporate sales. (Chapter 1 pg. 21) 8 When preparing interim financial statements, a company should comply with which of the following requirements? A. Defer recognition of seasonal revenue. B. Disregard permanent decreases in the market value of its inventory. C. Allocate revenues and expenses evenly over the quarters, regardless of when they actually occurred. D. Apply the same accounting principles used in the last year''s annual report. (Chapter 1, pg. 21) 9 Wilson Corp. experienced a $50,000 decline in the market value of its inventory in the first quarter of its fiscal year. Wilson had expected this decline to reverse in the third quarter, and the third quarter recovery exceeded the previous decline by $10,000. Wilson''s inventory did not experience any other declines in market value during the fiscal year. What amounts of loss or gain should Wilson report in its interim financial statements for the first and third quarters? A. $0 in first quarter, and $0 in third quarter B. $0 in first quarter, and $10,000 gain in third quarter C. $50,000 loss in first quarter, and $50,000 gain in third quarter D. $50,000 loss in first quarter, and $60,000 gain in third quarter 10 Groups impacted by the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX) include: CPA’s CPA firms auditing publicly companies, public traded companies, their employees, officers, owners, attorneys who work for clients at publicly traded companies. Which of the following is another group also impacted? A. Investment bankers (Chapter 1.8, pg. 34) B. Sole proprietors C. Agents and agencies D. Federal officers 11 The Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002 addressed all of the following issues EXCEPT: A. Created a public accounting oversight Board B. Increased the accuracy of corporate tax returns (Chapter 1.8, pg. 34) C. Strengthened the independence of firms that audit public companies D. Increased corporate responsibility 12 What are the regulatory bodies responsible for monitoring and enforcing the Sarbanes-Oxley Act? A. SEC, PCAOB (Chapter 1.8, pg. 34) B. CEO, CFO C. AICPA, FASB D. S&P, Moody’s 13 Which of the following is NOT one of the provisions of the Sarbanes-Oxley Act of 2002? A. The penalties (i.e., prison time and fines) for corporate fraud were increased. B. At least one audit committee member should be a financial expert. C. The company’s auditors assume responsibility for the financial statements. D. The CEO and CFO must certify that the financial statements fairly present the company’s operations and financial condition. 14 Which of the following is NOT a factor that an investor considers in evaluating a firm’s stock? A. Financial health B. Industry factors C. Market beta (Chapter 2.1, pg 50) D. Future outlook of the company 15 What ratio is used to measure a firm''s liquidity? A. Times interest earned B. Current ratio (Chapter 2.1 pg. 55) C. Return on equity D. P/E ratio 16 Given the following data, calculate the average collection period: Sales = $2,000; Cost of goods sold = $1,500; Average receivables = $100. A. 24.33 B. 18.25 C. 137.00 D. 20.00 17 What ratio is used to measure a firm''s leverage? A. Times interest earned B. Quick ratio C. Payout ratio D. Return on equity 18 What ratio is used to measure the profit earned on the available resources of a firm? A. Current ratio B. Asset turnover C. Return on sales D. Return on total asset 19 Division Q for Mott Company has a rate of return on investment of 28% and an asset turnover of 1.4. What is the profit margin? A. 28% B. 14% C. 20% D. 39.2% 20 Rate of Return on Investment (ROI) can be enhanced by which of the following actions? A. Improve margin by increasing expenses faster than sales B. Improve turnover by increasing the investment in assets C. Increase gross margin or asset turnover (Chapter 2.1 pg. 74) D. Enhance residual income 21 In order to determine the return on investment (ROI), you would divide net income by which of the following values? A. Non-allocated costs B. Total assets (Chapter 2.1 , pg 77) C. Revenue D. Indirect costs 22 If a company is profitable and is effectively using leverage, which one of the following ratios is likely to be the largest? A. Return on total assets B. Return on operating assets C. Return on equity (ROE) (Chapter 2.2 pg. 78) D. Return on total shareholders’ equity 23 What is the performance measure of a cost center? A. Variance B. Contribution margin C. Transfer pricing D. Profit markup 24 Which of the following activities will improve the Economic Value Added (EVA)? A. Invest capital in high-performing projects (Chapter 3, pg. 87) B. Use more capital C. Increase profit using more capital D. Enhancing return on equity 25 Why is the residual income a better measure for performance evaluation of an investment center manager than return on investment (ROI)? A. The problems associated with measuring the asset base are eliminated. B. It encourages investment in projects that would be rejected under ROI. C. Only the gross book value of assets needs to be calculated. D. The arguments about the implicit cost of interest are eliminated. 