Computer Accounting with QuickBooks® 2021 20th Edition By Donna Kay TEST BANK
$ 24

Davis's Comprehensive Manual of Laboratory and Diagnostic Tests With Nursing Implications (Davis's Comprehensive Handbook of Laboratory & Diagnostic Tests With Nursing Implications) 8th Edition
$ 15

PRACTICES OF IRRIGATION AND ON-FARM WATER MANAGEMENT.
$ 14
.png)
HSM543 | QUESTIONS AND 100% CORRECT ANSWERS WITH EXPLANATIONS | WEEK 1-7 WITH CITATIONS | 36 PAGES
$ 15

BIOS2150 Microbiology Exam Study guide
$ 4
.png)
Medical-Surgical RN A Prophecy Relias Updated 2022 Already Passed
$ 9

Diversity in Organizations 2nd Edition - by Myrtle P. Bell-|Instructors Manual |Testbank| Reviewed/Updated for 2021
$ 15

VSIM RED YODER part 2 Guided Reflection 6.16( Complete Solution)Score A
$ 15

Summary STR581 Week 1 Case Study.docx Wk1 Apply Case Study Analysis: "Case 6 Fixer Upper: Expanding the Magnolia Brand" STR/581 Wk1 Apply Case Study Analysis: "Case 6 Fixer Upper: Expanding the Magnolia Brand" Through a collection of busines
$ 4.5

ATI RN Fundamentals Proctored Focus
$ 8

CS1027A Midterm Exam Oct 26 2019 Final Solutions
$ 16

NR 507 Week 1 Assignment: Case Study – Hypersensitivit (graded)
$ 12.5

[TEST BANK] for Essentials of Statistics 7th Edition By Mario F. Triola
$ 25
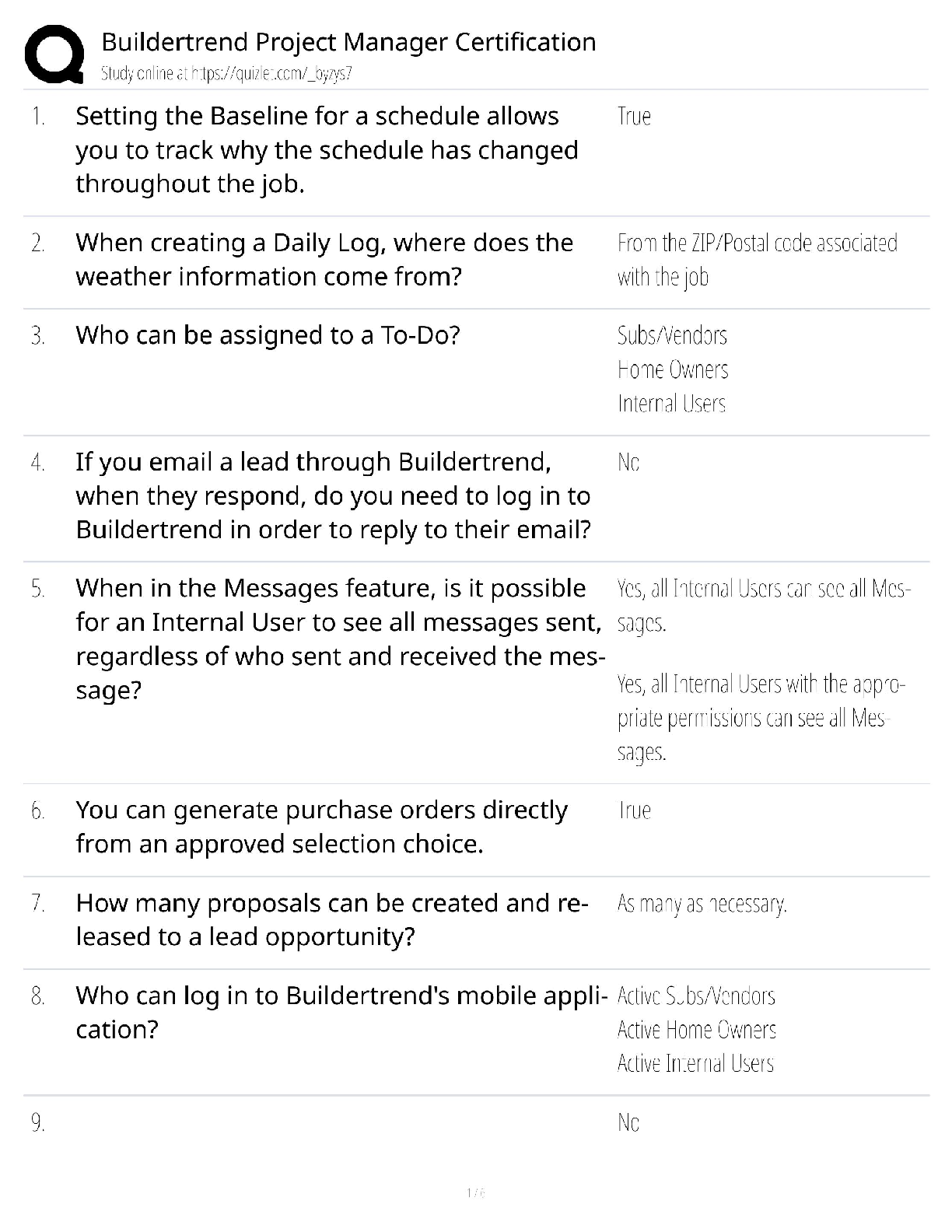
Buildertrend Project Manager Certification / Score 100% / 2025 Study Guide & Test Bank
$ 8

