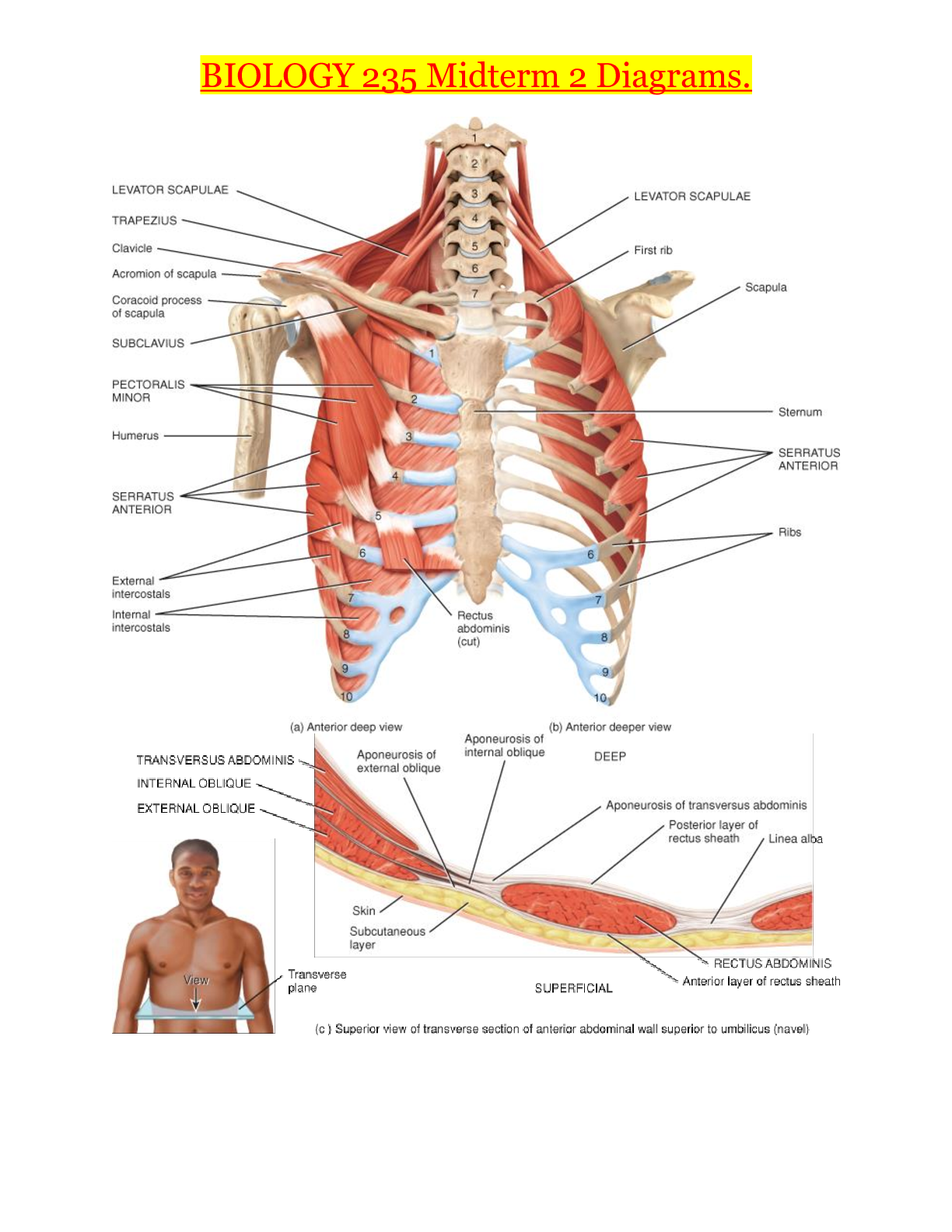
Pharm 293 -Evolve Question (completed chapter 1-22)
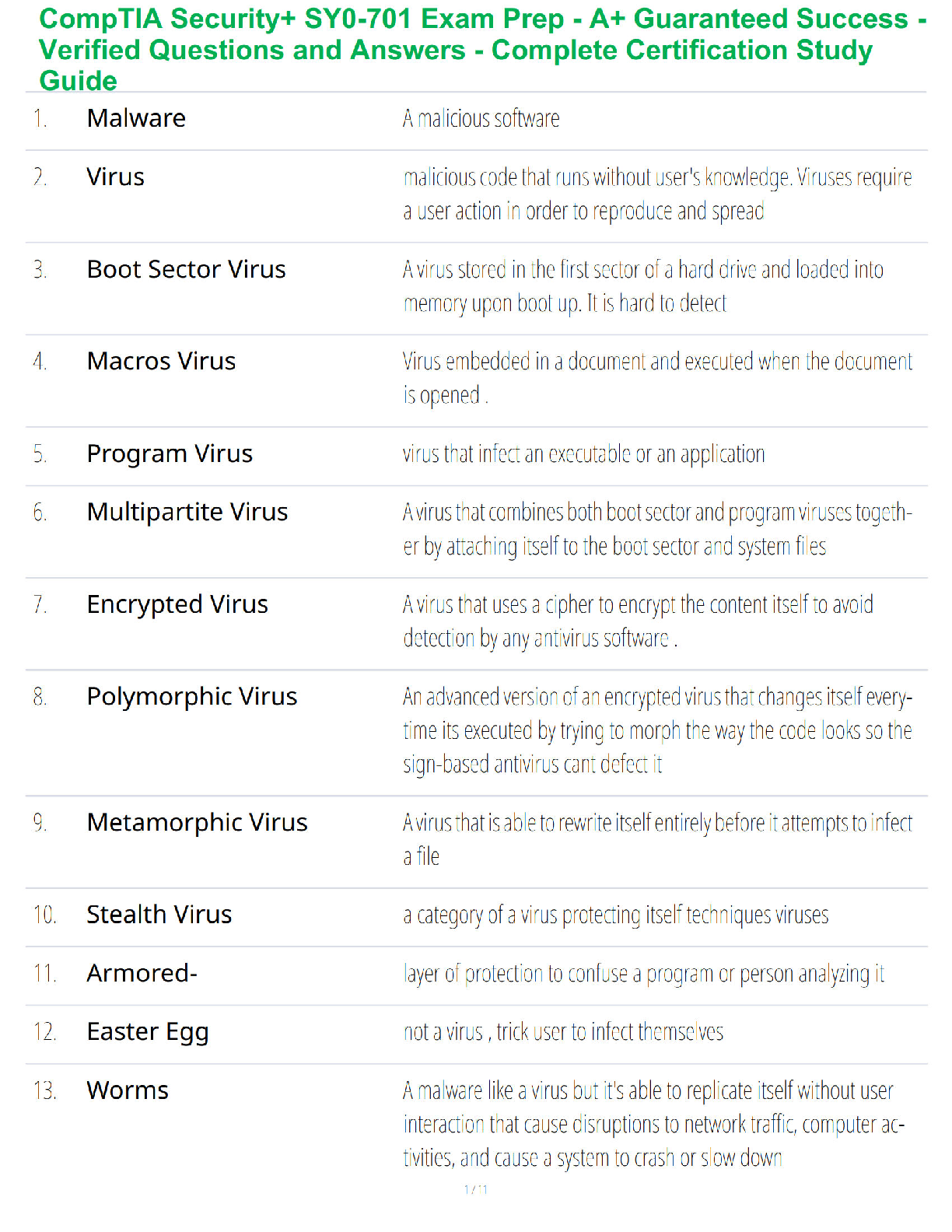
Chapter 1
1. In which step of the nursing process does the nurse determine the outcome of medication administration?
a. Implementation
b. Evaluation
c. Assessment
...
Pharm 293 -Evolve Question (completed chapter 1-22)
Chapter 1
1. In which step of the nursing process does the nurse determine the outcome of medication administration?
a. Implementation
b. Evaluation
c. Assessment
d. Planning
2. The nurse plans care for a male patient who is 80 years old. The nursing diagnosis is noncompliance with the medication regimen related to living alone, as evidenced by uncontrolled blood pressure. What should the nurse do next?
a. Collaborate with the provider on a new medication regimen.
b. Enlist the help of a home care nurse for pharmacotherapy.
c. Assess the impact of home self-management of medications.
d. Examine the results of nursing help with the medications.
3. Which statement is an example of objective data? (Select all that apply.)
a. The patient has had a fever for 5 days.
b. The patient says that she feels like someone is touching her arm.
c. The patient has clear urine.
d. The patient states that she has a headache.
e. The patient says that she has felt tired for almost a week.
4. What things should the nurse check when reviewing a prescription with a patient? (Select all that apply.)
a. The signature of the prescriber
b. The age of the patient
c. The patient‘s home address
d. The patient’s emergency contact
e. The route of administration
5. What information should the nurse chart when documenting medication administration? (Select all that apply.)
a. The dosage of medication administered
b. The time of administration
c. The patient’s age
d. Information about an “incident report” in the patient’s chart
e. The route of administration
Chapter 2
1. What is the study of physiochemical properties of drugs and how they influence the body called?
a. Pharmacokinetics
b. Pharmacotherapeutics
c. Pharmacology
d. Pharmacodynamics
2. Which statement best describes pharmacokinetics?
a. Physiologic interaction between a drug and body cells
b. Adverse effects and toxic reactions to medications
c. What the body does to the drug after it is administered
d. Converts medication into its active chemical substance
3. What is another term for biotransformation of a drug?
a. Excretion
b. Absorption
c. Metabolism
d. Dilution
4. A drug given by which route is altered by the first-pass effect?
a. Sublingual
b. Intravenous
c. Oral
d. Subcutaneous
5. Drug half-life is defined as the amount of time required for 50% of a drug to:
a. be absorbed by the body.
b. exert a response.
c. be eliminated by the body.
d. reach a therapeutic level.
6. Which nursing action will increase the absorption of a medication administered intramuscularly (IM)?
a. Administer the medication via the Z-track method.
b. Apply ice packs to the injection site.
c. Lower the extremity below the level of the heart.
d. Massage the site after injection.
