NR-507 Final Exam Study Guide/ DOWNLOAD TO SCORE A/LATEST VERSION
Document Content and Description Below
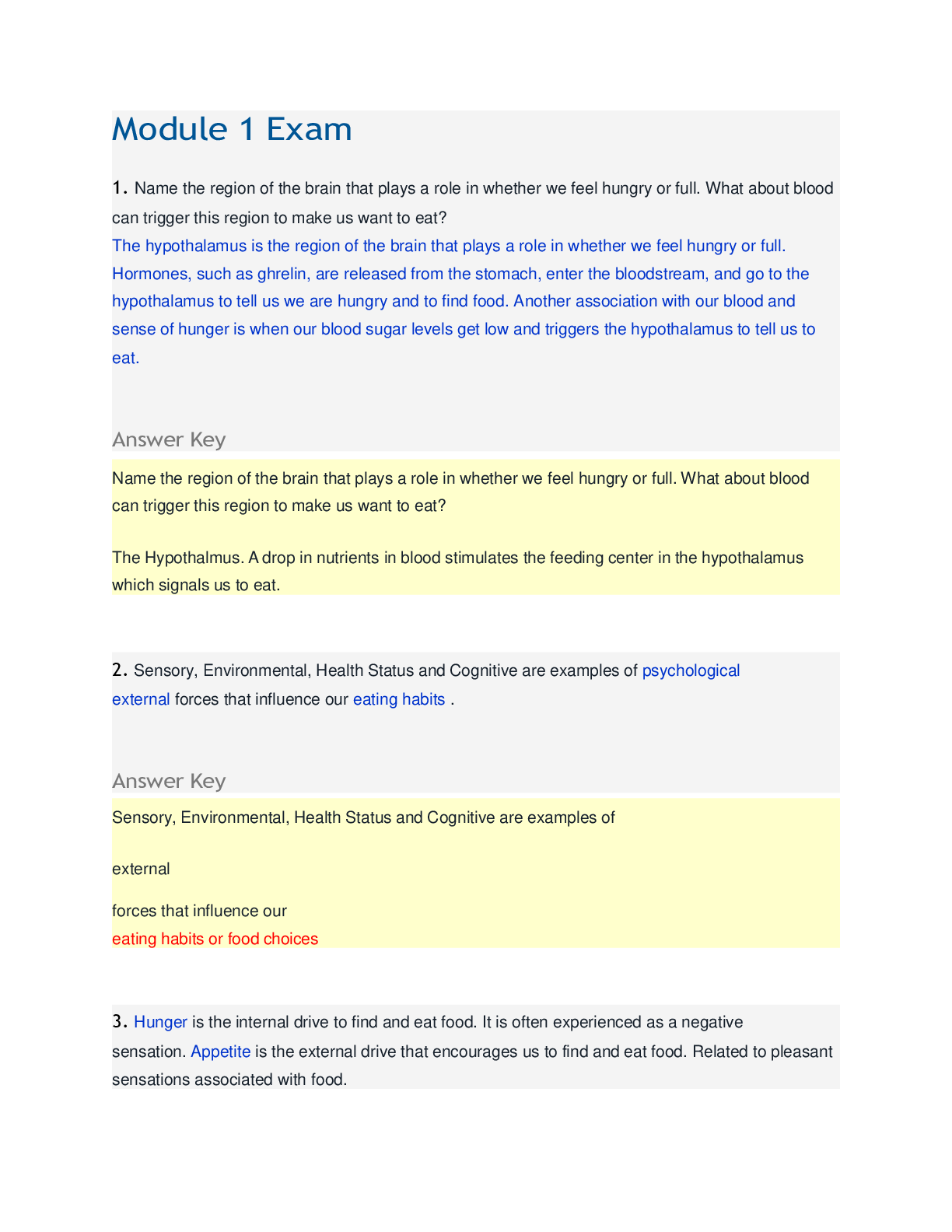
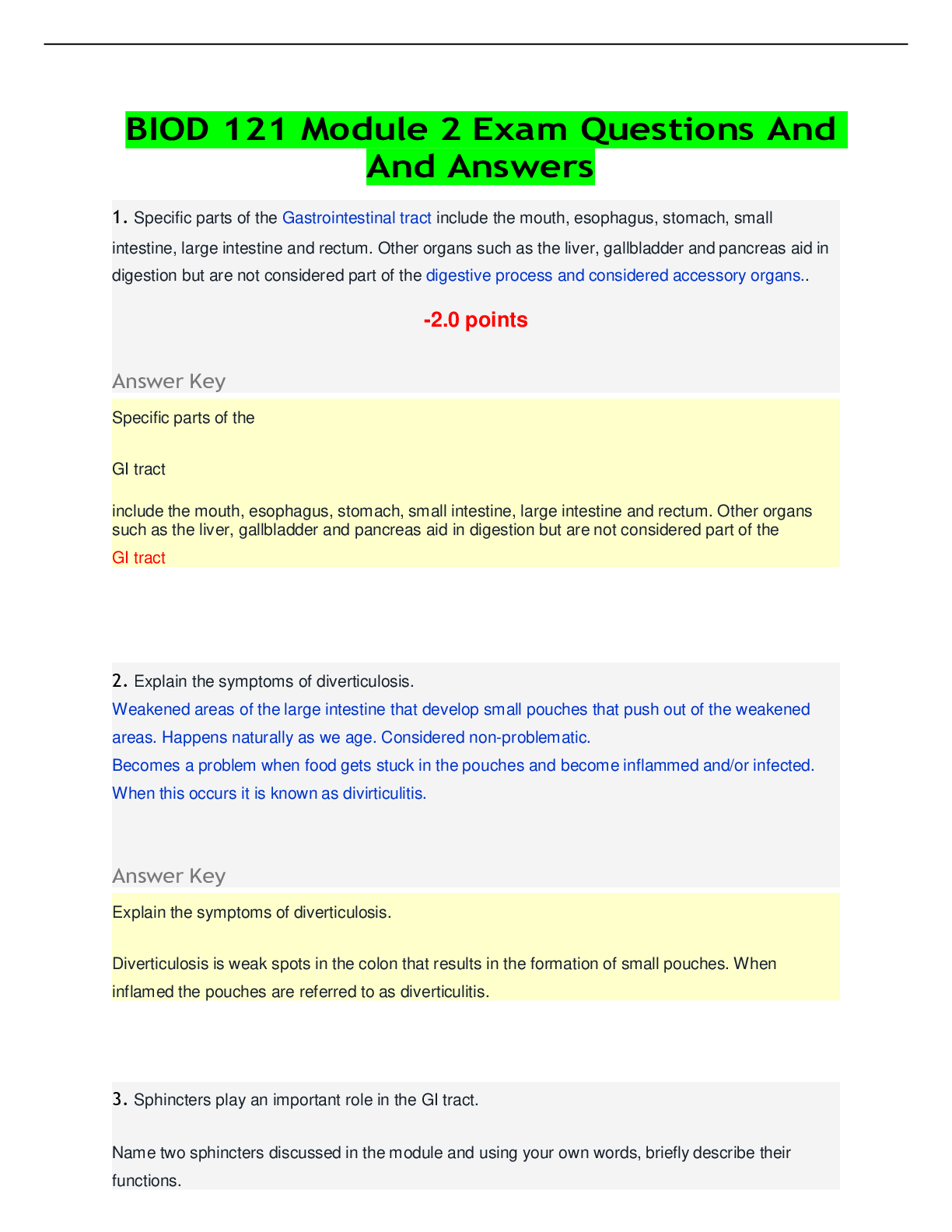
NR-507 Final Exam Study Guide This study guide is for the comprehensive final exam that will be given during Week 8. It will cover the following concepts: Reproductive: endometrial cycle and the occ... urrence of ovulation; uterine prolapse; polycystic ovarian syndrome; testicular cancer and conditions that increase risk; symptoms that require evaluation for breast cancer; signs of premenstrual dysphoric disorder; dysfunctional uterine bleeding; pathophysiology of prostate cancer; HPV and the development of cervical cancer Endocrine: body’s process for adapting to high hormone levels; Cushing’s Syndrome; causes of hypoparathyroidism; lab results that point to primary hypothyroidism; pathophysiology of thyroid storm; signs of thyrotoxicosis; Neurological: dermatomes; substance release at the synapse; Spondylolysis; location of the motor and sensory areas of the brain; pathophysiology of cerebral infarction and excitotoxins; agnosia; accumulation of blood in a subarachnoid hemorrhage; most common cause of meningitis; Genitourinary: diet and the prevention of prostate cancer; Impact of Benign Prostatic Hypertrophy (BPH) on the urinary system Genetics: the role of DNA in genetics; transcription; effects of genetic mutations; Trisomy; Down Syndrome; Klinefelter syndrome; diseases that have multifactorial traits; multifactorial inheritance; Duchenne muscular dystrophy; Neurofibromatosis Musculoskeletal: ions that initiate muscle contraction; growth of long bones in children; bones belonging to the appendicular skeleton; Immunity/Inflammation: how vaccines