Micro Biology > CASE STUDY > BIOS 242 Week 7 Assignment; Microbiology GI Case Study (Bacteria, Escherichia coli, indole) with att (All)
BIOS 242 Week 7 Assignment; Microbiology GI Case Study (Bacteria, Escherichia coli, indole) with attached pictures: Summer 2021 | 100% GUARANTEED PASS.
Document Content and Description Below
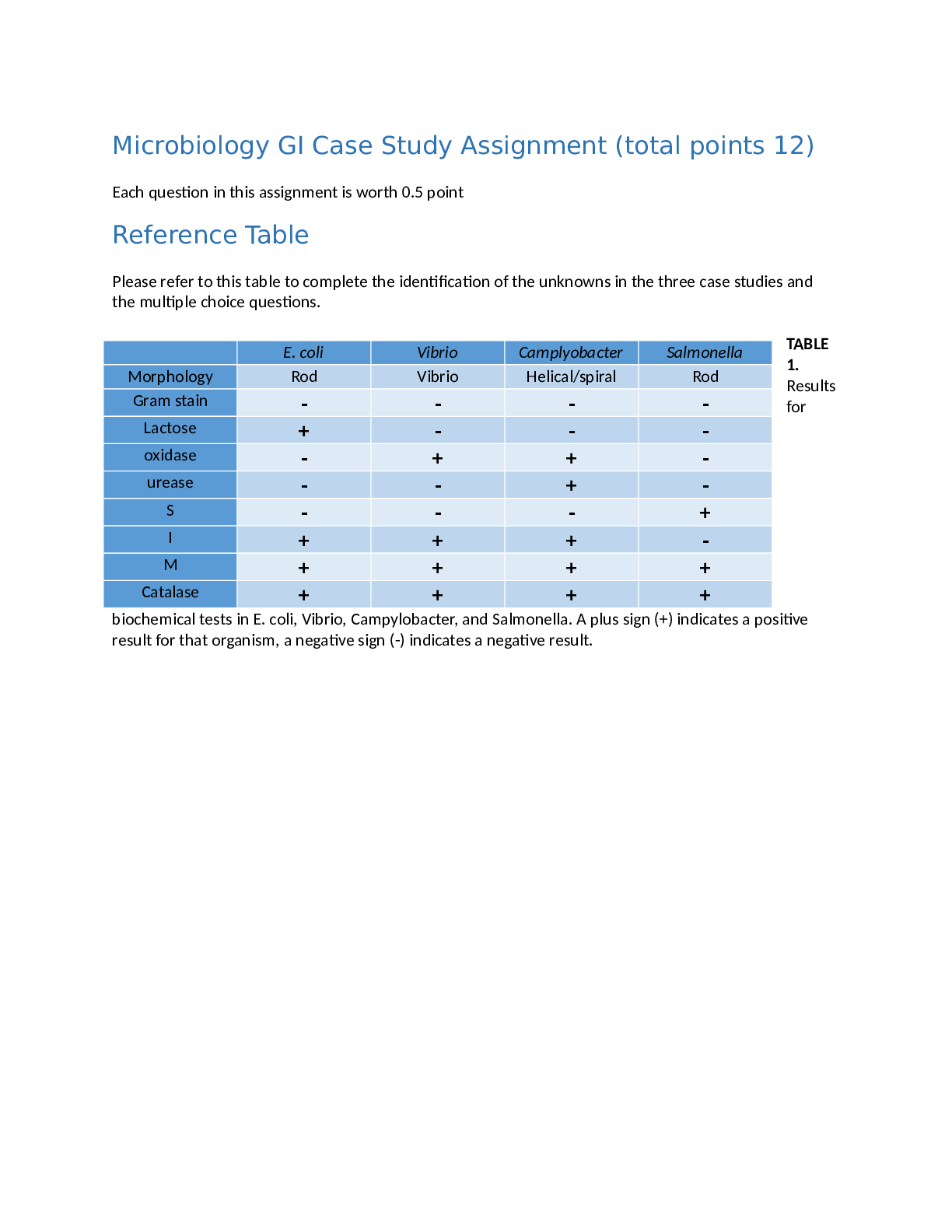
Microbiology GI Case Study Assignment (total points 12) Each question in this assignment is worth 0.5 point Reference Table Please refer to this table to complete the identification of the unknow ... ns in the three case studies and the multiple choice questions. TABLE 1. Results for biochemical tests in E. coli, Vibrio, Campylobacter, and Salmonella. A plus sign (+) indicates a positive result for that organism, a negative sign (-) indicates a negative result. Case Study 1 – Identify the unknown using biochemical tests Case Study 1: Patient is a 17 year old male recently returned from a mission trip to Central America. Presents with abdominal cramps and diarrhea that is unresponsive to antidiarrheal drugs. Stool cultures indicate the presence of a prokaryote. A Gram stain shows pink bacillus colonies. 1. Based on this result, is the microorganism Gram positive or Gram negative? What does this result tell us about its cell wall structure? Next, several biochemical tests are run to further identify the microorganism. Lactose fermentation is run for 24 hours at 37⁰C in lactose broth containing a Durham tube and phenol red indicator. The result shows a red broth with no air bubbles in the Durham tube. 2. What do these results mean in terms of this microorganism’s ability to ferment lactose? The next biochemical test is the oxidase test to detect the presence of cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme found in electron transport chain. This is done by using an oxidase swab on one of the colonies. The swab did not change color after 60 seconds. 3. What does this result tell us about cytochrome c oxidase in this organism? The next test is the urease test to test the microorganisms ability to convert urea to ammonia (a base) and carbon dioxide using the urease enzyme. Urea broth containing phenol red dye is used in this test. The result is a yellow broth color after incubation with the microorganism. 4. What does this result tell us about the presence of urease enzyme? The next test used is the SIM (sulfide, indole, motility) test. This tests for sulfide production, indole formation, and motility. This test is performed as a stab, and growth is noted after 24 hours at 37 C. This microorganism showed diffuse growth in the media with no black color along the stab line; upon adding three drops of Kovacs reagent, a pink color is noted. 5. Based on these results, determine if the following is positive or negative in the organism. A. Hydrogen sulfide Positive B. Indole Negative C. Motility Positive The final test is for the presence of the catalase enzyme. The catalase enzyme protects some organisms from the toxic effects of oxygen; this is an indicator that the microorganism can survive in the presence of oxygen either as an aerobe, facultative anaerobe, or microaerophile. This test is performed by adding the oxidizing agent hydrogen peroxide to a culture of the microorganism. The result showed bubbling. 