7. When administering two medications that are highly protein bound, the nurse understands to monitor the patient carefully for which effect?
a. Increase in the risk of drug–drug interactions
b. Hypovolemic shock caused by a low albumin level
c. Immediate improvement in the patient’s condition
d. A short duration of medication action
8. To achieve the most rapid onset of action, the health care provider will prescribe the medication to be administered by which route?
a. IM
b. IV
c. Subcut
d. Intrathecally
9. Patients with renal failure would MOST likely have problems with which pharmacokinetic process?
a. Absorption
b. Metabolism
c. Distribution
d. Excretion
10. What is the ratio between a drug’s therapeutic effects and toxic effects called?
a. Therapeutic index
b. Tolerance
c. Cumulative effect
d. Affinity
11. A patient asks the nurse why a lower dose of IV pain medication is being given than the previous oral dose. What is the nurse’s best response to the patient?
a. “A large percentage of an intravenously administered drug is metabolized into inactive metabolites in the liver.”
b. “Medications given intravenously are not affected by the first-pass effect.”
c. “Drugs administered intravenously enter the portal system before systemic distribution.”
d. “Medications given orally bypass the portal circulatory system.”
12. The nurse understands that drugs exert their actions on the body by what process? (Select all that apply.)
a. Inhibiting the action of a specific enzyme
b. Making the cell perform a new function
c. Altering metabolic chemical processes
d. Interacting with receptors
13. The nurse knows that which factors will affect the absorption of orally administered medications? (Select all that apply.)
a. Presence of food in the stomach
b. Time of day
c. pH of the stomach
d. Form of drug preparation
e. Patient in high-Fowler’s position
Chapter 3
1. When calculating pediatric dosages, the nurse understands which method is MOST accurate for dosing calculations?
a. Calculated doses based on body weight need to be increased by 10% because of immature renal and hepatic function
b. Medication dosing calculated according to body weight because it is based on maturational growth and development
c. Use of drug reference recommendations based on mg/kg of body weight.
d. Dosage calculation by body surface area because it takes into account the difference in size for children and neonates
2. The nurse is teaching a pregnant patient about the effects of medication on fetal development. The nurse understands the greatest risk for medication effects on developing fetuses occurs during which time period?
a. First trimester
b. Third trimester
c. Birthing process
d. Second trimester
3. Knowing that the albumin in neonates and infants has a lower binding capacity for medications, the nurse anticipates the health care provider will perform which action to minimize the risk of toxicity?
a. Increase the amount of drug given.
b. Decrease the amount of drug given.
c. Administer the medication intravenously.
d. Shorten the time interval between doses.
4. The physiologic changes that normally occur in older adult patients have which implication for drug response?
a. Protein binding is more efficient.
b. Drug metabolism is quicker.
c. Drug elimination is faster.
d. Drug half-life is lengthened. (b/c of slower digestion)
5. While conducting a health history for an older adult patient with heart failure, the patient tells the nurse, I have chronic constipation.” The nurse suspects this gastrointestinal complaint is caused by which class of drugs?
a. Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs
b. Calcium channel blockers
c. Potassium-sparing diuretics
d. Anticoagulants
6. The nurse working in a prenatal clinic recognizes that the safety or potential harm of drug therapy during pregnancy relates to which factor?
a. Maternal blood type
b. Drug properties
c. Fetal sex
d. Diet of the mother
7. A mother of a 1-month-old infant calls the clinic and asks the nurse if the medication she is taking can be passed to her infant during breastfeeding. What is the nurse’s best response to the mother’s question?
a. You should not take any medication while breastfeeding.
b. Only certain medications pass to infants while breastfeeding.
c. I will leave the health care provider a message to return your call.
d. Drugs can cross from mother to infant in breast milk, so it will depend on the drug you are taking.
8. A nurse working with older adult patients is concerned about the number of medications prescribed for each patient. Which older adult assessment should be of highest priority related to polypharmacy?
a. Nonadherence to drug regimen
b. Cost of medications
c. Drug Interactions
d. Schedule of medications
Chapter 4
1. What is the nurse’s role in the development of new and investigational drugs?
a. Select healthy older adult patients to participate in Phase I studies.
b. Inform patients of the specific drug they will receive during phase II studies.
c. Monitor and report any adverse effects observed during Phase IV studies.
d. Identify patients who receive a placebo drug during Phase III studies.
2. What is the professional responsibility of the nurse?
a. Transfer care of a patient to another professional nurse if caring for the patient would violate personal ethical principles.
b. Withhold information from the patient as requested by the family.
c. Impose his or her own values on the patient when doing so would help the patient??tre
d. Use beneficence, the duty to do no harm to a patient.
3. Which statement best reflects the nurse’s understanding of cultural influences on drug therapy and other health practices?
a. Most cultures are fairly standard in reference to the use of medications during illness.
b. Dietary habits and practices can be of little value to the care of a sick adult.
c. Administration of some drugs may elicit varied responses in specific racial/ethnic groups.
d. Regardless of one’s cultural background, it is crucial to adhere to recommended medical practices.
4. When teaching a patient about the legalities regarding a prescription for methylphenidate (Ritalin), which statement is most accurate?
a. Methylphenidate (Ritalin) is a C-IV controlled substance that is only to be refilled five times per prescription.
b. Methylphenidate (Ritalin) is a C-III controlled substance for which a prescription will expire in 6 months.
c. Methylphenidate (Ritalin) is a C-I controlled substance that can only be prescribed according to an approved protocol.
d. Methylphenidate (Ritalin) is a C-II controlled substance that cannot be refilled and can only be filled with a written prescription.
5. The nurse is assessing a patient’s culture and race on admission to the hospital. Which concept is important for the nurse to understand regarding drug therapy as it relates to different races of individuals?
a. Polypharmacy
b. Pharmacodynamics
c. Polymorphism
d. Pharmacokinetics
6. An emergency department nurse is documenting the medication history of a patient of Asian culture. The patient states, “I am not taking any medications,” but the nurse observes a bottle of capsules in the patient’s medicine bag. What information should the nurse collect next?
a. Health care provider name
b. Vital signs and pulse oximetry
c. Past use of medicine and home remedies
d. Use of herbs or over-the-counter medications
7. New drugs must go through extensive research and testing before approval for use in humans. The nurse knows that the average length of time a medication is researched before being prescribed for humans is how many years?
a. 6 to 8
b. 10 to 12
c. 2 to 4
d. 14 to 16
8. A pharmaceutical company is voluntarily conducting a postmarketing study to obtain further proof of the therapeutic effects of a new drug. What phase of drug study is this considered?
a. Phase II
b. Phase IV
c. Phase III
d. Phase I
9. What legislation, which was passed in 1996, ensures that the privacy of patient information is protected?
a. Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act
b. Durham-Humphrey Amendment
c. Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
d. Medicare Prescription Drug, Improvement, and Modernization Act
10. There are multiple factors that affect medication response. The nurse recognizes which factors have a possible effect on the medication response? (Select all that apply.)
a. Level of education
b. Diet and nutrition
c. Body composition
d. Patient compliance with therapy
e. Use of alternative therapies
f. Socioeconomic factors
g. Genetic influences
Chapter 5
1. A patient is transferred from an intensive care unit (ICU) to a general medical unit. Which nursing action is MOST appropriate to prevent a medication error?
a. Perform a medication reconciliation for the patient during care transition.
b. Ask the patient what medications need to be taken while in the hospital.
c. Communicate a verbal report face to face from the transferring nurse.
d. Contact the health care provider to rewrite all drug prescriptions.
2. When admitting an older adult patient to an acute care setting, which nursing strategy is most appropriate to prevent medication errors?
a.
b. Ask the patient to provide you with a written list of all medications being taken at home.
c. Call the primary care physician to verify current medications.
d. Ask the patient or family to bring in all medications the patient was taking at home.
e. Ask the patient’s family to verify medications the patient was taking at home.
3. Why are specific medications identified as “high-alert” medications?
a.
b. These medications are responsible for adverse drug events.
c. States require that these drugs be on the high-alert list.
d. These drugs have increased potential for significant patient harm.
e. Registered nurses must administer these medications.
4. The nurse administers a medication to the wrong patient. Which is the appropriate nursing action following this error?
a. Report the error and document the medication on the patient chart.
b. Document the medication error. No further action is required.
c. Notify the health care provider and document the error on an incident report.
d. Assess the patient for an adverse reaction and report if an adverse event occurs.
5. Which nursing action helps the nurse to prevent a medication error?
a. Ask the patient what condition the medication is for before administering.
b. Administer the patient’s medications using his or her own supply of medications while in the hospital.
c. Administer any medications that the patient had on admission or transfer.
d. Encourage the patient to ask questions if the medication is different than expected.
6. What organization announced new regulations requiring bar codes for all prescription and over-the-counter (OTC) medications?
a. Federal Bureau of Investigation (FBI)
b. U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA)
c. Department of Health and Human Services (DHHS)
d. Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA)
7. In which step of the medication process can a medication error occur? (Select all that apply.)
a. Procurement
b. Transcribing
c. Prescribing
d. Administration
e. Verification (Verification is a step in the medication reconciliation process.)
8. The nurse knows that the medication reconciliation process involves which steps? (Select all that apply.)
a. Clarification
b. Reporting
c. Verification
d. Administration
e. Reconciliation
Chapter 6
1. Which statement best supports the nursing diagnosis of “Deficient knowledge related to medication therapy”?
a. Patient is not reporting adverse effects as directed.
b. Patient is unwilling to comply with medication therapy.
c. Patient is not taking medication as directed.
d. Patient is unable to verbalize reason for taking the medication.
2. When planning care for an assigned patient, the nurse identifies the outcome of “Patient will be able to safely self-administer enoxaparin (Lovenox) subcutaneously upon discharge.” Which method is best for the nurse to use in evaluating the patient’s achievement of this outcome?
a. Give the patient detailed written instructions illustrating the procedure.
b. Ask the patient to verbalize the correct administration procedure step by step.
c. Demonstrate the correct administration procedure to the patient.
d. Observe the patient’s return demonstration of the administration procedure.
3. The nurse is educating a patient with newly diagnosed type 1 diabetes mellitus. When the nurse has the patient demonstrate self-injection of insulin, which domain of learning is the nurse assessing?
a. Psychomotor domain
b. Affective domain
c. Physical domain
d. Cognitive domain
4. What phase of the nursing process provides a framework for the nurse to provide patient and family education about a new medication?
a. Assessment
b. Evaluation
c. Planning
d. Implementation
5. How does the nurse best evaluate the patient’s understanding of teaching about a new medication?
a.
b. Assess the patient for response to the medication.
c. Observe the patient taking the medication.
d. Document the education session and most used teaching strategy.
e. Ask specific questions to assess the patient’s understanding.
