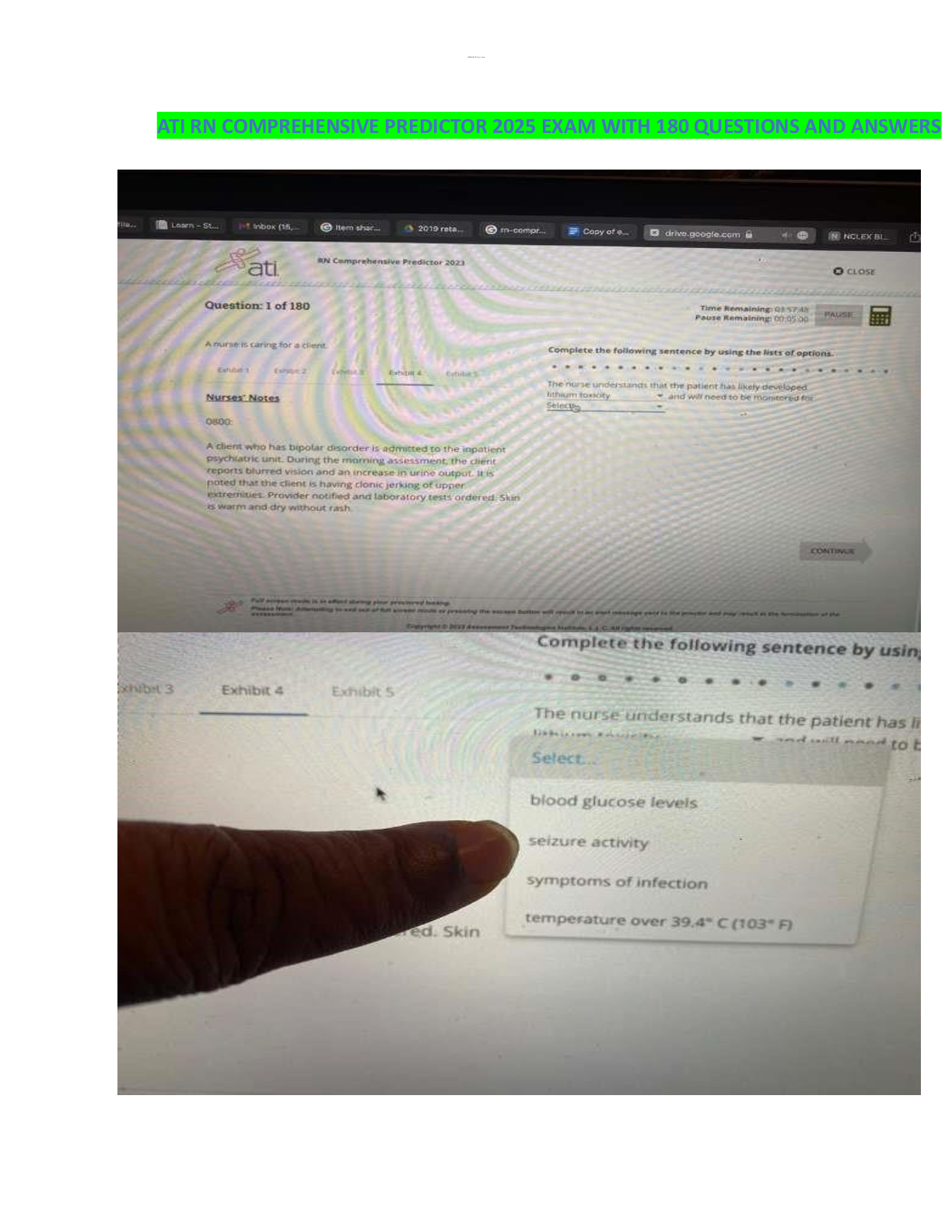
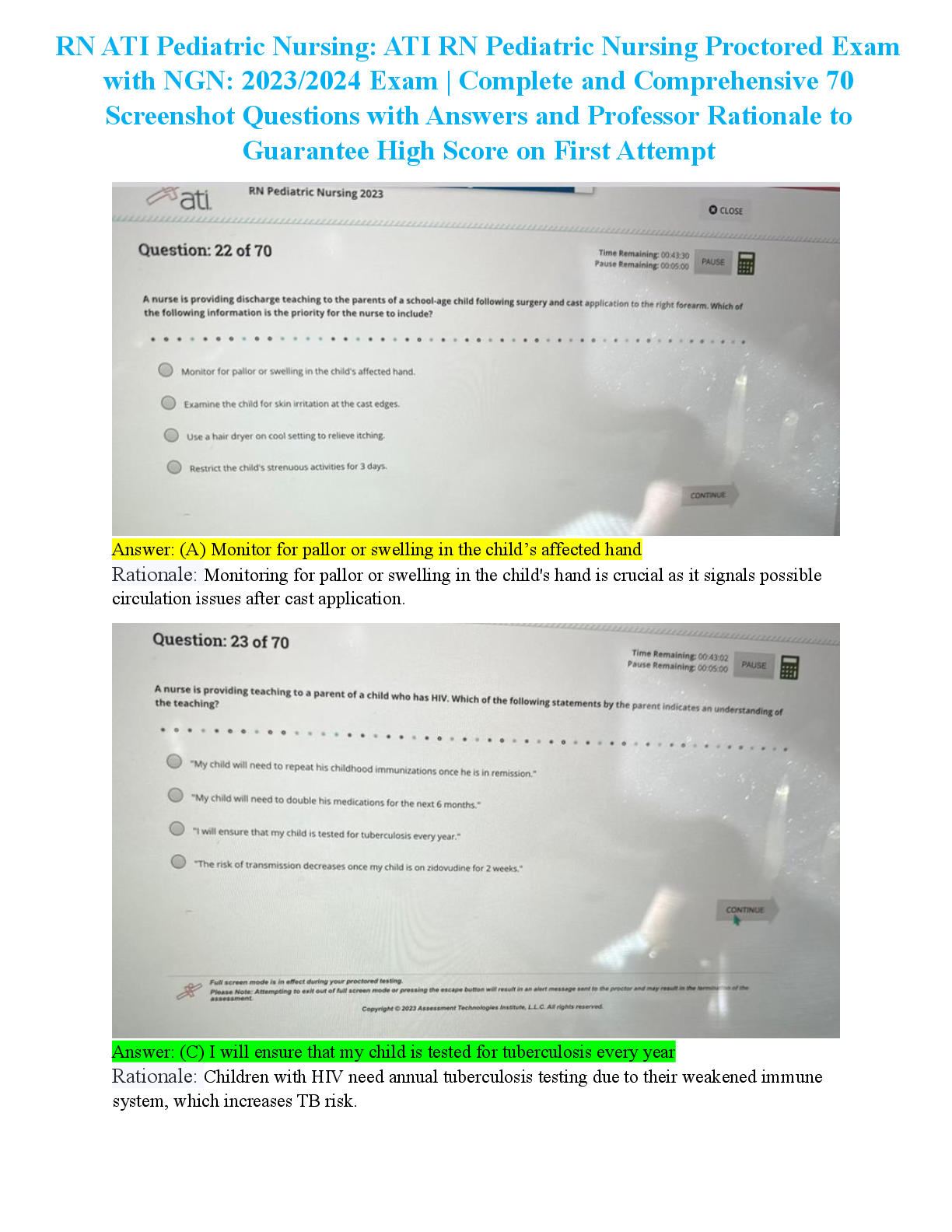
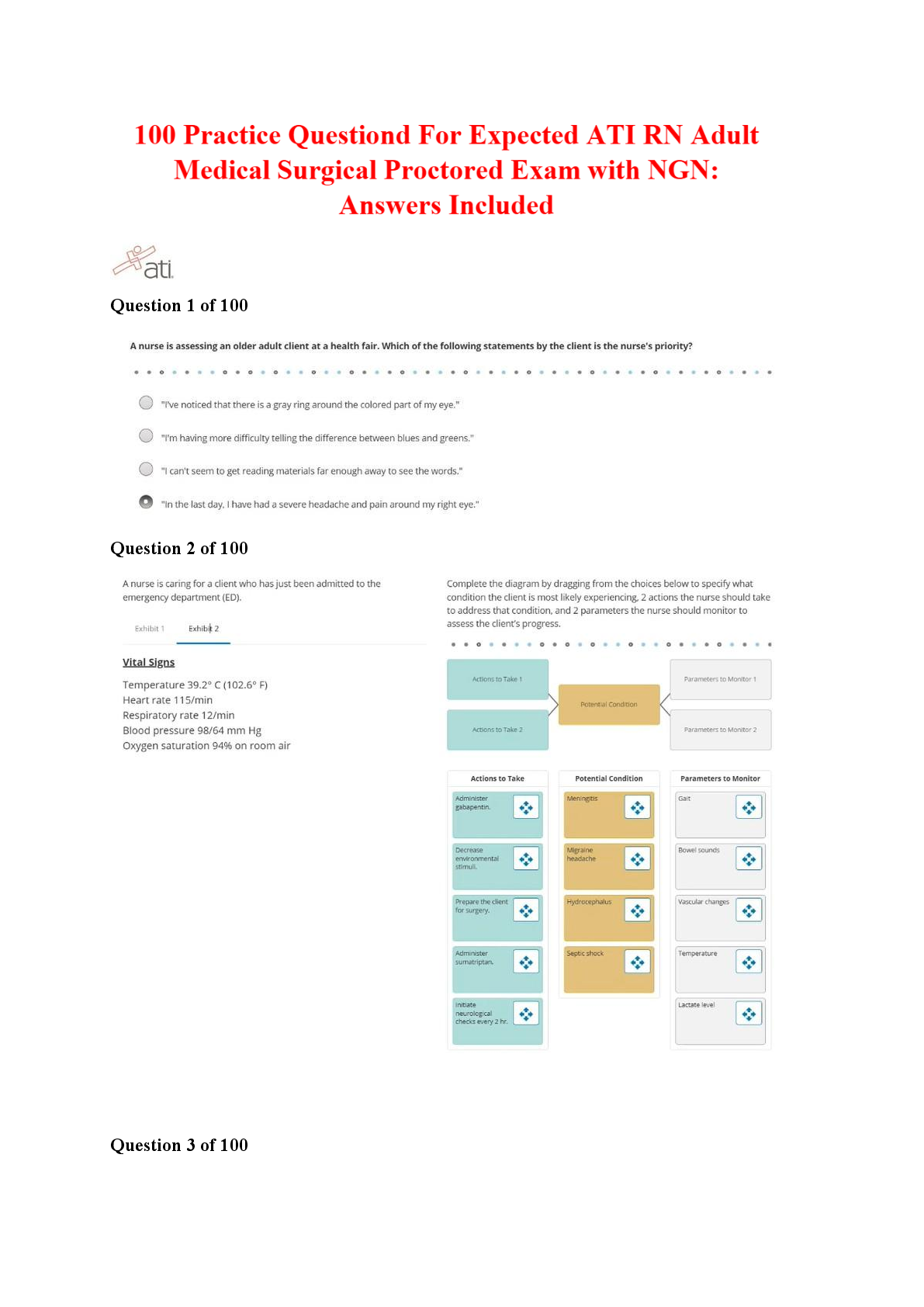
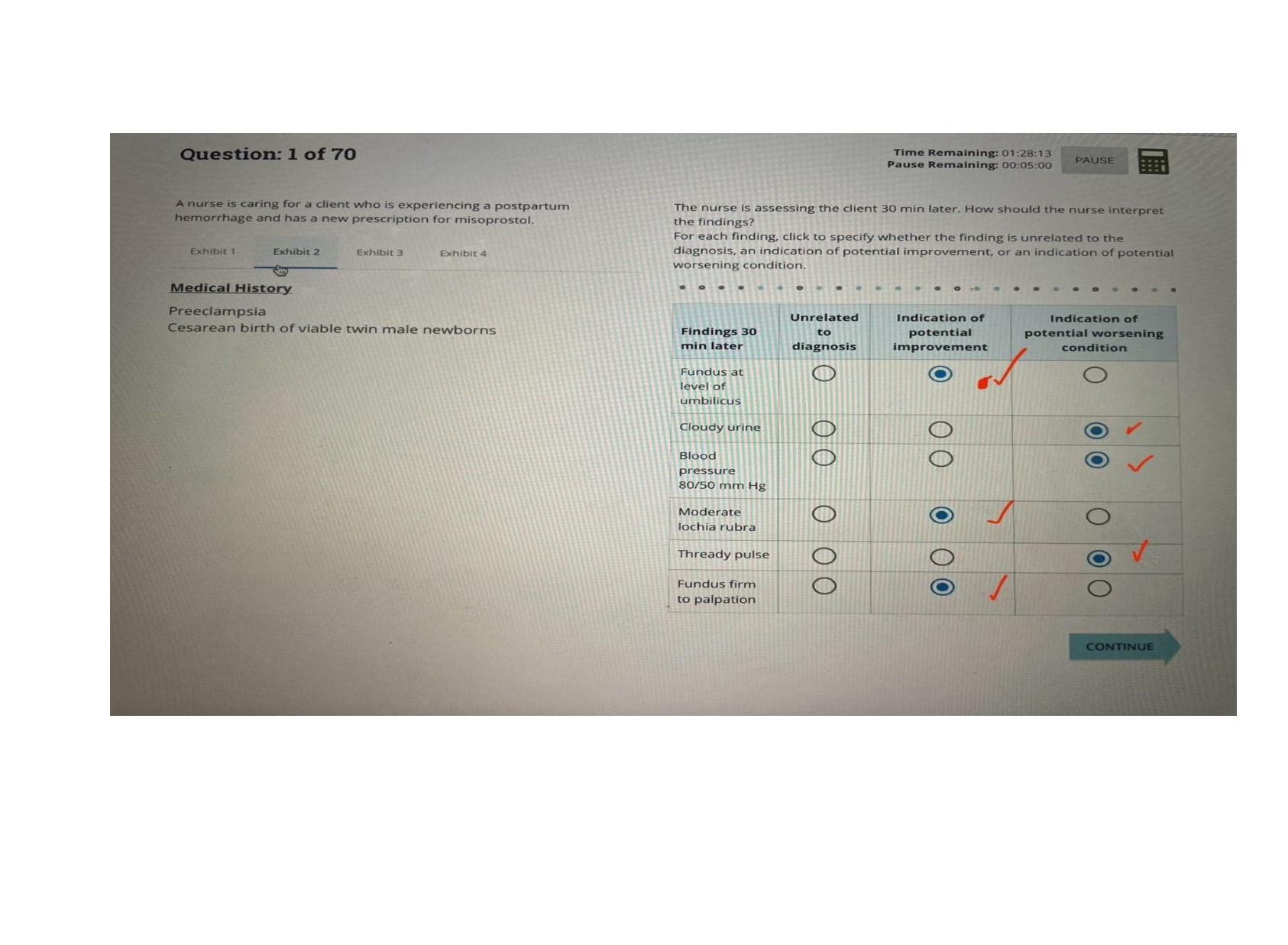
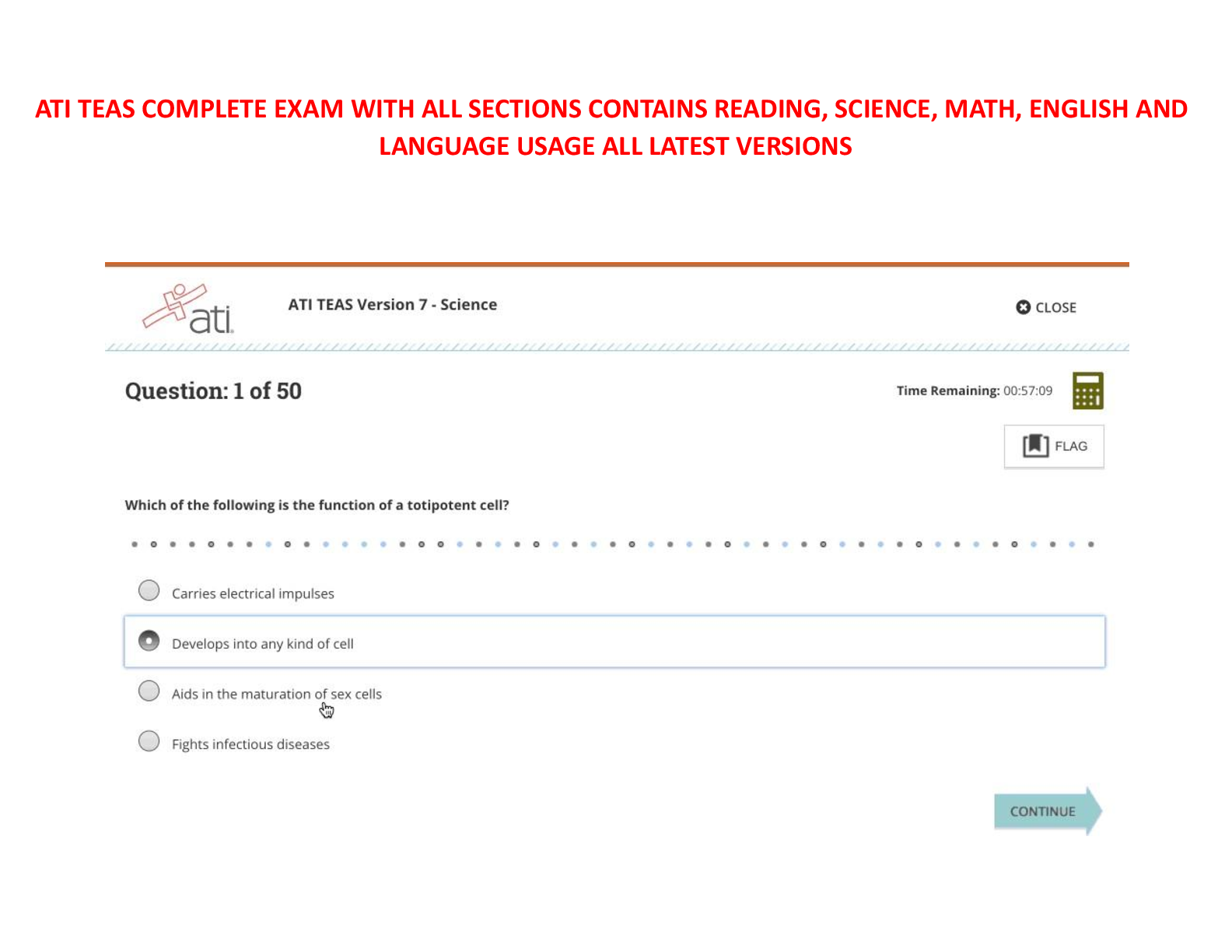
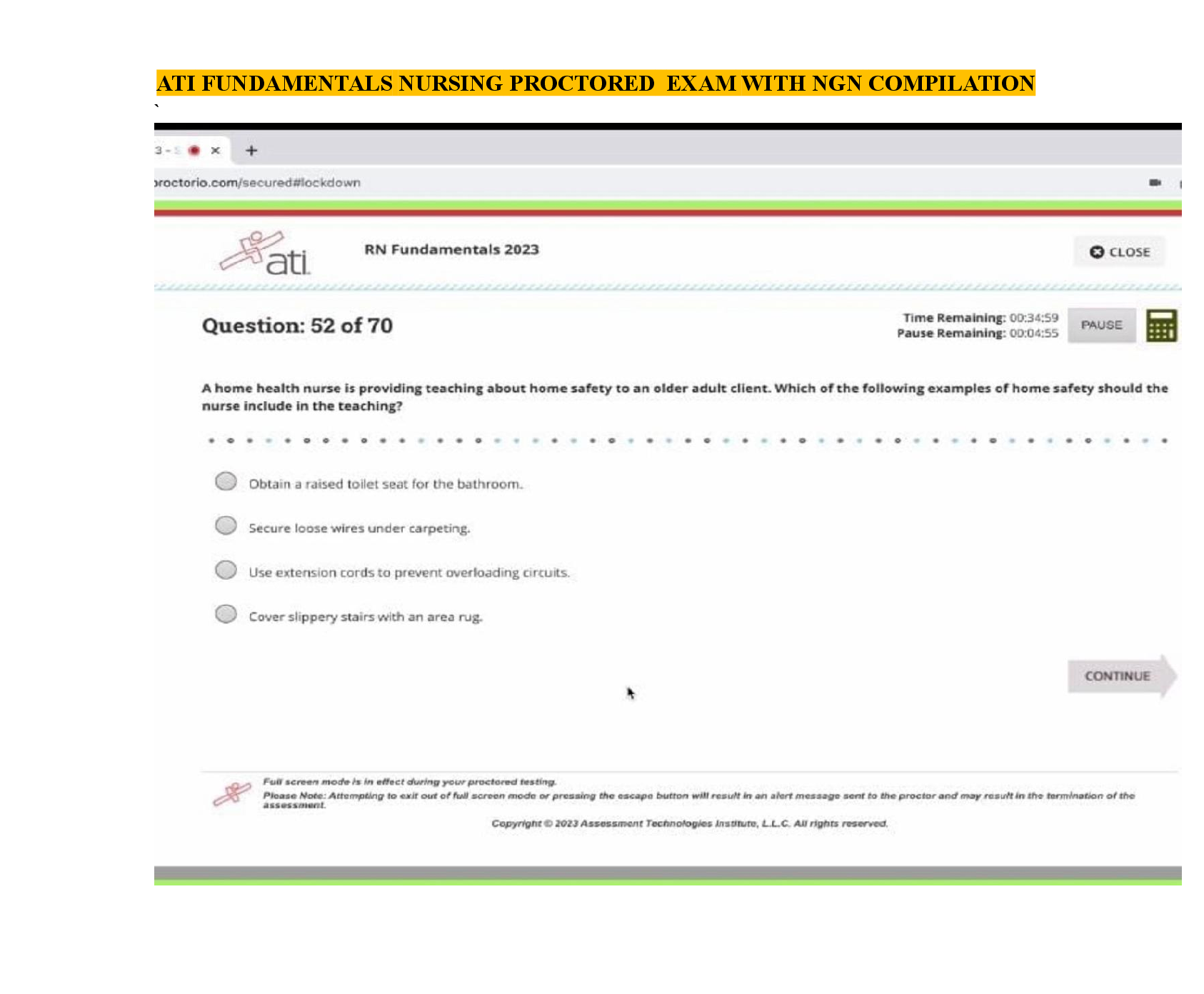
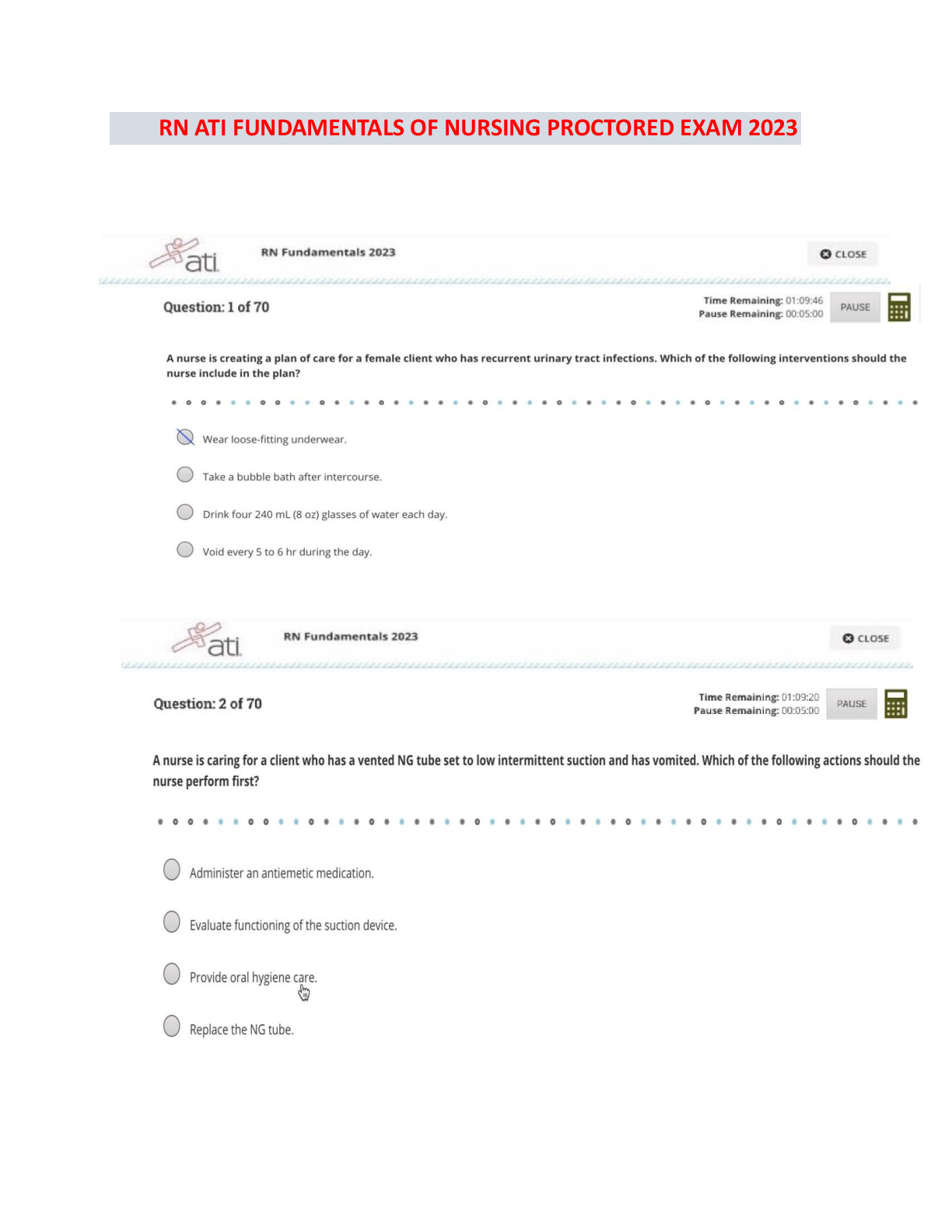
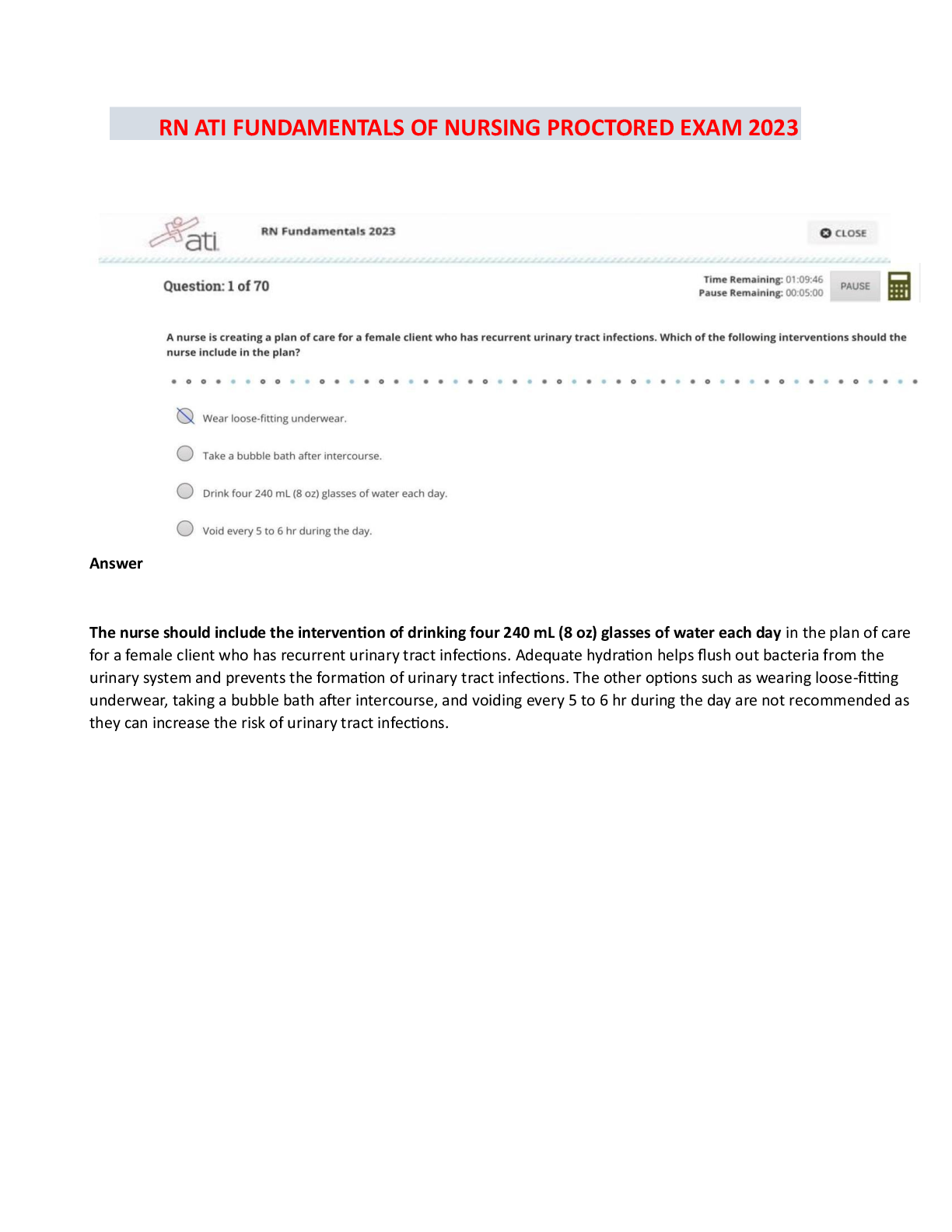
Focus Points NUR2790 Exam 2021
Document Content and Description Below
Here are some key focus areas for Exam 2 which covers Modules 3, 4, & 5. Review course modules for information. You are responsible for all content in the chapters, power points, lecture notes, table ... s, red flags, figures, boxes, with special focus points on the following topics: Module 3 Tissue Integrity Relate principles of triage to prioritize care delivery in a disaster situation. Appraise the roles of the nurse in emergency preparedness and response. Prioritize nursing care for the patient during the acute phase of burn injury. Develop a comprehensive plan of care for a patient with alteration in tissue integrity. Describe the physiological process involved in the maintenance and restoration of health and wellness, across the lifespan, as it relates to tissue integrity. o Burns Review RN delegation of tasks Infection prevention Hand washing and perform sterile dressing changes (LPNs can do dressing changes just reinforce that they have to be sterile) They also must have their PPEs