WGU patho D236 questions with correct answers
$ 14
.png)
SAFe Agilist 5.0 Questions and Answers with Complete Solutions
$ 10

Dynatrace Associate Certification Complete Study Guide Questions and Answers 2022
$ 11

{HESI TEST BANK V1 WITH}HESI Math Questions, HESI A&P Questions, HESI Reading Questions, HESI Vocabulary, HESI A2: Math practice test, BEST HESI A2 version 1 and 2, HESI Math Questions!!!, HESI A2 Vocabulary from book, HESI A2 - Reading Comprehension!, HESI A2 Entrance, HESI... WITH COMPLETE SOLUTIONS GRADE A+ (TOTAL 1059 QUESTIONS)
$ 11

Human Trafficking
$ 20

Critical Care HESI Practice exam With 600Questions and Answers 2024 2025 RATED A
$ 36.5
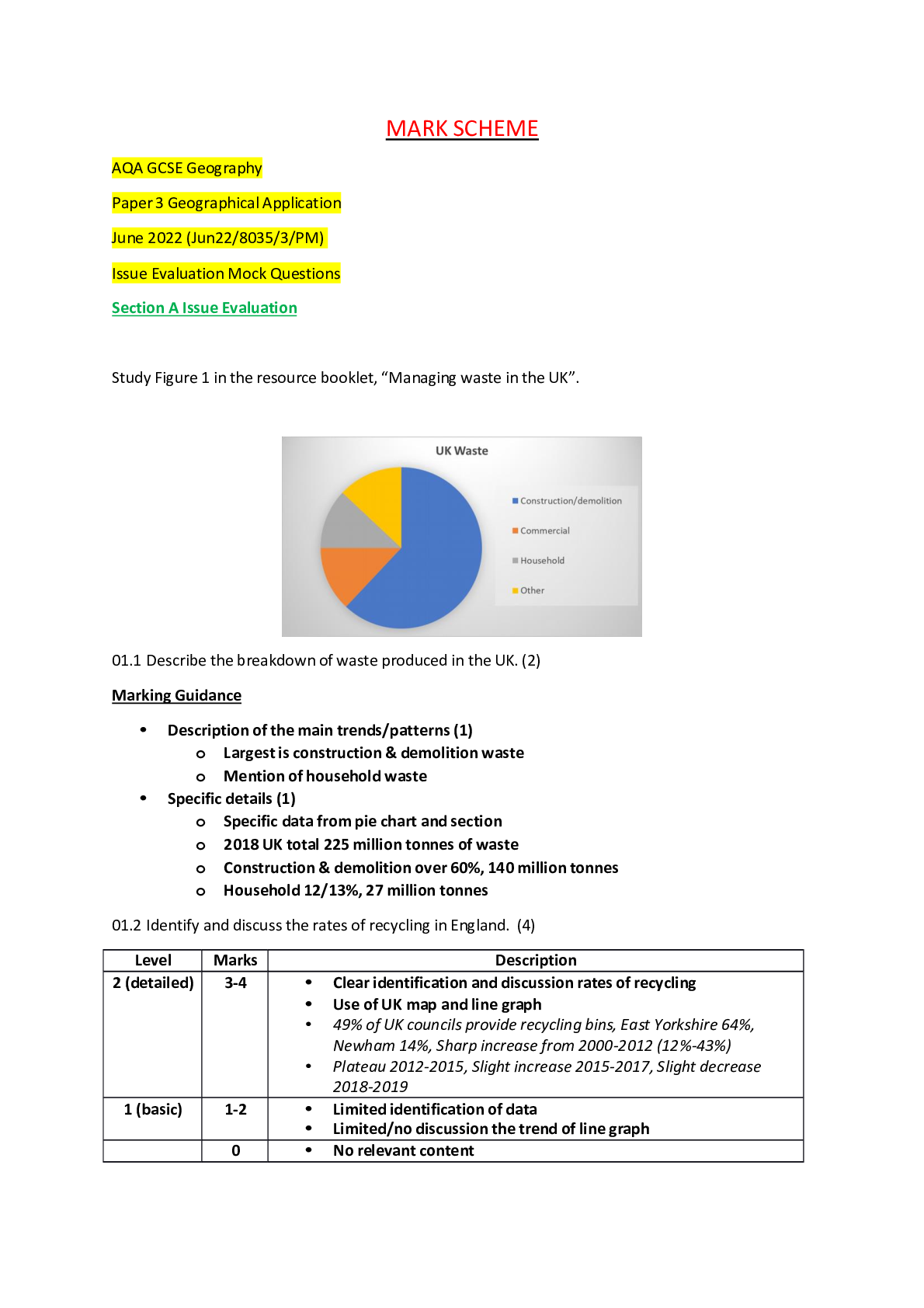
AQA GCSE Geography Paper 3 Geographical Application June 2022 (Jun22/8035/3/PM) Issue Evaluation Mock Questions MS
$ 10