26 The production budget process usually begins with which of the following budgets? A. Direct labor budget B. Direct materials budget C. Manufacturing overhead budget D. Sales budget (Chapter 3, pg. 102) 27 What is the major feature of zero-base budgeting (ZBB)? A. It takes the previous year’s budgets and adjusts them for inflation. B. It questions each activity and determines whether it should be ranked. C. It assumes all activities are legitimate and worthy of receiving budget increases to cover any increased costs. D. It focuses on planned capital outlays for property, plant, and equipment. (Chapter 3 pg. 103) 28 There are several principles of managing performance. Which method uses an analysis of variances to create a performance report? A. Management by Objective (MBO) B. Management by Exception (Chapter 3 pg. 104) C. Total Quality Management (TQM) D. Just-in-Time (JIT) 29 Which of the following will cause an unfavorable material price variance? A. Price increases for raw materials B. Price decreases for raw materials C. Less-than-anticipated levels of waste in the manufacturing process ( Chapter 3.7, pg. 107) D. More-than-anticipated levels of waste in the manufacturing process 30 Under a standard cost system, who usually takes the responsibility for the unfavorable materials price variances? A. Production manager ( Chapter 3.7, pg. 107) B. Purchasing manager C. Cost accounting manager D. Sales manager 31 How is labor price variance computed? A. The difference between standard and actual prices, times standard hours B. The difference between standard and actual hours, times actual rate C. The difference between standard and actual prices, times actual hours D. The difference between standard and actual hours, times the difference between standard and actual prices 32 What is an accounting system that collects financial and operating data on the basis of the underlying nature and extent of the cost drivers? A. Activity–based costing (ABC) B. Target costing C. Cycle–time costing D. Variable (direct) costing 33 Which of the following statements best describes ‘cost drivers’? A. Key activities that cause costs to increase B. Accounting techniques used to control costs C. Accounting measurements used to evaluate whether performance is proceeding according to plan D. A mechanical basis, such as machine hours, computer time, size of equipment, or square footage of factory, used to assign costs to activities 34 Which of the following will be limited by a binding constraint? A. A company’s profitability B. A company’s advertising C. The company’s accounting functions D. Employee benefits 35 Using the balanced scorecard approach, a company will evaluate managerial performance based on which of the following? A. A single ultimate measure of operating results, such as residual income B. Multiple nonfinancial measures only C. Multiple dimensions of financial and nonfinancial measures D. Multiple financial measures only 36 What is the difference between sales and the total variable costs? A. Gross operating profit B. Net profit C. The breakeven point D. The contribution margin 37 Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis allows management to determine the relative profitability of a product. How does CVP do this? A. By highlighting potential bottlenecks in the production process B. By keeping fixed costs to an absolute minimum C. By determining the contribution margin per unit and the projected profits at various levels of production D. By assigning costs to a product in a manner that maximizes the contribution margin 38 What is the role of “what-if” (sensitivity) analysis when used in conjunction with cost-volume-profit analysis? A. It evaluates various possible scenarios and computes the impact on profit of various predictions of future events. B. It determines the most profitable mix of products to be sold. C. It allows the decision maker to introduce probabilities in the evaluation of decision alternatives. D. It is limited because in cost-volume-profit analysis, costs are not separated into fixed and variable components. 