6. Based on the above results, does this microorganism have the catalase enzyme? 7. Based on all the test results above results and the provided table, what microorganism is this? Explain your reasoning in 1-2 sentences. Case Study 2 Case Study 2: Patient is a 60 year old male recently returned from biking/camping expedition around Lake Michigan. Patient reports eating primarily at fast food restaurants during this week-long excursion. Presents with fever, nausea, abdominal cramps and diarrhea. Stool cultures indicate the presence of a prokaryote. A Gram stain shows pink helical-shaped colonies. 8. Based on this result, is the microorganism Gram positive or Gram negative? Next, several biochemical tests are run to further identify the microorganism. Lactose fermentation is run for 24 hours at 37C in lactose broth containing a Durham tube and phenol red indicator. The result shows red broth with no gas bubbles. 9. What do these results mean in terms of this microorganism’s ability to ferment lactose? The next biochemical test is the oxidase test to detect the presence of cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme found in electron transport chain. This is done by using an oxidase swab on one of the colonies. The swab turns purple within 60 seconds. 10. What does this result mean about the presence of cytochrome c oxidase? The next test is the urease test to test the microorganisms ability to convert urea to ammonia (a base) and carbon dioxide using the urease enzyme. Urea broth containing phenol red dye is used in this test. The result is a red broth color after incubation with the microorganism. 11. What does this result mean about the presence of urease? The next test used is the SIM (sulfide, indole, motility) test. This tests for sulfide production, indole formation, and motility. This test is performed as a stab, and growth is noted after 24 hours at 37 C. This microorganism showed diffuse growth in the media with no black color along the stab line; upon adding three drops of Kovacs reagent, a pink color is noted. 12. Based on these results, determine if the following is positive or negative in the organism. A. Hydrogen sulfide Negative B. Indole Positive C. Motility Positive The final test is for the presence of the catalase enzyme. The catalase enzyme protects some organisms from the toxic effects of oxygen; this is an indicator that the microorganism can survive in the presence of oxygen either as an aerobe, facultative anaerobe, or microaerophile. This test is performed by adding the oxidizing agent hydrogen peroxide to a culture of the microorganism. The result showed bubbling. 13. Based on the above results, does this microorganism have the catalase enzyme? 14. Based on the above results, what microorganism is this? Explain your reasoning in 1-2 sentences. Case Study 3 Case Study 3 -- Patient is a 53 year old female. Presents with fever, nausea, abdominal cramps and watery, slightly cloudy appearance to diarrhea with no blood or foul odor. Cultures indicate the presence of a curved shaped prokaryote that is pink after Gram stain. 