>_ A Level Computer Science H446/01: Computer Systems || Question Paper OCT 2021
$ 6

WGU C965 - EDUC 4112 Teaching in the Middle School - Complete FA Review 2024
$ 11

📚 Case Study – Betty Neuman’s Theory Assignment 📚
$ 7.5
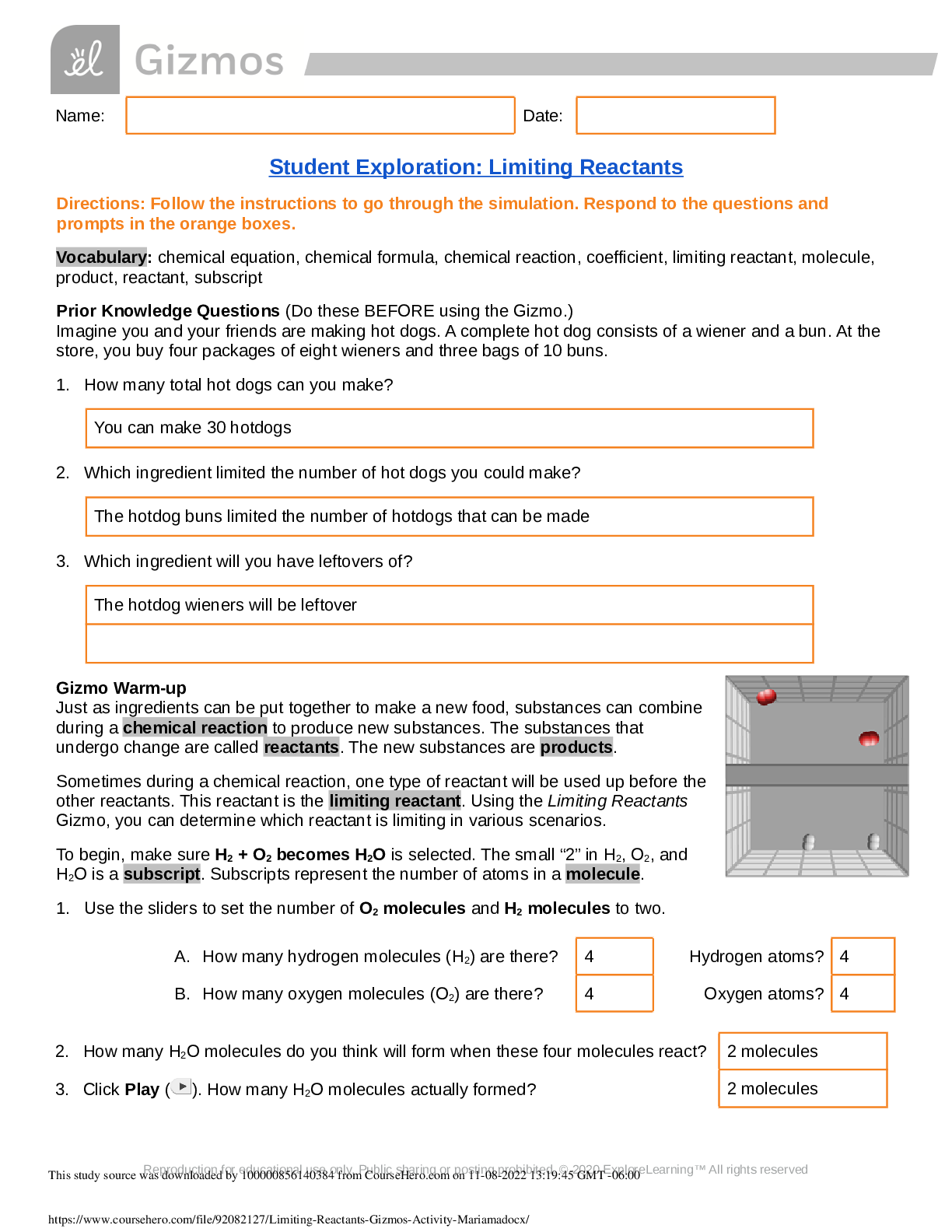
Limiting Reactants GIZMO {complete questions and answers}
$ 5

