Business > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Wilfrid Laurier UniversityEC 249Assignment 2 Answers (All)
Wilfrid Laurier UniversityEC 249Assignment 2 Answers
Document Content and Description Below
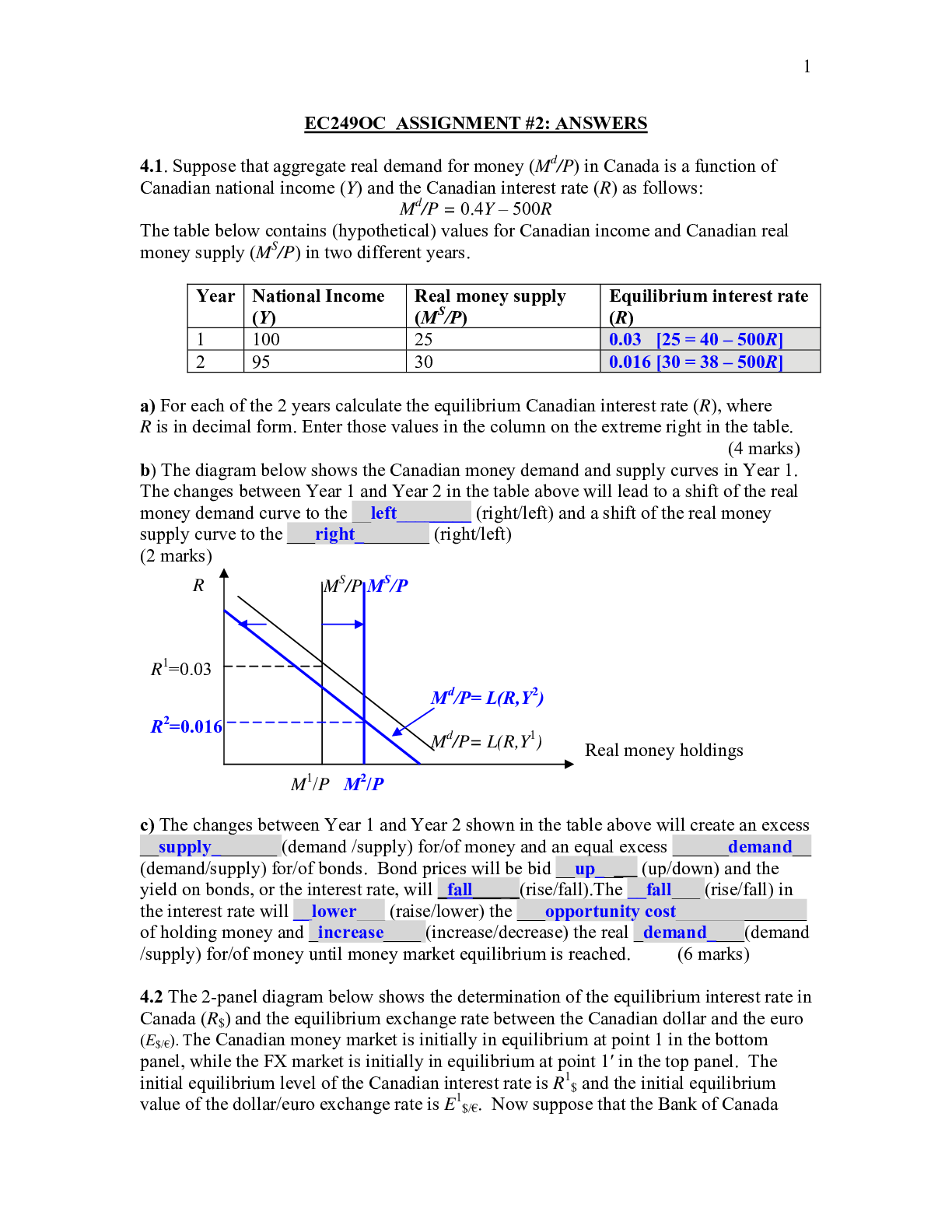
EC249OC ASSIGNMENT #2: ANSWERS 4.1. Suppose that aggregate real demand for money (Md/P) in Canada is a function of Canadian national income (Y) and the Canadian interest rate (R) as follows: Md/P =... 0.4Y – 500R The table below contains (hypothetical) values for Canadian income and Canadian real money supply (MS/P) in two different years. Year National Income (Y) Real money supply (MS/P) Equilibrium interest rate (R) 1 100 25 0.03 [25 = 40 – 500R] 2 95 30 0.016 [30 = 38 – 500R] a) For each of the 2 years calculate the equilibrium Canadian interest rate (R), where R is in decimal form. Enter those values in the column on the extreme right in the table. (4 marks) b) The diagram below shows the Canadian money demand and supply curves in Year 1. The changes between Year 1 and Year 2 in the table above will lead to a shift of the real money demand curve to the __left________ (right/left) and a shift of the real money supply curve to the ___right________ (right/left) (2 marks) c) The changes between Year 1 and Year 2 shown in the table above will create an excess __supply_______ (demand /supply) for/of money and an equal excess ______demand__ (demand/supply) for/of bonds. Bond prices will be bid __up___ (up/down) and the yield on bonds, or the interest rate, will _fall___ _(rise/fall).The __fall___ (rise/fall) in the interest rate will __lower___ (raise/lower) the ___opportunity cost______________ of holding money and _increase____ (increase/decrease) the real _demand____(demand /supply) for/of money until money market equilibrium is reached. (6 marks) 4.2 The 2-panel diagram below shows the determination of the equilibrium interest rate in Canada (R$) and the equilibrium exchange rate between the Canadian dollar and the euro (E$/€). The Canadian money market is initially in equilibrium at point 1 in the bottom panel, while the FX market is initially in equilibrium at point 1′ in the top panel. The initial equilibrium level of the Canadian interest rate is R1$ and the initial equilibrium value of the dollar/euro exchange rate is E1$/€. Now suppose that the Bank of Canada [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 9 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 14, 2021
Number of pages
9
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 14, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
43