6. What is the MOST appropriate time the nurse should begin the patient education and the teaching-learning process?
a. After the medical diagnosis is established
b. When there are written prescriptions for teaching
c. At the time discharge planning is begun
d. Upon the patient’s admission to the health care setting
7. The nurse is providing discharge teaching to an older patient with short-term memory problems. Which strategies will the nurse use in educating the patient? (Select all that apply.)
a. Instruct the patient to take all medications in the morning.
b. Provide written instructions for home use.
c. Repeat information frequently.
d. Encourage use of daily medication containers with alarms.
e. Perform several short teaching-learning sessions.
Chapter 7
1. What is the best description of the consumer safety precautions for herbal supplements?
a. Reliable data on product efficacy is scarce.
b. Medicinal herbs are under strict U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) control.
c. Herbs in tamper-resistant containers are safe.
d. The package labeling clearly states product safety.
2. Which entity regulates medicinal herbs?
a. FDA
b. Dietary Supplement Health and Education Act of 1994 (DSHEA)
c. U.S. Department of Agriculture (USDA)
d. American Medical Association (AMA)
3. A patient with atrial fibrillation requests a cup of chamomile tea. The nurse denies the patient’s request because of the medication the patient is taking. What is the medication?
a. Calcium channel blocker
b. Beta-adrenergic blocker
c. Cardiac glycoside
d. Anticoagulants
4. A male patient who abuses alcohol tells the nurse that he is treating himself with kava. Which instruction should the nurse include in patient teaching?
a. Avoid using the kava with alcohol.
b. Use another herb besides kava.
c. Stop taking the kava now.
d. Use either the kava or the alcohol.
5. A patient who takes ginseng to improve memory takes many prescription drugs as well. Which laboratory parameter should the nurse check before administering medication as a means of assessing the pharmacokinetic effect of ginseng in this patient?
a. Liver enzymes
b. Serum creatinine
c. Mental status
d. Urine bilirubin
6. Which descriptions apply to the market for medicinal herbs in the United States? (Select all that apply.)
a. Viewed with growing skepticism
b. Used with traditional therapies
c. Less than $1 million in sales annually
d. Used by less than 40% of the population
e. Growing in numbers of users
f. Heavily regulated by federal law
Chapter 38
1. What is the priority assessment data for a client prescribed antibiotic therapy?
a. Immunizations
b. Cardiac dysrhythmias
c. Allergies
d. History of seizures
2. Which information should the nurse include in discharge teaching for a client prescribed doxycycline (Vibramycin)?
a. “Take the medication with milk to minimize gastrointestinal upset.”
b. “Apply sunscreen or wear protective clothing when outdoors.”
c. “Take the medication until you have no fever and feel better.”
d. “Keep the remainder of the medication in case of recurrence.”
3. Which adverse effect can result if tetracycline is administered to children younger than 8 years of age?
a. Delayed growth development
b. Drug-induced neurotoxicity
c. Permanent discoloration of the teeth
d. Gastrointestinal (GI) and rectal bleeding
4. A client who is allergic to penicillin is at increased risk for an allergy to which drug?
a. Erythromycin (E-mycin)
b. Gentamicin (Garamycin)
c. Cefazolin sodium (Ancef)
d. Demeclocycline (Declomycin)
5. When planning care for a client receiving a sulfonamide antibiotic, it is important for the nurse to perform which intervention?
a. Take the medication with dairy products such as milk or yogurt.
b. Advise the client to report any tinnitus to the health care provider.
c. Avoid direct sun exposure and tanning beds.
d. Encourage fluid intake of 2000 to 3000 mL/day.
6. When administering a nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug and a penicillin drug together, the displacement of the penicillin antibiotic from the protein-binding sites will result in which effect?
a. Absence of free drug in the blood
b. Increased free drug in blood
c. Decreased free drug in blood
d. No change in free drug in blood
7. During antibiotic therapy, the nurse will assess the client for a condition that may occur because of the disruption of normal flora. The nurse knows this as what condition?
a. Superinfection
b. Hypersensitivity
c. Allergic reaction
d. Organ toxicity
8. A client prescribed azithromycin (Zithromax) expresses concern regarding GI upset that was experienced when previously prescribed an erythromycin antibiotic. What is the nurse’s best response?
a. “Take an over-the-counter antiemetic to lessen the nausea.”
b. “I will call the health care provider and request a different antibiotic.”
c. “Stop taking the drug if you experience heartburn and diarrhea.”
d. “This drug is like erythromycin with less gastrointestinal adverse effects.”
9. In an effort to prevent superinfections of the GI tract such as Clostridium difficile, the nurse will instruct clients to eat which foods?
a. Cultured dairy products such as yogurt
b. Low-fat meats such as chicken and pork
c. Multigrain wheat bfvc /.,m
d. Raw fruits and vegetables
10. Which statement best describes health care–associated infections?
a. The infection develops in response to various antibiotics.
b. Clients are admitted to the hospital with an infectious disease.
c. The infection was not incubating at the time of admission.
d. They develop in more than 15% of hospitalized clients.
11. A client with a known heart condition is prescribed an antibiotic before a dental procedure. What type of antibiotic therapy is this considered?
a. Prophylactic
b. Supportive
c. Definitive
d. Empiric
12. Bacterial resistance to antibiotics can occur with which situations? (Select all that apply.)
a. Antibiotics that are prescribed to treat a viral infection
b. Clients stop taking an antibiotic when they feel better.
c. Antibiotics that are prescribed according to culture and sensitivity reports
d. Microorganisms arriving from foreign countries and overseas ports
e. Taking an antibiotic and an antiviral medication at the same time
Chapter 39
1. For a client receiving an intravenous (IV) infusion of gentamicin (Garamycin), the nurse would monitor which laboratory values?
a. Serum glutamic-oxaloacetic transaminase and alanine transaminase
b. Prothrombin time and partial thromboplastin time
c. Hematocrit and hemoglobin
d. Blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and creatinine
2. The nurse will question the use of a fluoroquinolone antibiotic in a client already prescribed which medication?
a. Furosemide (Lasix)
b. Omeprazole (Prilosec)
c. Amiodarone (Cordarone)
d. Metoprolol (Lopressor)
3. Which is a complication of vancomycin IV infusions?
a. Cardiomyopathy
b. Neurotoxicity
c. Red man syndrome
d. Angioedema
4. When performing discharge teaching for a client prescribed oral linezolid (Zyvox) to treat methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA), the nurse should emphasize which important information?
a. Stop the drug as soon as you feel better.
b. Take the drug with an antacid to avoid gastrointestinal (GI) upset.
c. Report any occurrence of constipation or facial flushing.
d. Avoid ingestion of foods containing tyramine.
5. The nurse should assess a client for nephrotoxicity and ototoxicity when administering which antimicrobial?
a. Erythromycin
b. Clindamycin (Cleocin)
c. Cefazolin (Ancef)
d. Gentamicin (Garamycin)
6. The nurse is planning care for a client prescribed once-daily IV gentamicin (Garamycin) therapy. When should the nurse schedule a trough drug level to be drawn?
a. 12 hours after completing the antibiotic infusion
b. 30 minutes after beginning the antibiotic infusion
c. 18 hours after completing the antibiotic infusion
d. 60 minutes after beginning the antibiotic infusion
7. The nurse would teach a client prescribed metronidazole (Flagyl) to avoid ingestion of which drink?
a. Wine
b. Coffee
c. Milk
d. Orange juice
8. The client’s culture has grown gram-positive cocci, and the health care provider prescribes two different antibiotics, one of which is gentamicin (Garamycin). To treat this type of infection, which type of antibiotic is typically prescribed together with gentamicin (Garamycin)?
a. Aminoglycoside
b. Penicillin
c. Fluoroquinolone
d. Cephalosporin
9. A client who is prescribed metronidazole (Flagyl) for a gynecologic infection provides the nurse with a list of medications that are routinely taken. Which medication would lead the nurse to question the prescription for Flagyl?
a. Multivitamin (Thera-Tabs)
b. Lithium (Eskalith)
c. Ibuprofen (Advil)
d. Levothyroxine (Synthroid)
10. Quinolones are a class of antibiotics known for several significant complications. Which are possible adverse effects with these drugs? (Select all that apply.)
a. Prolongation of the QT interval
b. Ototoxicity
c. Nephrotoxicity
d. Tendon rupture
e. Abnormal cartilage development in children
11. When providing instructions to clients on use of antibiotics, which instructions would the nurse include in the teaching? (Select all that apply.)
a. Wash your hands before and after preparing food.
b. Complete the entire course of therapy.
c. Increase fluid intake up to 3000 mL/day.
d. Save unused medication in a cool dry place for later use.
e. Notify the provider of any possible reactions that occur.
Chapter 40
1. The nurse is obtaining a medication history from a client diagnosed with genital herpes. Which drug would the nurse expect this client to be prescribed?
a. Acyclovir (Zovirax)
b. Ribavirin (Virazole)
c. Amantadine (Symmetrel)
d. Zidovudine (Retrovir)
2. To assess for the dose-limiting toxicity of ganciclovir (Cytovene), the nurse will monitor which laboratory test result?
a. Creatine phosphokinase
b. Liver function tests
c. Blood urea nitrogen
d. Complete blood count (CBC)
3. Medications used to treat HIV infections are more specifically classified as what type of drugs?
a. Antiparasitic
b. Antiviral
c. Antifungal
d. Antiretroviral
4. How is the effectiveness of antiviral drugs administered to treat HIV infection assessed and evaluated?
a. Viral load
b. Red blood cell counts
c. Lymphocyte counts
d. Megakaryocytes
5. Which client statement regarding his or her diagnosis of HIV infection indicates a need that further teaching is necessary?
a. “I must take these medications exactly as prescribed for the rest of my life.”
b. “I don’t need to use condoms as long as I take my medication as prescribed.”
c. “I will notify my health care provider immediately if I bruise or bleed more easily than normal.”
d. “I should remain upright for 30 minutes after taking my zidovudine to prevent esophageal ulceration.”