on Understand how to support severely burned patients from resuscitation to discharge/rehab; identify priority actions in each phase Adequate fluid status during resuscitation phase by checking urine output; Priority for burn patient coming to ED are fluids; priority for patient that has been electrocuted make sure these patients are on a cardia monitor; what are potential consequences of burns are self-image and depression Treatment for patient that develops loud, brassy cough – what is going on here inhalation injury (They are about to lose their airway, so we want to get ready to intubate) You would do the same for a person who is having difficulty swallowing or drooling. Understand common medications administered to burn patients and why the medications are given i.e. for pain drug of choice is morphine, prevention of ulcers use Tagamet, famotidine, or ranitidine Understand nursing assessment of burn patient – what is continuously monitored – s/s to watch for i.e. drooling, difficulty swallowing-what does the nurse do first? Assess their airway and listen to their lungs; psychosocial impact of sever burn- would depression be normal? Yes Parkland Formula This study source was downloaded by 100000824623083 from CourseHero.com on 06-04-2021 15:17:17 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/37868811/Exam-2-Nursing-3docx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.comFocus Points NUR2790 Exam 2 Parklands 4mlx Body Space Affects x kg, remember 1st half goes in the first 8 hrs. 2nd half goes in over the next 16 hrs. Use Lactated Ringer How to calculate BSA% Understand lab/ABG values for a burn patient i.e. what is typically seen in burn patients? Hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, and edema Describe the different layers of burns r/t involvement of dermis/epidermis Superficial Partial-Thickness Burn effects epidermis and superficial dermis. They are very painful and blister formation is common. This study source was downloaded by 100000824623083 from CourseHero.com on 06-04-2021 15:17:17 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/37868811/Exam-2-Nursing-3docx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.comFocus Points NUR2790 Exam 2 o Disaster preparedness Understand colored tags and how would you educate others Yellow tag example: open fracture Red tag example: chest pain, suspected stroke/MI Green tag example: simple fracture Black tag example: agonal respirations, open head wound Understand personal preparedness plan – what do you include or consider? How many days should you pack for yourself? 