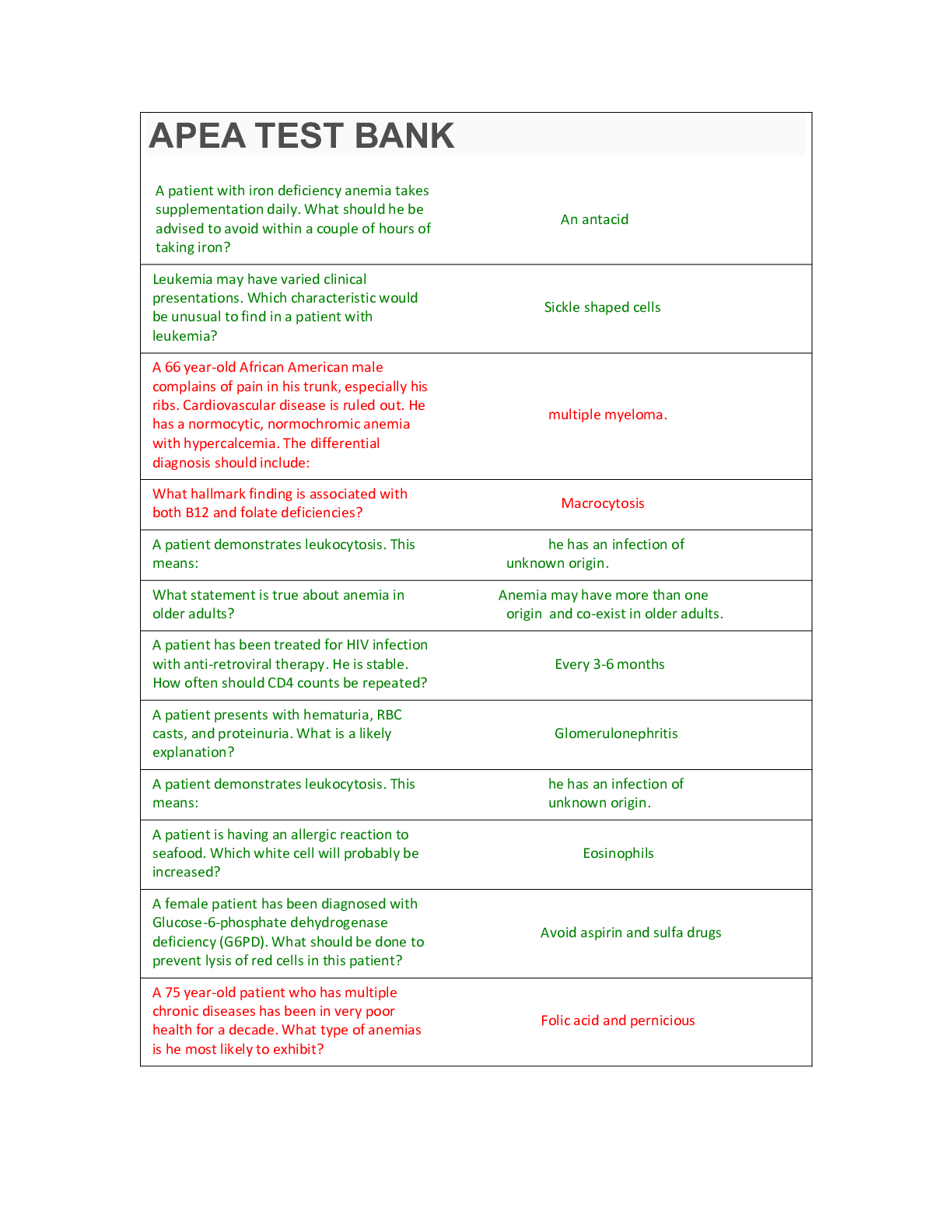
*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > HSC 4551 Pre Tests for Human Diseases A Systemic Approach; (Answered) (All)
HSC 4551 Pre Tests for Human Diseases A Systemic Approach; (Answered)
Document Content and Description Below
HSC 4551 Pre Test for Human Diseases A Systemic Approach, 8th Edition by Zelman Homework: Chapter 1 Pre Test Homework 1.1.1 What is the best definition of health? A. the condition in which the hum... an body is free from disease B. the condition of relative well-being without the presence of disorders or syndromes C. the condition of relative stability of internal structures under changing external conditions D. the condition in which the human body performs its vital functions normally Homework 1.1.2 What physical assessment technique produces sounds by tapping on specific areas of the body using fingers, hands, or a small instrument? A. inspection B. auscultation C. percussion D. Palpation Homework 1.1.3 What is the study of disease? A. anthropology B. chemistry C. biology D. Pathology Homework 1.2.1 What is the leading cause of death in the United States? A. malignant neoplasms (cancer) B. cerebrovascular diseases (stroke) C. diseases of the respiratory tract D. diseases of the heart Homework 1.2.2 What category of disease is sickle cell anemia? A. hereditary B. infectious C. degenerative D. Metabolic Homework 1.2.3 What category of disease best describes a disease in which the function or structure of the affected tissues or organs progressively deteriorates over time? A. inflammatory B. neoplastic C. metabolic D. Degenerative Homework 1.3.1 What is true regarding risk factors related to disease? A. Risk factors are the etiology of disease. B. Risk factors guarantee a disease will develop. C. Risk factors are always present with the development of disease. D. Risk factors increase a person's chance of developing a disease. Homework 1.4.1 According to the United States Health and Human Services, what choice best demonstrates a component of a healthy plate? A. lean, fatty fish covering 50% of the plate B. green leafy vegetables covering 50% of the plate C. whole grain rice covering 10% of the plate D. enriched white rice covering 25% of the plate Homework 1.4.2 The medical assistant is assisting the primary care provider during a client's annual health exam. Which statement will the medical assistant most likely hear the provider tell the client regarding smoking cessation? A. "Within three months of quitting, an ex-smokers lung function begins to improve." B. "Within one day of quitting, an ex-smoker's risk for heart attack drops." C. "Within one week of quitting, an ex-smoker's risk for heart disease is about the same as that of a lifelong nonsmoker." D. "Within five years of quitting, an ex-smoker's risk for heart disease is about the same as that of a lifelong nonsmoker." Homework: Chapter 2 Pre Test Homework 2.1.1 What is immunity? A. the ability to prevent pathogens from entering the body B. the cause of redness, heat, swelling, and pain in body C. a foreign substance that recognizes itself within the body D. the body's ability to resist infectious disease Homework 2.2.1 Which causes a patient with a cold to sneeze and cough? A. The inflammatory process releases histamines within the lungs to repair damaged tissue causing a reaction of sneezing and coughing. B. Antibodies binding to antigens cause a histamine reaction of sneezing and coughing. C. A high fever causes sneezing, coughing, dehydration, and nausea. D. The inflammatory process results in sneezing and coughing. Homework 2.2.2 What is the function of an interferon? A. stimulates uninfected cells to resist viral infections B. to eliminate virus-infected cells and cancer cells C. to slow the growth rate of pathogens by stimulating antibody production D. to decrease the immune response following antigen attack Homework 2.3.1 What is the difference between a B-cell and plasma cell in humoral immunity? A. B-cells are natural killer cells, and plasma cells increase phagocytosis and cytotoxic T-cell production. B. B-cells live about four or five days, and the plasma cells produce antibodies to live longer after initial exposure. C. An activated B-cell divides and develops into a short-lived plasma cell, which secretes antibodies. D. B-cells are responsible for secreting antibodies, and plasma cells are responsible for a more potent and rapid antibody response. What are antibodies? A. antiviral proteins produced by animal cells after viral infection to resist future infections B. proteins activated to aid in the inflammatory response to prevent further damage to injured tissues C. cells that originate in the red bone marrow that protect the body against viruses, abnormal cells, and other intracellular pathogens D. proteins produced by B-lymphocytes that defend the body against extracellular antigens Homework 2.3.3 What triggers humoral immunity? A. damaged skin B. antigens C. fever D. Chemicals Homework 2.4.1 Which type of immunity is responsible for tissue graft and organ transplant rejections? A. non-specific immunity B. interferon immunity C. cell-mediated immunity D. humoral immunity Homework 2.4.2 Where in the body do the T and B cells travel to await activation by a unique antigen? A. thymus and spleen B. lymph and bone marrow C. lymph nodes and spleen D. bone marrow and thymus Homework 2.5.1 Seventy percent of lupus cases are which type of lupus? A. cutaneous B. neonatal C. systemic D. drug-induced Homework 2.5.2 What are the signs and symptoms of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE)? A. fatigue, photosensitivity, and fibromyalgia-type symptoms B. fever, arthritis, and pain in two or more joints C. heartburn, fatigue, and butterfly rash across the cheeks and nose D. fatigue, fever, and photosensitivity Homework 2.5.3 According to the World Scleroderma Foundation, scleroderma affects 2.5 million people world-wide. Scleroderma more commonly affects which demographic? A. both men and women equally B. men C. women D. Teens Homework 2.6.1 What is an allergen? A. an inflammatory response within the body B. an antigen that causes an allergic response C. a pathogen that causes an allergic response D. triggered cell-mediated immunity Homework 2.6.2 Of the four types of hypersensitivity, which is the most common type of allergy? A. Type IV triggered cell-mediated immunity B. Type I triggered by IgE C. Type II triggered by IgM D. Type III triggered by antibodies Homework 2.7.1 How many people per hour are infected by HIV? A. 100 B. 300 C. 200 D. 150 Homework 2.7.2 How many people have died from AIDS since the epidemic began 30 years ago? A. 30 million B. 60 million C. 34 million D. 1.7 million Homework 2.7.3 How is HIV diagnosed? A. the ELISA test, which is repeated and confirmed with the Western blot test B. a C-reactive protein that is confirmed with an agglutination test C. a CD4 agglutination reaction test D. a CD4 fluorescent antibody test Homework 2.8.1 What is a risk factor for Hodgkin's lymphoma? A. the common cold B. HIV C. shingles D. herpes simplex Homework 2.8.2 Which diagnostic test is used to diagnose and stage Hodgkin's lymphoma? A. lumbar puncture B. physical exam C. CBC D. Biopsy Homework 2.8.3 What are signs and symptoms of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma? A. painless swelling of lymph nodes and chest pain B. coughing and anorexia C. night sweats and unexplained weight gain D. painful swelling of lymph nodes and generalized pain Homework: Chapter 3 Pre Test Homework 3.1.1 What is a pathogen? A. A pathogen is hospital-acquired infections that are acquired in a healthcare facility. B. A pathogen is any organism too small to be viewed by the unaided eye as bacteria, protozoa, and some fungi and algae. C. A pathogen is the study of the transmission, occurrence, distribution, and control of disease. D. A pathogen is a microorganism that can cause disease. Homework 3.1.2 Infectious diseases transmitted by human contact are said to be _______________. A. notifiable B. outbreak C. contagious or communicable D. Pathogens Homework 3.1.3 Epidemiology is ____. A. the study of science of life or living matter in all its forms and phenomena, especially with reference to origin, growth, reproduction, structure, and behavior B. the study of the transmission, occurrence, distribution and control of disease C. the study of the heart and its functions in health and disease D. the study of origin, nature, and course of disease Homework 3.1.4 Epidemiologist track the ______ of disease, the number of new cases of a disease in a population and the number of existing cases of a disease which is known as _______. A. incidence; prevalence B. endemic; epidemic C. incidence; endemic D. prevalence; epidemic Homework 3.2.1 Vertical transmission can occur when a mother infects her newborn with what type of infectious disease? A. measles B. influenza C. HIV/AIDS D. Tuberculosis Homework 3.2.2 Intravenous drug users can transmit infectious agents such as _______ A. Ophthalmia neonatorum B. cholera C. hepatitis B D. Giardiasis Homework 3.2.3 What is direct transmission? A. Occurs when infectious diseases are transmitted from one generation to the next. B. Occurs when food and beverages are contaminated then ingested. C. Occurs when a pathogen can withstand the environment outside its host for a long period of time before affecting another individual. D. Occurs when an individual is infected by contact with the reservoir. Homework 3.2.4 Tuberculosis and measles are examples of what type of transmission? A. vertical transmission B. direct transmission C. indirect transmission D. parenteral transmission Homework 3.2.5 Sally has been tested positive for an infectious disease and does not have any signs or symptoms. Sally is known to be a _______. A. reservoir B. fomites C. carrier D. Host Homework 3.3.1 What are infectious particles with a core of genetic material (either RNA or DNA) wrapped in a capsid? A. prions B. viruses C. bacteria D. Fungus Homework 3.3.2 Cocci, bacilli, spirilla, and spirochetes are characteristics of what type of pathogen? A. bacteria B. virus C. fungus D. Helminths Homework 3.3.3 Trichomonas vaginalis is an example of this type of pathogen? A. helminths B. fungi C. bacteria D. Protozoa Homework 3.4.1 What is a nosocomial infection? A. the 100 trillion microorganisms that are commonly present in and on the human body B. a community acquired infection acquired from the community C. the separation of persons who maybe or may not be infected from healthy people until the period of infectious risk is passed D. a hospital-acquired infection obtained from a health care facility Homework 3.4.2 What is the principal route of transmission for nosocomial infections? A. health care staff B. vertical transmission C. fecal-oral D. Burns Homework 3.5.1 Which drug can be used to treat gram-positive bacteria? A. Tamiflu B. penicillin C. fluconazole D. Flagyl Homework 3.5.2 Systemic treatment with antifungal drugs require careful dosing and monitoring for side effects. True False Homework 3.5.3 Ringworm can be treated with what type of drug? A. antivirals B. antifungals C. antibiotics D. Cephalosporins Homework 3.6.1 Antibiotic resistance is when bacteria _____. A. adapt to antibiotics making the antibiotics ineffective B. penetrate the cell wall and interfere with cell wall synthesis C. are susceptible to antibiotics D. interfere with bacteria reproduction in the cell by acting as nucleic acid analogues Homework 3.6.2 Which