39 What does the concept of “The time value of money” refer to? A. A dollar has the same value now as in the future. B. A dollar in the past had less value than now. C. A dollar now is worth more than a dollar to be received later. D. A dollar value is constant in time. 40 Which of the following tables would show the largest value for an interest rate of 5% for six periods? A. Future value of $1 B. Present value of $1 C. Future value of an ordinary annuity of $1 D. Present value of an ordinary annuity of 1 41 An ordinary annuity is defined as a series of payments or receipts A. of a variable amount for a definite period. B. of a variable amount for an indefinite period. C. of a fixed amount for an indefinite period. D. of a fixed amount at the end of the period for a specific number of periods. ( Chapter 4, pg. 147) 42 What is the current worth of future sums of money that will be received? A. Future value B. Present value C. Past value D. Limited value 43 When computing the time value of money, when are the payments for an ordinary annuity assumed to occur? A. At the end of the period ( Chapter 4, pg. 147) B. At the beginning of the period C. In the middle of the period D. Any time during the period 44 All of the following investments involve annuities EXCEPT: A. Bonds B. Stocks C. Insurance obligations D. Pension funds 45 What is the present value of $110,000 expected to be received one year from today at an interest rate (discount rate) of 10% per year? A. $121,000 B. $100,000 C. $110,000 D. $90,900 46 What is the capital budget? A. A plan to insure that there are sufficient funds available for the operating needs of the company. B. An exercise that sets the long-range goals of the company including the consideration of the company including the consideration of external influences. C. A plan that coordinates and communicates a company’s plan for the coming year to all departments and divisions. D. A plan that assesses the best selections and financing of long-term investments. 47 In order to grow, companies make all of the following capital budgeting investment decisions EXCEPT: A. Should we replace certain equipment? B. Should we invest in high-tech information technology (IT)? C. Should we decrease asset turnover? D. Should we engage in merger & acquisition (M&A) transactions? 48 Which of the following methods does NOT consider the investment’s profitability? A. Payback B. ARR C. NPV D. IRR 49 Which of the following methods uses accrual accounting income data rather than net cash flows as a basis for calculations? A. Payback B. ARR C. NPV D. IRR 50 Which of the following does NOT affect the present value of an investment? A. The interest rate B. The internal rate of return C. The number of time periods (length of the investment) D. The type of investment (annuity versus single lump sum) 51 What is the technique that recognizes the time value of money by discounting the cash flows for a project over its life to time period zero using the company’s minimum rate of return? A. Net present value method B. Capital rationing method C. Payback method D. Accounting rate of return method 52 Conditions under which mutually exclusive investments create contrary rankings include all EXCEPT: A. Projects that have different life expectancies. B. Projects that have different sizes of investment. C. Projects where the cost of capital is similar. D. Projects that have different cash flows over time. 53 During the year, Mason Company’s current assets increased by $120, current liabilities decreased by $50. What happened to working capital? A. Increased by $70 B. Did not change C. Decreased by $170 D. Increased by $170 54 All of the following strategies help a company accelerate cash receipts EXCEPT. A. Lockbox B. Cash rebates for increased sales. C. Concentration banking. D. Immediate transfer of funds between banks. 55 A change in credit terms has caused an increase in sales, an increase in discounts taken, a reduction in the investment in accounts receivable, and a reduction in the number of doubtful accounts. Based upon this information, what do we know? A. Net profit has increased B. The average collection period has decreased C. Gross profit has declined D. The size of the discount offered has decreased 56 When purchasing temporary investments, which one of the following best describes the risk associated with the ability to sell the investment in a short period of time without significant price concessions? A. Interest-rate risk B. Purchasing-power risk C. Financial risk D. Liquidity risk 57 Which of the following analyses looks at the direction and magnitude of the market in determining when or what to buy or sell? A. Financial analysis B. Business cycle analysis C. Technical analysis D. Fundamental analysis 58 What is usually the easiest type of short-term financing to secure? A. Bank loan B. Commercial paper C. Trade credit D. Inventory financing 59 What is the disadvantage of financing with commercial paper? A. Interest rates are higher B. Security is required C. Commercial paper is sold at a premium D. It is usually available only to large, financially sound companies. 