3 What do you need to consider? Food, medication, water, non-perishable foods, pets, childcare, and older adults What does the RN need to do to be prepared on the floor Gather supplies Organize Move stable patients Know the chain of command Module 4 Gas Exchange Develop a comprehensive plan of care for a patient with alteration in Gas Exchange. Describe the physiological process involved in the maintenance and restoration of health and wellness, across the lifespan, as it relates to Gas Exchange. Evaluate laboratory data and clinical manifestations to determine the adequacy of oxygenation and ventilatory interventions. Plan nursing care for the patient being mechanically ventilated. o Emergency Nursing/Mass casualty/Trauma Nursing Role of RN in ED when there is a mass casualty? Triage- The most experienced nurse should do this Understand critical incident stress debriefing? Process what they just went though (destress) How to prevent PTSD as a nurse? Exercise, stay hydrated, eat healthy, get enough sleep, avoid caffeine, and talk to someone Understand how you would triage incoming patients from mass casualty – examples know the difference between traditional and mass casualty Traditional, you would take care of the most critical first. Mass casualty, take care of the most viable (most likely to live with the least resources) This study source was downloaded by 100000824623083 from CourseHero.com on 06-04-2021 15:17:17 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/37868811/Exam-2-Nursing-3docx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.comFocus Points NUR2790 Exam 