Skyler Hansen - Medical Case 5 Documentation Assignment Complete Solution
$ 8

SPHR-SHRM-SCP Practice Exam With Complete Solution
$ 7

A Level Chemistry A H432/02 Synthesis and analytical techniques Sample Question Paper 2023/2024
$ 12

AQA GCSE MATHEMATICS 8300/3H Higher Tier Paper 3 Calculator Mark scheme June 2022 Version: 1.0 Final
$ 7
.png)
FL DCF 40 Hrs. CHILD CARE FACILITIES RULE AND REGULATIONS (RNRF)
$ 10.5

Cambridge International AS & A Level_Chemistry_9701/43 Mark Scheme_May/June 2021 | Paper 4 A Level Structured Questions
$ 7.5

Texas MPJE, Ultimate Texas MPJE 2022 | 343 Questions with 100% Correct Answers
$ 10

OCR Oxford Cambridge and RSA Monday 16 May 2022 - Morning GCSE (9-1) Religious Studies J625/03 Judaism Beliefs and teachings & Practices
$ 7

2025 CAPSTONE FUNDAMENTAL ASSESSMENT WITH NGN QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 17
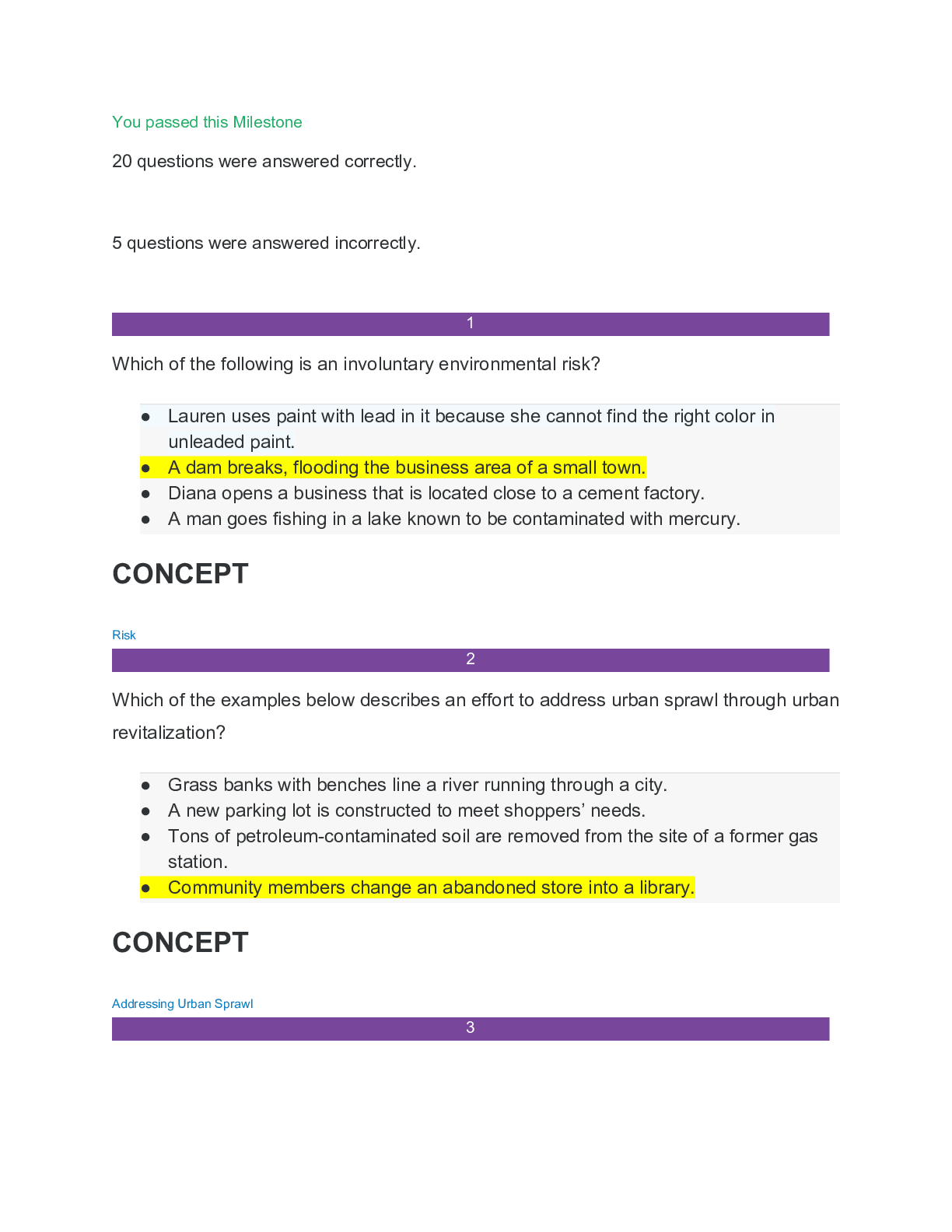
Environmental Science final milestone | 20 questions answered correctly
$ 9
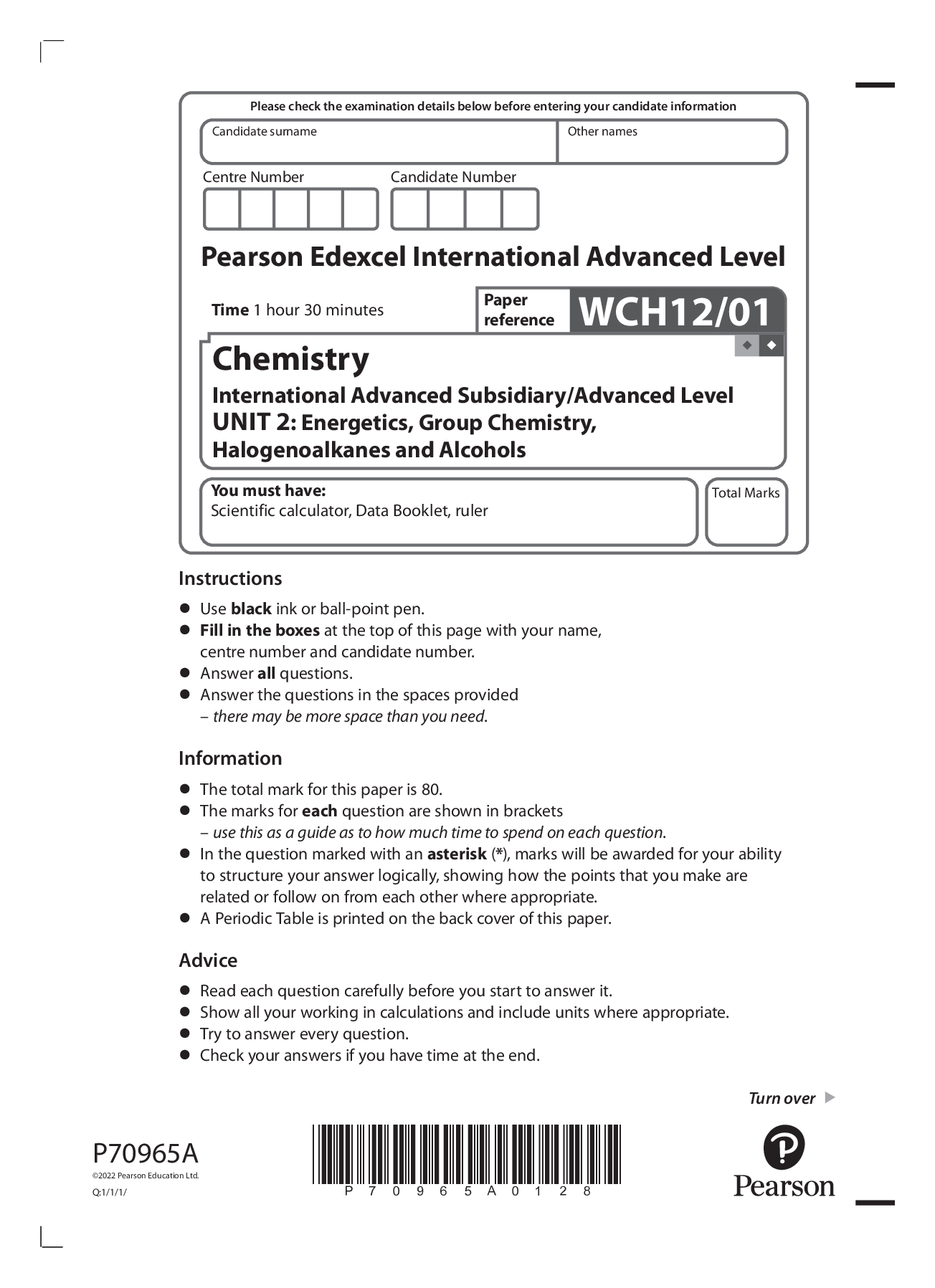
Pearson Edexcel WCH12/01 I AS/A Level Chemistry International Advanced Subsidiary/Advanced Level UNIT 2: Energetics, Group Chemistry, Halogenoalkanes and Alcohols. QP Jan 2022
$ 4
.png)
NCLEX LAB VALUES (from UWorld) Already Passed
$ 10

