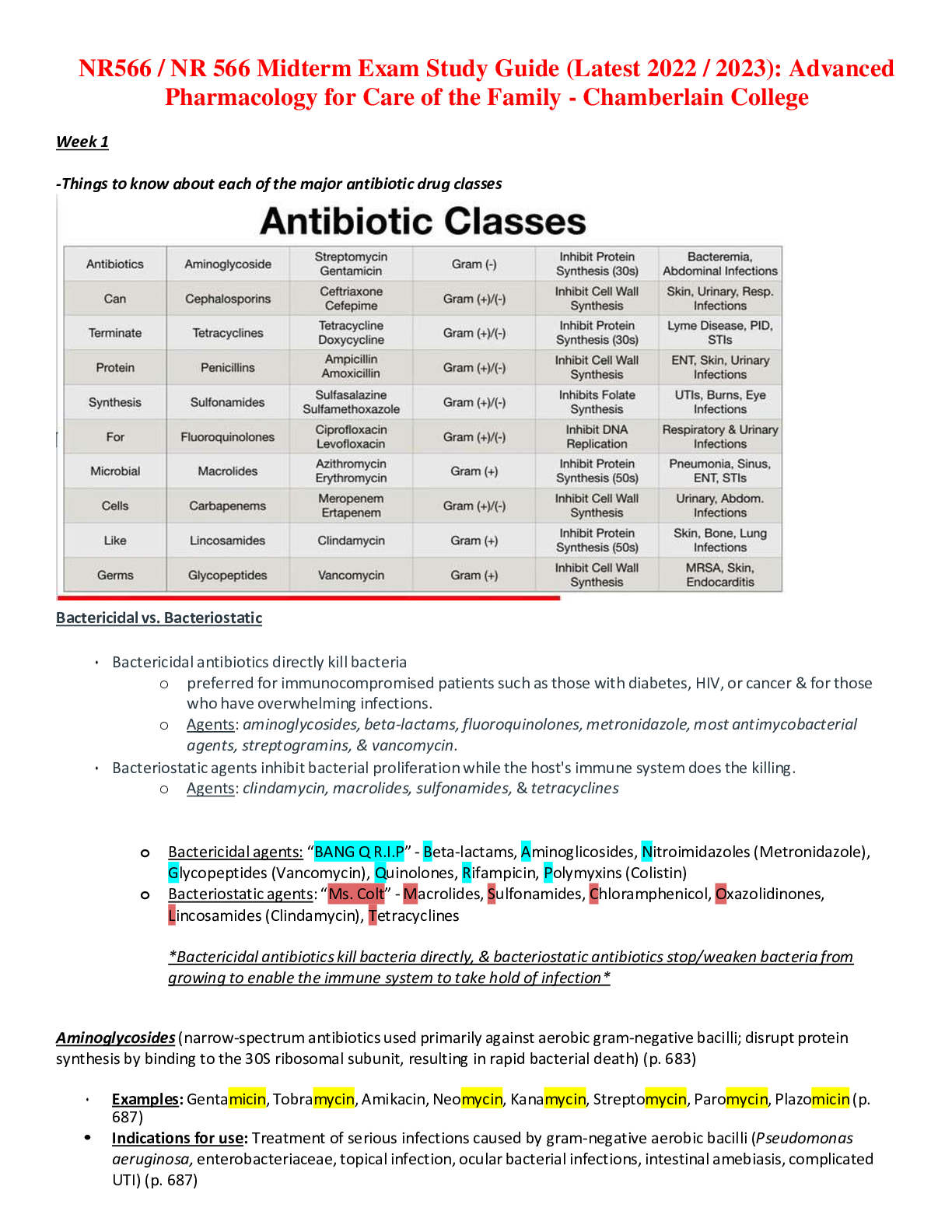
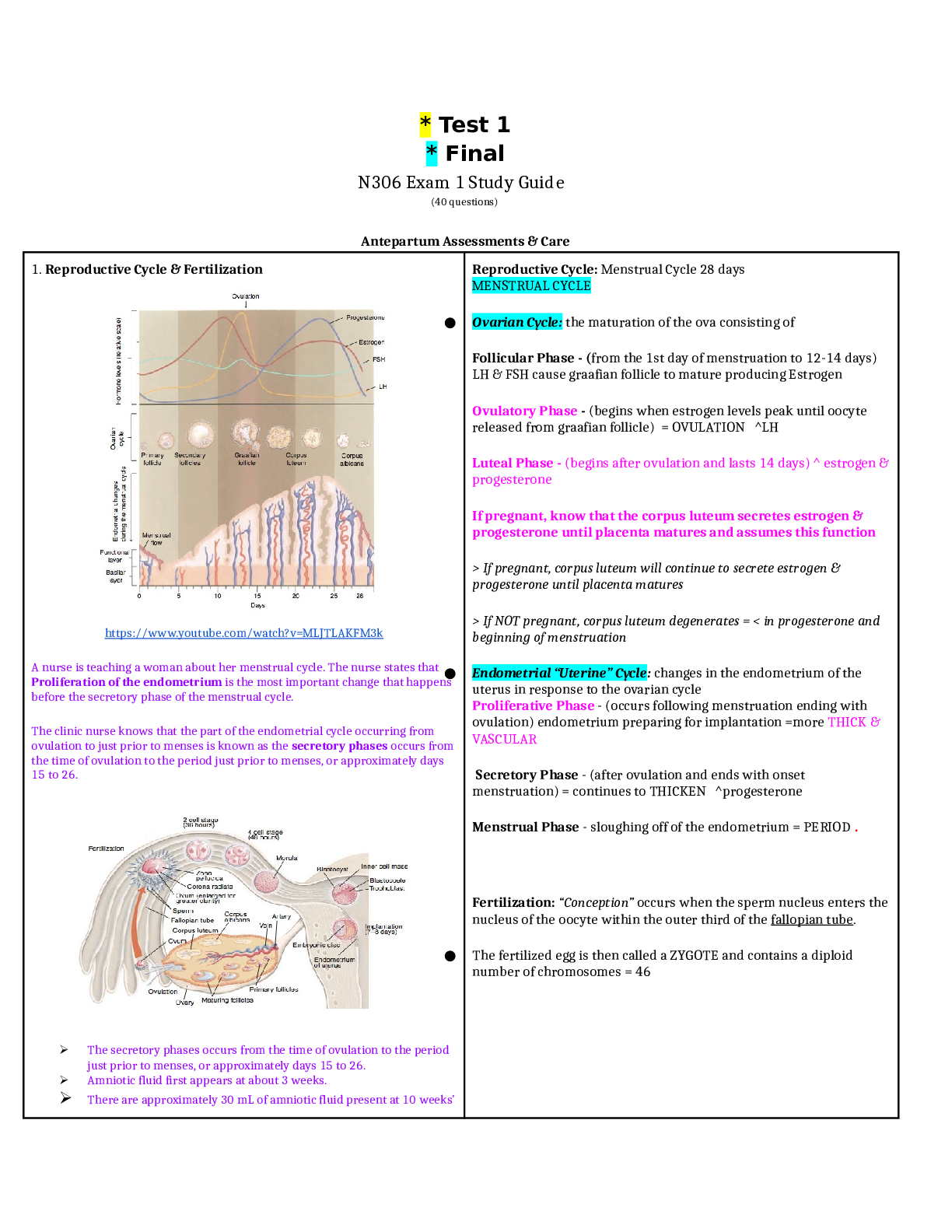
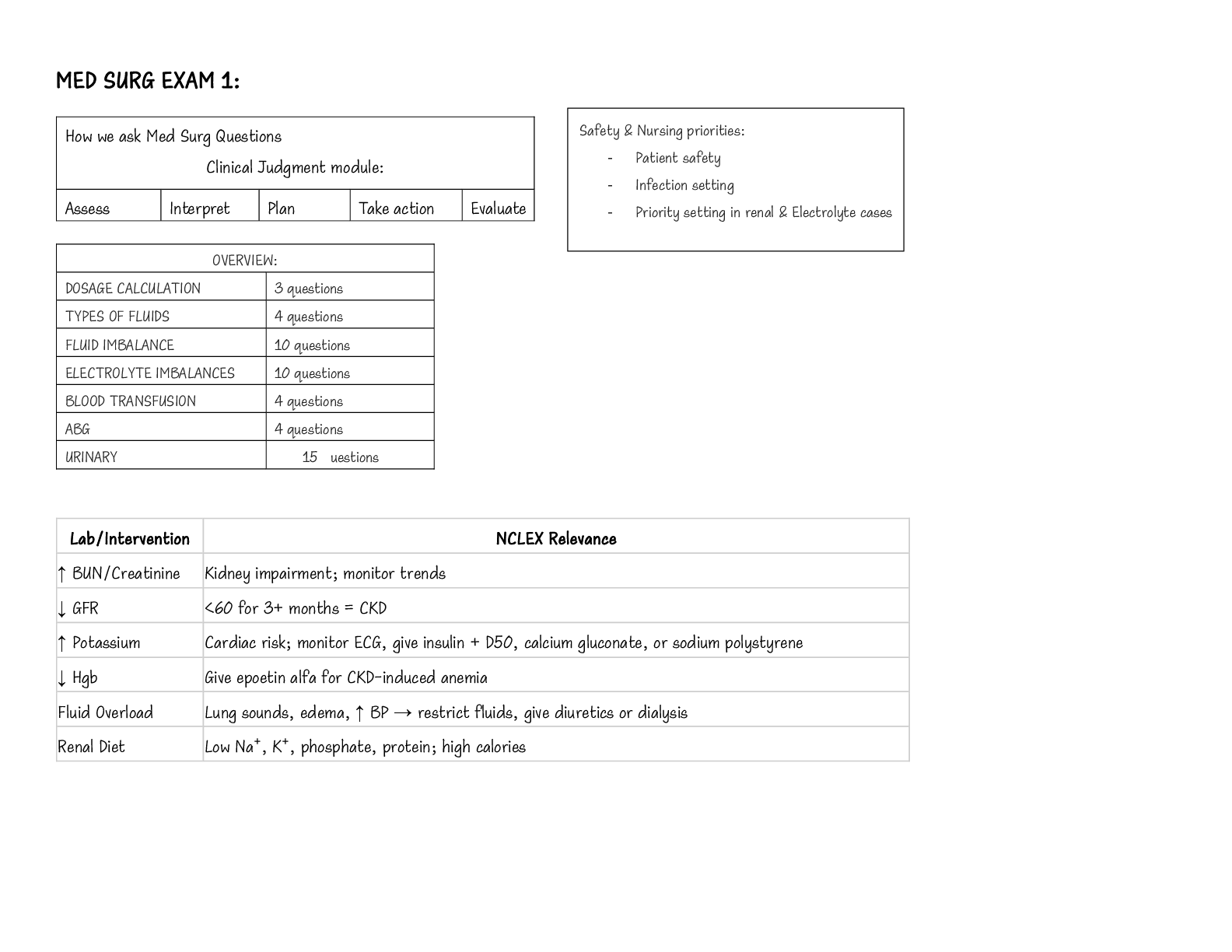
1. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has chronic kidney disease and is starting hemodialysis. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? Hemodialysis: Hemodiaylsis is needed
...
1. A nurse is providing teaching to a client who has chronic kidney disease and is starting hemodialysis. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching? Hemodialysis: Hemodiaylsis is needed three times per week for 3-5 sessions. It involves insertion of two needels one into an artery and the other into a vein. (page 379)
-Notify the nurse of headache, nausea, or dizziness during dialysis
-Do not eat during dialysis
-Have protamine sulfate ready to reverse the heparin
-Report hypotension, cramping, vomiting, bleeding at the access site, contamination of equipment.