is an example of antibiotic-resistant pathogens? A. Klebsiella B. Group A Streptococcus C. E.Coli D. Vancomycin-resistant enterococci (VRE) Homework 3.7.1 What are emerging infectious diseases? A. diseases that have been eradicated and no longer a threat to society B. diseases whose incidence in humans has significantly increased in the past two decades C. diseases that have reappeared after a significant decline in incidence D. diseases that reappear in the fall and winter seasons Homework 3.7.2 All the following are reemerging infectious diseases except? A. valley fever B. mumps C. cholera D. Coronavirus Homework 3.7.3 At least one dose of measles vaccine can decrease morbidity and mortality rates in children. True False Homework 3.8.1 Every year 1.4 million children worldwide die from vaccine-preventable diseases before they reach age five. True False Homework 3.8.2 Erin is a three-year-old who presents with fever, cough, runny nose, and fatigue followed by a rash that started at her head. Erin is most likely suffering from _____. A. rubella B. varicella C. Bordetella pertussis D. Measles Homework 3.8.3 What is the hallmark sign for mumps? A. pain in the mouth B. pain in the parotid glands C. headache D. mild conjunctivitis Homework 3.8.4 What vaccine can be administered to prevent mumps? A. MMR B. DTap C. Hib D. Td Homework 3.8.5 What is the mode of transmission for mumps? A. fecal-oral transmission B. vertical transmission C. direct transmission D. indirect transmission Homework: Chapter 4 Pre Test Homework 4.1.1 What is cancer? A. organ disease caused by an unhealthy lifestyle B. uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the body C. cells that have been disrupted by trauma D. tumors that form in the body Homework 4.1.2 What is the definition of "metastasis"? A. discovery of a tumor on an x-ray B. identification of a non-cancerous mass C. removal of cancerous cells D. spread of abnormal, cancerous cells Homework 4.2.1 What do the cells of a malignant tumor look like under a microscope? A. they do not have a uniform appearance B. similar to the cells of the surrounding tissue C. they are much smaller than the cells in normal tissue D. there are no distinct cells in a malignant tumor Homework 4.2.2 Why is a benign tumor easier to remove than a malignant tumor? A. it has more blood vessels B. it is large and easy to grasp with surgical tools C. it is encapsulated D. it does not have a covering that separates is from surrounding tissues Homework 4.3.1 Which describes a benign tumor of an epithelial surface? A. carcinoma B. cyst C. sarcoma D. Polyp Homework 4.3.2 The names of malignant tumors have two parts, a prefix and a suffix. What is the system for choosing these two parts? A. The prefix describes the shape of the tumor and the suffix indicates whether or not it has spread. B. The prefix names the type of cells that are cancerous and the suffix names the category of drug used to treat them. C. The prefix names where the cancer is located and the suffix grades its severity. D. The prefix names the tissue of origin and the suffix describes whether the cancerous cells are epithelial or supporting. Homework 4.4.1 The most important risk factor for cancer is A. lifestyle B. age C. diet D. Environment Homework 4.4.2 How is the immune system related to the development of cancer? A. It repairs abnormal cells. B. It removes of toxins that may damage cells and cause mutations. C. It has natural flaws that contribute to the development of cancer. D. It should recognize and eliminate abnormal cells. Homework 4.4.3 Which of these are sources of ionizing radiation? A. CT Scans B. chemotherapy C. MRIs D. Microwaves Homework 4.5.1 What is the cause of all cancers? A. smoking and drug use B. mutation of the genes that control cell division and cell death C. disruption of cell walls leading to an irregular shape D. a decrease in oxygen supply to the cancerous area Homework 4.5.2 How would a malfunction in the oncogene contribute to the development of cancer? A. failure to tell the cells when to divide and when not to divide B. failure to alert the immune system to the presence of cancerous cells C. failure to remove abnormal cells persisting in the tissues D. failure to signal the appropriate time for cell death Homework 4.5.3 Environmental substances that damage the DNA in cells and cause mutations resulting in cancer are known as A. apoptosis B. suppressors C. carcinogens D. Oncogenes Homework 4.6.1 What limits the potential for tumor marker tests to accurately diagnose cancer? A. They must be drawn so frequently that patients often decline complete testing. B. Some cancers produce chemicals that break down tumor markers. C. Tumor markers are sometimes produced by normal cells. D. The tests are very expensive and rarely covered by insurance. Homework 4.6.2 How does a mammogram help to diagnose cancer? A. It detects areas of increased temperature in the breast that may represent cancerous lesions. B. It creates an image of developing tumors with sound waves as they bounce off of structures in the breast. C. It is not a diagnostic procedure, but is done for cancer prevention. D. It creates an x-ray photograph of the breast that shows developing tumors. Homework 4.6.3 How might a CT computed tomography scan give a more details about cancerous structures inside of the body than other diagnostic methods? A. It allows the operator to take samples of suspicious tissues. B. It produces a three-dimensional image. C. It reveals cancerous lesions as white areas. D. Small scanners can be placed inside the body. Homework 4.6.4 What are the advantages of using ultrasonography for viewing potentially cancerous structures inside the body? A. The equipment required is very costly and gives patients a sense that they are getting the most up to date care. B. It does not use radiation, is inexpensive, and easy to use. C. It uses a magnetic field to create detailed images and cross sectional images. D. The images from various angles are combined by a computer. Homework 4.7.1 Which type of cancer therapy uses high-energy rays that damage the DNA of cells, interfering with cell division and growth? A. hormone therapy B. radiation therapy C. chemotherapy D. Immunotherapy Homework 4.7.2 What do chemotherapy and radiation therapy have in common? A. They require implants to be placed in the body. B. They are painful. C. They destroy normal cells along with cancerous cells. D. The treatment plans are very disruptive to daily routines. Homework 4.7.3 How do monoclonal antibodies work to destroy cancer cells? A. They are beamed from a machine aimed at the tumor site to kill the cells in that area. B. They block the action of hormones. C. They attach to cancer cells and signal the immune system to destroy them. D. They target all rapidly dividing cells. Homework 4.8.1 What percentage of worldwide cancer deaths are due to tobacco use occur each year? A. 56% B. 12% C. 75% D. 22% Homework 4.8.2 How can a person who regularly drinks alcohol reduce their risk of alcohol-related cancers? A. a maximum of one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for men B. drinking only on special occasions C. avoiding beverages with a high alcohol content by drinking only beer or wine D. drinking on weekends only Homework 4.8.3 A 51-year-old woman calls her physician's office because she has relatives with cancer and wants to know what type of cancer screenings are available to her. What is likely to be the physician's response? A. "You won't need any tests unless you have cancer symptoms." B. "You will need at least a pap test, an HPV test, a mammogram, and colorectal screening, but I might recommend additional tests after your visit." C. "You will need a pap test and HPV screening, but you're still too young to be at risk for breast or colon cancer." D. "These things vary with every person, so we will have to take your history and examine you before we can say." Homework: Chapter 5 Pre Test Homework 5.1.1 Which substance is the chemical blueprint that directs all cell activities? A. guanine B. adenosine C. DNA D. RNA Homework 5.1.2 Which structure does the double helix of DNA most closely resemble? A. A figure eight B. a spiral staircase C. a closed circle D. Ladder Homework 5.1.3 How many chromosomes are normally contained in each human cell? A. 22 pairs B. 26 pairs C. 46 D. 48 Homework 5.2.1 Which term describes alleles that always produce their trait when inherited? A. recessive B. heterozygous C. dominant D. Homozygous Homework 5.2.2 Which category of diseases maybe caused by unique environmental conditions or behaviors that are shared by family members? A. sex-linked inheritance B. familial diseases C. autosomal recessive disorders D. autosomal dominant disorders Homework 5.2.3 Which disease is an autosomal dominant disorder? A. fragile X syndrome B. hemophilia C. color blindness D. familial hypercholesterolemia Homework 5.3.1 Which disorder is associated with an abnormal number of chromosomes as opposed to being caused by a defective gene? A. Klinefelter syndrome B. albinism C. phenylketonuria D. Tay-Sachs Homework 5.3.2 Which disease is also called Down syndrome? A. hemochromatosis B. galactosemia C. albinism D. trisomy 21 Homework 5.3.3 What is the prevalence of Down syndrome? A. approximately 1 in 800 B. approximately 1 in 200 C. approximately 1 in 10,000 D. approximately 1 in 3,000 Homework 5.4.1 Which characteristic is associated with congenital disorders? A. they may be transmitted from parents to offspring B. they are caused by the inheritance of one or more defective genes C. they usually result from a failure during embryonic development D. they are commonly associated with chromosomal abnormalities Homework 5.5.1 At which stage of pregnancy is amniocentesis typically performed? A. before the 4th week B. before the 6th week C. at the 10th week D. after the 14th week Homework 5.5.2 Which statement best describes chorionic villus sampling? A. Samples may be taken between 18 and 20 weeks of pregnancy. B. Test results are not available until approximately two weeks after the procedure. C. It provides information about gender. D. It requires the removal of amniotic fluid. Homework: Chapter 6 Pre Test Homework 6.1.1 The chamber walls of the heart consist of the heart muscle, also known as which structure? A. atrium B. ventricle C. endocardium D. Myocardium Homework 6.1.2 Which structure acts as the pacemaker of the heart? A. sinoatrial node B. Purkinje fibers C. atrioventricular node D. Aorta Homework 6.1.3 Which blood vessel has the ability to change its diameter to dilate and contract in order to alter blood flow to the tissues? A. aorta B. arteriole C. capillary D. Venule Homework 6.2.1 What is the primary symptom of peripheral arterial disease? A. lower leg pulse faint or absent B. ulcers on the lower extremities C. feet are cold to touch D. intermittent claudication Homework 6.2.2 Raynaud's disease is characterized by which symptoms? A. cold, numb or tingling fingers B. pain with walking, thinning of skin and subcutaneous tissue of the lower legs C. pain in the muscles of the legs and ulcers D. headache, dizziness, agitation Homework 6.2.3 What are the signs and symptoms of coronary artery disease? A. dyspnea, orthopnea, weakness, fatigue, ascites, and peripheral edema B. angina pectoris, palpitations, and myocardial infarction C. fever, inflammation of the joints, and rash D. fever, chest pain, shortness of breath, and tachycardia Homework 6.3.1 Which statement is correct regarding arteriosclerosis? A. artery