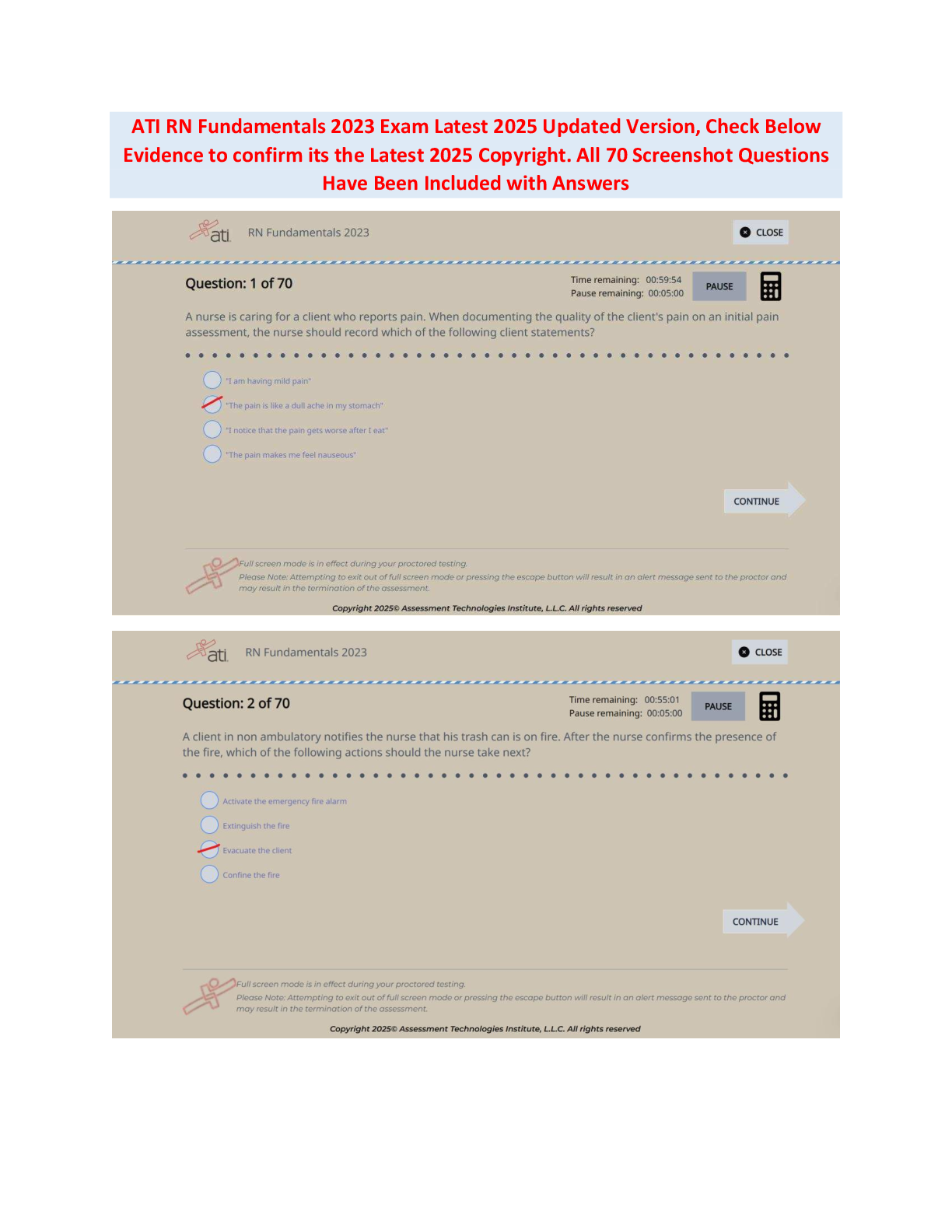
Northeastern UniversityNRSG 3323interventions EXAM 1 .
Document Content and Description Below
Anatomy Review • Four chambers separated by valves, whose main purpose is to prevent backflow of blood Atria right and left Ventricles right and left • Four valves in heart 2 atrioventricul ... ar (AV) valves – allow blood to go forward into the heart, and inhibit backflow of blood, open and close by pressure changes Tricuspid – right Mitral- left 2 semilunar (SL) separate from ventricles from specific structures Pulmonic – separates pulmonary artery from the left ventricle Aortic- stops bloods from aorta from the left ventricle Valves are unidirectional: can only open one way Valves open and close passively in response to pressure gradients in moving blood Subjective Data Collection Chest pain Dyspnea Orthopnea Cough Fatigue Cyanosis or pallor Edema Nocturia Cardiac history Family cardiac history Personal habits (cardiac risk factors) Objective Data INTERVENTIONS 2 Objective Data Collection: Inspection Eyes • Xanthelasma • Corneal arcus – yellowish/grey ring surrounding the iris associated with hyperlipidemia Neck vessels Neck vessels -Carotid artery -Jugular veins • Internal • External Palpation Note strength Compare palpation of carotid and auscultation of apical pulse Position the patient supine with the head of the table slightly elevated Using the palm of the hand palpate for pulsations going from apex to LSB to base. Palpate for apical pulse noting o location by ICS and distance from the midsternal line o size of pulsation o Quality of the apical pulse Auscultation Auscultate carotids with the bell listening for a bruit (blowing swishing sounds, blood flow turbulence) Ask the patient to stop breathing momentarily. Listen for a blowing or rushing sound--a bruit. Do not be confused by heart sounds or murmurs transmitted from the chest. Palpate carotid arteries Note strength Compare palpation of carotid and auscultation of apical pulse When auscultating the carotid pulses, what is a normal finding? 1. A soft blowing sound 2. A loud grunting noise 3. A beat simultaneous with the heart rate 4. No sound INTERVENTIONS 2 Objective Data: Inspection Objective Data Collection: Auscultation Auscultate the heart sounds Identify auscultatory areas Note the rate and rhythm Identify S1 and S2 Listen to S1 and S2 separately Listen for extra heart sounds Listen for murmurs Heart sounds Direction of blood flow Cardiac cycle Diastole Systole Events in the right and left sides Heart sounds First heart sound Second heart sound Effect of respiration Cardiac cycle S1 Heart Sound Occurs with closure of AV valves and thus signals beginning of systole Mitral component of first sound (M1) slightly precedes tricuspid component (T1) Usually hear these two components fused as one sound Can hear S1 over all precordium, but loudest at apex S2 Heart Sound Occurs with closure of semilunar valves and signals end of systole Aortic component of second sound (A2) slightly precedes pulmonic component (P2) Although heard over all precordium, S2 loudest at base [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 35 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$16.50
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 05, 2021
Number of pages
35
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 05, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
69