6. When providing health promotion teaching at a senior citizen center, the nurse would include information about which medication used to decrease the duration of influenza A and B?
a. Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
b. Ganciclovir (Cytovene)
c. Enfuvirtide (Fuzeon)
d. Indinavir (Crixivan)
7. A new vaccination, Zostavax (Zoster Vaccine Live), has been approved to prevent the development of what condition in adults older than the age of 60 years?
a. Herpes zoster (shingles)
b. Influenza A
c. Herpes simplex
d. Avian influenza
8. The most significant drug interactions with use of antivirals occur when antivirals are administered via which route?
a. Optically
b. Rectally
c. Topically
d. Intravenously
9. The nurse is aware that viruses can enter the body through various routes. Through which routes can viruses enter the body? (Select all that apply.)
a. Localized allergic reaction to medication
b. Inhalation through the respiratory tract
c. Transplacentally from mother to infant
d. Through an animal bite
e. Ingestion via the gastrointestinal (GI) tract
10. Which types of antiviral drugs are used to treat HIV infection? (Select all that apply.)
a. Nonnucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitors
b. Protease inhibitors
c. Neuraminidase inhibitors
d. Fusion inhibitors
e. Reverse transcriptase inhibitors
11. Before administration of any antiviral medication, what nursing responsibilities would be performed? (Select all that apply.)
a. Monitor for medication adverse effects
b. History of medication use
c. Documentation of known allergies
d. Baseline vital signs
e. Head-to-toe physical assessment
Chapter 42
1. What is the MOST common drug used to treat oral candidiasis?
a. Oseltamivir (Tamiflu)
b. Griseofulvin (Fulvicin P/G)
c. Amantadine (Symmetrel)
d. Nystatin (Mycostatin)
2. What is the MOST important action for the nurse to complete before administration of intravenous (IV) amphotericin B?
a. Monitor for cardiac dysrhythmias.
b. Assess for nausea and vomiting.
c. Monitor IV site for signs of phlebitis.
d. Check for premedication prescriptions.
3. Which antifungal drug can be given intravenously to treat severe yeast infections as well as a one-time oral dose to treat vaginal yeast infections?
a. Nystatin (Mycostatin)
b. Caspofungin (Cancidas)
c. Fluconazole (Diflucan)
d. Voriconazole (Vfend)
4. A client visits the health care provider for treatment of tinea pedis (athlete’s foot). Which medication would the nurse MOST likely instruct the client to take to treat this condition?
a. Voriconazole (Vfend)
b. Caspofungin (Cancidas)
c. Amphotericin B (Amphocin)
d. Terbinafine (Lamisil)
5. The nurse needs to know that major adverse effects are MOST common by which drug?
a. Griseofulvin (Fulvicin P/G)
b. Ketoconazole (Nizoral)
c. Amphotericin B (Amphocin)
d. Fluconazole (Diflucan)
6. The nurse would question a prescription for voriconazole (Vfend) if the client was taking which medication?
a. Prednisone (Deltasone)
b. Quinidine
c. Clindamycin (Cleocin)
d. Captopril (Capoten)
7. The nurse has provided education to a client about fungal skin infections. Further client teaching is necessary when the client includes which condition in the discussion of fungal skin infections?
a. Impetigo
b. Vaginal yeast infection
c. Athlete’s foot
d. Thrush
8. What are important for the nurse to monitor in a client receiving an antifungal medication? (Select all that apply.)
a. Blood urea nitrogen
b. Daily weights
c. Creatinine
d. Mental status
e. Intake and output
9. What conditions are considered contraindications for use of antifungal medications? (Select all that apply.)
a. Heart failure
b. Respiratory failure
c. Pancreatic failure
d. Liver failure
e. Kidney failure
Chapter 45
1. How would the nurse define the term nadir to a client?
a. The client’s tolerance and resistance to the chemotherapy’s bone marrow suppression effect
b. The average number of days it takes the bone marrow to recover from a dose of chemotherapy
c. The average number of days it takes for chemotherapy to have its peak effect on the bone marrow
d. The maximum dose for a chemotherapy medication in reference to bone marrow suppression
2. The nurse would anticipate administering which medication to clients receiving high-dose methotrexate (Trexall)?
a. Cisplatin (Platinol)
b. Dactinomycin (Cosmegen)
c. Bleomycin (Blenoxane)
d. Leucovorin (Wellcovorin)
3. Nausea and vomiting are frequent adverse effects associated with antineoplastic therapy. What should the nurse advise clients experiencing these unpleasant adverse effects?
a. Use antacids to relieve the irritation to the stomach, which should stop the nausea.
b. Try to maintain hydration and nutrition, which are very important during treatment.
c. Increase intake of dry or high-fiber foods, and foods that have a rough texture.
d. Consider relaxation techniques because these symptoms should improve over time.
4. Current research has led to discovery of cancer-causing viruses in humans. Which virus is linked to cancer and can be prevented in humans?
a. Leukemia viruses
b. Rous sarcoma virus
c. Human papillomavirus (HPV)
d. Shope papillomavirus
5. When teaching a client receiving paclitaxel (Taxol), the nurse should instruct the client about which common adverse effect?
a. Joint pain
b. Weight gain
c. Vertigo
d. Hypertension
6. Which are general adverse effects of chemotherapy? (Select all that apply.)
a. Urinary retention
b. Alopecia
c. Hypertension
d. Leukocytosis
e. Thrombocytopenia
7. Combinations of antineoplastic drugs are frequently used for which purpose? (Select all that apply.)
a. Lower cost of treatment
b. Prevent drug resistance
c. Decrease the severity of adverse effects
d. Decrease drug tolerance
e. Provide a synergistic action
Chapter 46
1. When a client is receiving cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan), the nurse should advise the client to drink plenty of fluids to prevent which condition?
a. Renal failure
b. Neutropenia
c. Hemorrhagic cystitis
d. Liver dysfunction
2. What is considered a major dose-limiting adverse effect of doxorubicin (Adriamycin)?
a. Hepatotoxicity
b. Nephrotoxicity
c. Cardiomyopathy
d. Hemorrhagic cystitis
3. The nurse should question a prescription of hydroxyurea (Hydrea) for a client with which laboratory test result?
a. Hemoglobin of 15 g/dL
b. White blood cell (WBC) count of 8000/mm3
c. Platelet count of 8000/mm3
d. Serum creatinine of 1.0 mg/dL
4. When a client is receiving tamoxifen (Soltamox), the nurse will suspect which type of cancer?
a. Colon
b. Breast
c. Lung
d. Renal
5. The nurse is discussing the use of alkylating drugs with a client. What is the best way for the nurse to describe the action of alkylating drugs on cancer cells?
a. They stop the meiosis of cell division and reproduction.
b. They interact within the cell through intercalation.
c. They alter the chemical structure of the deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
d. They specifically change the messenger ribonucleic acid sequence.
6. When a client is receiving cisplatin (Platinol), the nurse will monitor the client for which possible severe adverse effects? (Select all that apply.)
a. Nausea and vomiting
b. Peripheral neuropathy
c. Pulmonary toxicity
d. Ototoxicity
e. Nephrotoxicity
7. Which are known severe adverse effects of alkylating agents? (Select all that apply.)
a. Ototoxicity
b. Bone marrow suppression
c. Cardiotoxicity
d. Nephrotoxicity
e. Neurotoxicity
8. What are the possible severe adverse effects specific to the cytotoxic antibiotics?
a. Neurotoxicity
b. Nephrotoxicity
c. Liver toxicity
d. Pneumonitis
e. Cardiovascular toxicity
9. When providing education to a client undergoing antineoplastic drug therapy, the nurse instructs the client to immediately notify the health care provider for which signs and symptoms? (Select all that apply.)
a. Swollen tongue
b. Blood in urine
c. Difficulty sleeping
d. Nausea on the day of treatment
e. Bleeding gums
f. New and persistent cough
Chapter 10
1. A patient needs to switch analgesic drugs secondary to an adverse reaction to the current treatment regimen. The patient is concerned that the new prescription will not provide optimal pain control. The nurse’s response is based on knowledge that doses of analgesics are determined using an equianalgesic table with which drug prototype?
a. Fentanyl
b. Meperidine
c. Morphine
d. Codeine
2. The nurse is caring for a patient with opioid addiction. The nurse anticipates that the patient will be prescribed which medication?
a. Meperidine (Demerol)
b. Naloxone (Narcan)
c. Methadone (Dolophine)
d. Morphine (MS Contin)
3. While admitting a patient for treatment of an acetaminophen (Tylenol) overdose, the nurse prepares to administer which medication to prevent toxicity?
a. Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol)
b. Acetylcysteine (Mucomyst)
c. Naloxone (Narcan)
d. Phytonadione (vitamin K)
4. A patient prescribed massage therapy for musculoskeletal pain asks the nurse, “How is rubbing my muscles going to make the pain go away?” What is the nurse’s best response?
a. “Massaging muscles helps relax the contracted fibers and decrease painful stimuli.”
b. “Massaging muscles activates small sensory nerve fibers that send signals to the spinal cord to open the gate and allow endorphins to reach the muscles and relieve the pain.”
c. “Massaging muscles activates large sensory nerve fibers that send signals to the spinal cord to close the gate, thus blocking painful stimuli from reaching the brain.”
d. “Massaging muscles decreases the inflammatory response that initiates the painful stimuli.”
5. When assessing for the MOST serious adverse effect to an opioid analgesic, what does the nurse monitor for in this patient?
a. Blood pressure
b. Respiratory rate
c. Mental status
d. Heart rate
6. Which medication is used to treat a patient with severe adverse effects of a narcotic analgesic?
a. Flumazenil (Romazicon)
b. Methylprednisolone (Solu-Medrol)
c. Acetylcysteine (Mucomyst)
d. Naloxone (Narcan)
7. A patient with a diagnosis of pneumonia asks the nurse, “Why am I receiving codeine when I have no pain?” The nurse’s response is based on knowledge that codeine also has what effect?
a. Bronchodilation
b. Increased sputum production
c. Expectorant
d. Cough suppressant
8. In monitoring a patient for adverse effects related to morphine sulfate (MS Contin), the nurse assesses for stimulation of which area in the central nervous system (CNS)?
a. Autonomic control over circulation
b. Sympathetic baroreceptors
c. The cough reflex center
d. The chemoreceptor trigger zone
9. The nurse is preparing to administer an intravenous injection of morphine to a patient. The nurse assesses a respiratory rate of 10 breaths/min. Which action should the nurse perform?
a. Withhold the medication and notify the health care provider.
b. Administer a smaller dose and document in the patient’s record.
c. Administer the next prescribed dose intramuscularly.
d. Check the pulse oximeter reading and reevaluate respiratory rate in 1 hour.
10. A patient receiving narcotic analgesics for chronic pain can minimize the GI side effects by:
a. eating foods high in lactobacilli.
b. taking Lomotil with each dose.
c. taking the medication on an empty stomach.
d. increasing fluid and fiber in the diet.