15. Based on this result, is the microorganism Gram positive or Gram negative? Next, several biochemical tests are run to further identify the microorganism. Lactose fermentation is run for 24 hours at 37C in lactose broth containing a Durham tube and phenol red indicator. The result shows red broth with no gas bubbles. 16. What do these results mean in terms of this microorganism’s ability to ferment lactose? The next biochemical test is the oxidase test to detect the presence of cytochrome c oxidase, an enzyme found in electron transport chain. This is done by using an oxidase swab on one of the colonies. The swab turns purple within 60 seconds. 17. What does this result mean about the presence of cytochrome c oxidase? The next test is the urease test to test the microorganisms ability to convert urea to ammonia (a base) and carbon dioxide using the urease enzyme. Urea broth containing phenol red dye is used in this test. The result is a yellow broth color after incubation with the microorganism. What does this result mean? 18. What does this result mean about the presence of urease? The next test used is the SIM (sulfide, indole, motility) test. This tests for sulfide production, indole formation, and motility. This test is performed as a stab, and growth is noted after 24 hours at 37 C. This microorganism showed diffuse growth in the media with no black color along the stab line; upon adding three drops of Kovacs reagent, a pink color is noted. 19. Based on these results, determine if the following is positive or negative in the organism. A. Hydrogen sulfide Negative B. Indole Positive C. Motility Positive The final test is for the presence of the catalase enzyme. The catalase enzyme protects some organisms from the toxic effects of oxygen; this is an indicator that the microorganism can survive in the presence of oxygen either as an aerobe, facultative anaerobe, or microaerophile. This test is performed by adding the oxidizing agent hydrogen peroxide to a culture of the microorganism. The result showed bubbling. 20. Based on the above results, does this microorganism have the catalase enzyme? 21. Based on the above results, what microorganism is this? Multiple Choice Questions Choose the best answer to each of the following questions. Type your answer in the box provdied. 22. What is the organism that is gram negative, oxidase negative, urease negative, and H2S negative? a. Escherichia coli b. Vibrio c. Campylobacter d. Salmonella 23. Which of the following traits is characteristic of bacteria found in the GI tract? a. All are bacillus shape b. All can ferment lactose c. All contain oxidase d. All are gram negative 24. How can an E. coli infection be differentiated from a Salmonella infection? a. Gram stain b. SIM test c. Lactose fermentation d. Catalase test [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$15.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 06, 2021
Number of pages
12
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 06, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
135