HUMN 303 Week 7 Assignment, What is Art - 13 Reasons Why Netflix Series: 2021
$ 15

4.1.5 Practice: Personal Health Plan Practice Assignment Health (S4202153)
$ 6

Solutions Manual For 3D Modeling & Animation A Primer, 1st Edition By Magesh Chandramouli
$ 30

REL 3308 QUIZ 3 GRADE A LATEST UPDATE
$ 12

VATI RN COMPREHENSIVE PREDICTOR FOCUSED (REVIEW STUDY GUIDE).RATED A+
$ 10.5

Examination 2 - MGT Capstone Exam-MGT 4479 : MANAGEMENT SEMINAR 2020
$ 17

CCLE 2022 QUIZ BANK WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 12

ASSESSMENT OF VISUAL FUNCTION, STUDY GUIDE.
$ 11

2023 AQA GCSE FRENCH 8658/WF Paper 4 Writing Foundation Tier Question Paper & Mark scheme (Merged) June 2023 [VERIFIED]
$ 7
.png)
AAAE ACE Operations Module 4 Latest 2023 Already Passed
$ 10

Carolina-Road-Driving-School-Final-Exam | Download for quality grades |
$ 15
.png)
QUIZ_1_ANSWERS (1)
$ 10

Pearson Edexcel IAL In A Level Accounting (WAC12/01) Paper 02 Corporate and Management Accounting Mark Scheme (Results) January 2022
$ 4

AS Level Further Mathematics B (MEI) Y413/01 Modelling with Algorithms May 2023 QP
$ 4

ATI RN Comprehensive Predictor 2025 (Forms A, B, C + Practice & Retake Exams) | Verified Questions & Answers | A+ Graded | Guaranteed Pass EXAM QUESTIONS AND CORRECT DETAILED ANSWERS (VERIFIED ANSWERS) ||ALREADY GRADED A+|| GUARANTEED PASS ||
$ 15

[eBook] [PDF] Teaching Business and Human Rights By Anthony Ewing
$ 25

NR602 Quiz Solution.GRADE A UPDATED FOR 2022
$ 15

2023 RN Test 3 NCLEX / Score 100% / New Version / 2025 Update / Exam Prep Test Bank
$ 9

eBook [PDF] The Iran Nuclear Deal Non-proliferation and US-Iran Conflict Resolution 1st Edition By Saira Khan
$ 29

BestPracticesNetworkSecurity.docx ISSC421 Best Practices for Network Security American
$ 10
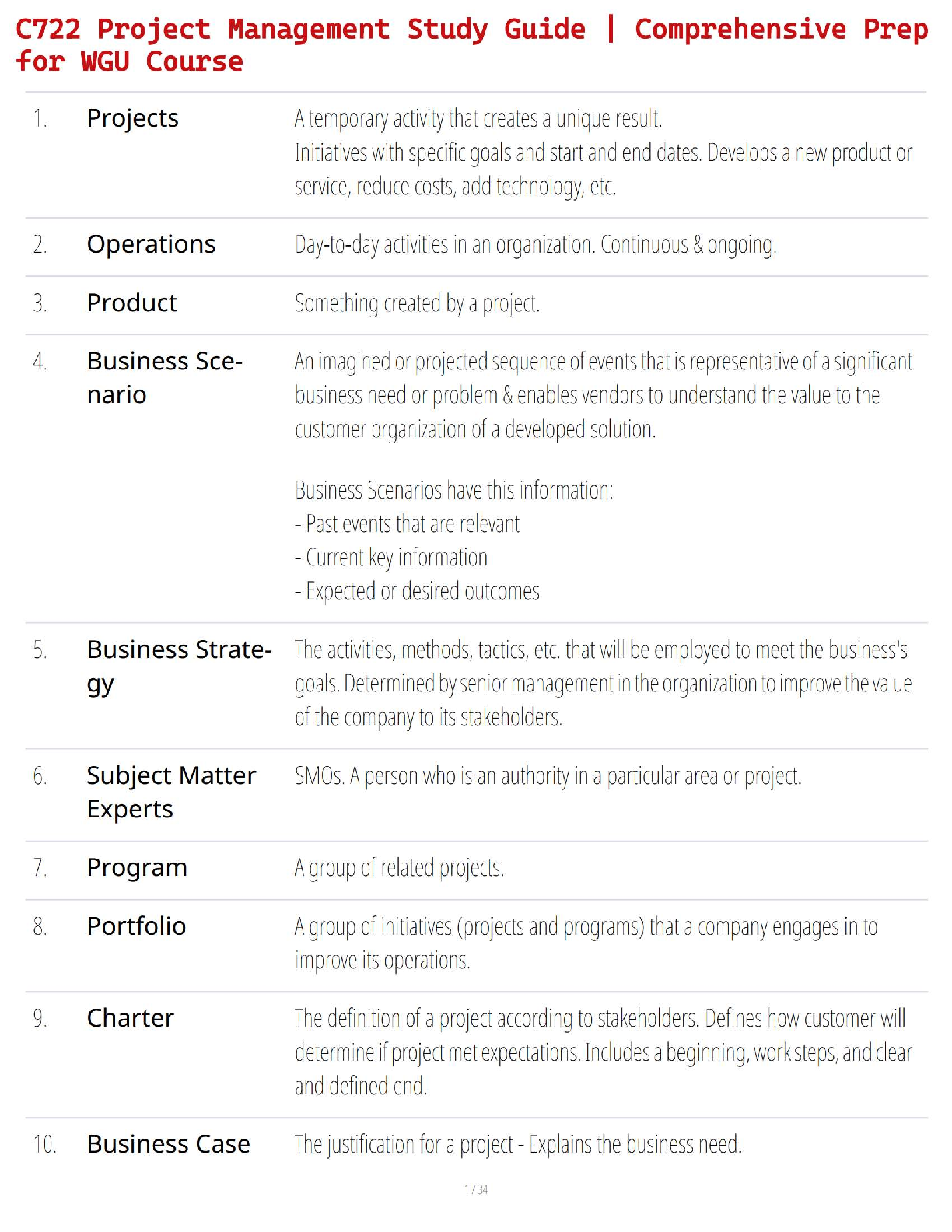
C722 Project Management Study Guide | Comprehensive Prep for WGU Course
$ 25.5

