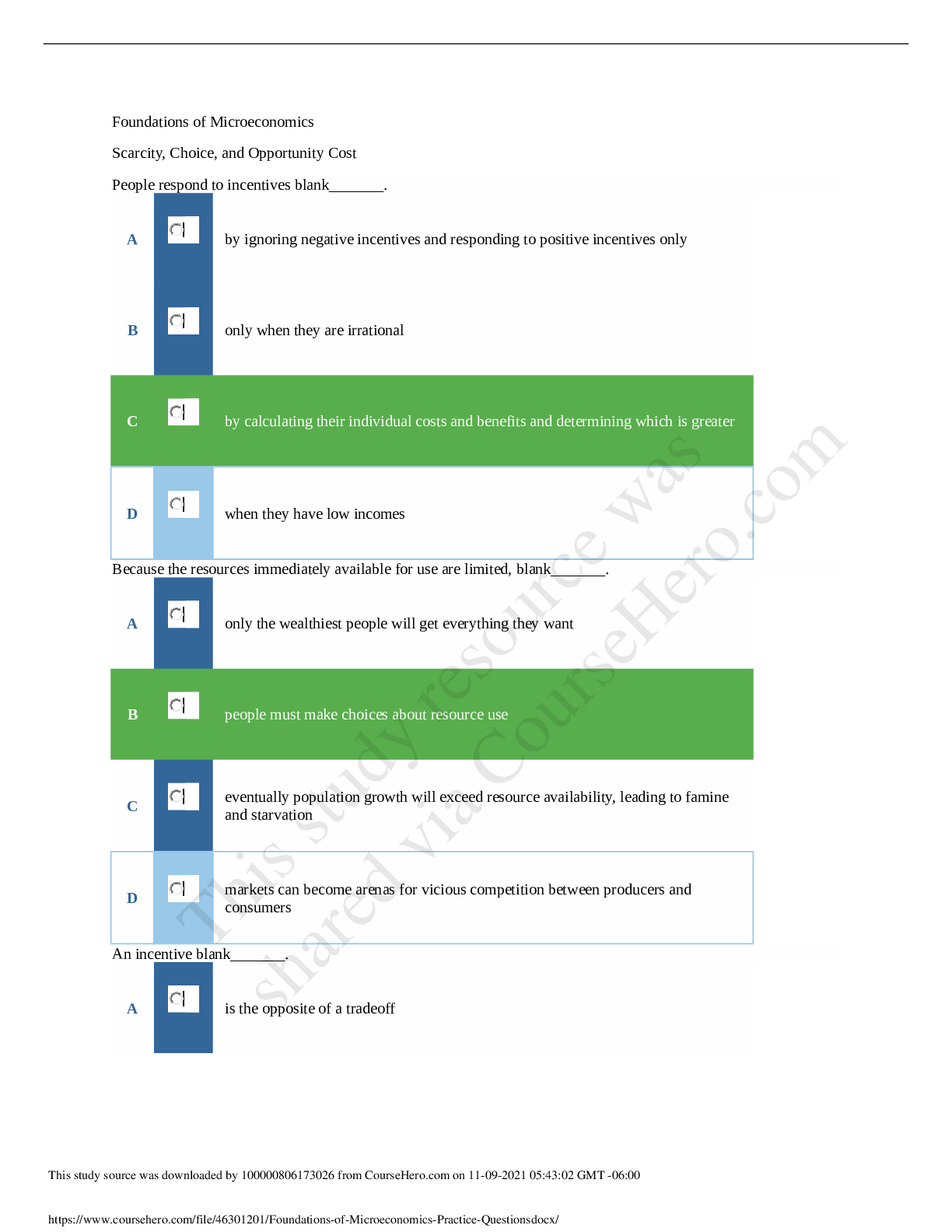
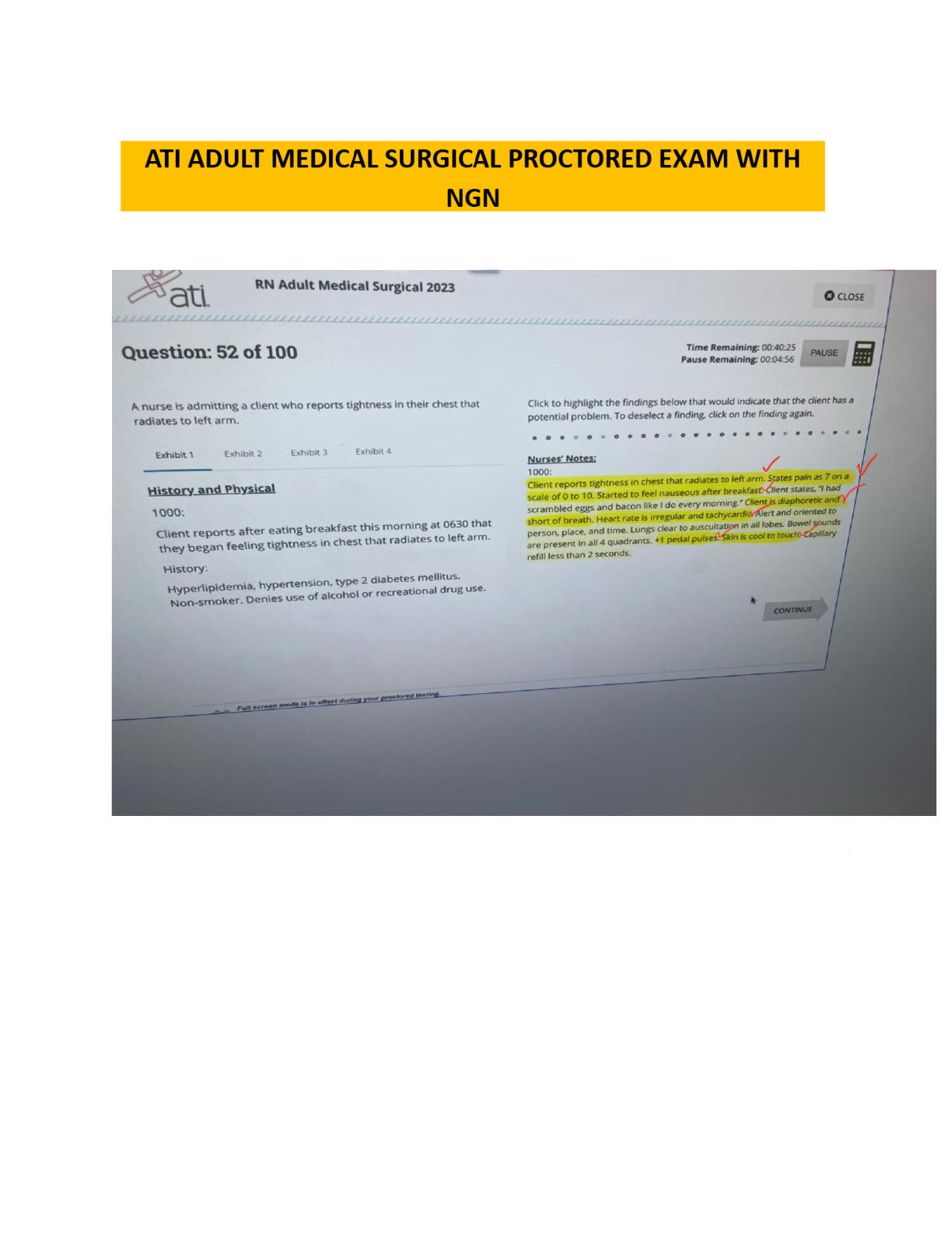
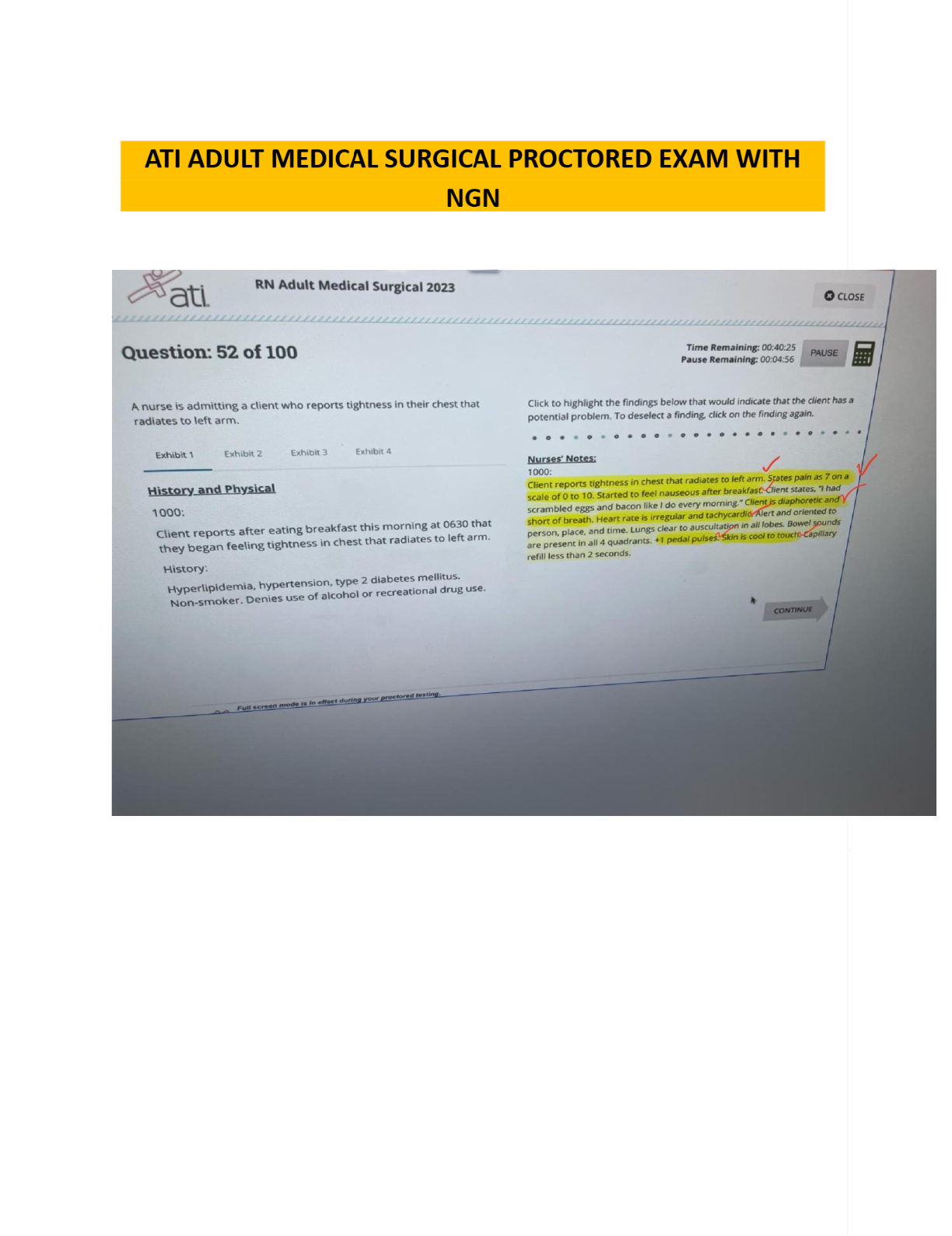
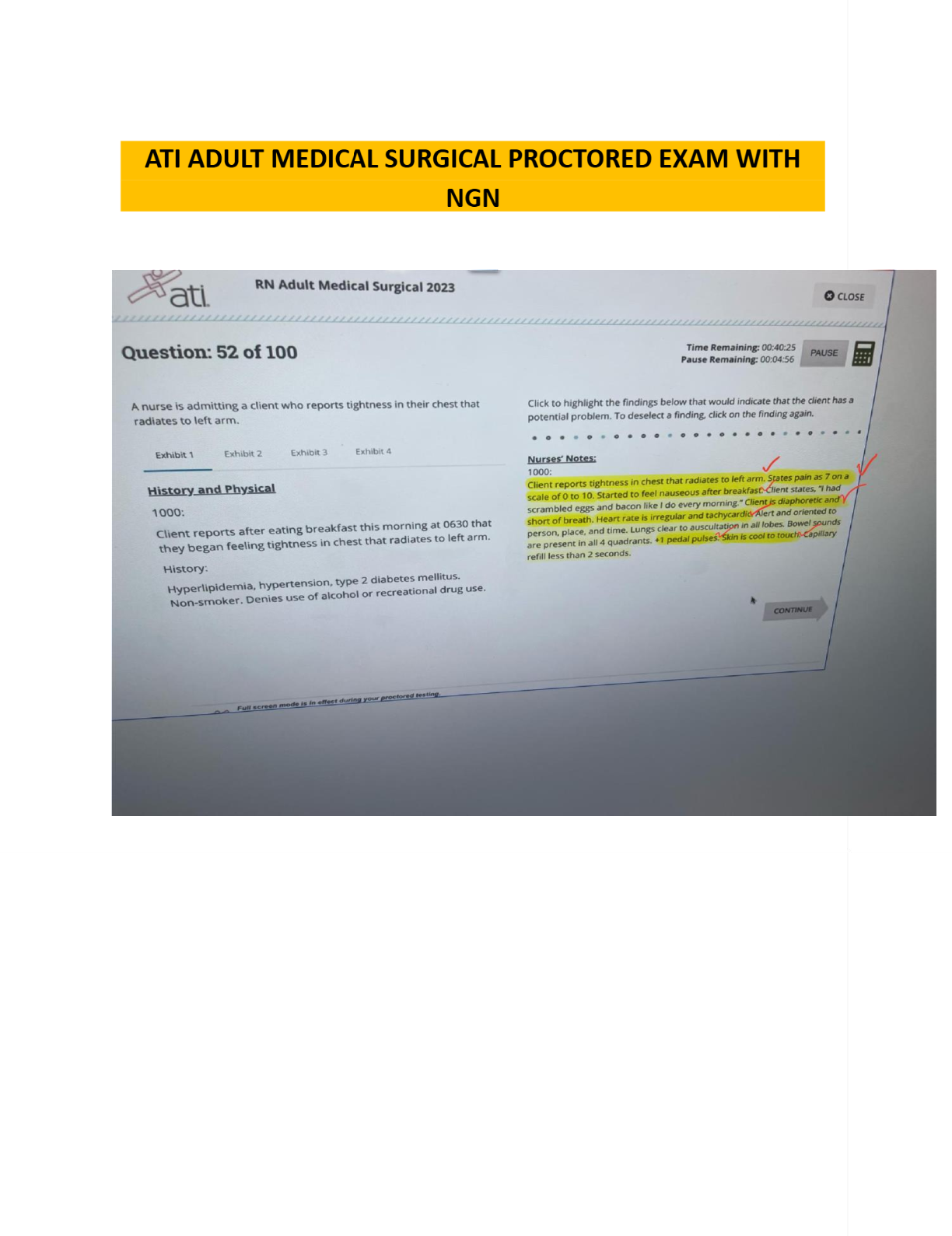
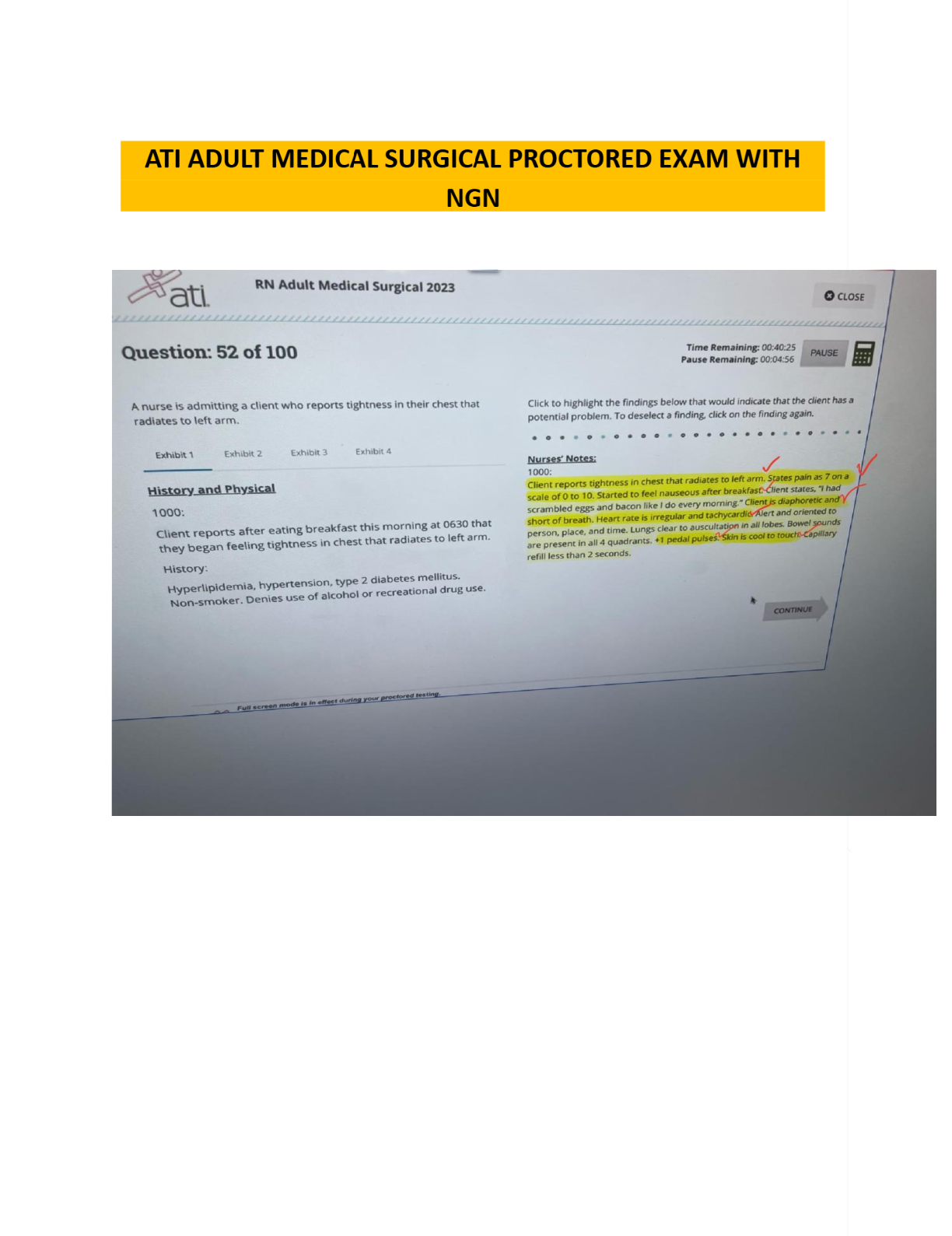
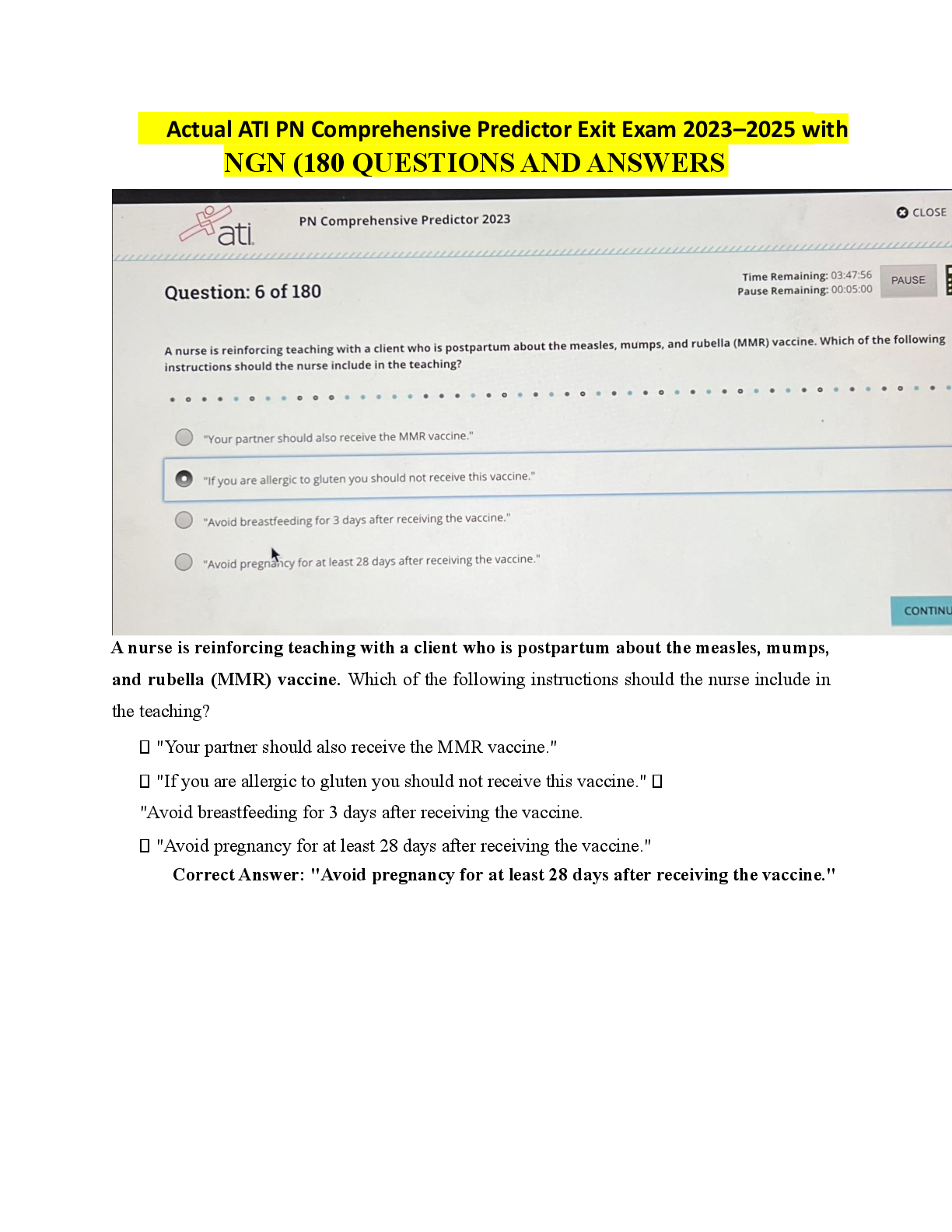
Management Information Systems (MIS) > EXAM > MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS FINAL. More than 500 MCQ With Answers Indicated. (All)
MANAGEMENT INFORMATION SYSTEMS FINAL. More than 500 MCQ With Answers Indicated.