-Provide emotional support and offer activities (books, magazines, music, cards, or television)
-Have an informed consent signed for hemodialysis
-Monitor the AV fistula (you want to hear a bruit but feel the thrill)
-Take medications to replace folate loss
-Eat a well balanced meal high in folate (beans, green vegetables) and take supplements.
-Diaylsis depletes protein so increase protein intake over prediaylsis limitations (page 380)
-Avoid sleeping on top of the extremity with the access device
2. Emergency care of the client in Addisonian crisis includes which one of the following interventions? This is a life threatening event. Occurs when there is an acute drop of adrenocorticoids due to sudden discontinue of glucocorticoid medication or when induced by severe trauma, infection, or stress. (page 542)
-Start a rapid infusion of 0.9% Na+ Cl. (administer hydrocortisone sodium IV bolus initially then a continuous infusion.
-PPI complication is C-Diff
-Causes hyperkalemia (loop or thiazide diuretics are used to manage this)
-It causes hyponatremia (neurologic changes are first, put them on seizure precautions), hypoglycemia, and hyperkalemia (telemetry)
-Place the patient in the recumberent position with legs elevated.
-Administer a H2 antagonist (rantidine) IV for ulcer prevention
-Administer vasopresssors to increase the blood pressure.
-Gi issues, salt cravings, weight loss, weakness, bronze pigmentation of the skin
3. A 40 year-old ale presents complaining of LUQ pain, diarrhea with oily, fowl-smelling stool, and abdominal distention. The nurse initially suspects which one of the following conditions?
-Pancreatitis
4. The nurse is caring for a client experiencing hypovolemic shock from blood loss. Which of the following interventions would be appropriate for this client? SATA
-Modified trendsdelenberg position
-Replace the fluids with crystalloids
-Packed RBC
-Blood cultures
-Hemoglobin and hemocrit
-Oxygen
5. A nurse is caring for a client with polycystic kidney disease. Which of the following would the nurse expect for this condition?
-Cyst can form on other parts of the body
-It is HEREDITARY
-Abdomen and flank pain
-Bloody and cloudy urine
-Ascitites
-Cyst multiply when patient reaches 30 years old
-Nocturia
-Hyponatremia
-Progressive kidney failure
-Low sodium diet
-Diagnostic lab test include: Hematuria, proteinuria, and bacteria indicating infection, gradual increase of blood creatine, BUN, creatine clearance (page 395)
6. The nurse is planning care for a client diagnosed with Graves’s disease. Which of the following nursing interventions would be appropriate for this client’s care? SATA
-Exothalmus (keeps eyes lubricated and anything concerning eye care)
-Reduce room temperature
-Provide cool showers/sponge bath
-Report a temperature of 1 degrees F (alert HCP because it could be thyroid storm)
-Thinomadies are used to treat Grave’s disease as an adjunct to radioactive iodine to decrease hormone levels in preparation for surgery and treat thyrotoxicosis.
7. General interventions for the client in a shock state include which of the following? SATA
• -Monitor:
• Oxygenation status (priority) - How?
• Level of consciousness
• Vital signs – look at trends
• Continuous cardiac monitoring
• Urine output – hourly: what’s normal? Report <
• Skin color, temperature, moisture, capillary refill, turgor
• Explain procedures
• Place the client on high-flow oxygen, such as a 100%
• nonrebreather face mask. If the client has COPD, insert a 2 L/min nasal cannula and increase the oxygen flow as needed. Why?
• Be prepared to intubate the client. Have emergency resuscitation equipment ready.
• Maintain patent IV access.
• Hypotension, place the client flat with his legs elevated to increase venous return.
• Change in status occurs, notify the rapid response team and provider of the findings.
• Prepare for and maintain client care during transfer
• Monitor central venou...........................CONTINUED
[Show More]