walls become flexible B. artery walls thicken and become soft C. is caused by minerals accumulating within the walls of the arteries D. it leads to hypertension Homework 6.3.2 What is the most common cause of arteriosclerosis? A. hypertension B. atherosclerosis C. smoking D. deep vein thrombosis (DVT) Homework 6.3.3 Arteriosclerosis can lead to which manifestation? A. increased blood flow B. elevated blood cholesterol levels C. hypertension D. elevated blood lipid levels Homework 6.4.1 What role do triglycerides play in hyperlipidemia and atherosclerosis? A. helps to decrease cholesterol synthesis B. increases the risk for coronary artery disease C. facilitates fat in the body to take the form of high density lipoprotein D. helps to remove cholesterol from the blood Homework 6.4.2 How does high-density lipoprotein function in the body to help prevent hyperlipidemia? A. it carries about one-half of the cholesterol in the body B. it helps to store cholesterol in the body C. it helps carry cholesterol away from the arteries D. it carries cholesterol to the kidneys so it can be eliminated from the body. Homework 6.4.3 What is the effect of low-density lipo-proteins on the arteries? A. narrowing of the arteries B. formation of a soft, sticky plaque C. increased blood flow D. cushioning of the walls Homework 6.5.1 Identify which blood pressure reading represents stage 1 hypertension? A. 128/82 B. 162/100 C. 138/88 D. 144/90 Homework 6.5.2 Which statement is true regarding hypertension? A. It affects about 30% of the adult population worldwide. B. It remains untreated or undertreated in the majority of affected individuals. C. Its most common symptom is headache. D. It is the second most common cardiovascular disorder. Homework 6.5.3 Which individual is at greatest risk for hypertension? A. excessive dietary intake of salt, consumes 2 beers a day, 52 years old, male B. African-American ancestry, obese, 42 years old, male C. family history of hypertension, sedentary lifestyle, 72 years old, female D. prehypertensive, marathon runner, 60 year old, female Homework 6.6.1 Identify the key manifestation of arterial hypertension. A. bradycardia B. tachycardia C. asymptomatic D. elevated blood pressure Homework 6.6.2 Identify the key sign/symptom of pulmonary arterial hypertension? A. bradycardia B. asymptomatic C. elevated blood pressure D. Tachycardia Homework 6.6.3 Identify the causes of arterial hypertension. A. ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus, unknown in many cases B. older age, sedentary lifestyle, overweight, excessive dietary salt intake, family history C. trauma, allergic reaction and drug, hemorrhage D. genetic, lifestyle, obesity and diabetes, diet high in saturated fat Homework 6.7.1 Which are the complications of varicose veins? A. ulcers, fever, and loss of sensation B. ulcers, thinning of the skin, and excessive itching C. ulcers, infection, and hemorrhage D. ulcers, necrosis, and numbness Homework 6.7.2 Which are the signs and symptoms of varicose veins? A. feet cool to the touch, faint pulses in the lower extremities B. swollen, twisted, and painful veins in the lower legs C. blood clots, numbness, and tingling of the lower legs D. feet warm to the touch, bounding pulses in the lower extremities Homework 6.7.3 Which intervention helps relieve symptoms of varicose veins? A. avoiding unnecessary walking B. elevating the legs when seated C. increasing calcium in the diet D. avoiding support hose Homework 6.8.1 Which patient would be at greatest risk of developing a venous thrombosis? A. patient with numerous spider veins on the lower legs B. patient on bedrest after abdominal surgery C. patient who wears compression stockings D. patient with infected ulcers on lower extremities Homework 6.8.2 In teaching a patient about the development of venous thrombosis, which statement would be correct? A. "Being 75 years old puts one at increased risk of developing venous thrombosis." B. "Try to avoid too much fiber as it is known to increase the risk of venous thrombosis." C. "Most individuals will have pain in the calf if a venous thrombosis develops in this area." D. "Excessive walking should be avoided, as it increases the risk of venous thrombosis formation." Homework 6.8.3 Which manifestation may indicate venous thrombosis? A. area is cool to the touch B. swelling C. intense itching D. superficial muscle cramping Homework 6.9.1 Which manifestation is present with acute infectious endocarditis? A. hypertension B. sub-normal temperature C. intense chest pain D. vegetations Homework 6.9.2 Signs and symptoms of rheumatic fever begin approximately _________ following a _________ infection? A. seven days, streptococcal B. two weeks, staphylococcal C. two weeks, streptococcal D. seven days, staphylococcal Homework 6.9.3 What are the signs and symptoms of aortic stenosis? A. usually asymptomatic B. dilation of the ventricle, backflow of blood into the left ventricle, decreased diastolic pressure, and symptoms of heart failure C. increased pressure in the heart, congestion of the veins, cyanosis, and congestive heart failure D. hypertrophy of the left ventricle and calcified deposits on the valve Homework 6.10.1 What is a supraventricular arrhythmia? A. an arrhythmia that is generated in the ventricular conduction system and in the ventricle B. an arrhythmia that is generated by an overload of blood in the myocardium and coronary arteries C. an arrhythmia that is generated by the pulmonary arteries D. an arrhythmia generated by electrical abnormalities in the sinoatrial (SA) node, atria, atrioventricular (AV) node, and junctional tissue in the heart Homework 6.10.2 Which etiology can be contributed to both supraventricular and ventricular arrhythmias? A. tachycardia B. drug abuse C. endocarditis D. unknown Homework 6.10.3 What is the most common heart rhythm disorder? A. atrial fibrillation B. bradycardia C. ventricular fibrillation D. Tachycardia Homework 6.11.1 Which etiologies are associated with shock? A. minor burns and bleeding B. genetic and mutation disorders C. chills and fever D. damage to the nervous system and trauma Homework 6.11.2 An allergic reaction to penicillin can cause which type of shock? A. neurogenic B. hypovolemic C. anaphylactic D. Cardiogenic Homework 6.11.3 Which statement is an accurate description of the basic physiology of shock? A. Shock is a life-threatening condition in which blood pressure drops too low to sustain life. B. Shock is the attempt of the body to correct metabolic imbalances. C. Shock is any condition that increases the heart's ability to pump effectively. D. Shock takes place when the heart is beating in a disorganized manner. Homework 6.12.1 After birth, the decrease in right and left atrial pressure produces a closure of which structure(s)? A. pulmonary semilunar valve B. displaced aorta C. foramen ovale D. pulmonary veins Homework 6.12.2 Cord clamping and removal of the placental circulation cause an increase in pressure in which heart chamber? A. left ventricle B. right atrium C. right ventricle D. left atrium Homework 6.12.3 Which action initiates the switch from placental to pulmonary oxygenation of blood? A. the baby takes its first breath and the lungs expand B. the pulmonary veins close C. the semilunar pulmonary valve closes D. the baby's passage through the birth canal and the change in atmospheric pressure Homework 6.13.1 Approximately how many infant births per 1,000 have some form of congenital heart disease? A. four B. ten C. eight D. Twenty Homework 6.13.2 Difficulty feeding, failure to gain weight, poor development, cyanosis, and fainting are signs and symptoms of which congenital heart defect? A. patent ductus arteriosus B. transposition of the great arteries C. coarctation of the aorta D. tetralogy of Fallot Homework 6.13.3 What is the etiology common to transposition of the great vessels, septal defects, patent ductus arteriosus, and coarctation of the aorta? A. maternal smoking B. maternal history of diabetes C. dilated vessels of the heart D. Unknown Homework 6.14.1 What effect does age have on systolic blood pressure? A. progressively decreases B. progressively increases C. remains unchanged D. Unknown Homework 6.14.2 Older age is an etiology of which cardiac disease? A. hypertrophic cardiomyopathy B. arterial hypertension C. chronic venous insufficiency D. mitral stenosis Homework 6.14.3 Peripheral arterial disease occurs most commonly in which gender and age group? A. men 70-80 years of age B. women 65-75 years of age C. women 50-60 years of age D. men 55-65 years of age Homework: Chapter 7 Pre Test Homework 7.1.1 Which is not true of blood plasma? A. it contains protein B. it carries hormones C. it destroys foreign objects in the bloodstream D. most of its volume consists of water Homework 7.2.1 How are erythrocytes produced in numbers sufficient for maintaining adequate gas exchange throughout the body? A. Low levels of erythrocytes in the blood triggers red blood cells to divide B. Stored iron from the liver goes to the spleen, the iron bonds with globin protein and is encased in a cell membrane. Mature erythrocytes are released through the splenic duct. C. Dead erythrocytes are absorbed by the liver, where iron stores are used to replenish their hemoglobin before they are returned to the bloodstream. D. Erythropoetin stimulates stem cells in the bone marrow to produce more red blood cells. Homework 7.2.2 How does an erythrocyte carry oxygen? A. it is bound to hemoglobin B. it binds to a receptor in the cell membrane C. it is held in the concave area on the cell surface D. it is held in microscopic gas pockets in the cytoplasm Homework 7.2.3 A patient has made an appointment with a health care provider because he has been suffering from unexplained fevers and frequent infections that take a long time to recover from. Which blood component would the provider be most interested in evaluating? A. plasma protein B. leukocytes C. erythrocytes D. Platelets Homework 7.2.4 You are working with a hematologist (specialist in diseases of the blood) and a patient with severe liver disease has been referred to your office. When preparing for the visit, you anticipate the patient will be evaluated for A. rapid heart beat B. abnormal bleeding C. high blood pressure D. Infection Homework 7.3.1 Susan is has a history of anemia and is looking for dietary supplements that will help her to avoid this condition. Which of these supplements would not be useful in preventing anemia? A. vitamin B12 B. calcium C. folic acid D. Iron Homework 7.3.2 You are helping to care for a patient who is severely anemic in the setting of a normal iron level. There is no elevation in serum bilirubin. The red blood cells are normal in size and shape. What would be the next step in determining the cause of this patient's anemia? A. assess for gastrointestinal bleeding B. measure B12 and folic acid levels C. perform a splenectomy D. perform kidney function tests Homework 7.3.3 Nausea, vomiting, and abdominal distress are symptoms of A. pernicious anemia B. anemia of chronic disease C. iron deficiency anemia D. hemolytic anemia Homework 7.3.4 How much B12 intake is needed to prevent pernicious anemia due to B12 deficiency? A. 400 micrograms B. 10 micrograms C. 1 microgram D. 2.5 micrograms Homework 7.3.5 You are reading threads in an online health forum and find a question from a woman who suffers from Crohn's disease. She says the doctor told her she has low blood counts but didn't have time to explain it to her. She is feeling very tired