Document Content and Description Below
MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 21) The six important business objectives of information technology are new products, services, ... and business models; customer and supplier intimacy; survival; competitive advantage; operational excellence; and A) improved flexibility. B) improved decision making. C) improved business practices. D) improved efficiency. 22) Dell Computer's use of information systems to improve efficiency and implement "mass customization" techniques to maintain consistent profitability and an industry lead illustrates which business objective? A) improved flexibility B) improved business practices C) competitive advantage D) survival 23) The use of information systems because of necessity describes the business objective of A) survival. B) improved business practices. C) competitive advantage. D) improved flexibility. Answer: A 24) Which of the following choices may lead to competitive advantage: (1) new products, services, and business models; (2) charging less for superior products; (3) responding to customers in real time? A) 1 only B) 1 and 2 C) 2 and 3 D) 1, 2, and 3 25) Verizon's implementation of a Web-based digital dashboard to provide managers with real-time information such as customer complaints is an example of A) improved flexibility. B) improved decision making. C) improved efficiency. D) customer and supplier intimacy. 26) The move of retail banking to use ATMs after Citibank unveiled its first ATMs illustrates the use of information systems to achieve which business objective? A) improved efficiency B) customer and supplier intimacy C) survival D) competitive advantage 27) The three activities in an information system that produce the information organizations use to control operations are A) information retrieval, research, and analysis. B) input, output, and feedback. C) input, processing, and output. D) data analysis, processing, and feedback. 28) Order data for baseball tickets and bar code data are examples of A) raw input. B) raw output. C) customer and product data. D) sales information. Answer: A 29) The average number of tickets sold daily online is an example of A) input. B) raw data. C) meaningful information. D) feedback. 30) Output A) is feedback that has been processed to create meaningful information. B) is information that is returned to appropriate members of the organization to help them evaluate the input stage. C) transfers data to the people who will use it or to the activities for which it will be used. D) transfers processed information to the people who will use it or to the activities for which it will be used. 31) Converting raw data into a more meaningful form is called A) capturing. B) processing. C) organizing. D) feedback. 32) An example of raw data from a national chain of automobile stores would be A) an average of 13 Toyotas are sold daily in Kentucky. B) 30 percent increase in Toyota RAV 4 sales during September in Kentucky. C) 1 Toyota RAV4 sold March 3, 2008 in Louisville, Kentucky. D) all of the above. 33) The field that deals with behavioral issues as well as technical issues surrounding the development, use, and impact of information systems used by managers and employees in the firm is called A) information systems literacy. B) information systems architecture. C) management information systems. D) information technology infrastructure. 34) In a hierarchical organization, the upper levels consist of A) managerial and professional employees. B) managerial, professional, and technical employees. C) professional and operational employees. D) managerial, professional, and operational employees. 35) Which of the following business objectives best describes the strategy behind the use of technology in the new Yankee Stadium? A) competitive advantage B) improved decision making C) new products and services D) survival 36) The fundamental set of assumptions, values, and ways of doing things that has been accepted by most of a company's members is called its A) culture. B) environment. C) atmosphere. D) values. Answer: A 37) Thomas Friedman's declaration that the world was now "flat" meant that A) the Internet has reduced the economic advantages of developed countries. B) globalization is starting to offer less advantage to large corporations. C) the global economy is increasingly commanded by fewer and larger corporations. D) global capitalism is homogenizing culture and business practices throughout the world. Answer: A 38) Data management technology consists of the A) physical hardware and media used by an organization for storing data. B) detailed, preprogrammed instructions that control and coordinate the computer hardware components in an information system. C) software governing the organization of data on physical storage media. D) hardware and software used to transfer data. Explanation: 39) The hardware and software used to transfer data in an organization is called A) data management technology. B) networking and data management technology. C) data and telecommunications technology. D) networking and telecommunications technology. 40) Networking and telecommunications technologies, along with computer hardware, software, data management technology, and the people required to run and manage them, constitute an organization's A) data management environment. B) networked environment. C) IT infrastructure. D) information system. 41) An example of a business using information systems to create new products and services is A) Wal-Mart's RetailLink system. B) the Mandarin Oriental hotel's customer-preference tracking system. C) Verizon's Web-based digital dashboard. D) Apple Inc.'s iPod. 42) An example of a business using information systems to attain operational excellence is A) Wal-Mart's RetailLink system. B) the Mandarin Oriental hotel's customer-preference tracking system. C) Verizon's Web-based digital dashboard. D) Apple Inc.'s iPod. Answer: A 43) An example of a business using information systems for customer and supplier intimacy is A) Wal-Mart's RetailLink system. B) the Mandarin Oriental hotel's customer-preference tracking system. C) Verizon's Web-based digital dashboard. D) Apple Inc.'s iPod. 44) Maintaining the organization's financial records is a central purpose of which main business function? A) manufacturing and accounting B) finance and accounting C) sales and manufacturing D) finance and sales 45) Based on the examples in the chapter, if you were asked to formulate a plan for a regional drive-in restaurant chain's efforts to use information technology to develop a loyal customer base, what would be the best use of information technology from the list below? A) Use IT to increase supplier loyalty. B) Use IT to increase operational efficiency. C) Use IT to create new products and business models. D) Use IT to help survive government reporting requirements. E) Use IT to achieve customer intimacy. 46) Which of the following would not be a complementary asset for a solar panel manufacturer? A) international solar equipment certification standards B) government funding for green technology C) centralized hierarchical decision making D) innovation-driven management team 47) The temp agency that you own is having serious difficulties placing temps because few of them are familiar with Internet research. Investing in training software to enhance your workers' skills is an example of using technology to achieve which business objective? A) customer and supplier intimacy B) survival C) competitive advantage D) improved decision-making 48) In a business hierarchy, the level that is responsible for monitoring the daily activities of the business is A) middle management. B) service workers. C) production management. D) operational management. 49) Which of the following are environmental actors that interact with an organization and its information systems? A) customers B) suppliers C) regulatory agencies D) all of the above 50) From a business perspective, raw data is transformed systematically during various stages, transforming it into valuable information, in a process called A) the information value chain. B) the IT value chain. C) information processing. D) feedback. Answer: A 51) A corporation that funds a political action committee, which in turn promotes and funds a political candidate who agrees with the values of that corporation, could be seen as investing in which main category of complementary assets? A) managerial B) governmental C) social D) organizational 52) Apple Computer dominates the online legal music sales industry primarily because of a failure of recording label companies to A) invest in technology. B) adopt a new business model. C) invest in complementary assets. D) modernize their information value chain. E) 53) An example of an organizational complementary asset is A) using the appropriate business model. B) a collaborative work environment. C) laws and regulations. D) all of the above. Answer: A 54) An example of a social complementary asset is A) technology and service firms in adjacent markets. B) training programs. C) distributed decision-making rights. D) all of the above. Answer: A 55) Disciplines that contribute to the technical approach to information systems are A) computer science, engineering, and networking. B) operations research, management science, and computer science. C) engineering, utilization management, and computer science. D) management science, computer science, and engineering. 56) The discipline that focuses on mathematical techniques for optimizing parameters of organizations, such as transportation and inventory control, is A) management science. B) MIS. C) operations research. D) utilization management. 57) Sociologists study information systems with an eye to understanding A) how systems affect individuals, groups, and organizations. B) how human decision makers perceive and use formal information. C) how new information systems change the control and cost structures within the firm. D) the production of digital goods. Answer: A 58) Psychologists study information systems with an eye to understanding A) how systems affect individuals, groups, and organizations. B) how human decision makers perceive and use formal information. C) how new information systems change the control and cost structures within the firm. D) the production of digital goods. 59) The costs for firms operating on a global scale have been drastically reduced by A) networking technology. B) investments in organizational complementary assets. C) the Internet. D) the rise of digital content. 60) Which of the following are key corporate assets? A) intellectual property, core competencies, and financial and human assets B) production technologies and business processes for sales, marketing, and finance C) knowledge and the firm's tangible assets, such as goods or services D) time and knowledge Answer: A 61) Overproduction or underproduction of goods and services, misallocation of resources, and poor response times are the results of a firm's having A) poor relationships with suppliers. B) poor relationships with customers. C) inadequate information. D) a surplus of information. 62) A firm that must invest in new information systems capabilities in order to comply with federal legislation can be said to be investing to achieve which business objective? A) customer intimacy B) operational excellence C) survival D) improved reporting 63) Which of the following would NOT be used as an input for an information system? A) digital dashboard B) handheld computer C) bar-code scanner D) cell phone Answer: A 64) Which field of study focuses on both a behavioral and technical understanding of information systems? A) sociology B) operations research C) economics D) management information systems 65) The three principal levels within a business organization hierarchy are A) senior management, operational management, and service workers. B) senior management, middle management, and operational management. C) senior management, operational management, and information systems. D) senior management, middle management, and service workers. 66) Engineers, scientists, or architects, who design new products or services for a firm, belong to which level of a business hierarchy? A) middle management B) production workers C) knowledge workers D) data workers 67) Which main business function is responsible for maintaining employee records? A) sales and marketing B) human resources C) finance and accounting D) manufacturing and production 68) Which of the following constitutes an organizational element in the UPS tracking system described in the chapter? A) the specification of procedures for identifying packages with sender and recipient information B) monitoring service levels C) promoting the company strategy of low-cost, superior service D) the use of handheld computers and networks for managing package delivery Answer: A 69) A managerial element in the UPS tracking system described in the chapter is A) taking inventory. B) providing package status reports to customers. C) the decision to use automation. D) in-house package tracking software. Chap 2: MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 21) An example of a collaboration tool that supports colocated, asynchronous collaboration is A) a team room. B) e-mail. C) a MUD. D) a wall display. Answer: A 22) Identifying customers is a responsibility of the function. A) finance and accounting B) human resources C) manufacturing and production D) sales and marketing 23) Producing bills of materials is a business process within the function. A) finance and accounting B) human resources C) manufacturing and production D) sales and marketing 24) Which of the following is an example of a cross-functional business process? A) identifying customers B) creating a new product C) assembling a product D) paying creditors 25) Which type of system would you use to change a production schedule if a key supplier was late in delivering goods? A) ESS B) TPS C) MIS D) DSS 26) To monitor the status of internal operations and the firm's relations with the external environment, managers need systems. A) decision-support B) knowledge C) transaction processing D) management information 27) Which systems are typically a major source of data for other systems? A) transaction processing systems B) management information systems C) executive support systems D) decision-support systems Answer: A 28) Which type of system would you use to determine the five suppliers with the worst record in delivering goods on time? A) ESS B) TPS C) MIS D) DSS 29) A relocation control system that reports summaries on the total moving, house-hunting, and home financing costs for employees in all company divisions would fall into the category of A) knowledge management systems. B) transaction processing systems. C) executive support systems. D) management information systems. 