are formed; populations at risk for getting systemic fungal infections and parasitic infections; systemic manifestations of infection; mechanisms responsible for the increase in antimicrobial resistance worldwide; functions of normal flora in the body; desensitization therapy; cells involved in “left shift” in the WBC count differential; forms of immunity; major histocompatibility class I antigens; inflammatory chemicals blocked by anti-inflammatory drugs; characteristics of acute phase reactant C-reactive protein Dermatology: process by which a deep pressure ulcer heals; complications of the development of contractures during wound healing Acid/Base: causes of respiratory alkalosis; molecules that act as buffers in the blood; Cardiovascular: most common cardiac valve disease in women; when myocardial ischemia may be reversible; symptoms of stable angina; orthostatic hypotension; isolated systolic hypertension; results of sustained controlled hypertension; the relationship of insulin resistance on the development of primary hypertension; defects in the normal secretion of natriuretic hormones and the impact on renal system; effects of increased sympathetic nervous system activity due to primary hypertension; complications of unstable plaque in the coronary arteries; forms of dyslipidemia associated with the development of the fatty streak in atherosclerosis; events that initiate the process of atherosclerosis; signs and symptoms of increased left atrial and pulmonary venous pressures in left sided heart failure; differences between left and right sided heart failure; infective endocarditis Peripheral vascular disease: pathophysiology of deep vein thrombosis; Vichow’s triad Hematology: physiological response to hypoxia in