and looking for things she could do to feel better. You see several responses. Which one do you agree with and encourage her to try? A. "I heard that taking extra vitamin C can help you absorb iron better so you can build your blood counts back up." B. "You should be checked for internal bleeding. That might be happening when you don't even know it." C. "If you have Crohn's disease, you have to take a lot of extra folic acid because you can only process a little bit of what you take in. You need folic acid for your blood." D. "I bet you have some kind of genetic problem that's messing up your bowels and your blood at the same time. You should have genetic testing." Homework 7.4.1 How much of the African American population has sickle cell trait? A. 0.5% B. 1-3% C. 10% D. 50% Homework 7.4.2 An African American couple have made an appointment with a certified nurse midwife for pre-conception counseling. Neither of them have been tested for sickle cell trait in the past and they don't know if it is necessary. The midwife's counseling should include A. suggesting the couple forego testing because risk for the disease can not be predicted B. strategies by which the mother can prevent transmission of trait or disease to her child C. informing the couple that only one of them needs to be tested because children with one parent who does not have the trait will be completely unaffected. D. informing the couple their child will likely have a severe form of the disease if they both have the trait Homework 7.4.3 What causes the pain and tissue damage associated with sickle cell anemia? A. shrinkage of blood vessels in response to toxins produced by abnormal cells B. damage to nerve cells resulting from decreased oxygenation C. red blood cells that cannot pass through blood vessels because of their abnormal shape, creating blockages D. the buildup of waste products from dead red blood cells Homework 7.4.4 What is the underlying cause of thalassemia? A. a genetic defect in the mechanism that releases erythropoietin B. a genetic defect that causes weakness in the red blood cell membrane C. a genetic defect in the synthesis of the proteins that make up hemoglobin D. a genetic inability to absorb iron Homework 7.5.1 Clotting disorders are problems associated with hemostasis. What is the definition of hemostasis? A. abnormal bleeding B. platelets in a resting state C. platelet aggregation D. the arrest of bleeding Homework 7.5.2 An emergency medical technician (EMT) has been called to the home of an elderly woman. Her children are very concerned because she fell in her carpeted bedroom and has multiple bruises (ecchymoses). They have also noticed little red spots on her skin lately but were not concerned until now. The EMT will be handle this patient very gently because he suspects she has A. hemolytic anemia B. thrombocytopenia C. immune deficiency D. Neutropenia Homework 7.5.3 How is vitamin K synthesized in the body? A. by stimulation of osseous bone tissues B. vitamin K is absorbed from cauliflower, carrots, and cucumbers C. by intestinal bacteria D. by exposure to sunlight Homework 7.6.1 The most common genetic disorder in the world is A. Kleinfelter's syndrome B. sickle cell anemia C. hemophilia D. Thalassemia Homework 7.6.2 A patient has been diagnosed with Von Willebrand's disease after a skiing accident. He should be counseled on A. lifestyle modifications aimed at avoiding future injuries B. the possibility of needing regular blood transfusions C. the need for regular vitamin K injections in the future D. the possibility of frequent hospitalizations for pain control Homework 7.6.3 You are a nurse at a hematology clinic. One of your patients is a 17-year-old boy with hemophilia. He hates to be at the doctor so frequently and often does not tell anyone when he has joint pain. You should encourage him to report his symptoms and explain that A. without proper treatment, the bleeding and inflammation in his joints could progress to severe disability. B. it would be better for him to take medications for the pain. C. the problems in his joints could initiate responses in his immune system that make his hemophilia worse. D. he could cure his hemophilia if he followed his medication regimen. Homework 7.7.1 A chemotherapy patient calls the cancer center's on-call nurse to report not feeling well and having a low grade fever. The nurse suspects she is suffering from A. polycythemia B. hemolysis C. thrombocytopenia D. neutropenia Homework 7.7.2 What is the best course of action for a chemotherapy patient who has been diagnosed with severe neutropenia? A. blood transfusion B. close follow up at an outpatient clinic C. bed rest at home D. hospitalization in an isolation room and intravenous antibiotics Homework 7.7.3 Neutropenia can be a complication of A. genetic disorders B. vitamin malabsorbtion C. rheumatoid arthritis D. trauma Homework: Chapter 8 Pre Test Homework 8.1.1 The mucus-coated lining of the respiratory tract is known as the respiratory ______________. A. endothelium B. epidermis C. smooth muscle tissue D. Epithelium Homework 8.1.2 As air is being inhaled, which structure in the respiratory tract does it pass through after the larynx, but before the bronchi? A. pharynx B. lungs C. trachea D. nasal cavity Homework 8.1.3 What term describes the small air sacs located in the lungs where gas exchange occurs? A. bronchioles B. capillaries C. alveoli D. Cilia Homework 8.1.4 The double-layered membrane that encases the lungs is called the __________. A. pleura B. squamous epithelium C. chest wall D. thoracic cavity Homework 8.2.1 Difficulty breathing is also known as ____________. A. asthma B. hyperventilation C. apnea D. dyspnea Homework 8.2.2 What does the term hemoptysis refer to? A. nonproductive cough B. abnormal breath sounds C. excessive sputum D. coughing blood Homework 8.2.3 What does cyanosis, a blue color in the skin and nails, indicate? A. low fever B. high fever C. high oxygen levels D. low oxygen levels Homework 8.2.4 Clubbing of the fingers or toes is an indicator of ___________ and __________. A. circulatory problems, malnutrition B. poor oxygenation, circulatory problems C. poor oxygenation, a compromised immune system D. poor oxygenation, malnutrition Homework 8.3.1 What does a spirometer measure? A. air capacity of the lungs B. air pressure in the lungs C. diaphragm strength D. amount of fluid in the lungs Homework 8.3.2 Which is incorrect about measuring peak expiratory flow? A. It can be done at home without supervision. B. It gauges the maximum force with which a patient is capable of exhaling. C. A patient's peak flow can indicate how well their lungs are functioning. D. The optimal peak expiratory flow is the same for everyone. Homework 8.3.3 What does a bronchial challenge test detect? A. blood in the sputum B. fluid in the lungs C. airway hypersensitivity D. an abnormal breathing rate Homework 8.3.4 Which describes a wheezing breath sound? A. a high-pitched whistling sound B. a creaking sound C. a bubbling sound D. high-pitched popping lung sounds Homework 8.4.1 Which of the following is not a symptom of the common cold? A. sneezing B. cough C. sore throat D. high fever Homework 8.4.2 Inflammation of the mucous membrane of the nose caused by an allergic reaction to an airborne substance is called allergic ____________. A. rhinitis B. iritis C. otitis D. phlebitis Homework 8.4.3 Which is not a treatment for sinusitis? A. decongestants B. nasal corticosteroids C. using a humidifier D. nasal endoscopy Homework 8.4.4 What would be an inappropriate treatment for viral pharyngitis? A. anti-inflammatory medications B. antibiotics C. gargling with saltwater D. pain relievers Homework 8.4.5 What is a main symptom of laryngitis? A. difficulty swallowing B. hoarseness C. throat pain D. fever Homework 8.5.1 Global pandemics of the influenza virus occur approximately every ____________. A. 2-5 years B. 25-30 years C. 10-15 years D. 1-3 years Homework 8.5.2 Which patient has a greater risk of developing complications from the flu? A. male, 40, with chronic bronchitis B. female, 4, in good health C. female, 72, with asthma and diabetes mellitus D. male, 60, with emphysema Homework 8.5.3 Which structures in the respiratory tract are primarily affected by pneumonia? A. alveoli B. bronchioles C. pleura D. bronchi Homework 8.5.4 Which of these statements about a person with a latent tuberculosis infection not accurate? A. The bacteria are present, but the person's immune system is able to keep them from growing. B. They cannot spread the infection to others. C. They are asymptomatic. D. They are immune from developing active TB. Homework 8.5.5 What is the main cause of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)? A. air pollution B. smoking cigarettes C. inhalation of dust particles D. inhalation of chemical fumes Homework 8.6.1 On average, how much of the respiratory membrane is typically lost every year after the age of 30? A. about 4 square inches B. about one square inch C. about 2 square feet D. about one square foot Homework 8.6.2 Which of these is a normal age-related change in respiratory function? A. emphysema B. deterioration of the elastic tissue of the lungs C. asthma D. shortness of breath Homework: Chapter 9 Pre Test Homework 9.1.1 The digestive tract includes all of the following except: A. trachea B. esophagus C. large intestine D. pharynx Homework 9.1.2 Where does digestion begin? A. the stomach B. the mouth C. the small intestine D. the large intestine Homework 9.1.3 Which part of the digestive system secretes hydrochloric acid? A. the stomach B. the small intestine C. the liver D. the large intestine Homework 9.1.4 Rhythmic, smooth muscle contractions of the intestinal wall is called _____________. A. peristalsis B. chyme C. bile D. swallowing Homework 9.2.1 Which is a symptom of stomatitis? A. fever B. redness, ulcers, patches, and bleeding C. abnormal growths, sores D. dysphagia Homework 9.2.2 All of the following are symptoms of esophagitis except: A. heartburn B. hematemesis C. acid reflux D. fever Homework 9.2.3 What disease is caused by inflammation of the lining of the stomach and is frequently accompanied by vomiting of blood? A. appendicitis B. peritonitis C. gastritis D. gastroenteritis Homework 9.2.4 All of the following are symptoms of gastroenteritis except? A. nausea B. vomiting C. anorexia D. hematemesis Homework 9.2.5 What gastrointestinal disease exhibits acute lower right quadrant abdominal pain, nausea, and fever? A. appendicitis B. duodenal ulcer C. malabsorption syndrome D. cholecystitis Homework 9.3.1 Which diagnostic test/procedure, allows for visualization of abnormalities in the esophagus, stomach, small intestine, and large intestine? A. ultrasound B. x-ray C. biopsy D. endoscopy Homework 9.3.2 A hiatal hernia can be diagnosed by all of the following except: A. endoscopy B. ultrasound C. x-ray D. CT scan Homework 9.3.3 All of the following are imaging techniques that can be used to diagnose digestive system diseases and disorders except? A. MRI B. ultrasound C. CT scan D. PET scan Homework 9.4.1 Tobacco is a cause for all of the following diseases except? A. gastritis B. cancer of the esophagus C. cancer of the mouth D. diverticulitis Homework 9.4.2 All of the following diseases have idiopathic, or unknown, causes except? A. regional enteritis B. stomatitis C. cancer of the stomach D. chronic ulcerative colitis Homework 9.4.3 Acid reflux is the cause of which of the following diseases? A. gastroenteritis B. gastritis C. stomatitis