60 Which of the following is an example of non-diversifiable risks? A. Business risk B. Market risk C. Default risk D. Liquidity risk E. Which of the following stocks has the highest risk? F. Stock A with a beta equal to 0.0 G. Stock B with a beta equal to 0.5 H. Stock C with a beta equal to 1.0 I. Stock D with a beta equal to 2.0 61 The arbitrage pricing model (APM) explains asset returns in terms of multiple macroeconomic factors. Assume the macroeconomic variables are the gross domestic product (RP1), inflation (RP2), and real interest rates (RP3). The expected return on ABC Stock is given as follows: r = 0.05 + b1(0.03) + b2(0.04) + b3(0.07). The beta coefficient (bj) for each variable are given as: Variable 1, b1 = 0.5; Variable 2, b2 = 0.3; Variable 3, b3 = 0.3. What is ABC''s expected return? A. 9.8% B. 10.8% C. 8.3% D. 6.5% 62 What is the process by which an issuer of new securities selects an investment banker? A. A negotiated deal B. Best efforts C. A general cash offer or a rights offer D. A firm commitment 63 In what way do investment bankers make money under ‘best-efforts’ offerings? A. By receiving the difference between the purchasing price and the offering price B. By receiving a commission C. By receiving a discount of the difference between the purchasing price and the offering price D. By purchasing unsold securities for their own account 64 When dealing with venture capital firms, a firm should generally avoid which of the following? A. Reading the fine print B. VCs who accelerate the process C. Guarding your trade secrets D. Giving up a majority ownership interest 65 Which of the following is false about junk bonds? A. Issued when the debt ratio is very high B. Securities rated at less than investment grade C. They are useless securities D. Securities that are highly risky but offer high yields 66 Common shareholders with preemptive rights are entitled to do which of the following? A. Vote first at annual meetings B. Purchase any additional bonds sold by the firm C. Purchase sufficient shares so as to maintain their ownership percentage D. Gain control of the firm in a proxy fight 67 What does an effective production planning process usually begin with? A. Sales forecast B. Forecasts for supply chain management C. Cash budget D. Overhead budget 68 Which of the following forecasts, covering topics such as GDP, interest rates, and foreign exchange rates, help business develop its own forecasts about external business outlook that will affect its product demand? A. Economic forecasts B. Financial forecasts C. Sales forecasts D. Forecasts for supply chain management 69 Which of the following is a quantitative forecasting technique? A. Expert opinion B. Regression analysis C. Sales force polling D. Consumer survey 70 Which of the following forecasting technique is based on historical data? A. Expert opinion B. Naive methods C. Sales force polling D. Consumer survey 71 Which method continually revises a forecast in the light of more recent experience? A. Regression B. Moving average C. Simple average D. Exponential smoothing 72 What are the ways to measure forecasting accuracy? A. MSE and MAD B. MAD and ALPHA C. ALPHA and BETA D. Mean and standard deviation 73 What is the heart of the software accounting system that contains the chart of accounts of a business? A. Accounts receivable B. Invoicing C. General ledger D. Accounts payable 74 What is the accounting software module that maintains default information for each employee? A. Inventory module B. Payroll module C. Job costing module D. Fixed asset module 75 Why has the SEC adopted Extensible Business Reporting Language (XBRL)? A. To establish new accounting standards B. To require additional disclosures from companies C. To make financial information available in an “easy to use” format D. Improving the information security of data exchange between companies 76 The PwC benchmark data shows that the top performers’ budget reporting times continue to drop. What is the main factor that drives the continued improvement? A. Outsourcing opportunity B. Enhanced technology and automation C. Demanding regulatory requirements D. Stability in the marketplace 77 Which of the following emerging technologies reduces the burden of auditing by providing a secure ledger of all data transfer activity? A. Artificial intelligence B. Big data C. Digital labor D. Blockchain 78 How does robotic process automation (RPA) transform the accounting operations? A. It allows the business to use shared applications on an as-needed basis B. It increases transparency to all transactions through a distributed ledger C. It reduces the labor required for all repetitive and rules-based transactions D. It creates new ways to analyze information of varying types, size and volume 79 Cloud computing has all of the following features EXCEPT: A. The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model B. Capabilities are available over the network and accessed through standard mechanisms C. Resource usage can be monitored, and reported, providing transparency for the provider and consumer D. All computer security issues go away [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 20 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Apr 13, 2021
Number of pages
20
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Apr 13, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
109