Health Care > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > HESI A2 Version 2, READING COMPREHENSION, Health Information Systems Test Bank, Complete Preparation (All)
HESI A2 Version 2, READING COMPREHENSION, Health Information Systems Test Bank, Complete Preparation Practice Test Questions, Questions 45 (Latest Update) (A Graded) Latest Questions and Complete Solutions
Document Content and Description Below
HESI A2 Version 2, READING COMPREHENSION, Health Information Systems Test Bank, Complete Preparation Practice Test Questions, Questions 45 (Latest Update) (A Graded) Latest Questions and Complete Solu... tions Questions 1-4 refer to the following passage. Passage 1 - The Respiratory System The respiratory system’s function is to allow oxygen exchange through all parts of the body. The anatomy or structure of the exchange system, and the uses of the exchanged gases, varies depending on the organism. In humans and other mammals, for example, the anatomical features of the respiratory system include airways, lungs, and the respiratory muscles. Molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged, by diffusion, between the gaseous external environment and the blood. This exchange process occurs in the alveolar region of the lungs. Other animals, such as insects, have respiratory systems with very simple anatomical features, and in amphibians even the skin plays a vital role in gas exchange. Plants also have respiratory systems but the direction of gas exchange can be opposite to that of animals. The respiratory system can also be divided into physiological, or functional, zones. These include the conducting zone (the region for gas transport from the outside atmosphere to just above the alveoli), the transitional zone, and the respiratory zone (the alveolar region where gas exchange occurs). 1. What can we infer from the first paragraph in this passage? a. Human and mammal respiratory systems are the same b. The lungs are an important part of the respiratory system c. The respiratory system varies in different mammals d. Oxygen and carbon dioxide are passive exchanged by the respiratory system B We can infer an important part of the respiratory system are the lungs. From the passage, “Molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged, by diffusion, between the gaseous external environment and the blood. This exchange process occurs in the alveolar region of the lungs.” Therefore, one of the primary functions for the respiratory system is the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide, and this process occurs in the lungs. We can therefore infer that the lungs are an important part of the respiratory system. 2. What is the process by which molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged? a. Transfusion b. Affusion c. Diffusion d. Respiratory confusion C The process by which molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide are passively exchanged is diffusion. This is a definition type question. Scan the passage for references to “oxygen,” “carbon dioxide,” or “exchanged.” [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 19 pages
 (A Graded) Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$23.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jun 03, 2021
Number of pages
19
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jun 03, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
124
 Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)

 AANP-FNP LIGHTNING ROUND REVIEW-2.png)
 MACROECONOMICS QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS.png)





 W2 SH [TRANSCRIPT] – ASTHMA - RESPIRATORY COMPLETED SHADOW HEALTH.png)






 Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)
 Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)
 Chamberlain College of Nursing NR 341 (A Graded) Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)
 Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)
 Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)
 Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)
 Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)
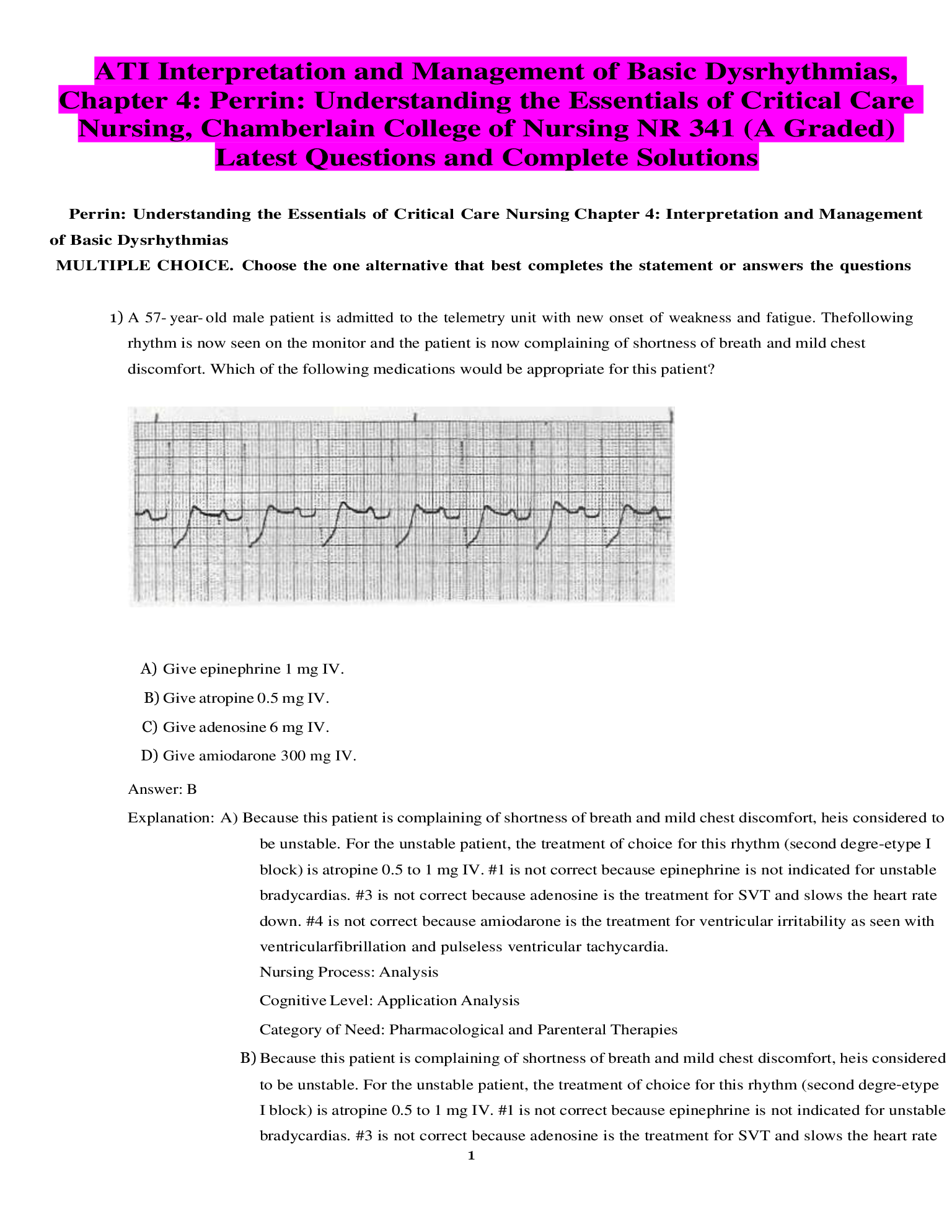
 Latest Questions and Complete Solutions.png)