anemia; populations at the highest risk for developing folate deficiency anemia; causes of iron deficiency anemia; expected lab test results found in long standing iron deficiency anemia; Sickle Cell Anemia; causes of aplastic anemia; underlying pathophysiologic mechanisms leading to autoimmune hemolytic anemia; secondary polycythemia; anemia of chronic renal failure; Fluid and Electrolytes: conditions that result in pure water deficit (hypertonic volume depletion); osmoreceptors that stimulate thirst and the release of ADH; causes of hypernatremia; effects of increased aldosterone; dependent edema; definition of isotonic; principle of capillary oncotic pressure; types of fluid compartments in the body; Pulmonary: most effective measure to prevent pulmonary embolus from developing in patients; when the practitioner will note tactile fremitus; cause of acute airway obstruction in the patient with chronic bronchitis; types of pneumothorax; results of the loss of alph-1-antitrypsin in emphysema; the result of loss of surfactant in ARDS; Characteristics of Cheyne-Stokes respirations Shock: causes of hypovolemic shock; how the body maintains glucose levels during shock I wish you the best as you take the final exam in Week 8. . Remember that you have until Saturday of Week 8, 11:59 p.m. MT to complete the final exam. Respondus Lockdown Browser is used for all quizzes and exams. Please let me know if you have any questions. [Show More]
Last updated: 2 years ago
Preview 1 out of 2 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$14.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Jul 23, 2021
Number of pages
2
Written in
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Jul 23, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
49