30) The term "management information systems" designates a specific category of information systems serving A) integrated data processing throughout the firm. B) transaction process reporting. C) employees with online access to historical records. D) middle management functions. 31) Non-typical business problems with causes and effects that are rapidly changing are typically handled by which type of information system ? A) MIS B) TPS C) ESS D) DSS 32) systems are especially suited to situations in which the procedure for arriving at a solution may not be fully defined in advance. A) Management information B) Transaction processing C) Decision-support D) Knowledge management 33) Which type of system would you use to forecast the return on investment if you used new suppliers with better delivery track records? A) ESS B) TPS C) MIS D) DSS 34) Which of the following is not one of the four main classifications for collaboration tools identified by the space/time matrix? A) synchronous/colocated B) same time/remote C) different time/remote D) remote/colocated 35) All of the following statements regarding Lotus Notes are true except for A) It began as an e-mail and messaging client. B) It is the most widely used collaboration tool at Fortune 1000 companies. C) Firmwide installations at a large company require specialized servers and may cost millions of dollars per year. D) It provides tools for e-mail, calendars, help desk, CRM, blogs, and wikis. Answer: A 36) ESS are specifically designed to serve which level of the organization? A) operational B) end-user C) middle management D) senior management 37) Executive support systems are information systems that support the A) long-range planning activities of senior management. B) knowledge and data workers in an organization. C) decision-making and administrative activities of middle managers. D) day-to-day processes of production. Answer: A 38) interface to present Which systems often deliver information to senior executives through a portal, which uses a Web integrated personalized business content? A) transaction processing systems B) executive support systems C) management information systems D) decision-support systems 39) Which type of system would you use to determine what trends in your supplier's industry will affect your firm the most in five years? A) ESS B) TPS C) MIS D) DSS Answer: A 40) What is the most important function of an enterprise application? A) increasing speed of communicating B) enabling business functions and departments to share information C) enabling a company to work collaboratively with customers and suppliers D) enabling cost-effective e-business processes 41) are designed to support organization-wide process coordination and integration. A) Decision-support systems B) Management information systems C) CRM systems D) Enterprise applications 42) The point-of-sale Pulse system used by Domino's to maintain consistent and efficient management functions in its restaurants is best categorized as which type of system? A) TPS B) DSS C) CRM D) more than one of the above 43) In Domino's upgraded Pulse Evolution system, it incorporated a Pizza Tracker functionality that shows the progression of individual pizza orders. This is an example of using information systems to achieve which business objective? A) customer and supplier intimacy B) survival C) improved decision making D) operational excellence Answer: A 44) The four major enterprise applications are A) SCMs, CRMs, DSSs, and KMSs. B) SCMs, CRMs, ESSs, and KMSs. C) enterprise systems, SCMs, DSSs, and CRMs. D) enterprise systems, SCMs, CRMs, and KMSs. 45) Enterprise systems are also known as systems. A) resource planning B) enterprise resource planning C) enterprise support D) management information 46) Enabling management to make better decisions regarding organizing and scheduling sourcing, production, and distribution is a central feature of A) SCMs B) TPSs C) KMSs D) ERPs Answer: A 47) systems integrate supplier, manufacturer, distributor, and customer logistics processes. A) Collaborative distribution B) Supply-chain management C) Reverse logistics D) Enterprise planning 48) systems are designed to help firms manage their relationships with their customers. A) CRM B) MIS C) CLE D) CLU Answer: A 49) Which types of systems consolidate the relevant knowledge and experience in the firm to make it available to improve business processes and management decision making? A) TPS B) extranets C) KMS D) CRM 50) You are planning the launch of your new company, an application service provider that provides an online timesheet and project tracking application. To best communicate with and manage your relationship with your users, you would want to implement a(n) A) extranet. B) intranet. C) KMS. D) CMS. 51) All of the following are direct business benefits of collaboration, except for A) improved quality. B) improved financial performance. C) improved customer service. D) improved compliance with government regulations. 52) Which of the following types of system helps expedite the flow of information between the firm and its suppliers and customers? A) intranet B) extranet C) KMS D) TPS 53) Which of the following occupations would NOT be categorized as an "interaction" job? A) sales representative B) business manager C) engineer D) operations manager 54) E-government refers to the application of to digitally enable government and public sector agencies' relationships with citizens, businesses, and other arms of government. A) the Internet and networking technologies B) e-commerce C) e-business D) any computerized technology Answer: A 55) Which of the following decisions requires knowledge based on collaboration and interaction? A) How long will it take to manufacture this product? B) Should we work with with outside vendors on new products and services? C) In which geographical locations are our products garnering the most sales? D) Which product design is the most efficient for the user in terms of energy use? 56) Buying or selling goods over the Internet is called A) e-commerce. B) e-business. C) an intranet. D) an extranet. Answer: A 57) The use of digital technology and the Internet to execute the major business processes in the enterprise is called A) e-commerce. B) e-business. C) enterprise applications. D) MIS. 58) The principal liaison between the information systems groups and the rest of the organization is a(n) A) programmer. B) information systems manager. C) systems analyst. D) CTO. 59) A is a senior manager who oversees the use of IT in the firm. A) CEO B) CFO C) CIO D) CTO 60) The helps design programs and systems to find new sources of knowledge or to make better use of existing knowledge in organizational and management processes. A) CTO B) CSO C) CKO D) CPO 61) The CPO is responsible for A) ensuring that the company complies with existing data privacy laws. B) making better use of existing knowledge in organizational and management processes. C) enforcing the firm's information security policy. D) overseeing the use of information technology in the firm. Answer: A 62) Which of the following types of collaboration tools allows you to communicate with avatars using text messaging? A) virtual worlds B) screen sharing C) collaborative writing D) large audience Webinars Answer: A 63) Which of the following roles falls into the duties of an information systems manager? A) writing software instructions for computers B) acting as liaison between the information systems group and the rest of the organization C) translating business problems into information requirements D) managing data entry staff 64) Which of the following statements about collaboration is not true? A) In business, a collaboration can last as little as a few minutes. B) Business collaboration relies on the formation of teams that are assigned a specific task or goal. C) Successful collaboration can be achieved through technology regardless of the organization's culture or structure. D) One business benefit of collaboration is improved innovation. 65) Which of the following is not one of the fifteen categories of collaborative software tools? A) file sharing B) event scheduling C) white boarding D) extranets 66) You work for a highly successful advertiser that is just about to expand nationally. Of utmost importance will be finding a way to store and disseminate their clients' continually updated branding guides, which include multiple image files and text documents, to all of the firm's branches. What system will best serve these needs? A) an intranet with KMS capabilities B) an extranet with KMS capabilities C) a TPS with KMS capabilities D) a CRM 67) You have been hired by a worldwide non-profit agency to implement a system to handle their donations. The system must be able to handle and record telephone, sms, and Internet donations, provide up-to-theminute reports, and create highly customizable mailing lists. In addition, event fundraisers need to be able to quickly access a donor's information and history. Which of the following systems will best meet these needs? A) TPS B) TPS with DSS capabilities C) TPS with MIS capabilities D) TPS with ESS capabilities 68) You have been hired by Inspiration Inc. to help improve their profit margin. Inspiration Inc. is a business commun ications consulta ncy that services many clients in different industries throughout the United States. The end products of the company are customized recommendations for the best use of a client's existing resources for improving internal communications, typically delivered via documentation in different media. The company has approximately 100 consultants, all of whom are located in their central headquarters in Chicago. What system do you recommend to improve the company's business processes and increase their profit margin? A) extranet, to enable quick collaboration over the Internet , minimize the time spent communicating with the client, and minimize the amount of paperwork needed B) CRM, to maintain easily accessible customer records to minimize the time spent looking for client data C) KMS, for minimizing redundant work on similar clients D) marketing system, for improving sales levels Answer: A MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 21) As discussed in the chapter opening case, which of the four generic strategies did Verizon employ to combat the competition offered by AT&T? A) low-cost leadership B) focus on market niche C) customer and supplier intimacy D) product differentiation 22) The interaction between information systems and organizations is influenced A) primarily by the decision making of middle- and senior-managers. B) by many factors, including structure, politics, culture, and environment. C) by two main microeconomic forces: capital and labor. D) primarily by the organization's business processes and culture. 23) An organization is a A) stable, formal social structure that takes resources from the environment and processes them to produce outputs. B) formal, legal entity with internal rules and procedures that must abide by laws. C) collection of social elements. D) B and C E) A, B, and C 24) How does the technical view of organizations fall short of understanding the full impacts of information systems in a firm? A) It sees information systems as a way to rearrange the inputs and outputs of the organization. B) It sees capital and labor as primary production factors. C) It sees the inputs and outputs, labor and capital, as being infinitely malleable. D) It sees the organization as a social structure similar to a machine. 25) According to the definition of organizations, an organization is seen as a means by which primaryproducti on factors are transformed into outputs consumed by the environment. A) microeconomic B) macroeconomic C) sociotechnical D) behavioral Answer: A 26) All of the following are major features of organizations that impact the use of information systems EXCEPT for A) business processes. B) environments. C) goals. D) : agency costs. 27) Business processes are collections of A) informal practices and behaviors. B) formalized and documented practices. C) routines. D) rights and privileges. 28) Which of the following would NOT be considered a disruptive technology? A) instant messaging B) e-mail C) Internet telephony D) PCs Answer: A 29) Mintzberg's classification of organizational structure categorizes the knowledge-based organization where goods and services depend on the expertise and knowledge of professionals as a(n) A) entrepreneurial structure. B) divisionalized bureaucracy. C) professional bureaucracy. D) adhocracy. 30) A large bureaucracy existing in a slowly changing environment that produces standard products and is dominated by centralized management making is classified by Mintzberg as a bureaucracy. A) machine B) professional C) divisionalized D) multidivisional Answer: A 31) An example of a professional bureaucracy is a A) small startup firm. B) school system. C) mid-size manufacturing firm. D) consulting firm. 32) The costs incurred when a firm buys on the marketplace what it cannot make itself are referred to as A) switching costs. B) transaction costs. C) procurement. D) agency costs. 33) Which of the following statements is NOT true about information technology's impacts on business firms? A) It helps firms expand in size. B) It helps firms lower the cost of market participation. C) It helps reduce internal management costs. D) It helps reduce transaction costs. Answer: A 34) According to agency theory, the firm is viewed as a(n) A) unified, profit-maximizing entity. B) task force organization that must respond to rapidly changing environments. C) entrepreneurial endeavor. D) "nexus of contracts" among self-interested individuals. 35) According to Leavitt's model of organizational resistance, the four components that must be changed in an organization in order to successfully implement a new information system are A) environment, organization, structure, tasks. B) technology, people, culture, and structure. C) organization, culture, management, and environment D) tasks, technology, people, and structure. 