11. A patient is prescribed an opioid analgesic for chronic pain. Which information should the nurse discuss with the patient to minimize the GI adverse effects?
a. Avoid eating foods high in lactobacilli.
b. Increase fluid intake and fiber in the diet.
c. Take diphenoxylate–atropine (Lomotil) with each dose.
d. Take the medication on an empty stomach.
12. The nurse teaches a patient prescribed the fentanyl (Duragesic) transdermal delivery system to change the patch at what interval?
a. When pain recurs
b. Every 72 hours
c. Once a week
d. Every 24 hours
13. The nurse plans pharmacologic management for a patient with pain. The nurse should administer the pain medication based on what dosage schedule?
a. Pain relief is best obtained by administering analgesics around the clock.
b. Administer the analgesic when the pain level reaches a “6” on a scale of 1 to 10.
c. Opioid analgesics should not be used for more than 24 hours to prevent drug addiction.
d. Analgesics should be administered as needed (prn) to minimize adverse effects.
14. In developing a plan of care for a patient receiving morphine sulfate (MS Contin), which nursing diagnosis has the highest priority?
a. Constipation related to decreased GI motility
b. Acute pain related to metastatic tumor cancer
c. Impaired gas exchange related to respiratory depression
d. Risk for injury related to CNS adverse effects
15. When assessing a patient for adverse effects related to morphine sulfate (MS Contin), which clinical findings is the nurse MOST likely to find? (Select all that apply.)
a. Weight gain
b. Excessive bruising
c. Constipation
d. Inability to void
e. Diarrhea
Chapter 11
1. While completing preoperative patient teaching, which information should the nurse include for a surgery with a general anesthetic?
a. It produces muscle relaxation and loss of consciousness.
b. It affects a specific region of the body to block pain sensation.
c. It uses only one type of medication to produce sedation.
d. It provides moderate sedation that allows you to relax.
2. A patient verbalizes concern to the nurse regarding postoperative nausea and vomiting from the anesthesia. Which is the nurse’s best response?
a. “I understand your concern but intermittent vomiting often occurs after surgery.”
b. “Don’t worry because you’ll be heavily or completely sedated if that occurs.”
c. “You will need to notify the charge nurse and health care provider if you feel nauseated after surgery.”
d. “Nausea and vomiting occur less frequently than in the past because of the use of a balanced approach to anesthesia.”
3. An intubated, mechanically ventilated patient in the intensive care unit (ICU) is becoming increasingly restless and anxious. The nurse expects to administer which intravenous (IV) anesthetic drug?
a. Propofol (Diprivan)
b. Isoflurane (Forane)
c. Halothane (Fluothane)
d. Nitrous oxide (Anesoxyn)
4. Which postoperative nursing action will help the patient avoid serious complications from general anesthesia?
a. Teach to turn, cough, and deep breathe.
b. Monitor input and output closely.
c. Place in a semi-Fowler's position.
d. Provide a quiet, calm environment.
5. Immediate postoperative assessment of a patient reveals a body temperature of 102° F. Which action will the nurse perform?
a. Notify the health care provider.
b. Administer acetaminophen as prescribed and recheck temperature in 1 hour.
c. Apply a cooling blanket per protocol.
d. Assess for signs and symptoms of infection related to the surgical wound.
6. A patient questions the use of epinephrine for repair of a laceration, stating, “I thought that was the drug used in the emergency department for someone who is coding.” Which is the nurse’s best response?
a. “Epinephrine is used with lidocaine to prevent adverse effects.”
b. “The systemic absorption of lidocaine is maximized by the epinephrine, and the anesthetic effect is reached more quickly.”
c. “Vasoconstriction caused by epinephrine enhances the duration of action for lidocaine and minimizes bleeding at the laceration site.”
d. “Epinephrine is metabolized more quickly than lidocaine so that the anesthetic effect wears off more quickly after the laceration is sutured.”
7. A mechanically ventilated patient receiving a neuromuscular-blocking drug has tearing in the eyes and increased heart rate and blood pressure. How does the nurse interpret this clinical finding?
a. The patient is having an adverse reaction to the medication.
b. The patient’s response to the drug is appropriate.
c. The patient’s level of sedation is inadequate.
d. The patient’s dose of the neuromuscular-blocking drug is insufficient.
8. While taking a patient’s history before surgery for a cardiac problem, the patient tells the nurse, “I am addicted to cocaine.” The nurse notifies the anesthesiologist of this finding because use of cocaine can cause which effect when a patient is under anesthesia?
a. Blood-clotting problems
b. Complications during recovery
c. Immediate withdrawal symptoms
d. Anesthetic-induced complications
Chapter 12
1. A patient is admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of benzodiazepine overdose. The nurse anticipates the health care provider will prescribe which antidote for benzodiazepine overdose?
a. Nalmefene (Revex)
b. Flumazenil (Romazicon)
c. Naltrexone (ReVia)
d. Naloxone (Narcan)
2. The nurse should monitor an older adult patient prescribed a benzodiazepine for treatment of insomnia for which potential adverse effect?
a. Shortness of breath
b. Muscle spasms
c. Unsteady gait
d. Red rash
3. Which nursing diagnosis is appropriate for a patient who has just been administered a sedative-hypnotic drug?
a. Risk for injury and falls
b. Imbalanced nutrition
c. Deficient knowledge
d. Risk for infection
4. A patient is admitted to the emergency department after taking an overdose of a barbiturate 15 minutes before arrival. The nurse can anticipate that which drug will be prescribed?
a. Naloxone (Narcan)
b. Charcoal (Activated charcoal)
c. Flumazenil (Romazicon)
d. Ipecac syrup
5. During patient teaching, the nurse explains the difference between a sedative and hypnotic with which statement?
a. “Most drugs produce sedation at low doses and sleep, the hypnotic effect, at higher doses.”
b. “Whereas sedative drugs induce sleep, hypnotic drugs induce a state of hypnosis.”
c. “There really is no difference; the terms are used interchangeably.”
d. “Sedatives are much stronger than hypnotic drugs and should only be used for short periods of time.”
6. The health care provider prescribes dantrolene (Dantrium) to a patient immediately after surgery. What condition does the nurse expect the patient has experienced?
a. Tonic-clonic seizure
b. Respiratory arrest
c. Delirium tremens
d. Malignant hyperthermia
7. An intravenous dose of midazolam (Versed) has been prescribed for a patient before a colonoscopy. The nurse informs the patient that one of the most common adverse effects of this medication is what effect?
a. Constipation
b. Amnesia
c. Dry mouth
d. Chest pain
Chapter 13
1. The nurse is providing care for a neonate diagnosed with apnea of prematurity. The prescription by the health care provider is for caffeine citrate intravenously 5 mg/kg once daily. The infant's weight is 5.4 lb. What is the correct dosage to administer to the patient?
a. 12.3 mg
b. 5.4 lb ÷ 2.2 = 2.45 kg × 5 mg/kg = 12.27 mg. Because doses are rounded to tenths for neonates, the answer is 12.3 mg.
2. A child is prescribed methylphenidate (Ritalin) to treat attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). The parent expresses concern about using a controlled substance to treat ADHD and asks the nurse about using a noncontrolled substance. The nurse knows ADHD can be treated with which noncontrolled substance?
a. Methylphenidate (Concerta)
b. Atomoxetine (Strattera)
c. Amphetamine aspartate (Adderall)
d. Dextroamphetamine sulfate (Dexedrine)
3. A patient diagnosed with narcolepsy is prescribed a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant. Which statement best describes the action of CNS stimulants?
a. CNS stimulants activate cyclic adenosine monophosphate.
b. CNS stimulants block or reduce the activity of inhibitory neurons.
c. CNS stimulants increase release of and block reuptake of neurotransmitters.
d. CNS stimulants decrease the production of excitatory neurotransmitters.
4. The nurse explains to a patient that using caffeine may exacerbate which health condition?
a. Cardiac dysrhythmias
b. Constipation
c. Heart block
d. Myelin degeneration
5. Which instructions should the nurse discuss to reduce the gastrointestinal (GI) adverse effects of orlistat (Xenical)?
a. Advise to take vitamin C supplement.
b. Take the medication with an antacid.
c. Limit dietary intake of fat.
d. Increase fluid and fiber in the diet.
6. Ergot alkaloids exert their therapeutic effect by which action?
a. Simulation of the alpha receptors.
b. Vasodilation.
c. Vasoconstriction.
d. Blockade of the beta2 receptors.
7. A nurse working with patients who are diagnosed with ADHD is aware that such patients often take CNS stimulant drugs. These medications are potent with a high potential for abuse and dependence. Based on this potential, how are these medications classified?
a. Schedule IV
b. Schedule II
c. Schedule I
d. Schedule III
8. A patient with narcolepsy is prescribed methylphenidate (Ritalin). Which adverse effects should the nurse include in the teaching of this drug? (Select all that apply.)
a. Insomnia
b. Headache
c. Weight Loss
d. Decreased blood pressure
e. Increased appetite
Chapter 14
1. The nurse instructs a patient receiving phenytoin (Dilantin) to visit the dentist regularly and perform frequent oral hygiene. What common adverse effect is the nurse educating the patient about for this medication?
a. Oral candidiasis
b. Increased incidence of dental caries
c. Increased risk of tooth abscess
d. Gingival hyperplasia
2. A patient receiving phenytoin (Dilantin) has a serum drug level drawn. Which level will the nurse note as therapeutic?
a. 6 mcg/mL
b. 12 mcg/mL (10-20 is therapeutic)
c. 8 mcg/mL
d. 30 mcg/mL
3. While obtaining a patient history, the nurse notes that the patient has been prescribed ethosuximide (Zarontin). The nurse suspects that the patient has which type of seizure?
a. Partial
b. Generalized
c. Absence
d. Tonic-clonic
4. While teaching a patient newly diagnosed with a seizure disorder, what does the nurse state as the goal of pharmacologic therapy of this medication?
a. Eradicate all seizure activity and discontinue prescribed medication after the patient is seizure free for 3 months.
b. Maximize drug dosages to control seizure activity.
c. Reduce seizure occurrence to one per week.
d. Maximally reducing seizure activity while minimizing the adverse effects of medication therapy.