D. esophagitis Homework 9.4.4 Which of the following can cause stomatitis? A. use of tobacco products, especially in conjunction with consuming alcohol B. aspirin, coffee, tobacco, alcohol, and infection C. bacteria, viruses, and fungi D. acid reflux due to an incompetent cardiac sphincter Homework 9.5.1 Surgery is a treatment option for all of the following diseases except? A. cancer of the mouth B. hiatal hernia C. appendicitis D. stomatitis Homework 9.5.2 Which of the following is a treatment option for stomatitis? A. surgery B. antibiotics C. antacids D. antidiarrheal medications Homework 9.5.3 What is a treatment option for chronic atrophic gastritis? A. nonirritating diet, antacids, and acid-reducing medications B. avoiding irritants, drinking ice water, using antacid medications, and surgery to control bleeding C. antibiotics and managing the diet D. vitamin B12 supplements Homework 9.6.1 Which of the following is not one of the accessory organs of the digestive system? A. pancreas B. stomach C. gallbladder D. liver Homework 9.6.2 Which part of the digestive system has both endocrine and exocrine functions? A. gallbladder B. liver C. appendix D. pancreas Homework 9.6.3 The endocrine portion of the pancreas secretes which of the following? A. proteases B. hydrochloric acid C. glucagon D. bile Homework 9.7.1 All of the following are symptoms of hepatitis except: A. anorexia B. jaundice C. nausea D. high fever Homework 9.7.2 What type of hepatitis is also known as serum hepatitis and has a two to six-month incubation period? A. hepatitis A B. hepatitis C C. hepatitis E D. hepatitis B Homework 9.7.3 Jaundice is a symptom of all of the following diseases except? A. pancreatitis B. cirrhosis C. hepatitis D. cholecystitis Homework 9.8.1 All of the following can be diagnosed using an ultrasound except: A. cholelithiasis B. pancreatitis C. cancer of the liver D. hepatitis Homework 9.8.2 How can cholecystitis be diagnosed? A. x-ray B. fecal fat test C. blood test D. needle biopsy Homework 9.8.3 How can hepatitis be diagnosed? A. immunodiagnostics B. CT scan C. ultrasound D. fecal fat test Homework 9.9.1 Which of the following hepatitis infections is not a sexually transmitted or bloodborne infection? A. hepatitis C B. hepatitis D C. hepatitis A D. hepatitis B Homework 9.9.2 What causes Hepatitis A? A. food or water borne infection B. blood borne C. sexually transmitted D. alcohol-induced Homework 9.9.3 Causes of pancreatic cancer include all of the following except: A. diabetes B. obesity C. cigarette smoking D. alcohol abuse Homework 9.10.1 What is the treatment for Hepatitis E? A. no treatment or vaccine B. immunoglobulin injections C. liver transplant D. antivirals Homework 9.10.2 What is the treatment for cholecystitis? A. fluid replacement B. immunoglobulin injections C. symptomatic treatment D. surgical removal Homework 9.10.3 The treatment for this disease calls for symptomatic treatment for edema and portal hypertension or bleeding; an improved diet, or a liver transplant. A. hepatitis D B. cancer of the liver C. hepatitis C D. cirrhosis Homework 9.11.1 Which of the following is the leading cause of death in children worldwide? Correct. Infectious diarrheal diseases is the leading cause of death in children worldwide. A. pancreatic disorders B. infectious diarrheal diseases C. hepatitis D. dental caries Homework 9.11.2 A hiatal hernia is a common disorder in _________________. Correct. A hiatal hernia is a common disorder in older adults. A. young adults B. teenagers C. older adults D. middle-aged adults Homework 9.11.3 The incidence of which type of cancer peaks in the 60s and is most common among older men? Correct. The incidence of pancreatic cancer peaks in the 60s and is most common among older men. A. esophageal B. pancreatic C. colon D. stomach Homework: Chapter 10 Pre Test Homework 10.1.1 Which structure drains urine from the kidney? A. urethra B. nephron C. kidney D. ureter Homework 10.1.2 Where are the kidneys located? A. floor of the pelvic cavity B. retroperitoneal C. mid-thoracic D. anterior abdomen Homework 10.1.3 What do the kidneys produce that stimulates red blood cell production? A. antidiuretic hormone B. erythropoietin C. urine D. renin Homework 10.1.4 What is a function of the nephron? A. regulate salt and water reabsorption B. reabsorb acid and urea C. drain urine from the urinary bladder D. filter metabolic waste products Homework 10.1.5 Which structure within the nephron leads to a collecting duct? A. proximal tubule B. afferent arteriole C. Loop of Henle D. distal convoluted tubule Homework 10.2.1 What is a cause of acute kidney injury? A. cystitis B. shock C. seasonal influenza D. diabetes mellitus Homework 10.2.2 Which sign will a patient with acute kidney injury demonstrate? A. dysuria B. oliguria C. joint pain D. blood in the urine Homework 10.2.3 In the patient with acute kidney injury, which electrolyte should be monitored to prevent cardiac arrest? A. potassium B. sodium C. magnesium D. chloride Homework 10.2.4 What should be prescribed to treat lupus nephritis? A. decreased dietary calcium intake B. increased oral fluid intake C. anti-inflammatory drugs D. decreased oral protein intake Homework 10.2.5 What symptom suggests that a patient has IgA nephropathy? A. groin pain B. ammonia odor on the breath C. facial edema D. swelling of the hands and feet Homework 10.3.1 What causes lower urinary tract infections (UTIs)? A. bacteria B. immunoglobulin deposits in the kidney C. dehydration D. high carbohydrate diet Homework 10.3.2 How do bacteria enter the bladder during a lower urinary tract infection (UTI)? A. descend from the kidneys B. bacteria are always present in the bladder C. ascend the urethra D. through the blood stream Homework 10.3.3 What predisposes a patient to develop a lower urinary tract infection (UTI)? A. trauma to the kidney B. high sugar content in the diet C. poor hygiene D. after collecting a urine culture Homework 10.3.4 A person is diagnosed with inflammation of the urethra. How should this be documented in the medical record? A. cystitis B. hematuria C. pyuria D. urethritis Homework 10.3.5 What symptoms is a patient with dysuria experiencing? A. urgency B. painful burning with urination C. pain in the lower back D. pus in the urine Homework 10.4.1 How should the buildup of toxic materials in the blood be documented in the medical record of a patient with renal failure? A. uremia B. anuria C. anemia D. pyuria Homework 10.4.2 Which medication if used long-term is associated with the development of chronic kidney disease? A. antibiotics B. aspirin C. acetaminophen D. antacids Homework 10.4.3 A patient with diabetes has frothy urine. Which diagnostic test will most likely be prescribed to determine if the patient has diabetic nephropathy? A. kidney biopsy B. renal ultrasound C. urinalysis D. fasting blood glucose Homework 10.4.4 What instructionshould be provided to a patient with hypertensive kidney disease? A. follow a low carbohydrate diet B. control high blood glucose levels C. smoking cessation D. take antibiotics as prescribed Homework 10.4.5 What physical finding indicates that a patient has nephrotic syndrome? A. elevated blood pressure B. extreme hunger C. edema around the eyes D. morning headache Homework 10.5.1 At which point should a patient with renal failure consider renal dialysis? A. when a kidney biopsy shows tissue changes B. when diagnostic tests indicate small kidneys C. prior to considering kidney transplant surgery D. when urine output volume changes Homework 10.5.2 A patient with chronic renal failure asks for an explanation about hemodialysis. What should be explained to this patient? A. corrects electrolyte imbalances B. removes toxic substances from the blood C. improves kidney function D. removes toxic substances through the abdomen Homework 10.5.3 A patient has been instructed on the process of hemodialysis. Which patient statement about dialysis is correct? A. "I will schedule a treatment when I start to have symptoms." B. "I can come home in the middle of a dialysis treatment." C. "I will only need two to three treatments until my kidneys heal." D. "A dialysis treatment takes 3 to 6 hours." Homework 10.5.4 A patient with renal failure has limited financial resources. What approach should be considered for this patient to receive required hemodialysis treatments? A. instruct the patient to schedule a treatment when resources are available B. schedule one fewer treatments a week C. consider a portable dialysis unit to use in the home D. discuss different banks with loan options for patients needing hemodialysis Homework 10.6.1 What is a major risk factor for the development of renal cell carcinoma? A. alcohol intake B. high-fat diet C. smoking D. low fluid intake Homework 10.6.2 What is the main sign of renal cell carcinoma? A. dysuria B. hematuria C. polyuria D. pyuria Homework 10.6.3 A patient has a large tumor on the right kidney. Which sign would this patient be expected to experience? A. increased red blood cell count B. weight loss C. low white blood cell count D. increased appetite Homework 10.6.4 A patient is diagnosed with renal cell carcinoma. For which treatment should this patient receive teaching? A. chemotherapy B. surgical removal of the kidney C. radiation D. insertion of a urinary catheter Homework 10.6.5 Which patient should be evaluated for a Wilm's tumor? A. 23-year old young adult B. 18-year-old adolescent C. 12-year-old school-age child D. 4-year-old preschooler Homework 10.7.1 What other part of the body might be affected in the patient with polycystic kidney disease (PKD?) A. mouth B. liver C. muscles D. blood Homework 10.7.2 What causes the symptoms of polycystic kidney disease (PKD)? A. growth of tumors B. high blood pressure C. blood in the urine D. enlarging cysts Homework 10.7.3 What should be prescribed to a cure a patient with polycystic kidney disease (PKD)? A. surgery to drain cysts B. nothing, there is no cure for PDK C. antihypertensive medication D. antibiotics Homework 10.7.4 A patient being treated for polycystic kidney disease (PKD) for 15 years is experiencing new symptoms. Which course of treatment should be considered for this patient? A. bedrest B. increase physical activity C. fluid restriction D. dialysis Homework 10.7.5 What is a characteristic of medullary sponge kidney? A. causes reduced urine output B. responsive to antibiotic therapy C. present at birth but asymptomatic D. diagnosed immediately upon birth Homework 10.8.1 What is a cause for the development of urinary incontinence in an older patient? A. increase release of renin B. urethral sphincter muscles lose tone C. reduction in the number of functioning nephrons D. lack of bladder tone Homework 10.8.2 An 80-year-old patient has high sodium content in the urine. What could be the cause of this finding? A. loss of urethral sphincter muscle tone B. undiagnosed kidney cancer C. loss of urinary bladder muscle tone D. reduced aldosterone activity Homework 10.8.3 A patient is experiencing urinary retention. Which health problem is this patient at risk for developing? A. renal hypertension B. kidney cancer C. urinary tract infection D. bladder cancer Homework: Chapter 11 Pre Test Homework 11.1.1 Identify the components that make up female external genitalia. A. mons pubis, estrogen, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, greater vestibular glands. B. mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, greater vestibular glands, perineum. C. mons pubis, vagina, labia majora, labia minora, greater