Anatomy > STUDY GUIDE > BIOL 235 Assignment 2 (All)
BIOL 235 Assignment 2
Document Content and Description Below
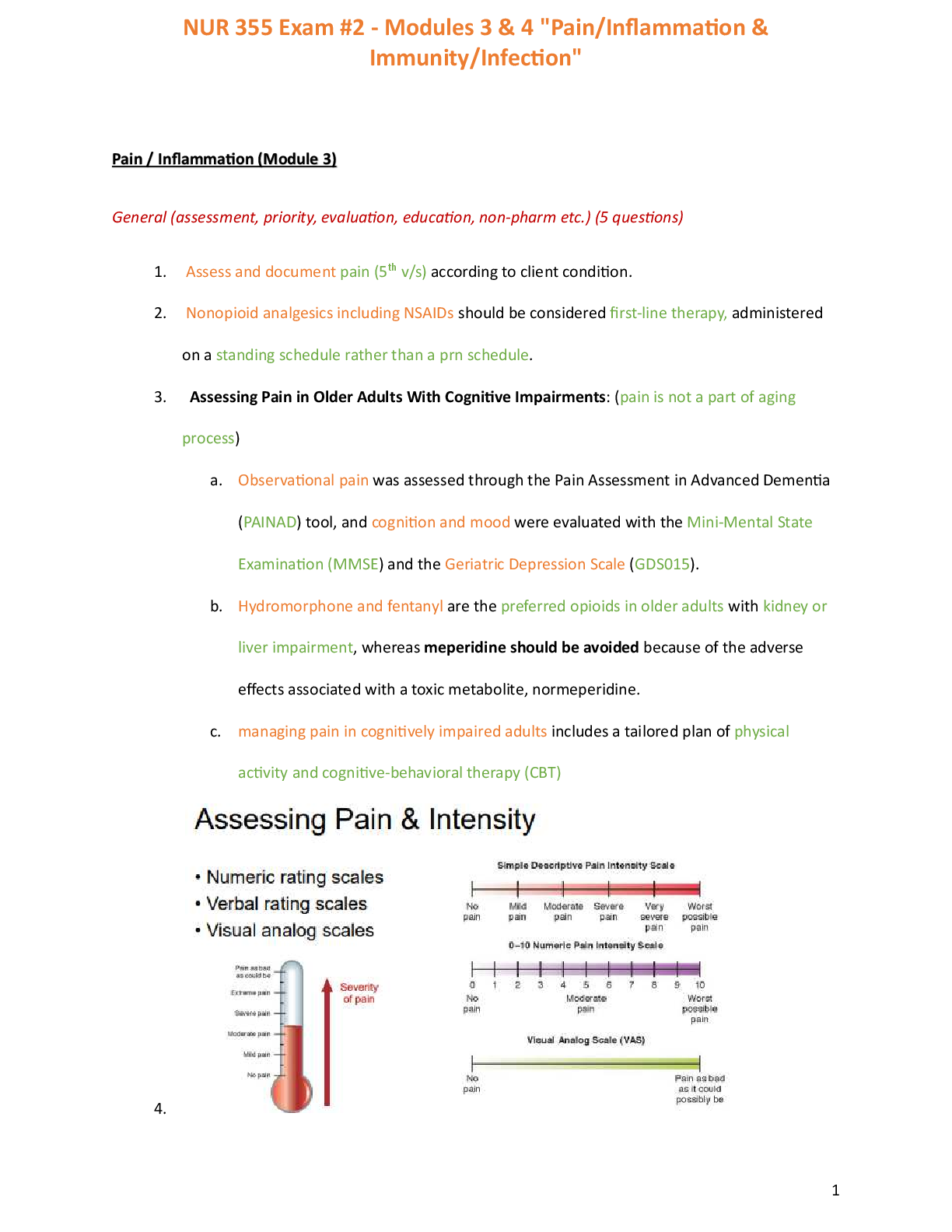
2. What are EPSPs and IPSPs, and how are they produced? Explain how these electrical currents are used in spatial and temporal summation to initiate or inhibit the generation of an action potential. ... EPSPs means Excitatory and Inhibitory ? Postsynaptic Potentials while IPSPs means Inhibitory Postsynaptic Potential (IPSP). A neurotransmitter causes either an excitatory or an inhibitory graded potential. A neurotransmitter that causes depolarization of the postsynaptic membrane is excitatory because it brings the membrane closer to threshold√. Excitatory neurotransmitters cause an opening of the ligand-gated sodium ion channels. As a result, Na+ ions influx and the cell becomes negative on the inside (depolarization). When the depolarization crosses certain threshold, neuron fires action potential. A neurotransmitter that causes hyperpolarization of the post- synaptic membrane is inhibitory√. During hyperpolarization, generation of an action potential is more difficult than usual because the membrane potential becomes inside more negative and thus even farther from threshold √ than in its resting state. When an inhibitory neurotransmitter activates the receptor site, it causes additional K+ channels to open which may cause k+ ions to flow out of the cell. This makes the inside of the cell to become negative. Inhibitory neurotransmitter can also open a ligand-gated Cl- ion channels causing influx of chloride ions which causes further hyperpolarization. Whether a neuron generates an action potential or not, it all balls down to the overall sum of EPSP’s and IPSP’s occurring at the neuron at any given time. Therefore, it is the summation of EPSP’s and IPSP’s that determines if a cell fires action potential or not. There are two types of summation, namely; Spatial summation - occurs when subthreshold EPSPs, occurring simultaneously at different points along the postsynaptic membrane, combine to cause a depolarization that reaches the threshold of excitation. For example, two EPSPs that depolarize the membrane close to the axon hillock by -2.5 millivolts may summate to bring the resting membrane potential of -70 millivolts to the neuron's threshold of excitation at -65 millivolts. Conversely, EPSPs and IPSPs may cancel each other out resulting in no triggered action potential. One EPSP depolarizes the membrane by -2.5 millivolts, while one IPSP hyperpolarizes the membrane by +2.5 millivolts. The threshold of excitation is not reached and no action potential is triggered.