5. While completing discharge teaching for a patient prescribed an antiepileptic drug, the nurse instructs the patient of which potential complication if the medication is stopped abruptly?
a. Rebound seizure activity
b. Orthostatic hypotension
c. Acute withdrawal syndrome
d. Confusion and delirium
6. The nurse is caring for a postoperative craniotomy patient. Which prescribed drug does the nurse make sure is readily available to treat acute seizure activity?
a. Flumazenil (Romazicon) ( benzodiazepine overdose)
b. Gabapentin (Neurontin) (anticonvulsants)
c. Diazepam (Valium)
d. Ethosuximide (Zarontin) (absent seizure)
7. When administering intravenous (IV) phenytoin (Dilantin), which action should the nurse perform?
a. Flush the line with normal saline before and after administration to prevent precipitation.
b. Administer through peripheral IV sites only.
c. Monitor blood pressure and pulse oximetry.
d. Obtain an infusion pump for the medication.
8. A patient receiving valproic acid (Depakote) should be monitored for which adverse effects? (Select all that apply.)
a. Tremors
b. Insomnia
c. Hepatotoxicity
d. Weight gain
e. Hypoglycemia
Chapter 15
1. A patient with Parkinson’s disease who has been positively responding to carbidopa-levodopa (Sinemet) asks the nurse, “Why have I suddenly developed a relapse of my symptoms.” Which explanation by the nurse is appropriate?
a. “This is called the “on–off phenomenon.” Your health care provider can change your medication regimen to help manage this effect.”
b. “This is very common and it is temporary. Continue to take the medicine, and you will feel better in a few weeks.”
c. “You have developed drug tolerance to your current medication, and a higher dose will need to be prescribed.”
d. “You have developed medication toxicity. Thus, the drug dose will be reduced to avoid potentially toxic drug blood levels.”
2. When teaching a patient about carbidopa-levodopa (Sinemet), what information should the nurse include about this medication?
a. Carbidopa crosses the blood–brain barrier to increase the metabolism of levodopa to dopamine in the brain.
b. Giving both drugs together minimizes adverse effects and decreases the risk of kidney or liver disease.
c. Carbidopa increases levodopa’s conversion in the periphery, enhancing the amount of dopamine available to the brain.
d. Carbidopa decreases levodopa’s conversion in the periphery, increasing the levodopa available to cross the blood–brain barrier.
3. Which antiparkinson drug causes an increase in the levels of dopaminergic stimulation in the central nervous system (CNS) and therefore allows a decreased dose of other medications?
a. Carbidopa- levodopa (Sinemet)
b. Selegiline (Eldepryl)
c. Diphenhydramine (Benadryl)
d. Tolcapone (Tasmar)
4. What is the goal of pharmacologic therapy in treating Parkinson’s disease?
a. To balance cholinergic and dopaminergic activity in the brain
b. To increase the amount of acetylcholine at the presynaptic neurons
c. To decrease the amount of dopamine available in the substantia nigra
d. To block dopamine receptors in both presynaptic and postsynaptic neurons
5. The patient asks the nurse to explain the difference between carbidopa-levodopa (Sinemet) and ropinirole (Requip). How will the nurse respond?
a. “Both drugs have the same pharmacodynamic and adverse effect profiles.”
b. “Ropinirole is a dopamine agonist that has fewer adverse effects than carbidopa-levodopa.”
c. “Carbidopa-levodopa is less effective than ropinirole in treating the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.”
d. “Whereas carbidopa-levodopa acts as a dopamine agonist, ropinirole directly replaces dopamine.”
6. The nurse is caring for a patient with Parkinson’s disease who has been taking entacapone (Comtan) for the past week to treat an on–off phenomenon. The patient expresses concern over brown-orange urine. What information will the nurse provide to the patient?
a. Laboratory tests are needed to determine kidney function.
b. Brown discoloration of urine may indicate a urinary tract problem.
c. This is a normal adverse effect of entacapone (Comtan) and is not harmful.
d. Abdominal ultrasonography will be performed to evaluate for liver damage or failure.
7. A patient who has been taking antiparkinson medications for years begins to have increased symptoms on a constant basis. In documenting these symptoms, what term will the nurse use?
a. On-off phenomenon
b. Wearing-off phenomenon
c. Dystonia
d. Chorea
8. The nurse is providing care for a patient with a diagnosis of Parkinson’s disease who has preexisting liver failure. What class of medications, if prescribed, would the nurse question?
a. Anticholinergics
b. Dopamine modulator
c. Catechol ortho-methyltransferase (COMT) inhibitors
d. Ergot derivative
9. A patient with Parkinson’s disease discusses with the nurse experiencing insomnia recently. The patient asks the nurse, “Can I take my old prescription of benzodiazepine that is prescribed to treat my insomnia?” What does the nurse know about the use of benzodiazepines in patients taking levodopa (Larodopa)?
a. Use of benzodiazepines decreases the therapeutic effect of the levodopa and may result in an increase in the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
b. Use of benzodiazepines increases the therapeutic effect of the levodopa and may result in a decrease in the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
c. Use of benzodiazepines increases the therapeutic effect of the levodopa and may result in an increase in the symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
d. Use of benzodiazepines decreases the therapeutic effect of the levodopa and may result in a decrease in the symptoms of Parkinson’s
10. A patient is prescribed selegiline (Eldepryl), an MAO-B inhibitor, as adjunctive therapy in treatment of Parkinson’s disease. What potential adverse effects should the nurse include in education for this patient? (Select all that apply.)
a. Weight gain
b. Headache
c. Blood pressure changes
d. Depression
e. Insomnia
Chapter 16
1. When doing an admission drug history, the nurse notes that the patient has a prescription for lithium (Lithobid). The nurse suspects that this patient has been diagnosed with which condition?
a. Paranoid schizophrenia
b. Absence seizures
c. Obsessive-compulsive disorder
d. Bipolar disorder
2. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) both function by which mechanism?
a. Inhibit an enzyme that stops the action of neurotransmitters
b. Block the reuptake of neurotransmitters at nerve endings
c. Stimulate areas of the brain associated with mental alertness
d. Decrease the catecholamine release into the blood
3. A patient diagnosed with depression is being discharged with a prescription for TCAs after no improvement of symptoms on an SSRI. Which instruction should the nurse include about this new medication?
a.
b. This drug does not cause problems with sleep, constipation, or low blood pressure.
c. Take St. John’s wort every day to minimize the adverse effects of the medication.
d. There is a risk of toxicity when this medication is taken with alcohol.
e. There are no drug or food contraindications with this medication.
4. A patient who is prescribed duloxetine (Cymbalta) comes to the medical clinic complaining of restlessness, sweating, and tremors. The nurse suspects serotonin syndrome and questions the patient regarding concurrent use of which herbal product or dietary supplement?
a. Zinc
b. St. John’s wort
c. Glucosamine chondroitin
d. Vitamin E
5. A patient with a diagnosis of depression is being discharged with a prescription for an MAOI. Which instruction should the nurse include for this medication?
a. Emphasize that tremors are a common adverse effect.
b. Avoid eating aged cheese.
c. Explain the symptoms of tardive dyskinesia.
d. Encourage use of fiber supplements.
6. What is another approved and indicated use for the antidepressant bupropion (Zyban)?
a. Tourette’s syndrome
b. Orthostatic hypotension
c. Smoking cessation
d. Nocturnal enuresis
7. A patient prescribed lorazepam (Ativan) for the treatment of anxiety states, “I feel drowsy all the time, and it’s interfering with every aspect of my life.” The nurse knows that a better drug therapy option for this patient is which anxiolytic medication?
a. Chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
b. Hydroxyzine hydrochloride salt (Vistaril)
c. Alprazolam (Xanax)
d. Buspirone (BuSpar)
8. Which statement by the patient indicates the need for additional teaching on phenothiazine (Thorazine) drug therapy?
a. “I need to change positions slowly to prevent dizziness.”
b. “I will call my health care provider for abnormal tongue movements”
c. “It is okay to take this drug with a small glass of wine to help relax me.”
d. “I will need to wear sunscreen and protective clothing when outdoors.”
9. Which laboratory test should be monitored closely to assess for a potential life-threatening adverse effect to clozapine (Clozaril)?
a. Glomerular filtration rate
b. Liver function studies
c. Immunoglobulin levels
d. Complete blood count
10. The nurse is monitoring a patient taking an antipsychotic medication for extrapyramidal symptoms. Which clinical finding indicates an adverse effect of this drug?
a. Presence of myoglobin in the blood
b. Muscle cramps of the head and neck
c. Dry mouth and constipation
d. Blood pressure of 80/50 mm Hg
11. What atypical antipsychotic medication should the nurse anticipate the health care provider prescribing for treatment of refractory schizophrenia?
a. Prazodone (Desyrel)
b. Phenelzine (Nardil)
c. Amoxapine (Asendin)
d. Risperidone (Risperdal)
Chapter 26
1. The nurse would assess which laboratory value to determine the effectiveness of intravenous heparin (Hemochron)?
a. Complete blood count
b. Activated partial thromboplastin time (aPTT)
c. Blood urea nitrogen
d. Prothrombin time (PT)
2. The nurse is caring for a patient admitted with gastrointestinal bleeding who is anticoagulated with warfarin (Coumadin). Which medication should the nurse anticipate administering?
a. Vitamin E
b. Vitamin K (Phytonadione) (agonist for warfarin)
c. Protamine (Protamine sulfate)
d. Calcium gluconate
3. The nurse notes a patient’s international normalized ratio (INR) value of 2.5. What is the meaning of this reported value?
a. The patient’s warfarin dose is within the therapeutic range.
b. The patient needs the subcutaneous heparin dose increased.
c. The patient is not receiving enough warfarin for a therapeutic effect.
d. The patient is receiving too much heparin and is at risk for bleeding.
4. The nurse is giving discharge instructions to a patient prescribed warfarin (Coumadin) for atrial fibrillation. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further instruction from the nurse?
a. “I will take my medication in the early evening each day.”
b. “I will contact my health care provider if I develop excessive bruising.”
c. “I will increase the dark green leafy vegetables in my diet.”
d. “I will avoid activities that have a risk for injury such as contact sports.”
