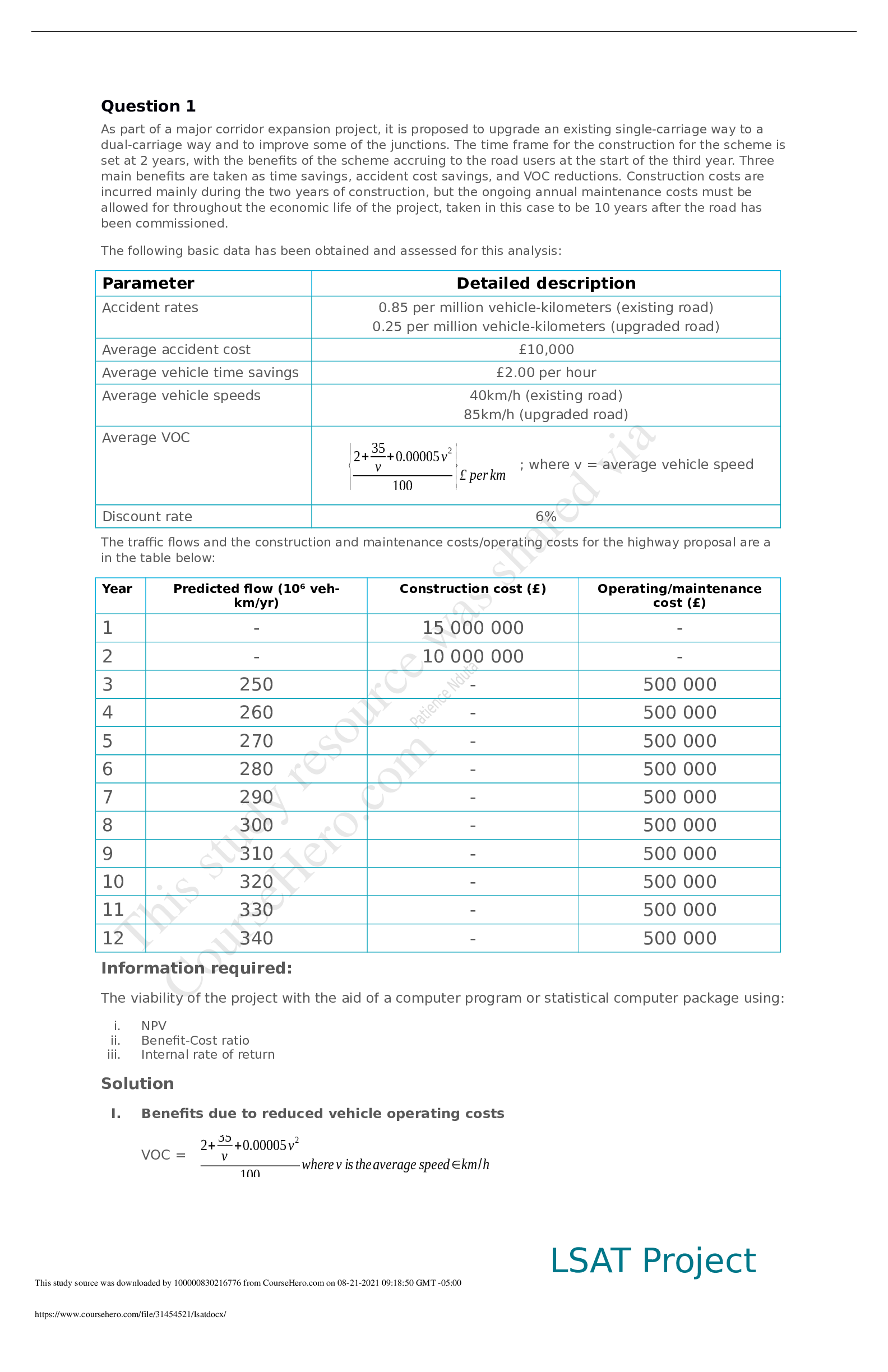
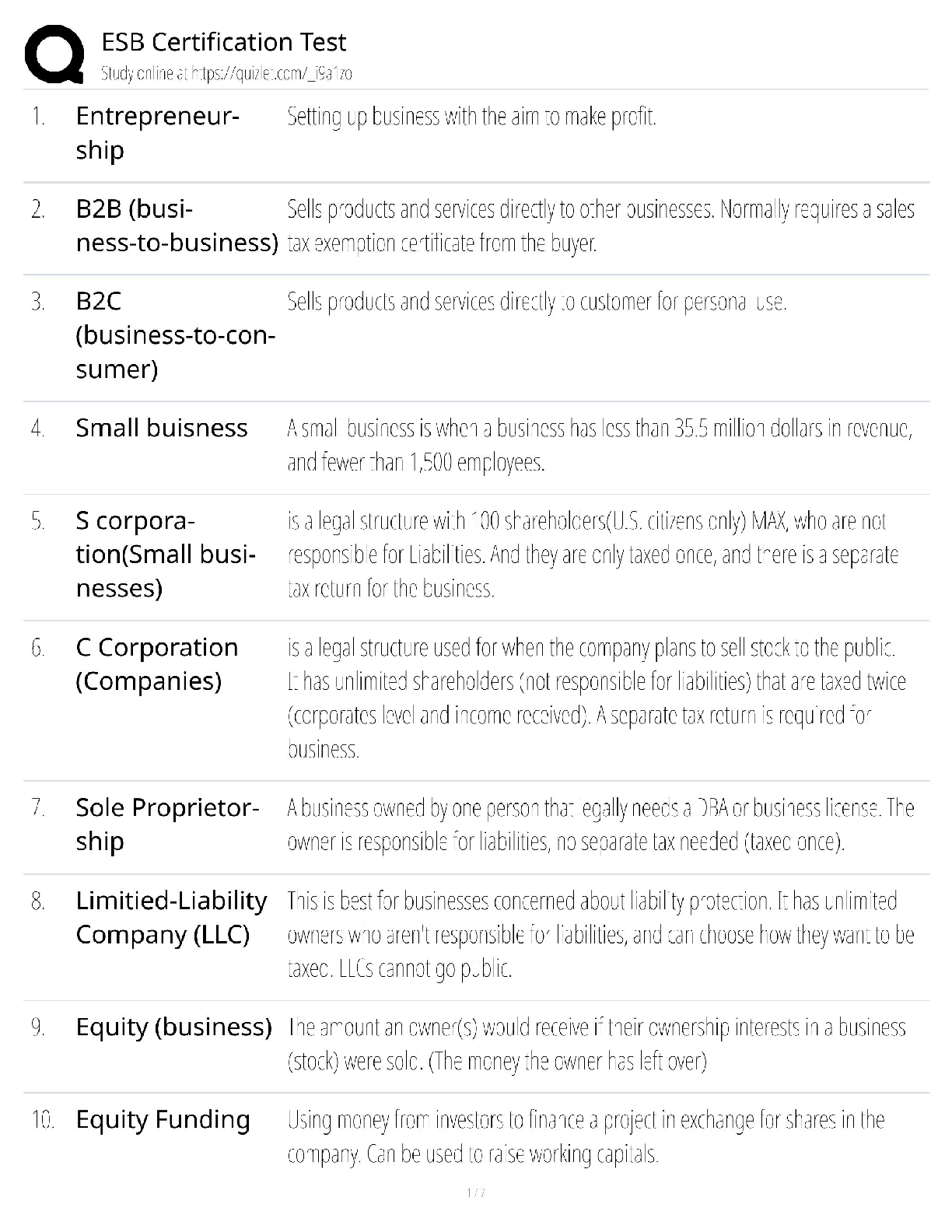
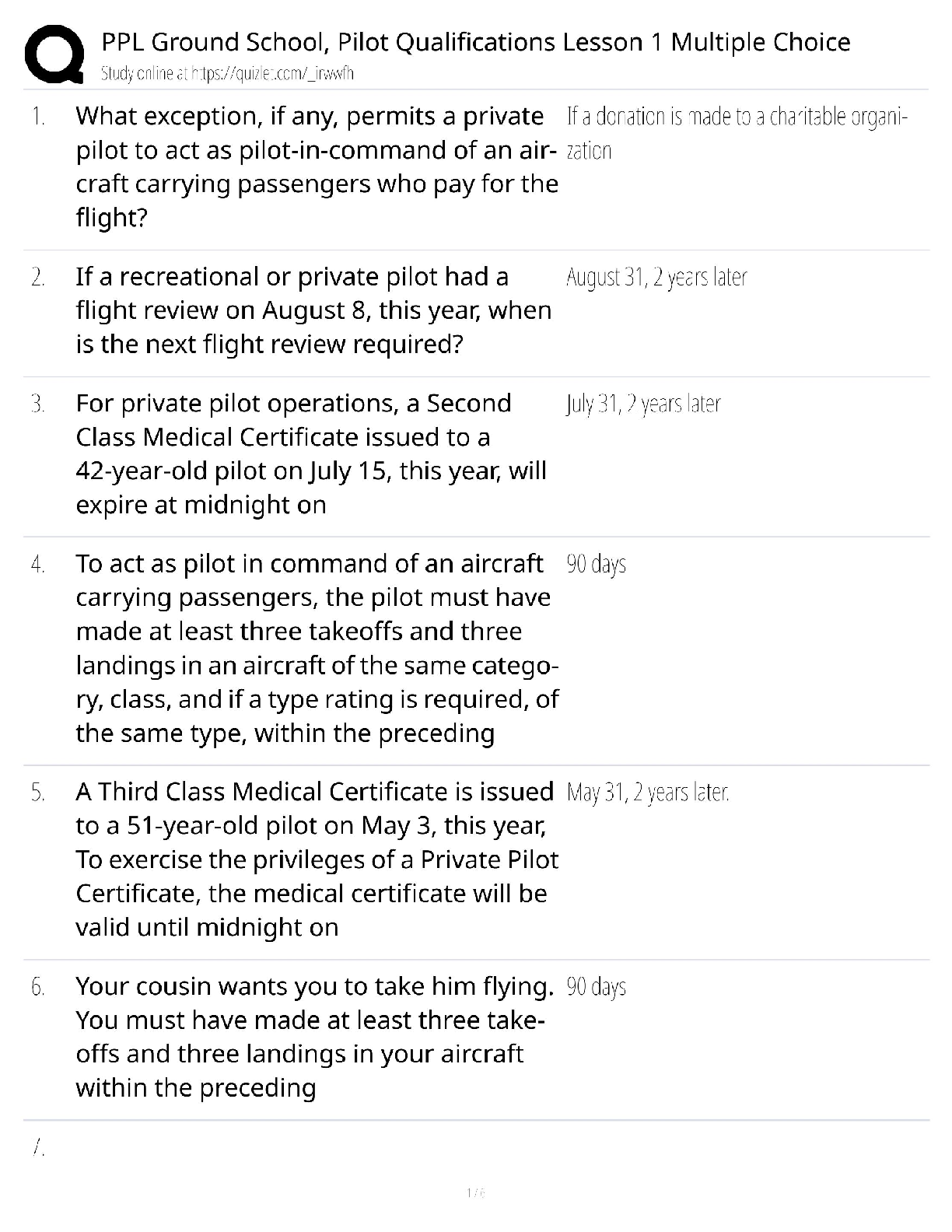
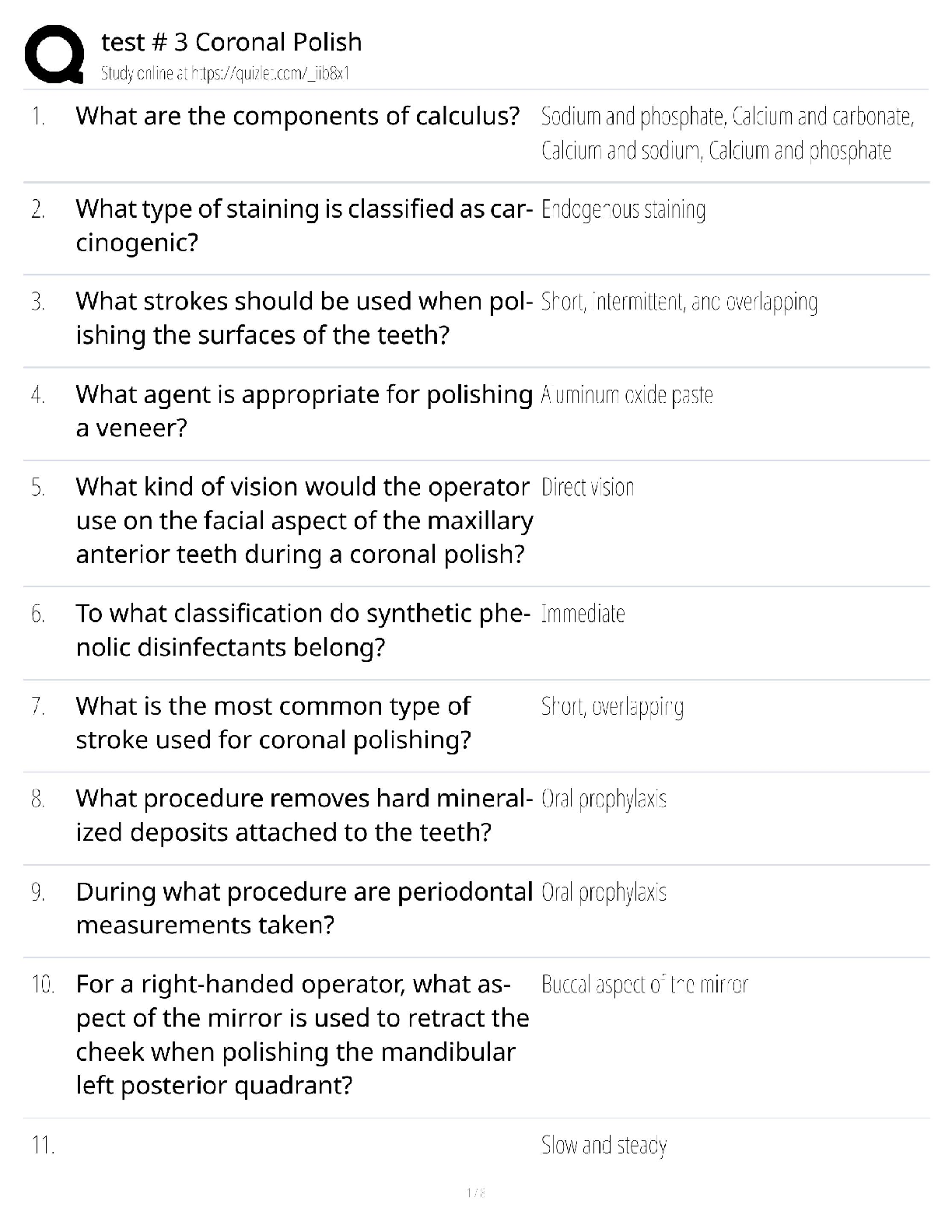
Operating system questions with their answers (Memory management, Virtual
memory, Processes synchronization) Part two
Q1: Why does the computer must keep several processes in main memory?
Q2: What are the differences
...
Operating system questions with their answers (Memory management, Virtual
memory, Processes synchronization) Part two
Q1: Why does the computer must keep several processes in main memory?
Q2: What are the differences between?
a) Logical and physical address?
b) Page table and segment table?
c) First-fit placement and best-fit placement?
d) Contiguous and non – contiguous storage allocation