[ CITATION Tut \l 4105 ] Temporal summation - occurs when multiple subthreshold EPSPs from one neuron occur close enough in time to combine and trigger an action potential at the axon hillock. Postsynaptic potentials last for approximately 4 millliseconds. Action potentials last for only 2 millliseconds. Hence, multiple action potentials coming from a single neuron may cause graded EPSPs of longer duration that summate across time to trigger another action potential.[ CITATION Tut \l 4105 ]√ 10/10 3. Match the items in column A with the descriptions in column B to create the BEST MATCHES. Items in column A can be used only once when making matches to column B. There is only one correct answer for each blank space. Column A Column B 1. pia mater 2. denticulate ligaments 3. epidural space 4. dura mater 5. arachnoid mater 6. tract 7. nucleus 8. horn 9. nerve 10.ganglion 11.endoneurium 12.meningeal branch 13.ventral ramus 14.rami communicantes 15.dorsal ramus 16.tendon reflex 17.cranial reflex 18.spinal reflex 19.autonomic reflex 20.contralateral reflex 21.polysynaptic reflex 22.crossed extensor 12 √branch of spinal nerve serving vertebrae; vertebral ligaments and blood vessels of the spinal cord 6 √a group of axons with common functions within the spinal cord (or brain) 28 √responsible for transmitting nerve impulses for sensing crude touch 10 √a group of cell bodies found outside the spinal cord (or brain) 13 √branch of spinal nerve serving anterior trunk and extremities 1 √ composed of collagen and fine elastic fibers; highly vascular 11 √connective tissue coverings of axons within spinal nerves 29 √coordinate movements with head movement 25 √extension of the leg at the knee joint in response to tapping the patellar ligament 2 √extensions of pia mater; suspend spinal cord within vertebral canal [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 17 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Sep 12, 2021
Number of pages
17
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Sep 12, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
69