AQA GCSE GEOGRAPHY 8035/2 Paper 2 Challenges in the Human Environment Insert
$ 7

AZ 104 RENEWAL EXAM QUESTION AND ANSWER UPDATED 2023/2024 GRADED A+
$ 18

MLO SAFE NMLS safe test practice questions with accurate answers, 100% Accurate. 2022/2023
$ 11

NCLEX PRACTICE
$ 30.5

[eBook] [PDF] International Perspectives on Critical English Language Teacher Education Theory and Practice 1st Edition By Ali Fuad Selvi, Ceren Kocaman
$ 25

NUR 4500
$ 22

MSN 570 FINAL EXAM ADVANCED PATHOPHYSIOLOGY 2023 VERSION 3
$ 25

Intro To Python For Computer Science And Data Science TEST BANK
$ 27

eBook [PDF] Neoliberal Urban Governance Spaces Culture and Discourses in Buenos Aires and Chicago 1st Edition By Carolina Sternberg
$ 29
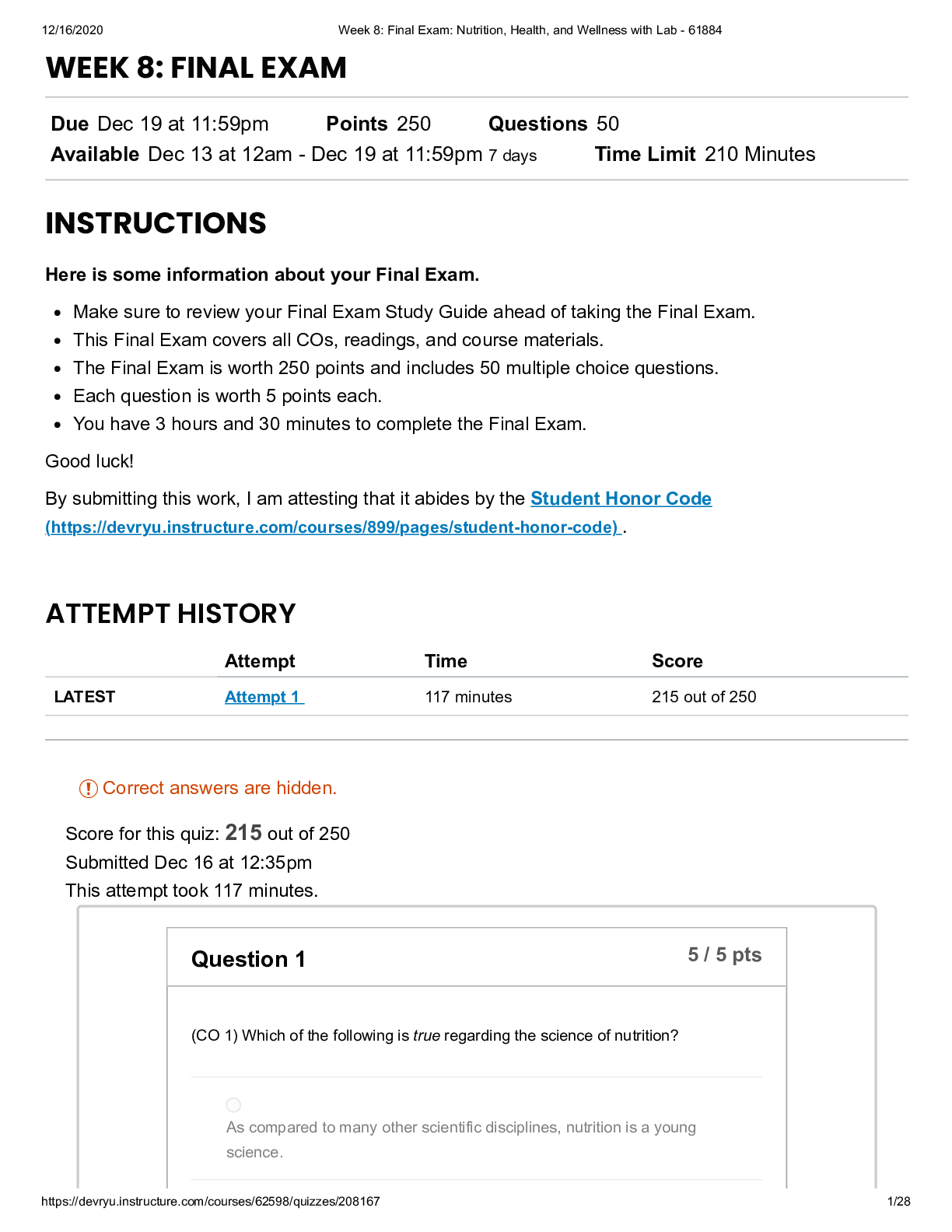
SCI 228 Week 3 Quiz: Nutrition, Health, and Wellness with Lab (May 2020)
$ 12