36) The model is used to describe the interaction of external forces that affect an organization's strategy and ability to compete. A) network economics B) competitive forces C) competitive advantage D) demand control 37) Which of the following industries has a low barrier to entry? A) automotive B) computer chip C) restaurant D) airline 38) Which of the following is NOT one of the competitive forces? A) suppliers B) other competitors C) external environment D) customers 39) A manufacturer of deep-sea oil rigs may be least concerned about this marketplace force. A) product differentiation B) traditional competitors C) low number of suppliers D) new market entrants 40) A substitute product of most concern for a cable TV distributor is A) satellite TV. B) broadcast TV. C) satellite radio. D) the Internet. Answer: A 41) Which of the following can force a business and its competitors to compete on price alone? A) transparent marketplace B) high product differentiation C) poor process efficiency D) demand control Answer: A 42) A firm can exercise greater control over its suppliers by having A) more suppliers. B) fewer suppliers. C) global suppliers. D) local suppliers. Answer: A 43) Amazon's use of the Internet as a platform to sell books more efficiently than traditional bookstores illustrates a use of information services for A) low-cost leadership. B) marketing effectiveness. C) focusing on market niche. D) strengthening supplier intimacy. Answer: A 44) The four major types of competitive strategy are A) low-cost leadership; substitute products and services; customers; and suppliers. B) low-cost leadership; product differentiation; focus on market niche; and customer and supplier intimacy. C) new market entrants; substitute products and services; customers; and suppliers. D) low-cost leadership; new market entrants; product differentiation; and focus on market niche. 45) Wal-Mart's continuous replenishment system allows it to A) provide mass customization. B) provide an efficient customer response system. C) strengthen customer intimacy. D) achieve economy of scale. 46) When a firm provides a specialized product or service for a narrow target market better than competitors, they are using a strategy. A) product differentiation B) market niche C) mass customization D) process efficiency 47) is the ability to offer individually tailored products or services using the same production resources as bulk production. A) Mass customization B) Size customization C) Magnitude customization D) Dimension customization Answer: A 48) Hilton Hotels' use of customer information software to identify the most profitable customers to direct services to is an example of using information systems to A) strengthen customer intimacy. B) differentiate their service. C) focus on market niche. D) increase efficiency. 49) An information system can enable a company to focus on a market niche through A) complex trend forecasting. B) tailoring products to the client. C) intensive product trend analysis. D) intensive customer data analysis. 50) Upon which of the following industries has the Internet as a whole been a disruptive technology? A) bill payments B) air travel C) books D) real estate 51) A rival of your company, AutoTown, is going to implement analytic software that mines customer data with a goal of enabling the building of automobiles that customers actually want. This can be categorized as using information systems for which competitive strategy? A) low-cost leadership B) product differentiation C) focus on market niche D) customer intimacy 52) Internet technology A) makes it easy for rivals to compete on price alone. B) imposes a significant cost of entry, due to infrastructure requirements. C) increases the difference between competitors because of the wide availability of information. D) makes it easy to sustain operational advantages. Answer: A 53) The Internet raises the bargaining power of customers by A) creating new opportunities for building loyal customer bases. B) making more products available. C) making information available to everyone. D) lowering transaction costs. 54) To what competitive force did the printed encyclopedia industry succumb? A) positioning and rivalry among competitors B) low cost of entry C) substitute products or services D) customer's bargaining power 55) The value chain model A) categorizes five related advantages for adding value to a firm's products or services. B) sees the supply chain as the primary activity for adding value. C) categorizes four basic strategies a firm can use to enhance its value chain. D) helps a firm identify points at which information technology can most effectively enhance its competitive position. 56) The primary activities of a firm include A) inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, sales and marketing, and service. B) inbound logistics, operations, outbound logistics, technology, and service. C) procurement, inbound logistics, operations, technology, and outbound logistics. D) procurement, operations, technology, sales and marketing, and services. Answer: A 57) Which of the following is one of the support activities in a firm's value chain? A) inbound logistics B) operations C) sales and marketing D) technology 58) Which of the following activities would you perform to measure and compare your business processes to similar processes of other companies within your industry? A) benchmarking B) best practices C) value chain analysis D) strategic systems analysis Answer: A 59) The most successful solutions or methods for achieving a business objective are called A) value activities. B) best processes. C) core competencies. D) best practices. 60) A collection of independent firms that use information technology to coordinate their value chains to produce a product or service for a market collectively is called a(n) A) industry value chain. B) business ecosystem. C) value web. D) consortia. 61) How are information systems used at the industry level to achieve strategic advantage? A) by building industry-wide, IT-supported consortia and symposia B) by raising the bargaining power of suppliers C) by encouraging the entry of new competitors D) by enforcing standards that reduce the differences between competitors Answer: A 62) If two organizations pool markets and expertise that result in lower costs and generate profits it is often referred to as creating A) a value web. B) a value chain. C) synergies. D) core competencies. 63) An example of synergy in business is A) Amazon's use of the Internet to sell books. B) JP Morgan Chase's mergers with other banks that provided JP Morgan with a network of retail branches in new regions. C) Blockbuster combining traditional video rental with online video rental. D) Wal-Mart's order entry and inventory management system to coordinate with suppliers. 64) An information system can enhance core competencies by A) providing better reporting facilities. B) creating educational opportunities for management. C) allowing operational employees to interact with management. D) encouraging the sharing of knowledge across business units. 65) The more any given resource is applied to production, the lower the marginal gain in output, until a point is reached where the additional inputs produce no additional output. This is referred to as A) the point of no return. B) the law of diminishing returns. C) supply and demand. D) network inelasticity. 66) Network economics A) applies the law of diminishing returns to communities of users. B) applies traditional economics to networked users. C) sees the cost of adding new members as inconsequential. D) balances the high cost of adding new members to a community against the lower cost of using network infrastructure. Classification: 67) An example of a keystone firm within a business ecosystem is A) Apple and software application writers in the mobile platform ecosystem. B) GUESS and the fashion ecosystem. C) Citibank and the ATM ecosystem. D) American Airlines and the computerized reservation ecosystem. Answer: A 68) A virtual company A) uses the capabilities of other companies without being physically tied to those companies. B) uses Internet technology to maintain a virtual storefront. C) uses Internet technology to maintain a networked community of users. D) provides entirely Internet-driven services, or virtual products. Answer: A 69) The emergence, for Amazon.com, of new competitors in the sphere of online shopping illustrates what disadvantage posed by the use of information systems to achieve competitive advantage? A) E-commerce is affected by the law of diminishing returns. B) Internet technologies are universal, and therefore usable by all companies. C) Internet shopping produces cost transparency. D) The Internet enables the production or sales of substitute products or services. 70) You are consulting for a beverage distributor who is interested in determining the benefits it could achieve from implementing new information systems. What will you advise as the first step? A) Identify the business ecosystem the distributor is in. B) Implement a strategic transition to the new system. C) Perform a strategic systems analysis. D) Benchmark existing systems. MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 21) Which of the following is NOT an IT infrastructure service component? A) operating system software B) computing platforms to provide a coherent digital environment C) physical facility management to manage the facilities housing physical components D) IT management services to plan and develop the infrastructure and provide project management Answer: A 22) Which type of infrastructure services provides voice and video connectivity to employees, customers, and suppliers? A) networking B) telephone C) VOIP D) telecommunications 23) Place the following eras of IT infrastructure evolution in order, from earliest to most recent: (1) Cloud Computing Era (2) Client/Server, (3) Enterprise Era, (4) Personal Computer, and (5) Mainframe and Minicomputer. A) 4, 5, 3, 2, 1 B) 5, 4, 2, 3, 1 C) 4, 5, 2, 3, 1 D) 5, 4, 2, 1, 3 Answer: A 24) The introduction of the minicomputer A) allowed computers to be customized to the specific needs of departments or business units. B) enabled decentralized computing. C) offered new, powerful machines at lower prices than mainframes. D) all of the above. 25) A client computer networked to a server computer, with processing split between the two types of machines, is called a(n) A) service-oriented architecture. B) on-demand architecture. C) multi-tiered client/server architecture. D) two-tiered client/server architecture. 26) In a multi-tiered network A) the work of the entire network is centralized. B) the work of the entire network is balanced over several levels of servers. C) processing is split between clients and servers. D) processing is handled by multiple, geographically remote clients. 27) Interpretations of Moore's law assert that A) computing power doubles every 18 months. B) transistors decrease in size 50% every two years. C) data storage costs decrease by 50% every 18 months. D) none of the above. Answer: A 28) Which of the following factors provides an understanding of why computing resources today are ever more available than in previous decades? A) network economics B) law of mass digital storage and Moore's law C) declining communications costs, universal standards, and the Internet D) all of the above 29) Today's nanotechnology-produced computer transistors are roughly equivalent in size to A) the width of a fingernail. B) a human hair. C) a virus. D) an atom. 30) Specifications that establish the compatibility of products and the ability to communicate in a network are called A) network standards. B) telecommunicationsstandards. C) technology standards. D) Internet standards. 31) unleash powerful economies of scale and result in declines in manufactured computer products. A) Internet and web technologies B) Technology standards C) Linux and open-source software D) Client/server technologies 32) The multitasking, multi-user, operating system developed by Bell Laboratories that operates on a wide variety of computing platforms is A) Unix. B) Linux. C) OS X. D) COBOL. Answer: A 33) The network standard for connecting desktop computers into local area networks that enabled the widespread adoption of client/server computing and local area networks and further stimulated the adoption of personal computers is A) TCP/IP B) COBOL C) Ethernet D) ASCII 34) Software that manages the resources of the computer is called A) operating system software. B) application software. C) data management software. D) network software. Answer: A 35) A SAN is a network. A) server area B) storage area C) scalable architecture D) service-oriented architecture 36) The leading networking hardware providers include A) Dell, HP/Compaq, and IBM. B) Cisco, Alcatel-Lucent, and Nortel. C) Seagate, Maxtor, and Western Digital. D) IBM, Oracle, and Sun. 37) As referred to in the text, legacy systems are A) traditional mainframe-based business information systems. B) electronic spreadsheets used on a PC. C) any pre-1990 Wintel systems. D) systems found on older ASPs. Answer: A 38) Legacy systems are still used because they A) can only be run on the older mainframe computers. B) are too expensive to redesign. C) integrate well using new Web services technologies. D) contain valuable data that would be lost during redesign. 39) Which of the following is NOT an example of the emerging mobile computing platforms? A) netbooks B) the Kindle C) cell phones D) CRM 40) Connecting geographically remote computers in a single network to create a "virtual supercomputer" is called A) co-location. B) edge computing. C) grid computing. D) utility computing. 41) The business case for using grid computing involves all of the following EXCEPT A) cost savings. B) increased accuracy. C) speed of computation. D) agility. 