5. Which medication is an antiplatelet drug?
a. Clopidogrel (Plavix)
b. Alteplase (Activase)
c. Enoxaparin (Lovenox)
d. Heparin (Hemochron)
6. The nurse is preparing a patient with acute chest pain for an emergency angioplasty. The nurse would anticipate administering which medication to prevent platelet aggregation?
a.
b. Warfarin (Coumadin)
c. Aminocaproic acid (Amicar)
d. Protamine (Protamine sulfate)
e. Tirofiban (Aggrastat)
7. Enoxaparin sodium (Lovenox) is an anticoagulant used to prevent and treat deep vein thrombosis and pulmonary embolism. This medication is in which drug class?
a. Oral anticoagulant
b. Glycoprotein IIb/IIIa inhibitor
c. Low-molecular-weight heparin
d. Thrombolytic drug
8. The patient asks the nurse, “What is the difference between dalteparin (Fragmin) and heparin?” What is the nurse’s best response?
a. “Dalteparin is a low-molecular-weight heparin that has a more predictable anticoagulant effect.”
b. “The only difference is that the heparin dosage calculation is based on the patient’s weight.”
c. “There is really no difference, but dalteparin is preferred because it is less expensive.”
d. “I’m not really sure why some health care providers choose dalteparin and some heparin.”
9. Before emergency surgery, the nurse would anticipate administering which medication to a patient receiving heparin?
a. Vitamin K (Phytonadione)
b. Protamine (Protamine sulfate) (reverses heparin)
c. Phenytoin (Dilantin)
d. Vitamin E
10. A patient who is prescribed an anticoagulant requests an aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) for headache relief. What is the nurse’s best action?
a. Administer 650 mg of acetylsalicylic acid and reassess pain in 30 minutes.
b. Inform the patient of potential drug interactions with anticoagulants.
c. Explain that a common initial adverse effect is a headache for this drug.
d. Explain that acetylsalicylic acid is contraindicated and administer ibuprofen.
11. A patient is prescribed oral anticoagulant therapy while still receiving IV heparin infusion. The patient is concerned about risk for bleeding. What is the nurse’s best response?
a. “Bleeding is a common adverse effect of taking warfarin. If bleeding occurs, your health care provider will prescribe an injection of medication to stop the bleeding.”
b. “Because of your mechanical valve replacement, it is especially important for you to be fully anticoagulated, and the heparin and warfarin together are more effective than one alone.”
c. “Because you are now getting out of bed and walking around, you have a higher risk of blood clot formation and therefore need to be on both medications.”
d. “It usually takes 4 to 5 days to achieve a full therapeutic effect for warfarin, so the heparin infusion is continued to help prevent blood clots until the warfarin reaches its therapeutic effect.”
12. The nurse determines the patient has a good understanding of the discharge instructions regarding warfarin (Coumadin) with which patient statement?
a. “I will double my dose if I forget to take it the day before.”
b. “I should keep taking ibuprofen for my arthritis.”
c. “I should use a soft toothbrush for dental hygiene.”
d. “I should decrease the dose if I start bruising easily.”
13. While observing a patient self-administer enoxaparin (Lovenox), the nurse identifies the need for further teaching when the patient performs which self-injection action?
a. Massages the site after administration of the medication (increased risk for hematoma formation if patient massages)
b. Does not aspirate before injecting the medication
c. Administers the medication into subcutaneous (fatty) tissue
d. Injects the medication greater than 2 inches away from the umbilicus
14. The nurse recognizes that the patient understands the teaching about warfarin (Coumadin) when the patient verbalizes an increased risk of bleeding with concurrent use of which herbal product? (Select all that apply.)
a. Garlic
b. St. John’s wort
c. Glucosamine
d. Dong quai
e. Ginkgo
15. For a patient receiving an IV infusion of alteplase (Activase), which nursing actions should be taken? (Select all that apply.)
a. Record vital signs and report changes.
b. Assess for cardiac dysrhythmias.
c. Observe for signs and symptoms of bleeding.
d. Administer injections intramuscularly.
e. Monitor for an increase in liver enzymes.
Chapter 27
1. The nurse provides discharge instructions to a patient prescribed cholestyramine (Questran). Which statement by the patient indicates teaching was effective for this drug?
a. “I will increase fiber in my diet and drink more fluids.”
b. “This drug can cause flushing, itching and gastrointestinal upset.”
c. “I will take Questran 1 hour before my other medications.”
d. “I will notify my health care provider if I have muscle pain.”
2. To decrease the skin flushing adverse effect reaction of niacin (nicotinic acid), which action should the nurse take?
a. Administer niacin with a liquid antacid.
b. Administer aspirin 30 minutes before each dose.
c. Give niacin with all other morning medications.
d. Apply cold compresses to the head and neck.
3. Hydroxymethylglutaryl–coenzyme A (HMG–CoA) reductase inhibitors (statins) are generally administered at which time of day?
a. Evening
b. 12:00 noon
c. Afternoon
d. Morning
4. Which discharge instruction should the nurse include for a patient prescribed an antilipemic medication?
a. “It is important to take a double dose to make up for a missed dose.”
b. “Stop taking the medication if it causes nausea and vomiting.”
c. “Continue your exercise program and maintain a low-fat diet.”
d. “Lifestyle changes are no longer necessary when taking this medication.”
5. What is the mechanism of action of ezetimibe (Zetia)?
a. Binds to bile acids in the intestine, inhibiting its reabsorption into the blood.
b. Inhibits absorption of dietary and biliary cholesterol in the small intestine.
c. Decreases the adhesion of cholesterol in the arteries.
d. Inhibits the biosynthesis of cholesterol in the liver.
6. Which statement by the nurse explains to the patient the action of cholestyramine (Questran) to decrease blood lipid levels?
a. Inhibits lipolysis in adipose tissue and decreases the hepatic synthesis of triglycerides in the liver.
b. Stimulates the biliary system to increase excretion of dietary cholesterol.
c. Binds to bile in the intestinal tract, forming an insoluble complex that is excreted in the feces.
d. Inhibits absorption of dietary cholesterol in the small and large intestine.
7. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further instruction about colestipol (Colestid) from the nurse?
a. “I will mix and stir the powder thoroughly with at least 1 to 2 oz of fluid.”
b. “I should take this medication 1 hour after or 4 hours before my other medications.”
c. “The potential adverse effects of this drug are rash and itching.”
d. “I might need to take fat-soluble vitamins to supplement my diet.”
8. By which action does atorvastatin (Lipitor) decrease lipid levels?
a. Inhibiting HMG-CoA reductase, the enzyme responsible for the biosynthesis of cholesterol in the liver
b. Decreasing the amount of triglycerides produced by the liver and increasing the removal of triglycerides by the liver
c. Binding to bile in the intestinal tract, forming an insoluble complex that is excreted in the feces
d. Stimulating the gallbladder and biliary system to increase excretion of dietary cholesterol
9. To assess for a potentially serious adverse effect to HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors, the nurse should monitor which laboratory results?
a. Serum electrolytes
b. Urine specific gravity
c. Liver function studies
d. Complete blood count
10. The nurse is providing discharge teaching for a patient about potential serious adverse effects to simvastatin (Zocor). Which symptom may indicate the patient is experiencing a serious adverse effect to this medication?
a. Muscle pain
b. Itching
c. Headache
d. Weight loss
11. The nurse would question a prescription for simvastatin (Zocor) in a patient with which condition?
a. Hepatic disease
b. Diabetes
c. Leukemia
d. Heart failure
12. A patient with elevated triglyceride levels unresponsive to HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors will most likely be prescribed which drug?
a. Colestipol (Colestid)
b. Gemfibrozil (Lopid)
c. Simvastatin (Zocor)
d. Cholestyramine (Questran)
13. The nurse would question a prescription for colesevelam (Welchol) in a patient with which condition?
a. Hepatic disease
b. Bowel obstruction
c. Renal disease
d. Glaucoma
14. The nurse will assess a patient receiving gemfibrozil (Lopid) and warfarin (Coumadin) for the increased risk of which adverse effect?
a. Bleeding
b. Clotting
c. Vitamin K toxicity
d. Deep vein thrombosis
Chapter 36
1. What body system will the nurse assess for known common adverse effects of traditional antihistamines?
a. Respiratory
b. Gastrointestinal
c. Central nervous
d. Cardiovascular
2. What advantage does loratadine (Claritin) have compared with traditional antihistamines such as diphenhydramine (Benadryl)?
a. Less sedative effect
b. Minimal gastrointestinal upset
c. Increase in bronchodilation
d. Decreased risk of cardiac dysrhythmias
3. A patient complains of worsening nasal congestion despite the use of oxymetazoline (Afrin) nasal spray every 2 to 4 hours for the past 5 days. The nurse’s response is based on knowledge that:
a. oxymetazoline should be administered in an hourly regimen for severe congestion.
b. sustained use of nasal decongestants over several days may result in rebound congestion.
c. oxymetazoline is not an effective nasal decongestant.
d. the patient is probably displaying an idiosyncratic reaction to oxymetazoline.
4. Which statement by the client demonstrates an understanding about beclomethasone dipropionate (Beconase) mechanism of action?
a. “I will monitor my blood sugar because I may develop drug-induced diabetes.”
b. “I only need to take this medication when my symptoms get bad.”
c. “This medication will help prevent the inflammatory response of my allergies.”
d. “I will need to taper off the medication to prevent acute adrenal crisis.”
5. The nurse is discussing use of antitussive medications with a client. What common adverse effect does the nurse include in the client teaching?
a. Diarrhea and abdominal cramping
b. Drowsiness and dizziness
c. Flushing and decreased heart rate
d. Tremors and palpitations
6. Which instruction should the nurse include when teaching a client who is prescribed an expectorant?
a. Take a drug with oral codeine when cough worsens.
b. Increase fluid intake to decrease viscosity of secretions.
c. Take the medication once a day at bedtime.
d. Restrict fluids to decrease mucus production.
7. The nurse would question a prescription for pseudoephedrine (Sudafed) in a client with a history of which condition?
a. Pneumonia
b. Peptic ulcer disease
c. Hypertension
d. Osteoporosis
8. When providing general education on use of over-the-counter (OTC) medications for allergies, which instruction should the nurse to include?
a. Discontinue use 4 days before allergy testing.
b. It may cause dry mouth and difficulty urinating.
c. Do not use in children younger than 2 years of age unless prescribed.
d. The medication treats the signs and symptoms but is not a cure.