vestibular glands, perineum. D. mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, breasts, greater vestibular glands. Homework 11.1.2 Where are the fimbriae located? A. on the ends of the fallopian tubes B. between the bladder and the rectum C. around the nipples D. on either side of the uterus Homework 11.1.3 The cervix is part of what female internal reproductive organ? A. endometrium B. perineum C. vagina D. uterus Homework 11.1.4 Rising levels of what hormone trigger onset of puberty in males and females? A. FSH B. PMS C. LH D. GnRH Homework 11.1.5 What is another term for the menstrual period? A. menarche B. menopause C. ovulation D. premenstrual syndrome Homework 11.2.1 Which diagnostic method does not permit visualization of reproductive organs? A. colposcopy B. hysteroscopy C. ultrasound D. bimanual examination Homework 11.2.2 Which statement about pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) is not true? A. Left untreated, PID can lead to infertility, ectopic pregnancy, and chronic pelvic pain. B. PID is treated with antibiotics, but that does not reverse damage that has already occurred to the reproductive organs. C. PID can be prevented with abstinence, monogamy, latex condoms, and early diagnosis and treatment of STIs. D. The age of a woman is not a contributing factor to develop PID. Homework 11.2.3 Which is the medical term for fibroid tumors, the most common tumors of the female reproductive system. A. leiomyomas B. uterinomas C. lesion D. osteoma Homework 11.2.4 What is the most important risk factor for developing cervical cancer? A. contracting genital warts B. receiving the HPV vaccine C. smoking tobacco D. becoming infected with human papillomavirus Homework 11.2.5 Select the statement about breast cancer that is not true. A. Women in their 20s and 30s should have a clinical breast exam every three years. B. Women should begin self-screening for breast cancer in their 40s. C. The overall five-year survival rate for breast cancer is about 90%. D. Risk factors to develop breast cancer include lack of physical exercise, drinking alcohol, and family history of breast cancer. Homework 11.3.1 Which statement about ectopic pregnancy is not true? A. Classic signs of ectopic pregnancy include one-sided abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and a positive pregnancy test. B. Ectopic pregnancy occurs when the fertilized ovum implants in tissue other than the uterus. C. The most common site for ectopic pregnancy is in the fallopian tubes. D. Ectopic pregnancy can continue to term with early diagnosis. Homework 11.3.2 What is the most common cause of blocked or scarred fallopian tubes? A. pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) B. internal bleeding C. previous spontaneous abortion D. vaginal bleeding Homework 11.3.3 Spontaneous abortion, or miscarriage, occurs in an estimated ________ of all fertilized ova, usually before the woman knows she is pregnant. A. 10% B. 20% C. 50% D. 35% Homework 11.3.4 What is the cause of most spontaneous abortions? A. genetic abnormality of the fetus B. physical problems in the mother C. systemic disease of the mother D. hormonal imbalance Homework 11.4.1 Sexually transmitted infections (STIs) are spread by___________ oral, anal, or vaginal intercourse. A. protected B. unprotected C. monogamous D. regular Homework 11.4.2 In the United States, about 20 million new cases of STIs occur annually, almost half among people ages __________. A. 15 dash 24 B. 25 dash 49 C. 12 dash 18 D. 18 dash 39 Homework 11.4.3 What do syphilis, gonorrhea, chlamydia, and trichomoniasis all have in common? A. They are all incurable infections. B. They are infections that have been eradicated. C. They are infections that can all cause death. D. They are all curable infections. Homework 11.4.4 Which statement about gonorrhea is not true? A. Gonorrhea is becoming more difficult to treat in the United States because more strains are becoming drug-resistant. B. Gonorrhea is caused by a bacterium and is treated with an injection of an antibiotic plus an oral antibiotic. C. Most people infected with gonorrhea experience pain or burning while urinating and a green discharge. D. Erythromycin is dropped in the eyes of newborn babies to prevent gonorrheal transmission by an infected mother. Homework 11.4.5 Which stage of syphilis is characterized by a non-itchy, widespread rash? A. late B. primary C. latent D. secondary Homework 11.5.1 Which statement about menopause is not true? A. Hormone replacement therapy may help with some symptoms of menopause, such as, hot flashes and vaginal dryness. B. Menopause is an age-related disease of the female reproductive system. C. Menopause usually takes place between 45 and 55 years, but early removal of the ovaries also causes menopause. D. Menstrual periods cease during menopause because the ovaries produce less estrogen and progesterone. Homework 11.5.2 Uterine prolapse occurs when the uterus slides from its normal position into the vaginal canal. Which statement about uterine prolapse is not true? A. Never giving birth is a risk factor for uterine prolapse. B. A woman with uterine prolapse may feel heaviness in the pelvis and have trouble urinating. C. The uterus slides from its normal position because the pelvic ligaments and muscles are overstretched. D. Uterine prolapse can be treated but not prevented. Homework 11.5.3 What is cystocele? A. collapse of pelvic organs into the vagina B. downward displacement of the bladder into the vagina C. bulging of the rectal wall into the vagina D. displacement of the uterus into the vagina Homework 11.5.4 Signs and symptoms of rectocele may include __________ and _________ incontinence. A. night sweats, fecal B. constipation, urinary C. urinary, fecal D. constipation, fecal Homework 11.5.5 Enlargement of the prostate gland, or benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), effects _________ of men in their 70s and 80s. A. 60-70% B. 80-90% C. 20-30% D. 40-50% Homework: Chapter 12 Pre Test Homework 12.1.1 What is the function of the endocrine system? A. to increase energy metabolism B. to control the function of pituitary hormones C. to secrete insulin D. to secrete chemical messengers into the blood Homework 12.1.2 When does the body secrete hormones? A. when the body needs more glucagon B. during body heat production and tissue growth C. during sexual development D. only as needed to regulate various body processes Homework 12.1.3 What is the function of the posterior pituitary gland? A. Testosterone regulates sexual development and secondary sex characteristics in males. B. The ADH hormone stimulates water absorption by the kidneys and oxytocin aids in the ejection of prostate gland secretions. C. The follicle-stimulating (FSH) stimulates egg and sperm production and luteinizing hormone (LH) stimulates the production of sex hormones. D. Epinephrine causes vasodilation and norepinephrine general vasoconstriction. Homework 12.2.1 Which hormone(s) regulate(s) salt balance? A. mineralocorticoids B. antidiuretic hormone C. glucocorticoids D. calcitonin Homework 12.2.2 What are the two iodine-containing hormones of the thyroid gland? A. TH and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) B. triiodothyronine and isthmus C. thyroxine and triiodothyronine D. thyroid hormone (TH) and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH) Homework 12.2.3 Which hormone causes sodium retention and potassium secretion by the kidneys? A. hydrocortisone B. ACTH C. aldosterone D. norepinephrine Homework 12.3.1 Trauma to the pituitary gland results in which disorder? A. acromegaly B. dwarfism C. gigantism D. diabetes insipidus Homework 12.3.2 What are some causes of pituitary dwarfism? A. maternal alcoholism B. medications and surgery C. genetics, tumor, radiation D. delayed sexual development and short stature for age Homework 12.3.3 What is the treatment of choice for acromegaly? A. GH replacement therapy B. medication C. radiation D. surgery Homework 12.4.1 Which disease is characterized by risk factors such as, being female, over 50, and having an autoimmune disorder? A. hyperthyroidism B. goiter C. hypothyroidism D. thyroid cancer Homework 12.4.2 Failure of the thyroid gland to migrate to its normal anatomical position results from which condition? A. hyperparathyroidism B. Grave's disease C. goiter D. congenital hypothyroidism Homework 12.4.3 What are the signs and symptoms of hyperparathyroidism? A. GI disturbances, abdominal pain, vomiting, and constipation B. tetany and lethargy C. GI disturbances, weight loss, and fatigue D. nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, and tachycardia Homework 12.5.1 A decrease in which hormone manifests in a decrease in lean body mass in men after age 30? A. growth hormone B. aldosterone C. insulin D. T3:T4 ratio Homework 12.5.2 A decrease in the kidney's ability to secrete renin as we age may result in which symptoms? A. changes in blood pressure and dehydration B. obesity and tachycardia C. hypertension and increased body fat D. hypotension and heart disease Homework 12.5.3 A decrease in insulin resistance leads to a greater incidence of which disease? A. T1DM B. obesity C. T2DM D. pancreatic cancer Homework: Chapter 13 Pre Test Homework 13.1.1 What organs compose the central nervous system, integrating and interpreting sensory output, and directing all activities of the body? A. neurons B. pia mater and dura mater C. brain and spinal cord D. CSF and CNS Homework 13.1.2 The peripheral nervous system is controlled by _________________________. A. CNS B. sensory nerves C. motor nerves D. glial cells Homework 13.1.3 What is the basic unit of the nervous system? A. brain B. spinal cord C. neuron D. meninges Homework 13.1.4 What type of neuron sends messages to muscles from the central nervous system, causing muscle contractions? A. sensory neuron B. motor neuron C. axon D. interneuron Homework 13.1.5 In what part of the brain do intelligence and personality reside? A. medulla oblongata B. cerebrum C. cerebellum D. thalamus Homework 13.2.1 Traumatic injury to the brain may result from ____________________. A. external physical force B. stroke C. epilepsy D. spinal cord injury Homework 13.2.2 What noninvasive test records the brain's electrical activity? A. electroencephalography B. ultrasound C. angiography D. myelography Homework 13.2.3 What is the leading cause of traumatic brain injury? A. firearms incidents B. motorcycle accidents C. sports injuries D. falls Homework 13.2.4 Which is a symptom of the traumatic brain injury called concussion? A. long-term impairment of brain function B. muscle incoordination C. short-term loss of consciousness D. amnesia Homework 13.2.5 Severe traumatic brain injuries are involved in what percentage of injury-related deaths in the U.S.? A. one third 1/3 B. one half 1/2 C. two thirds 2/3 D. one fourth 1/4 Homework 13.3.1 The type of generalized epileptic seizure that has symptoms of repeated jerking movements of muscles on both sides of the body is ______________. A. absence B. myoclonic C. clonic D. tonic Homework 13.3.2 What type of generalized epileptic seizure has symptoms of loss of normal muscle tone? A. atonic B. simple focal C. tonic D. absence Homework 13.3.3 What is a symptom of myoclonic seizure? A. loss of consciousness B. jerking or twitching of the upper body and arms. C. repeated jerking movements of muscles on both sides of the body. D. loss of normal muscle tone Homework 13.3.4 The type of generalized epileptic seizure that is referred