42) Which of the following does grid computing utilize to create enormous supercomputing power? A) massive unused data centers B) underutilized mainframe computers C) networked computers with idle resources D) networks with low usage 43) The process of presenting a set of computing resources (such as computing power or data storage) so that they can all be accessed in ways that are not restricted by physical configuration or geographic location is called A) cloud computing. B) autonomic computing. C) virtualization. D) multicore processing. Answer: A 44) Which type of computing refers to firms purchasing computing power from remote providers and paying only for the computing power they use? A) on-demand B) grid C) edge D) autonomic Answer: A 45) An example of autonomic computing is A) spyware protection software that runs and updates itself automatically. B) software programmed to run on any hardware platform. C) cell phones taking on the functions of handheld computers. D) programming languages that allow non-programmers to create custom applications. Answer: A 46) An industry-wide effort to develop systems that can configure, optimize, tune, and heal themselves when broken, and protect themselves from outside intruders and self-destruction is called A) grid computing. B) utility computing. C) virtualization. D) autonomic computing. 47) Which type of software is created and updated by a worldwide community of programmers and available for free? A) software packages B) mashups C) outsourced D) open source 48) Linux is A) primarily concerned with the tasks of end users. B) designed for specific machines and specific microprocessors. C) an example of open-source software. D) especially useful for processing numeric data. 49) Which of the following statements about Linux is NOT true? A) It plays a major role in the back office running local area networks. B) It is available in free versions downloadable from the Internet. C) It has garnered 80 percent of the server operating system market. D) Linux applications are embedded in cell phones, smartphones, netbooks, and other handheld devices. 50) Running a Java program on a computer requires A) a Java Virtual Machine to be installed on the computer. B) a Java Virtual Machine to be installed on the server hosting the Java applet. C) a miniature program to be downloaded to the user's computer. D) no specialized software, as Java is platform-independent. Answer: A 51) A software tool with a graphical user interface for displaying Web pages and for accessing the Web and other Internet resources is called a Web A) service. B) client. C) browser. D) app. 52) Which of the following is a technique used to allow users to interact with a Web page without having to wait for the Web server to reload the Web page? A) UDDI B) widgets C) Ajax D) Java 53) Sets of loosely coupled software components that exchange information with each other using standard Web communication standards and languages are referred to as A) Web services. B) EAI software. C) SOA. D) SOAP. Answer: A 54) What is the foundation technology for Web services? A) XML B) HTML C) SOAP D) UDDI Answer: A 55) A set of self-contained services that communicate with each other to create a working software application is called A) Web services. B) EAI software. C) SOA. D) SOAP. 56) Which of the following is NOT one of the current software platform trends? A) grid computing B) open source software C) mashups and apps D) software outsourcing Answer: A 57) All of the following are contemporary and growing hardware platform trends except A) green computing. B) virtualization. C) cloud computing. D) Unix. 58) are created by combining and customizing components from different online software applications. A) Apps B) Mashups C) SaaS D) Web services 59) Prewritten, commercially available sets of software programs that eliminate the need for a firm to write its own software programs for certain functions, are referred to as A) software packages. B) mashups. C) outsourced software. D) open source software. Answer: A 60) Your firm needs to implement electronic timesheet software and needs to keep within a small budget. Which of the following would be the most costly method of implementing this new software? A) purchasing a software package B) programming the new software in-house C) leasing the software over the Internet D) outsourcing the software programming to an overseas vendor 61) The practice of contracting custom software development to an outside firm is commonly referred to as A) outsourcing. B) scaling. C) service-oriented architecture. D) application integration. Answer: A 62) A formal contract between customers and their service providers that outlines the specific responsibilities of the service provider and to the customer is called a(n) A) SOA. B) SLA. C) TCO. D) RFQ. 63) SaaS refers to A) supplying online access over networks to storage devices and storage area network technology. B) managing combinations of applications, networks, systems, storage, and security as well as providing Web site and systems performance monitoring to subscribers over the Internet. C) hosting and managing access to software applications delivered over the Internet to clients on a subscription basis. D) none of the above. 64) Which of the following is NOT a challenge being faced by Salesforce.com, as discussed in the chapter case? A) increased competition from traditional industry leaders such as Microsoft and SAP B) continuing to differentiate its product and develop complementary new products and services C) maintaining 24/7 availability for clients D) moving into a more scalable, on-demand environment 65) Which of the following refers to the ability of a computer, product, or system to expand to serve a larger number of users without breaking down? A) modality B) scalability C) expandability D) disintermediation 66) How would you determine the market demand for your firm's IT services? A) Perform a TCO analysis. B) Benchmark your services. C) Hold focus groups to assess your services. D) Analyze sales returns on key investments. 67) Which of the following is NOT one of the main six factors to consider when evaluating how much your firm should spend on IT infrastructure? A) your firm's business strategy B) the IT investments made by competitor firms C) market demand for your firm's services D) your firm's organizational culture 68) Your firm, an auto parts manufacturer, has just merged with an automobile engine manufacturer, and the two companies have different SCM systems. Which of the following strategies would be the most likely course to help to reduce the TCO of the merged firms' technology investments? A) Use Web services to join the two systems. B) Move one firm into using the other's system in order to centralize management and support services. C) Develop a single ERP system that encompasses the information needs and business processes of both firms. D) Purchase a hosted, on-demand ERP system that encompasses the needs and processes of both firms. 69) Which model can be used to analyze the direct and indirect costs to help firms determine the actual cost of specific technology implementations? A) total cost of ownership B) return on investment C) breakeven point D) cost benefit analysis Answer: A 70) Hardware and software acquisition costs account for about percent of TCO. A) 20 B) 40 C) 60 D) 80 Answer: A MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 21) Which of the following best illustrates the relationship between entities and attributes? A) the entity CUSTOMER with the attribute PRODUCT B) the entity CUSTOMER with the attribute PURCHASE C) the entity PRODUCT with the attribute PURCHASE D) the entity PRODUCT with the attribute CUSTOMER 22) Which of the following is not one of the main problems with a traditional file environment? A) data inconsistency B) program-dataindependence C) lack of flexibility in creating ad-hoc reports D) poor security 23) A DBMS reduces data redundancy and inconsistency by A) enforcing referential integrity. B) uncoupling program and data. C) utilizing a data dictionary. D) minimizing isolated files with repeated data. 24) A characteristic or quality describing an entity is called a(n) A) field. B) tuple. C) key field. D) attribute. 25) Which of the following non-digital data storage items is most similar to a database? A) library card catalog B) cash register receipt C) doctor's office invoice D) list of sales totals on a spreadsheet Answer: A 26) The confusion created by makes it difficult for companies to create customer relationship management, supply chain management, or enterprise systems that integrate data from different sources. A) batch processing B) data redundancy C) data independence D) online processing 27) Duplicate data in multiple data files is called data . A) redundancy B) repetition C) independence D) partitions Answer: A 28) A DBMS makes the A) physical database available for different logical views. B) logical database available for different analytical views. C) physical database available for different analytical views. D) logical database available for different physical views. Answer: A 29) The logical view A) shows how data are organized and structured on the storage media. B) presents an entry screen to the user. C) allows the creation of supplementary reports. D) presents data as they would be perceived by end users. 30) DBMS for midrange computers include all of the following EXCEPT A) DB2. B) Oracle. C) Microsoft SQL Server. D) Microsoft Access. 31) The type of logical database model that treats data as if they were stored in two-dimensional tables is the A) OODBMS. B) pre-digital DBMS. C) relational DBMS. D) hierarchical DBMS. 32) Oracle Database Lite is a(n) A) DBMS for small handheld computing devices. B) Internet DBMS. C) mainframe relational DBMS. D) DBMS for midrange computers. Answer: A Classification: 33) Microsoft SQL Server is a(n) A) DBMS for small handheld computing devices. B) Internet DBMS. C) desktop relational DBMS. D) DBMS for midrange computers. 34) In a table for customers, the information about a single customer would reside in a single A) field. B) row. C) column. D) table. 35) In a relational database, a record is referred to in technical terms as a(n) A) tuple. B) row. C) entity. D) field. Answer: A 36) A field identified in a table as holding the unique identifier of the table's records is called the A) primary key. B) key field. C) primary field. D) unique ID. Answer: A 37) A field identified in a record as holding the unique identifier for that record is called the A) primary key. B) key field. C) primary field. D) unique ID. 38) In a relational database, the three basic operations used to develop useful sets of data are A) select, project, and where. B) select, join, and where. C) select, project, and join. D) select, from, and join. 39) The select operation A) combines relational tables to provide the user with more information than is otherwise available. B) creates a subset consisting of columns in a table. C) identifies the table from which the columns will be selected. D) creates a subset consisting of all records in the file that meet stated criteria. 40) The join operation A) combines relational tables to provide the user with more information than is otherwise available. B) identifies the table from which the columns will be selected. C) creates a subset consisting of columns in a table. D) organizes elements into segments. Answer: A 41) The project operation A) combines relational tables to provide the user with more information than is otherwise available. B) creates a subset consisting of columns in a table. C) organizes elements into segments. D) identifies the table from which the columns will be selected. 42) You are creating a video and animation sharing Web site whose content will be supplied by content, video, and applets stored in a database and you anticipate very high loads on the server. Which of the following DBMSs will most likely serve your needs? A) object-relational DBMS B) relational DBMS C) hierarchical DBMS D) OODBMS Answer: A 43) The type of database management approach that can handle multimedia is the A) hierarchical DBMS. B) relational DBMS. C) network DBMS. D) object-oriented DBMS. 44) The data dictionary serves as an important data management tool by A) assigning attributes to the data. B) creating an inventory of the data elements contained in the database. C) presenting data as end users or business specialists would perceive them. D) maintaining data in updated form. 45) An automated or manual file that stores information about data elements and data characteristics such as usage, physical representation, ownership, authorization, and security is the A) data dictionary. B) data definition diagram. C) entity-relationship diagram. D) relationship dictionary. Answer: A 46) The specialized language programmers use to add and change data in the database is called A) a data access language. B) a data manipulation language. C) Structured Query Language. D) a data definition language. 47) The most prominent data manipulation language today is A) Access. B) DB2. C) SQL. D) Crystal Reports. 48) DBMSs typically include report-generating tools in order to A) retrieve and display data. B) display data in an easier-to-read format. C) display data in graphs. D) perform predictive analysis. 49) The process of streamlining data to minimize redundancy and awkward many-to-many relationships is called A) normalization. B) data scrubbing. C) data cleansing. D) data defining. Answer: A 50) A schematic of the entire database that describes the relationships in a database is called a(n) A) data dictionary. B) intersection relationship diagram. C) entity-relationship diagram. D) data definition diagram. 51) A one-to-one relationship between two entities is symbolized in a diagram by a line that ends with A) two short marks. B) one short mark. C) a crow's foot. D) a crow's foot topped by a short mark. Answer: A 52) Which of the following is not one of the techniques used in Web mining? A) content mining B) structure mining C) usage mining D) user mining 53) You work for a retail clothing chain whose primary outlets are in shopping malls and are conducting an analysis of your customers and their preferences. You wish to find out if there are any particular activities that your customers engage in, or the types of purchases made in the month before or after purchasing select items from your store. To do this, you will want to use data mining software that is capable of A) identifying associations. B) identifying clusters. C) identifying sequences. D) classification. 54) You work for an national car rental agency and want to determine what characteristics are shared among your most loyal customers. To do this, you will want to use data mining software that is capable of A) identifying associations. B) identifying clusters. C) identifying sequences. D) classification. 