NRNP 6645 Week 7 Assignment; Week 7: Impulse Control Disorder
$ 9.5

Second Course in Statistics, A Regression Analysis, 8th edition By William Mendenhall, (Test Bank )
$ 25

ARCO SAT Subject Chemistry Practice Test
$ 11

ICS 100c final exam 2023.
$ 16

PROJ 587 Week 4 Discussion Two – Conflict Management - Paper Graded An A
$ 8

BIBL 104 Quiz 6, BIBL 104 - Quiz 6 LUO. Exam Questions and answers. Rated A+
$ 5

GCSE (9–1) Geography B _J384/03 Mark Scheme Nov 2020 | Geographical Exploration
$ 7.5

Introduction to Law 5th Edition By Joanne Hames, Yvonne Ekern (Instructor Manual)
$ 20

TEST BANK FOR INTERNATIONAL FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT 9TH EDITION BY CHEOL EUN, BRUCE RESNICK AND TUUGI CHULUUN. ISBN-13: 9781260013870 FULL TESTBANK ALL CHAPTERS INCLUDED|| LATEST AND COMPLETE UPDATE GRADED A+
$ 7.5

eBook PDF for Python for Accounting and Finance An Integrative Approach to Using Python for Research 1st Edition By Sunil Kumar
$ 25

AHIP module 1 | with 100% Correct Answers
$ 7

NRSE_4600_M3_A6_WA_TEMPLATE_Clinical Practice Project (CPP) Research: Module 3
$ 8

HESI EXIT LATEST EXAM 2022
$ 18

Pearson Edexcel IAL WCH14/01 I A Level Chemistry International Advanced Level UNIT 4: Rates, Equilibria and Further Organic Chemistry. Jan 2022
$ 4

AQA_AS-LEVEL CHEMISTRY. Exampro. MARK SCHEME. Practice Paper 2. Maximum marks: 101. Predicted Papers 2022.
$ 6
Roy adaptation model and Neuman system model
$ 12

NSG 310 FINAL EXAM STUDY GUIDE | VERIFIED GUIDE
$ 10

MAS-209-NOTE-pages-4-pdf
$ 10

ATI RN COMPREHENSIVE PREDICTOR 2024/ RN ATI COMPREHENSIVE FINAL EXAM RECENT UPDATE QUESTIONS AND VERIFIED SOLUTIONS WITH RATIONALLES/ ALREADY GRADED A+
$ 9.5

eBook Beyond Happiness and Meaning Transforming Your Life Through Ethical Behavior by Steven Mintz
$ 29
.png)
CLG 0010 DoD Government wide Commercial Purchase Card Spring 2022 Already Passed
$ 5
.png)
Pearson Edexcel Merged Question Paper + Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2022 Pearson Edexcel GCSE In Geography Spec A (1GA0) Paper 01
$ 6
.png)
Level 1 Anti-terrorism Awareness Training (JKO) Pre-Test(QUESTIONS & ANSWERS)
$ 4

[eTextBook] [PDF] Natural Philosophy On Retrieving a Lost Disciplinary Imaginary 1st Edition By Alister McGrath