9. A client is making an appointment for allergy testing. The nurse instructs the client not take what class of medications at least 4 days before allergy testing?
a. Antitussives
b. Decongestants
c. Antihistamines
d. Bronchodilators
10. The nurse is providing education to a client with a history of chronic nasal congestion secondary to allergic rhinitis. Which class of medications should the nurse anticipate the provider would recommend for the client to use on a long-term basis?
a. Intranasal steroids
b. Expectorants
c. Antihistamines
d. Antitussives
11. The nurse is discussing with the client the management of symptoms of an upper respiratory tract infection. Which classes of medications are often used in treating the symptoms of upper respiratory tract infections? (Select all that apply.)
a. Antibiotics
b. Antihistamines
c. Antitussives
d. Expectorants
e. Nasal decongestants
12. The nurse is discussing use of antihistamines for allergic rhinitis. Which medications would be included in the list of H1 antagonists used in the treatment of allergic rhinitis? (Select all that apply.)
a. Nizatidine (Axid)
b. Loratadine (Claritin)
c. Fexofenadine (Allegra)
d. Ranitidine (Zantac)
e. Cetirizine (Zyrtec)
Chapter 37
1. The nurse receives laboratory values for a client with a theophylline level of 14 mcg/mL. How does the nurse interpret this theophylline level?
a. Toxic
b. Life threatening
c. Therapeutic
d. Subtherapeutic
2. Discharge teaching to a patient receiving a beta-agonist bronchodilator should emphasize reporting which side effect?
a. Tachycardia
b. Nonproductive cough
c. Hypoglycemia
d. Sedation
3. Which herbal product, when taken with theophylline, can decrease theophylline’s serum drug levels?
a. Peppermint oil
b. St. John’s wort
c. Garlic
d. Echinacea
4. The nurse is providing care to a client prescribed a nonselective adrenergic agonist bronchodilator. Which condition documented in the client's medical history would alert the nurse to question this prescription?
a. Coronary artery disease
b. Thrombocytopenia
c. Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease
d. Mycobacterium tuberculosis
5. The nurse is providing care to a client prescribed a nonselectA nurse is providing education to a client taking two different bronchodilator medications. The nurse identifies which characteristic as the advantage of salmeterol (Serevent) over other beta2 agonists such as albuterol (Proventil)?ve adrenergic agonist bronchodilator. Which condition documented in the client's medical history would alert the nurse to question this prescription?
a. Shorter onset of action
b. Extended time of action
c. Longer duration of action
d. Quicker peak action
6. Client teaching regarding the use of leukotriene receptor antagonists (LTRAs) drugs such as zafirlukast (Accolate) would include which statement by the nurse?
a. “It will take about 3 or 4 weeks before you notice a therapeutic effect.”
b. “This medication works by preventing the inflammation that causes your asthma attack.”
c. “Increase fiber and fluid in your diet to prevent the common adverse effect of constipation.”
d. “Take the medication when you are short of breath and begin wheezing.”
7. What is the role of corticosteroids in the treatment of acute respiratory disorders?
a. They increase gas exchange in the alveoli.
b. They stimulate the immune system.
c. They directly dilate the bronchi.
d. They decrease inflammation.
8. Which statement by a client best indicates an understanding of the teaching on flunisolide (AeroBid)?
a. “I will wash the plastic inhaler casing once a month.”
b. “I will not use my albuterol inhaler while I am taking AeroBid.”
c. “I will rinse my mouth with water after each use.”
d. “I will take two puffs to treat an acute asthma attack.”
9. Which statement by the nurse should be included when teaching a client about the proper use of metered-dose inhalers?
a. “After you inhale the medication once, repeat until you obtain relief.”
b. “Make sure that you puff out air several times after you inhale the medication.”
c. “Hold the inhaler in your mouth, take a deep breath, and then compress the inhaler.”
d. “Wait 1 to 2 minutes before you take a second puff of the same drug.”
10. The nurse performs discharge teaching with a client who is prescribed the anticholinergic inhaler ipratropium bromide (Atrovent). Which statement by the client indicates to the nurse that teaching has been successful?
a. “Nausea and vomiting are common adverse effects of this medication.”
b. “I may gain weight as a result of taking this medication.”
c. “I will not drink grapefruit juice while taking this drug.”
d. “This inhaler is not to be used alone to treat an acute asthma attack.”
11. Which laboratory value would the nurse assess before administering zafirlukast (Accolate) to a client?
a. Renal function tests
b. Complete blood count
c. Liver enzymes
d. Cardiac enzymes
12. Before administering an LTRA medication, the nurse would assess the client for allergies to which substance? (Select all that apply.)
a. Latex
b. Cellulose
c. Chlorhexidine
d. Povidone
e. Lactose
Chapter 54
1. A pediatric client is prescribed ferrous fumarate (Feostat) for iron-deficiency anemia. The dose prescribed is 3 mg/kg/day. The client's weight is 7.5 kg. What amount will the nurse administer per day?
a. 22.5 mg
b. 3 mg/kg/day × 7.5 kg = 22.5 mg/day dosage
2. When administering ferrous sulfate (iron) to a client, the nurse plans to give this medication with which fluid to increase absorption of the iron?
a. Orange juice
b. Black tea
c. 8 oz of water
d. 4 oz of milk
3. The nurse will plan to inject iron dextran by which technique?
a. Subcutaneous injection with a ½-inch, 25-gauge needle
b. Intramuscular (IM) injection using the Z-track method
c. Intradermal injection with a sunburst technique of administration
d. IM injection with a ½-inch, 18-gauge needle
4. The nurse is educating a client on dietary sources of folic acid. The nurse should teach the client that which food source has the highest amount of folic acid?
a. Apples
b. Steak
c. Dried beans
d. Swiss cheese
5. The nurse knows iron supplementation has which common adverse effect?
a. Flatus
b. Heartburn
c. Constipation
d. Fatigue
6. The formation of erythrocytes and maturation of the red blood cell (RBC) is driven by what hormone?
a. Progesterone
b. Testosterone
c. Erythropoietin
d. Free thyroxin
7. The nurse is caring for a client who is prescribed epoetin alfa (Epogen). What does the nurse expect as the reason for use of this medication in this client?
a. Treatment of anemia due to renal failure
b. To replace blood loss from surgery
c. To cure or reverse kidney failure
d. Management of pregnancy-associated anemia
8. A client states to the nurse, “I must take my iron supplement with a meal to avoid stomach upset.” To increase uptake of oral iron, which food group should the nurse instruct the client to avoid?
a. Proteins
b. Dairy
c. Vegetables
d. Fruits
9. The nurse would question the prescription for epoetin alfa (Epogen) in a client with which condition?
a. End-stage renal disease
b. Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
c. Uncontrolled hypertension
d. Chemotherapy-induced anemia
10. When developing a nursing care plan for a client receiving epoetin alfa (Epogen), the nurse will include monitoring for which adverse effect?
a. Change in level of consciousness
b. Impaired liver function
c. Severe hypotension
d. Chronic diarrhea
11. Which are known contraindications for use of erythropoiesis-stimulating agents (ESAs) in clients? (Select all that apply.)
a. History of thrombosis
b. Cancer of the neck
c. End-stage renal disease
d. Uncontrolled hypertension
e. Hemoglobin level of 15 g/dL
12. Which groups of individuals are at highest risk for development of iron deficiency anemia? (Select all that apply.)
a. Women ages 12 to 40 years
b. Men ages 20 to 40 years
c. Children
d. Men older than age 50 years
e. Pregnant women
Chapter 22
1. The nurse is assessing the patient's knowledge regarding drug therapy prescribed for the treatment of hypertension. Which statement by the patient indicates the need for further teaching by the nurse?
a. "I will move slowly from a sitting to standing position."
b. "Blood pressure drugs can cause changes in sexual functioning."
c. "When my blood pressure is over 140/90, I will take my medication."
d. "I will wear a medical alert bracelet."
2. The nurse understands a patient who is treated for hypertension may be switched to an angiotensin receptor blocker (ARB) because of which angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor adverse effect?
a. Dry, nonproductive cough
b. Hypokalemia
c. Fatigue
d. Orthostatic hypotension
3. Which medication should the nurse question if prescribed together with ACE inhibitors?
a. Docusate sodium (Colace)
b. Furosemide (Lasix)
c. Potassium chloride (K-Dur)
d. Morphine
4. Before administering eplerenone (Inspra) to a patient, what is the priority nursing action?
a. Auscultate heart sounds.
b. Obtain serum thiocyanate level.
c. Assess level of consciousness.
d. Check serum electrolytes.
5. To prevent cerebral artery spasms after a subarachnoid hemorrhage, the nurse anticipates administering which calcium channel blocker?
a. Amlodipine (Norvasc)
b. Nimodipine (Nimotop)
c. Diltiazem (Cardizem)
d. Verapamil (Calan)
6. The nurse should question a prescription for a calcium channel blocker in a patient with which condition?
a. Dysrhythmia
b. Hypotension
c. Angina pectoris
d. Increased intracranial pressure
7. During discharge teaching, which statement by the nurse would be MOST appropriate for a patient prescribed a transdermal clonidine (Catapres)?
a. “Prolonged sitting or standing does not cause hypotension symptoms.”
b. “Occasional drooling is a common adverse effect of this medication.”
c. “Your blood pressure should be checked by your healthcare provider two to three times a week.”
d. “The patch should be applied to a non hairy site, and you should not suddenly stop using this drug.”
8. The nurse is conducting a community education program. When explaining different medication regimens to treat hypertension, it would be accurate to state that African Americans probably respond best to which combination of medications?
a. Diuretics and calcium channel blockers
b. ACE inhibitors and diuretics
c. Diuretics and beta blockers
d. ACE inhibitors and beta blockers
9. What is the classification of carvedilol (Coreg)?
a. Beta blocker
b. ACE inhibitor
c. Alpha2 blocker
d. Dual-action alpha1 and beta receptor blocker
10. What is the classification of carvediloWhen administering nitroprusside (Nipride) by continuous intravenous infusion, the nurse monitors for which symptom of drug toxicity? (Coreg)?
a. Wheezing
b. Hypotension
c. Fever
d. Hyperglycemia
11. A patient who is prescribed tamsulosin (Flomax) does not have a history of hypertension. The nurse knows this medication is also used for what condition?
a. Migraine headache
b. Pulmonary emboli
c. Subarachnoid hemorrhage
d. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH)
12. ACE inhibitors and ARBs both work to decrease blood pressure by which action?
a. Enhance sodium and water resorption
b. Increase the breakdown of bradykinin
c. Prevent the formation of angiotensin II
d. Prevent aldosterone secretion
13. When teaching a patient about a new prescription for carvedilol (Coreg), the nurse explains that this medication reduces blood pressure by which action? (Select all that apply.)
a. Decreases heart rate
b. Promotes excretion of sodium
c. Relaxes muscle tone
d. Peripheral vasodilation
e. Increases urine output
[Show More]



 - South University.png)
 - South University.png)
 - South University.png)