55) A data warehouse is composed of A) historical data from legacy systems. B) current data. C) internal and external data sources. D) historic and current internal data. 56) A data mart usually can be constructed more rapidly and at lower cost than a data warehouse because A) a data mart typically focuses on a single subject area or line of business. B) all the information is historical. C) a data mart uses a Web interface. D) all of the information belongs to a single company. Answer: A 57) Tools for analyzing data to help users find patterns, relationships, and insights and make better business decisions are known as A) DSS. B) business intelligence. C) OLAP. D) data mining. Explanation: A) 58) The tool that enables users to view the same data in different ways using multiple dimensions is A) predictive analysis. B) SQL. C) OLAP. D) data mining. 59) OLAP is a tool for enabling A) users to obtain online answers to ad-hoc questions in a rapid amount of time. B) users to view both logical and physical views of data. C) programmers to quickly diagram data relationships. D) programmers to normalize data. Answer: A 60) Data mining is a tool for allowing users to A) quickly compare transaction data gathered over many years. B) find hidden relationships in data. C) obtain online answers to ad hoc questions in a rapid amount of time. D) summarize massive amounts of data into much smaller, traditional reports. 61) In terms of data relationships, associations refers to A) events linked over time. B) patterns that describe a group to which an item belongs. C) occurrences linked to a single event. D) undiscovered groupings. 62) tools are used to analyze large unstructured data sets, such as e-mail, memos, survey responses, etc., to discover patterns and relationships. A) OLAP B) Text mining C) Web mining D) Web content mining 63) An alternative to using application server software for interfacing between a Web server and back-end databases is A) CGI. B) HTML. C) Java. D) SQL. Answer: A 64) The organization's rules for sharing, disseminating, acquiring, standardizing, classifying, and inventorying information is called a(n) A) information policy. B) data definition file. C) data quality audit. D) data governance policy. Answer: A 65) The special organizational function whose responsibilities include the technical and operational aspects of managing data, including physical database design and maintenance, is called A) data administration. B) database administration. C) information policy administration. D) data auditing. 66) Which common database challenge is illustrated by a person receiving multiple copies of an L.L. Bean catalog, each addressed to a slightly different variation of his or her full name? A) data normalization B) data accuracy C) data redundancy D) data inconsistency 67) Detecting and correcting data in a database or file that are incorrect, incomplete, improperly formatted, or redundant is called A) data auditing. B) defragmentation. C) data scrubbing. D) data optimization. 68) You are creating a database to store temperature and wind data from national airport locations. Which of the following fields is the most likely candidate to use as the basis for a primary key in the Airport table? A) address B) city C) airport code D) state 69) Data cleansing not only corrects errors but also A) establishes logical relationships between data. B) structures data. C) normalizes data. D) Classification: enforces consistency among different sets of data. 70) Which of the following is NOT a method for performing a data quality audit? A) surveying entire data files B) surveying samples from data files C) surveying data definition and query files D) surveying end users about their perceptions of data quality MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 21) From your reading of the Cannondale case study, the firm implemented new information systems in order to achieve which of the main six business objectives? A) customer and supplier intimacy B) survival C) competitive advantage D) operational excellence 22) Which of the following is not an example of next-generation enterprise applications? A) open-source solutions B) on-demand solutions C) solutions incorporating SCM D) solutions incorporating SOA 23) A suite of integrated software modules for finance and accounting, human resources, manufacturing and production, and sales and marketing that allows data to be used by multiple functions and business processes best describes A) SCM software. B) ERP systems. C) ERM software. D) CRM modules. 24) Enterprise software is built around thousands of predefined business processes that reflect A) the firm's organization. B) industry goals. C) best practices. D) cutting edge workflow analyses. Ex 25) Which of the following is not true about enterprise systems? A) Enterprise systems help firms respond rapidly to customer requests for information or products. B) Enterprise system data have standardized definitions and formats that are accepted by the entire organization. C) Enterprise software is expressly built to allow companies to mimic their unique business practices. D) Enterprise software includes analytical tools to evaluate overall organizational performance. Answer: C 26) You have been asked to implement enterprise software for a manufacturer of kitchen appliances. What is the first step you should take? A) Select the functions of the system you wish to use. B) Select the business processes you wish to automate. C) Map the company’s business processes to the software’s business processes. D) Map the software’s business processes to the company’s business processes. Answer: A 27) When tailoring a particular aspect of a system to the way a company does business, enterprise software can provide the company with A) configuration tables. B) Web services. C) data dictionaries. D) middleware. Answer: A 28) In order to achieve maximum benefit from an enterprise software package, a business A) customizes the software to match all of its business processes. B) uses only the processes in the software that match its own processes. C) changes the way it works to match the software’s business processes. D) selects only the software that best matches its existing business processes. 29) Supply chain complexity and scale increases when firms A) move to globalization. B) manage the procurement, manufacturing, and distribution functions themselves. C) produce products and services that coordinate with hundreds or more firms and suppliers. D) modify their existing workflows to comply with supply-chain management systems. 30) Why is overstocking warehouses not an effective solution for a problem of low availability? A) It does not speed product time to market. B) It is an inefficient use of raw materials. C) It increases sales costs. D) It increases inventory costs. 31) A network of organizations and business processes for procuring raw materials, transforming these materials into intermediate and finished products, and distributing the finished products to customers is called a A) distribution channel. B) supply chain. C) value chain. D) marketing channel. 32) Components or parts of finished products are referred to as A) upstream materials. B) raw materials. C) secondary products. D) intermediate products. 33) A company’s suppliers and the processes for managing relationships with them is the A) supplier's internal supply chain. B) external supply chain. C) upstream portion of the supply chain. D) downstream portion of the supply chain. 34) A company’s organizations and processes for distributing and delivering products to the final customers is the A) supplier's internal supply chain. B) external supply chain. C) upstream portion of the supply chain. D) downstream portion of the supply chain. 35) Uncertainties arise in any supply chain because of A) inaccurate or untimely information. B) poor integration between systems of suppliers, manufacturers, and distributors. C) inefficient or inaccurate MIS. D) unforeseeable events. 36) Which of the following traditional solutions enables manufacturers to deal with uncertainties in the supply chain? A) safety stock B) continuous replenishment C) just-in-time strategies D) demand planning Answer: A 37) A scheduling system for minimizing inventory by having components arrive exactly at the moment they are needed and finished goods shipped as soon as they leave the assembly line best describes a strategy. A) just-in-time B) frictionless C) bullwhip D) safety-stock Answer: A 38) A distortion of information about the demand for a product as it passes from one entity to the next across the supply chain is called the effect. A) network B) bullwhip C) ripple D) whirlpool 39) Supply chain software can be classified as either supply chain systems or supply chain systems. A) push; pull B) demand; continual C) upstream; downstream D) planning; execution 40) Systems that enable a firm to generate demand forecasts for a product and to develop sourcing and manufacturing plans for that product best describes supply chain systems. A) demand B) delivery C) planning D) execution 41) Supply chain planning systems A) track the physical status of goods. B) identify the transportation mode to use for product delivery. C) track the financial information involving all parties. D) track the status of orders. 42) Which supply chain planning function determines how much product is needed to satisfy all customer demands? A) distribution management B) replenishment planning C) demand planning D) order planning 43) Supply chain systems manage the flow of products through distribution centers and warehouses to ensure that products are delivered to the right locations in the most efficient manner. A) demand B) delivery C) planning D) execution 44) Capabilities of supply chain execution systems would not include A) identifying the optimal transportation mode. B) tracking the flow of finished goods. C) managing materials. D) managing warehouse operations. Answer: A 45) A supply chain driven by actual customer orders or purchases follows a model. A) pull-based model B) build-to-stock C) push-based D) replenishment-driven Answer: A 46) A build-to-order supply-chain model is also called a model. A) supply-based B) demand-driven C) replenishment-driven D) push-based 47) Concurrent supply chains are made possible by which technology? A) ERP systems B) the Internet C) supply chain management systems D) just-in-time supply-chain technologies 48) The business value of an effective supply chain management system includes all of the following except A) faster time to market. B) cost reduction. C) supply matched to demand. D) increased inventory levels. 49) A is a method of interaction with a customer, such as telephone or customer service desk. A) point of presence B) touch point C) sales point D) client channel 50) Which of the following would not be considered a contact point? A) e-mail B) Web site C) intranet D) retail store E 51) modules use many of the same data, tools, and systems as CRM to enhance collaboration between a company and its selling partners. A) SCM B) SFA C) ERM D) PRM 52) modules deal with issues such as setting objectives, employee performance management, and performance-basedcompensation. A) SCM B) SFA C) ERM D) PRM 53) Customer relationship management systems typically provide software and online tools for sales, customer service, and A) marketing. B) account management. C) advertising. D) public relations. Answer: A 54) SFA modules in CRM systems would provide tools for A) assigning and managing customer service requests. B) capturing prospect and customer data. C) identifying profitable and unprofitable customers. D) managing sales prospect and contact information. 55) Customer service modules in CRM systems provide tools for A) assigning and managing customer service requests. B) capturing prospect and customer data. C) identifying profitable and unprofitable customers. D) managing sales prospect and contact information. Answer: A 56) Marketing modules in CRM systems would provide tools for A) assigning and managing customer service requests. B) capturing prospect and customer data. C) identifying profitable and unprofitable customers. D) managing sales prospect and contact information. 57) software deals with employee issues that are closely related to CRM, such as setting objectives, employee performance management, performance-based compensation, and employee training. A) Enterprise B) ERM C) PRM D) ERP 58) Selling a customer with a checking account a home improvement loan is an example of A) operational CRM. B) direct marketing. C) cross-selling. D) cross-channel promotions. 59) management is an important capability for service processes that is found in most major CRM software products. A) Returns B) Lead C) Account D) Events Answer: A 60) Which of the following is an important capability for sales processes that is found in most major CRM software products? A) returns management B) lead management C) channel promotions management D) events management 61) Customer relationship management applications dealing with the analysis of customer data to provide information for improving business performance best describes applications. A) operational CRM B) analytical CRM C) operational SCM D) analytical SFA 62) Analytical CRM applications A) include tools for marketing automation. B) provide consolidated data for operational CRM applications. C) are based on data warehouses consolidated from operational CRM applications. D) provide customer-facing applications. 63) Operational CRM applications include tools for A) identifying buying patterns. B) calculating CLTV. C) salesforce automation. D) pinpointing unprofitable customers. 64) Analyzing customer buying patterns is an example of A) CLTV. B) analytical CRM. C) operational CRM. D) demand planning. 