to as petit mal and includes symptoms of daydreaming is ______________________. A. tonic B. absence C. clonic D. tonic-clonic Homework 13.3.5 What type of generalized epileptic seizure is referred to as grand mal and includes a mixture of all generalized seizure symptoms? A. tonic B. clonic C. tonic-clonic D. atonic Homework 13.4.1 Which risk factor for stroke is uncontrollable? A. prior stroke B. high blood pressure C. atrial fibrillation D. atherosclerosis Homework 13.4.2 What is the cause of the sudden interruption of blood flow to part of the brain during stroke? A. burst blood vessel B. abnormal electrical activity C. cranial nerve inflammation D. simple focal Homework 13.4.3 How many people have strokes in the U.S. each year? A. 800,000 B. 400,000 C. 600,000 D. 200,000 Homework 13.4.4 How many people does stroke kill in the U.S. each year? A. 120,000 B. 110,000 C. 100,000 D. 130,000 Homework 13.4.5 What percentage of all strokes result from a burst blood vessel? A. 10% B. 20% C. 5% D. 15% Homework 13.5.1 Disorders of the cranial nerves may affect _________________________. A. speaking B. cognitive function C. motor function D. hearing Homework 13.5.2 Inflammation of the cranial nerves is associated with _______________. A. facial paralysis B. viral infection of the brain C. acute inflammation of the first two meninges D. inflammation of the brain Homework 13.5.3 What is the main symptom of trigeminal neuralgia? A. involuntary movements B. repeated jerking movements C. stiffening of muscles D. severe chronic pain Homework 13.5.4 What is another name for trigeminal neuralgia? A. Lou Gehrig's disease B. grand mal C. petit mal D. tic douloureux Homework 13.5.5 The cause of trigeminal neuralgia may be related to __________________. A. demyelation of neurons B. immune disorder C. bacteria infection D. viral infection Homework 13.6.1 How many cases of meningitis and how many deaths from the disease are there in the U.S. each year? A. 1,000 cases and 200 deaths B. 4,000 cases and 500 deaths C. 3,000 cases, and 400 deaths D. 2,000 cases and 300 deaths Homework 13.6.2 Meningitis is an acute inflammation of the ______________________. A. medulla oblongata B. cerebellum C. pia mater D. pia dura Homework 13.6.3 What is the most common type of meningitis? A. Neisseria meningitides B. herpes simplex C. Streptococcus pneumoniae D. enterovirus Homework 13.6.4 How is encephalitis diagnosed? A. CT B. MRI C. lumbar puncture D. physical examination of the face Homework 13.6.5 What body parts does the poliomyelitis virus infect? A. sensory neuron B. interneuron C. motor neuron D. meninges Homework 13.7.1 What percentage of people over age 85 have Alzheimer's disease? A. 10% B. 50% C. 25% D. 75% Homework 13.7.2 What abnormalities appear in Alzheimer's disease brain tissue? A. damage to myelin sheath surrounding axons of motor neurons B. dense knots of protein deposits called plaques C. death of dopamine-producing neurons D. destruction of motor areas and nerves Homework 13.7.3 Which is a symptom of Alzheimer's disease? A. shaking of the hands and head B. masklike facial muscles C. twitching and weakness in the limbs D. loss of spatial and temporal orientation Homework 13.7.4 What degenerative central nervous system disease begins with memory loss and confusion? A. Parkinson's disease B. Huntington's chorea C. Alzheimer's disease D. multiple sclerosis Homework 13.7.5 What is the life expectancy of a person who has been diagnosed with amyotrophic lateral sclerosis? A. 6 months B. 5-7 years C. 1-3 years D. 3-5 years Homework 13.8.1 The cause of spina bifida is _____________________________. A. a brain tumor B. an imbalance in cerebrospinal fluid production and drainage C. a neural tube defect D. brain damage Homework 13.8.2 In what form of spina bifida does an opening expose the spinal cord? A. myelocele B. occulta C. meningocele D. hydrocephalus Homework 13.8.3 What is the treatment for spina bifida? A. folic acid supplements B. surgery C. amniocentesis D. alpha-feto protein Homework 13.8.4 Of the four million babies born in the U.S. each year, how many are born with spina bifida? A. 1,500 B. 15,000 C. 15 D. 150 Homework 13.8.5 How many children are born with the common birth defect, hydrocephalus, in the U.S.? A. 1 in 1,000 births B. 1 in 100 births C. 1 in 5,000 births D. 1 in 500 births Homework 13.9.1 How many new cases of brain tumors occur in the U.S. each year? A. 13,000 B. 23,000 C. 33,000 D. 43,000 Homework 13.9.2 How many people die from brain tumors each year in the U.S.? A. 14,000 B. 24,000 C. 4,000 D. 34,000 Homework 13.9.3 What are brain tumors? A. dense knots of protein deposits B. viral infection C. death of dopamine producing neurons D. abnormal masses of tissue Homework 13.9.4 What type of brain tumor arises from other cancers? A. metastatic B. trismus C. hydrocephalus D. primary Homework 13.9.5 Which group has the most cases of brain tumor? A. Blacks or African Americans B. Hispanic, Latino, or Spanish C. Whites D. American Indians or Alaskan Natives Homework 13.10.1 Which disease is associated with older age? A. cerebral palsy B. hydrocephalus C. Alzheimer's D. Reye syndrome Homework 13.10.2 Aging is a factor in _____. A. botulism B. tetanus C. shingles D. rabies Homework 13.10.3 Which disease typically has its onset in middle age? A. amyotrophic lateral sclerosis B. encephalitis C. Multiple sclerosis D. Alzheimer's Homework 13.10.4 What is the average onset age of Parkinson's disease? A. 70 B. 80 C. 60 D. 50 Homework 13.10.5 What percentage of Parkinson's disease cases occur as early-onset cases before age 50? A. 15% B. 10% C. 20% D. 5% Homework: Chapter 14 Pre Test Homework 14.1.1 What is the portion of the outer ear that is external to the skull called? A. cochlea B. pinna C. stapes D. cornea Homework 14.1.2 What is the name of the waxy substance that keeps the tympanic membrane soft and flexible? A. cerumen B. uvea C. ossicles D. retina Homework 14.1.3 Which part of the ear is sensitive to head position and motion? A. vestibular apparatus and semicircular canals B. malleus C. cochlea D. pinna Homework 14.1.4 Which part of the eye controls the amount of light entering the eyeball? A. lens B. sclera C. pupil D. cornea Homework 14.2.1 A 38-year-old male presents with difficulty reading small print and focusing on near objects. What type of eye problem is he experiencing? A. hyperopia B. presbyopia C. myopia D. astigmatism Homework 14.2.2 Risk factors for presbyopia are age and family history. True False Homework 14.2.3 What is the most common risk factor for myopia? A. sex B. race C. age D. family history Homework 14.3.1 What is the leading cause of blindness in the United States among adults? A. cataracts B. keratitis C. diabetic retinopathy D. glaucoma Homework 14.3.2 A 50-year-old female with a history of smoking states she had difficulty seeing sharp images. What eye disorder is associated with these symptoms? A. retinal detachment B. glaucoma C. hordeolum D. macular degeneration Homework 14.3.3 Becky is a 36-year-old- female with a history of nearsightedness. She complains of sudden appearance of flashes of light while she was reading. What eye condition is Becky experiencing? A. diabetic retinopathy B. retinal detachment C. uveitis D. conjunctivitis Homework 14.3.4 After the age of 60, what group is at the greatest risk for glaucoma? A. Latinos B. Mexican Americans C. African Americans D. Whites Homework 14.3.5 By age 65, almost half of all Americans have some degree of cataract formation and resulting impaired vision. True False Homework 14.4.1 A 68-year-old male presents with tinnitus, right earache, and diminished hearing on the right side. He states he uses cotton tip swabs every day to clean his ears. What ear condition is he experiencing? A. otitis externa B. cerumen impaction C. Meniere's disease D. otitis media Homework 14.4.2 Otitis media occurs in more than 5 million children each year. True False Homework 14.4.3 Drying the external ear opening after bathing or swimming will not prevent otitis externa. True False Homework 14.5.1 With age, the lens increases in thickness and decreases in elasticity, making it more difficult to accommodate and focus on objects at a close distance. True False Homework 14.5.2 Falls are not the leading cause of injury in older adults. True False Homework: Chapter 15 Pre Test Homework 15.1.1 Which statement expresses how genes influence the development of some mental disorders? A. A family history of mental disorders may increase the risk of developing one. B. Children that experience stress from poverty may develop mental disorders. C. A parent's death may impact emotional well-being. D. Loss of family support may result from chronic illness. Homework 15.1.2 Which of these is an environmental factor that may contribute to the onset of mental disorders? A. toxins B. death of a spouse C. accident D. war Homework 15.1.3 Being aware of risk factors that can impact mental health __________. A. can aid in maintaining good mental health B. can cause loss of necessary support from family and friends C. may contribute to the onset of mental disorders D. may increase the risk of developing a mental disorder Homework 15.1.4 How can a severe brain injury affect the level of risk for developing a mental disorder? A. no impact on risk B. decreased risk C. definite risk certain risk D. increased risk Homework 15.1.5 How is The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM) used in the U.S. and much of the world? A. It is used as a textbook for health care students. B. It is used for the training of health care workers. C. It is used as a diagnosis guide. D. It is used for its describing all mental disorders. Homework 15.2.1 ______ is an early warning signs of a mental disorder. A. decreased anxiety or agitation B. increased ability to concentrate C. maintenance of eating or sleeping habits D. prolonged sadness Homework 15.2.2 As a rule, mental disorders come on suddenly. True False Homework 15.2.3 Which is an early warning sign of a mental disorder? A. brain injury B. death of a parent C. withdrawal D. alcohol abuse Homework 15.2.4 Deterioration in personal hygiene is an early warning sign of a mental disorder. True False Homework 15.2.5 Drug abuse is an early warning sign of a mental disorder. True False Homework 15.2.6 What is the most commonly diagnosed mental disorder? A. schizophrenia B. eating C. mood D. anxiety Homework 15.3.1 Mental disorders may arise from an interaction among environmental and biological factors. True False Homework 15.3.2 Which is typically a factor in the onset of mental disorders? A. psychology B. confused thinking C. anxiety D. good grades at school and good performance at work Homework 15.3.3 Which may be a biological factor in the onset of mental disorders? A. poverty B. domestic violence C. fetal development D. sexual abuse Homework 15.3.4 Which may be a psychological factor in the onset of mental disorders? A. bullying B. neurotransmitters C. genes D. prenatal infection Homework 15.4.1 Which mental disorder is diagnosed by screening for developmental milestones from birth to at least 36 months? A. intellectual disability disorder B. attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder C. autism spectrum disorders D. schizophrenia Homework 15.4.2 Which of these mental disorders is diagnosed by a brain wave test? A. intellectual disability disorder B. personality disorder C. schizophrenia D. attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder Homework 15.4.3 Which disorder is definitively diagnosed