2 Mass casualty event – paramedic, Hospital incident commander-can end a mass casualty event, public information officer, triage officer, medical command physician – hierarchy and roles Review RN delegation of tasks Never delegate what you can’t EAT (evaluation, assessment, and teaching) also invasive stuff Specialty teams available Trauma, Anesthesia, rapid response, stroke team, and forensic nursing CPR – family presence Recommended so they can see what’s going on Consider vulnerable populations – establishing trust Children, elderly, rape victim, intellectual disability, homeless, migrant workers it’s important to establish trust Priority assessments i.e. which color would nurse focus on first? Red; patient arrives with O2 mask on? Assess airway and make sure he/she is having effective respirations o Gas Exchange Understand Rapid Response Team role The respond to emergencies hopefully before the person codes Pulmonary embolus – patho? Clot in the lungs Risk factors? DVT, a. fib, post surgical, long bone fracturs S/S you may see? SOB, dyspnea, cyanotic, anxiety Assessment Treatment? Oxygen, elevated HOB, anticoagulant Test? D-dimer will be elevated Anticoagulants –monitor PTT and PLT for heparin (hold, call doctor, and assess for bleeding if PLT are out of range) is for heparin patient education? Soft tooth brush, electric razor, avoid NSAIDs, ibuprofen, injuries, and check for