e) Multiple contiguous fixed partitions (MFT) and multiple contiguous
variable partitions (MVT).
f) Segmentation and paging storage?
Q3: State and explain Storage management strategies?
Q4: Suppose that we have free segments with sizes: 6, 17, 25, 14, and 19. Place a
program with size 13kB in the free segment using first-fit, best-fit and worst
fit?
Q5: What are the advantages of?
a) Overlays allocation storage.
b) Compaction.
c) Page table.
d) Segment table.
Q6: Consider a user program of logical address of size 6 pages and page size is 4
bytes. The physical address contains 300 frames. The user program consists of
22 instructions a, b, c, . . . u, v . Each instruction takes 1 byte. Assume at that
time the free frames are 7, 26, 52, 20, 55, 6, 18, 21, 70, and 90.
Find the following? (10 degrees)
A) Draw the logical and physical maps and page tables?
B) Allocate each page in the corresponding frame?
C) Find the physical addresses for the instructions m, d, v, r?
D) Calculate the fragmentation if exist?
Q7: Consider a program consists of five segments: S0 = 600, S1 = 14 KB, S2= 100
KB, S3 =580 KB, and S4 = 96 KB. Assume at that time, the available free
space partitions of memory are 1200–1805, 50 – 160, 220-234, and 2500-3180.
Find the following:
1. Draw logical to physical maps and segment table?
2. Allocate space for each segment in memory?
3. Calculate the external fragmentation and the internal fragmentation?
4. What are the addresses in physical memory for the following logical
addresses: 0.580, (b) 1.17 (c) 2.66 (d) 3.82 (e) 4.20?
Q8: Define the virtual memory? What are its advantages?
Q9: What is the demand paging?
Q10: What are the advantages of using pager (i.e. demand paging)?
Q11: What are the differences between pager and swapper?
The system uses valid-invalid bit is used. This bit is set to "valid" when the page
in memory, while it set to "invalid" when the page either not valid or is the page is
valid but is on the disk, as in the following figure.
The system uses valid-invalid bit is used. This bit is set to "valid" when the page
in memory, while it set to "invalid" when the page either not valid or is the page is
valid but is on the disk, as in the following figure.
Q13: When will the page faults occur? What is the procedure for handling the
page fault?
Answer Q13
The page fault will occur w
[Show More]





.png)




.png)

.png)