only after death? A. schizophrenia B. Alzheimer's disease C. major depressive disorder D. bipolar disorder Homework 15.4.4 Which mental disorder uses genetic testing for diagnosis? A. intellectual disability disorder B. bipolar disorder C. attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder D. schizophrenia Homework 15.4.5 Which mental disorder is diagnosed using metabolic screening? A. autism spectrum disorders B. intellectual disability disorder C. eating disorders D. bipolar disorder Homework 15.5.1 Which mental disorder(s) may be treated with electroconvulsive therapy? A. autism spectrum disorders B. anxiety disorders C. major depressive disorder D. intellectual disability disorder Homework 15.5.2 A patient with psychosis usually experiences which of these symptoms? A. euphoria B. delusions C. suicidal thoughts D. impulsivity Homework 15.5.3 Which mental disorder(s) may be treated with mood-stabilizing and antidepressant medications? A. personality disorder B. bipolar disorder C. eating disorders D. schizophrenia Homework 15.5.4 Which mental disorder(s) may be treated with parenting skills training? A. eating disorders B. personality disorder C. bipolar disorder D. attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder Homework 15.5.5 Which mental disorder(s) may be treated with hospitalization? A. attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder B. anxiety disorders C. eating disorders D. autism spectrum disorder Homework 15.6.1 What percentage of adults in the U.S. experience major depressive disorder each year? A. seven B. six C. four D. five Homework 15.6.2 Which mental disorder is more prevalent in males than in females? A. anorexia nervosa B. major depressive disorder C. autism spectrum disorder D. binge eating disorder Homework 15.6.3 What is the typical age of onset of schizophrenia for men? A. late teens B. at birth C. early 30s D. early teens Homework 15.6.4 What is the median age of onset of generalized anxiety disorder? A. 20 B. 7 C. 13 D. 31 Homework 15.6.5 What is the median age of onset of posttraumatic stress disorder? A. 24 B. 19 C. 25 D. 23 Homework: Chapter 16 Pre Test An ___________ is a mature bone cell. A. epiphyseal plate B. osteocyte C. osteoblast D. ossification Homework 16.1.2 Which does spongy bone contain? A. periosteum B. yellow-colored marrow C. red-colored marrow D. fat Homework 16.1.3 Which determines how much a joint moves and its type of movement? A. the shape and number of bones B. the amount of collagen and calcium C. the shape and length of bones D. the shape of bones and type of connective tissue Homework 16.2.1 Which can be a risk factor for osteomyelitis? A. diabetes B. puberty C. flu virus D. hysterectomy Homework 16.2.2 Which is not a true statement about osteomyelitis? A. It is hereditary. B. Surgery may be required. C. It is uncommon. D. It may be the result of a compound fracture. Homework 16.2.3 Which are ways to confirm the presence of osteomyelitis? A. x-ray B. nerve conduction test C. white blood cell count, bone biopsy, MRI D. bone density scan Homework 16.3.1 Vitamin D and mineral deficiencies can lead to _____________. A. infection of the bones B. a small-framed individual C. rigid bones D. malformed or fragile bones Homework 16.3.2 What percentage of those affected by osteoporosis are women? A. 80 B. 60 C. 20 D. 40 Homework 16.3.3 What is osteoporosis? A. a congenital condition in which bones that don't grow properly B. a bacterial infection of the bone C. bones that are fragile and susceptible to fracture D. muscle atrophy Homework 16.4.1 Paget's disease affects A. women over the age of 50. B. Asians C. boys during puberty D. men in the U.S. over the age of 40. Homework 16.4.2 Paget's disease can lead to which of the following? A. muscle weakness B. kidney disease C. impaired vision D. arthritis Homework 16.4.3 Scoliosis is a condition marked by __________________. A. abnormal lateral curvature of the spine B. exaggerated posterior curve of the thoracic spine C. arthritis of the spine D. inward curvature of lumbar vertebrae Homework 16.5.1 Which is a symptom of arthritis? A. numbness of a joint B. fracture of a joint C. internal bleeding of a joint D. swelling of a joint Homework 16.5.2 Which is true of rheumatoid arthritis? A. It affects only muscles. B. Its onset is usually during childhood. C. It is an autoimmune disease. D. It is caused by smoking. Homework 16.5.3 Ankylosis is a sign of ____________. A. unhealed fracture B. pannus C. osteoarthritis D. rheumatoid arthritis Homework 16.5.4 Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis includes: A. balance between exercise, rest, and DMARDS B. antibiotics C. bed rest D. rigorous exercise and DMARDS Homework 16.5.5 Primary osteoarthritis is associated with: A. normal aging B. obesity C. joint injury D. joint trauma Homework 16.6.1 Which is not a risk factor for herniated discs? A. genetics B. smoking C. obesity D. age Homework 16.6.2 Which of is a true statement about a dislocation? A. A dislocation occurs only in finger and shoulder joints. B. A dislocation can occur anywhere. C. A dislocation is the softening of bones at a joint. D. A dislocation is untreatable if congenital. Homework 16.6.3 What is the proper treatment for a sprain? A. Heat is applied immediately. B. Do not use the joint when severely inflamed. C. Make plans for surgery. D. Exercise to get blood flowing to the injured joint. Homework 16.6.4 Strains can be a result of _______________. A. too little exercise B. untreated infections C. trauma D. excessive use of muscle Homework 16.7.1 Duchenne's muscular dystrophy is caused by __________________. A. a weak heart muscle B. a sex-linked gene C. an inability to absorb calcium D. a nerve disorder Homework 16.7.2 Which protein is missing in Duchenne's muscular dystrophy? A. desmin B. actin C. dystrophin D. myosin Homework 16.7.3 Which of the following is accurate? A. Muscular dystrophy can cause calf muscles to atrophy. B. Muscular dystrophy can be cured in a very small percentage of people. C. Muscular dystrophy is usually diagnosed after adolescence. D. Muscular dystrophy treatment includes physical therapy. Homework 16.8.1 Loss of bone strength happens with age partly because _______________. A. osteocytes are no longer present B. osteoblast activity declines with age C. bone marrow decreases with age D. compact bone becomes flatter Homework 16.8.2 A majority of women over the age of ___ have low bone density. A. 30 B. 60 C. 50 D. 20 Homework: Chapter 17 Pre Test Homework 17.1.1 What is the outermost layer of skin? A. adipose tissue B. subcutaneous tissue C. epidermis D. dermis Homework 17.1.2 Finger and toe nails are produced by what type of cells? A. epidermal B. sebaceous C. subcutaneous D. dermal Homework 17.1.3 Where are apocrine sweat glands located? A. feet B. forehead C. axillary D. hands Homework 17.2.1 A child has honey-colored crusted lesions on face and neck. What bacterial infection is this child experiencing? A. folliculitis B. furbuncle C. impetigo D. cellulitis Homework 17.2.2 What symptoms may a patient with cellulitis experience? A. bumpy and scaling B. fever and chills C. itching and swelling D. patches and burning Homework 17.2.3 What condition is a superficial bacterial infection of the hair follicle? A. carbuncle B. cellulitis C. furuncle D. folliculitis Homework 17.2.4 What is a known risk factor for oral herpes? A. touching an infected person's leg B. being obese C. sharing utensils with an infected person D. using a hot tub Homework 17.2.5 A patient has a thick patch of skin with dark specks on the right foot that is painful. What is the patient experiencing? A. filiform wart B. plantar wart C. flat wart D. periungual wart Homework 17.3.1 A patient has patches on arms and legs that have red edges and pale center. The patient states that the patches appeared suddenly and itch. What is this patient experiencing? A. rosacea B. candidiasis C. hives D. scabies Homework 17.3.2 What type of skin condition occurs when an individual has a skin reaction to latex? A. allergic contact dermatitis B. rosacea C. psoriasis D. atopic dermatitis Homework 17.3.3 What additional finding is atopic dermatitis frequently associated with? A. sunlight B. asthma C. topical medication D. fragrance in soap Homework 17.4.1 How often should a patient perform self-examination of the skin? A. yearly B. weekly C. monthly D. daily Homework 17.4.2 What device does a patient need when performing a skin self-exam? A. mirror B. scissors C. pen light D. bed Homework 17.4.3 What diagnostic test will a physician perform when a patient reports a sudden elevation of a dark skin growth that has changed in shape and color? A. phototherapy B. radiation C. biopsy D. surgery Homework 17.5.1 What is the lifetime prevalence of skin cancer in the United States? A. About 1 in 10 people will develop skin cancer. B. About 1 in 15 people will develop skin cancer. C. About 1 in 5 people will develop skin cancer. D. About 1 in 3 people will develop skin cancer. Homework 17.5.2 Which strategy is most effective for use in the prevention of skin cancer? A. using tanning beds instead of outdoor tanning B. avoiding sun exposure between 1:00 p.m. and 5:00 p.m. C. avoiding sun exposure between 10:00 a.m. and 2:00 p.m. D. using sunlamps instead of outdoor tanning Homework 17.5.3 Which skin condition is the most common type of skin cancer? A. hemangioma B. basal cell carcinoma C. squamous cell carcinoma D. melanoma Homework 17.6.1 Which term refers to a plug made of old skin cells that traps oil and bacteria inside a hair follicle, leading to the development of inflammatory acne? A. papule B. pustule C. comedo D. nodule Homework 17.7.1 Which scenario is most likely to cause hypopigmentation of the skin? A. Exposure to UV radiation B. absence of melanin C. increased number of melanocytes D. melasma Homework 17.7.2 Which condition is caused by a loss of melanin and produces white patches of skin that usually start as small areas of pigment loss? A. ephelides B. oculocutaneous albinism C. vitiligo D. lentigines Homework 17.7.3 Which condition is also called chloasma? A. melanoma B. albinism C. melasma D. vitiligo Homework 17.8.1 Which skin injury is caused when blood vessels are damaged or broken as a result of a blow to the skin? A. contusion B. abrasion C. puncture D. laceration Homework 17.8.2 Tetanus is most likely to result as a complication of which skin condition or injury? A. abrasion B. puncture C. open comedone D. closed comedone Homework 17.8.3 Which skin injury is also called a scrape? A. avulsion B. abrasion C. laceration D. ecchymosis Homework 17.8.4 What is the estimated prevalence of pressure ulcers among nursing home residents? A. 8-16% B. 36-45% C. 29-35% D. 17-28% Homework 17.8.5 In which area of the body is a pressure ulcer most likely to develop? A. the heel B. the shoulder C. the buttock D. the elbow Homework 17.8.6 Which step comes first in the treatment of pressure ulcers? A. administering antibiotics B. eliminating pressure C. wound debridement D. pain management Homework 17.9.1 Which change in skin composition or function is associated with aging? A. decreased sweat production B. decreased nail thickness C. increased blood supply to the dermis D. increased vascularity in the subcutaneous tissue [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 112 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 15, 2020
Number of pages
112
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 15, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
55