bruising and occult blood ABGs for respiratory issues i.e. COPD? Respiratory Acidosis ph low (7.35-7.45), co2 high (45-35), bicarb low (22-26) Common medications for intubated patients – Propofol, sedatives, pain meds, antianxiety, Pepcid (stress ulcers) what to monitor, patient education This study source was downloaded by 100000824623083 from CourseHero.com on 06-04-2021 15:17:17 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/37868811/Exam-2-Nursing-3docx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.comFocus Points NUR2790 Exam 2 Mechanical ventilation – assessment PEEP of 20cm (it’s too high which can cause a pneumothorax) treatment- prevent VAP ETT removed by suction and provide oral care Low pressure alarm is cause by disconnect; high pressure alarm is caused by patient bucking or coughing If you can’t figure out why the alarm is going off what do you do? Bag them Agitated patient what does the nurse assess? Assess and then treat what is causing the agitation Dyspneic with normal O2 sat? Assess and try to find out what is making the patient short of breath. If it’s pain give morphine if it’s anxiety give benzos. Flail chest-anticipated interventions? Monitor educate patient to splint when coughing and provide pain management as long as gas exchange is good. Understand refractory hypoxemia- wide spread inflammatory response seen in what disease process? ARDS (doesn’t respond to O2) Module 5 objectives Plan collaborative care for patients experiencing common dysrhythmias. Describe the physiological process involved in the maintenance and restoration of health and wellness, across the lifespan, as it relates to Perfusion. Educate patients and families about current procedures and other interventions for common dysrhythmias. Appraise evidence-based practice in the current treatment of cardiac arrest. o Perfusion Understand ECG complex – think about what is going on in the heart if there is no P wave with every QRS, or if a segment lengthens- Blocks What part of the conduction system of the heart controls the rate? SA node What wave is not normally seen on ECG? U wave Common medications – i.e. beta blockers, anticoagulants, calcium channel blockers – know why prescribed and patient education i.e. take own pulses; what two meds will patient with afib have long term? Anticoagulant and Cardizem (Calcium channel blocker) Why? Because if they don’t the patient will be a risk for clots and stroke This study source was downloaded by 100000824623083 from CourseHero.com on 06-04-2021 15:17:17 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/37868811/Exam-2-Nursing-3docx/ This study resource was shared via CourseHero.comFocus Points NUR2790 Exam 2 You notice a change in rhythm on patient telemetry – what do you do? Assess patient and then do a 12 lead and call provider Treatment for VFib – priority before shock? Defibrillate Substance abuse cocaine and meth are usually the cause of dysthymias of patient’s 20-40 so ask if they are doing any illegal drugs Identify rhythm strips [https://www.practicalclinicalskills.com/ekg-practice-drill] What treatments would the RN initiate for fatal dysrhythmias? Vfib and vtach CHF – assessment for physiologic alterations during bradycardia and tachycardia Asystole- assess patient and check leads if patient is no responsive start compressions Bradycardia- assess patient and check leads administer atropine What is normal cardiac output? 6L/min Pacemaker- patient education? don't lift, stay away from electronics over chest, no mri, pacer teaching, keep your card with you, where medic alert bracelet, no arms over head, watch for infection What patient would need an external pacemaker? Patient who is symptomatic bradycardia and is waiting for a permanent pacemaker to be put in. Usually the patient that has the 2nd and 3rd degree blocks ICD- patient education i.e. avoid what? Electromagnetic area because magnets will turn them off so avoid MRIs [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 20 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 13, 2021
Number of pages
20
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 13, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
70