65) Which metric is based on the relationship between the revenue produced by a specific customer, the expenses incurred in acquiring and servicing that customer, and the expected life of the relationship between the customer and the company? A) churn rate B) CLTV C) cost per lead D) cost per sale 66) The measurement of the number of customers who stop using or purchasing products or services from a company is called A) switching costs. B) churn rate. C) CLTV. D) switch rate. 67) All of the following statements about enterprise applications are true except for A) Enterprise applications are more successfully implemented when an organization has prepared for organizational change. B) Once you have purchased and implemented a vendor's enterprise system, it is much less expensive to switch vendors. C) The total implementation cost of a large system runs into millions of dollars. D) Enterprise applications are based on organization-wide definitions of data. 68) integrate(s) multiple applications from multiple business functions, business units, or business partners to deliver a seamless experience for the customer, employee, manager, or business partner and provide a greater degree of cross-functional integration than the traditional enterprise applications. A) PRM software B) SFA software C) ERP suites D) Service platforms 69) Enterprise application vendors have created to make their own customer relationship management, supply chain management, and enterprise systems work closely together with each other. A) e-business suites B) ERP systems C) middleware D) legacy systems Answer: A MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 21)Which of the following events signified the beginning of e-commerce? A) the first online advertisements B) the first telephone sales C) the first online retail store D) the first web site Answer: A 22) Based on your reading of the chapter, e-commerce is A) still in a revolutionary phase. B) widely accepted by consumers, although technology is still quickly changing. C) not yet fully accepted by consumers, although much of its driving technology is firmly in place. D) Answer: well entrenched as a form of modern commerce. A 23) The quality of ubiquity, as it relates to e-commerce, is illustrated by A) the same set of standards being used across the globe. B) the spread of plentiful, cheap information. C) the enabling of commerce worldwide. D) the availability of the Internet everywhere and anytime. 24) A marketplace extended beyond traditional boundaries and removed from a temporal and geographic location is called a(n) A) exchange. B) marketspace. C) online marketplace. D) Answer: e-hub. B 25) Which of the following is not a recent development in e-commerce? A) Wireless Internet connections grow rapidly. B) Social networking sites become a new platform for e-commerce. C) The music recording industry is disrupted as music creation and distribution become decentralized. D) Answer: Online entertainment business models surge. C 26) How are the Internet and e-commerce causing severe disruption to the existing advertising business model? A) Ties between customer and businesses are being rethought. B) Technology players such as Yahoo! seek to dominate online advertising and expand into offli C) ne ad brokerage. New methods of advertising, such as blog advertising, are emerging. D) Answer: The market entry costs for online advertising services are extremely low. B 27) Which of the following is not one of the unique features of e-commerce technology? A) information density B) transparency C) richness D) social technology 28) The act of engaging consumers in a dialog that dynamically adjusts the experience to the individual describes which dimension of e-commerce technology? A) ubiquity B) personalization/customization C) richness D) interactivity 29) The integration of video, audio, and text marketing messages into a single marketing message and consumer experience describes which dimension of e-commerce technology? A) ubiquity B) personalization/customization C) richness D) interactivity 30) The effort required to locate a suitable product is called A) price discrimination. B) search costs. C) menu costs. D) shopping costs. 31) The lowered costs of information storage, processing, and communication, along with the improvement of data quality, has resulted in which unique quality of e-commerce? A) information density B) richness C) customization D) interactivity Answer: A 32) Information density refers to the A) richness complexity and content of a message. B) total amount and quantity of information delivered to consumers by merchants. C) total amount and quantity of information available to all market participants. D) Answer: amount of information available to reduce price transparency. C 33) Selling the same goods to different targeted groups at different prices is called A) cost customization. B) cost optimization. C) price gouging. D) price discrimination. 34) Information ________ exists when one party in a transaction has more information that is important for the transaction than the other party. A) transparency B) asymmetry C) complexity D) discrimination 35) Which of the following businesses uses the market creator business model? A) an online auction house B) an online newspaper C) a video-sharing site D) an online bookseller Answer: A 36) Varying a product's price according to the supply situation of the seller is called ________ pricing. A) menu B) flexible C) dynamic D) Answer: asymmetric C 37) Compared to digital markets, traditional markets have A) lower search costs. B) stronger network effects. C) higher delayed gratification effects. D) higher transaction costs. 38) Reducing the business process layers in a distribution channel is called A) disintermediation. B) BPR. C) market segmentation. D) network effects. Answer: A 39) Digital goods are goods that are A) produced digitally. B) sold over digital networks. C) delivered digitally. D) used with digital equipment. 40) Compared to traditional goods, digital goods have A) greater pricing flexibility. B) lower marketing costs. C) higher production costs. D) higher inventory costs. Answer: A 41) Compared to traditional markets, digital markets have A) lower distributed delivery costs. B) higher marginal costs per unit. C) equivalent copying costs. D) similar inventory costs. Answer: A 42) Selling products and services directly to individual consumers via the Internet best describes A) B2B e-commerce. B) C2C e-commerce. C) M-commerce. D) B2C e-commerce. 43) Consumers selling goods and services electronically to other consumers best describes A) disintermediation. B) C2C e-commerce. C) M-commerce. D) B2C e-commerce. 44) EBay is an example of A) C2C e-commerce. B) B2B e-commerce. C) B2C e-commerce. D) M-commerce. Answer: A 45) Your company provides online tax preparation software. Users can download forms and read tips online without paying, but a fee is charged for using the advanced tax form management services. T h i s is an example of which type of revenue model? A) subscription B) affiliate C) transaction fee D) free/freemium 46) Which of the following businesses utilizes the content provider Internet business model? A) Amazon.com B) eBay.com C) CNN.com D) Motocross.com 47) In which of the following Internet business models does a merchant create an online digital environment that enables people with like interests to share information or buy and sell goods? A) community provider B) service provider C) market creator D) transaction broker Answer: A 48) Transaction brokers A) generate revenue from advertising or from directing buyers to sellers. B) save users money and time by processing online sales transactions. C) provide a digital environment where buyers and sellers can establish prices for products. D) sell physical products directly to consumers or individual businesses. 49) Market creators A) save users money and time by processing online sales transactions. B) provide a digital environment where buyers and sellers can establish prices for products. C) create revenue by providing digital content over the Web. D) sell physical products directly to consumers or individual businesses. 50) Which of the following best illustrates the sales revenue model? A) EBay receives a small fee from a seller if a seller is successful in selling an item. B) Epinions receives a fee after steering a customer to a participating Web site where he or she makes a purchase. C) Flickr provides basic services for free, but charges a premium for advanced services. D) Apple accepts micropayments for single music track downloads. 51) Which of the following best illustrates the transaction fee revenue model? A) EBay receives a small fee from a seller if a seller is successful in selling an item. B) Epinions receives a fee after steering a customer to a participating Web site where he or she makes a purchase. C) Flickr provides basic services for free, but charges a premium for advanced services. D) Apple accepts micropayments for single music track downloads. Answer: A 52) In which of the following revenue models does a Web site charge a fee for access to some or all of its offerings on a continual, regular basis? A) subscription B) free/freemium C) transaction fee D) sales Answer: A 53) Which of the following best illustrates the affiliate revenue model? A) EBay receives a small fee from a seller if a seller is successful in selling an item. B) Epinions receives a fee after steering a customer to a participating Web site where he or she makes a purchase. C) Flickr provides basic services for free, but charges a premium for advanced services. D) Apple accepts micropayments for single music track downloads. 54) In a phenomenon called ________, some argue that large numbers of people can make better decisions about a wide range of topics or products than a single person or even a small committee of experts. A) the wisdom of crowds B) outsourcing C) crowdsourcing D) social networking Answer: A 55) Netflix's public announcement of a reward for a technology solution to its movie recommendation system is an example of A) prediction markets. B) behavioral targeting. C) long-tail marketing. D) crowdsourcing. 56) Exposing an individual to ads that are chosen and based on the recorded and analyzed online behavior of the individual is referred to as A) clickstream advertising. B) behavioral targeting. C) online profiling. D) Answer: long-tail marketing. B 57) Which of the following was the leading marketing format in 2010? A) display ads B) e-mail C) classifieds D) search engine 58) Which of the following statements about B2B commerce is not true? A) Eighty percent of online B2B e-commerce is still based on EDI. B) B2B e-commerce represents approximately three-quarters of the overall B2B marketplace. C) B2B e-commerce only includes commercial transactions between firms. D) B2B e-commerce revenues in 2009 were over $3 trillion. 59) Which of the following describes long-tail marketing? A) The unexpected growth of sales of a product long after its initial release. B) The yearly sales of one or two copies each of thousands of obscure films. C) The dwindling sales of a once-popular book. D) The continued successful sales of a product over years. 60) Which of the following statements about m-commerce is not true? A) In 2010, m-commerce represented less than 10 percent of all e-commerce. B) M-commerce is the fastest growing form of e-commerce. C) M-commerce applications are especially popular in Europe, Japan, and South Korea. D) In 2010, the top-grossing category of m-commerce was e-book sales. 61) The system functionalities of an e-commerce site are best described as the A) general capabilities wanted. B) information systems capabilities wanted. C) information elements needed. D) software and hardware required. 62) EDI is A) the use of Internet technologies for electronic data transactions. B) the exchange between two organizations of standard transactions through a network. C) electronic data invoicing. D) electronic delivery infrastructure. 63) The process of sourcing goods and materials, negotiating with suppliers, paying for goods, and making delivery arrangements is called A) procurement. B) e-procurement. C) SCM. D) sourcing. Answer: A 64) An extranet that links a large firm to its suppliers and other key business partners is called a(n) A) e-hub. B) marketspace. C) exchange. D) private industrial network. 65) E-hubs are more ________ than private industrial networks. A) transaction-oriented B) collaborative C) independent D) supply-chain oriented Answer: A 66) Net marketplaces A) focus on continuous business process coordination between companies for supply chain management. B) are industry owned or operate as independent intermediaries between buyers and sellers. C) are geared towards short-term spot purchasing. D) are more relationship oriented than private industrial networks. 67) A third-party Net marketplace that connects many buyers and suppliers for spot purchasing is called a(n) A) exchange. B) vertical market. C) private exchange. D) e-hub. Answer: A 68) Which of the following is not one of the categories of services that are popular for m-commerce? A) location-based services B) financial services C) games and entertainment D) retail shopping 69) In the United States, m-commerce A) has become widely adopted. B) is still in its infancy. C) now represents a major fraction of total e-commerce transactions. D) is growing slowly. 70) You are planning the requirements for a site tracking and reporting system for your company Web site. Which of the following information requirements would not be essential for this function? A) number of unique visitors B) pages visited C) products purchased D) secure credit card clearing MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 22) Based on your reading of the chapter, e-commerce is A) still in a revolutionary phase. B) widely accepted by consumers, although technology is still quickly changing. C) not yet fully accepted by consumers, although much of its driving technology is firmly in place. D) well entrenched as a form of modern commerce. Answer: A 23) The quality of ubiquity, as it relates to e-commerce, is illustrated by A) the same set of standards being used across the globe. B) the spread of plentiful, cheap information. C) the enabling of commerce worldwide. D) the availability of the Internet everywhere and anytime. 24) A marketplace extended beyond traditional boundaries and removed from a temporal and geographic location is called a(n) A) exchange. B) marketspace. C) online marketplace. D) e-hub. 25) Which of the following is not a recent development in e-commerce? A) Wireless Internet connections grow rapidly. B) Social networking sites become a new platform for e-commerce. C) The music recording industry is disrupted as music creation and distribution become decentralized. D) Online entertainment business models surge. 26) How are the Internet and e-commerce causing severe disruption to the existing advertising business model? A) Ties between customer and businesses are being rethought. B) Technology players such as Yahoo! seek to dominate online advertising and expand into offline ad brokerage. C) New methods of advertising, such as blog advertising, are emerging. D) The market entry costs for online advertising services are extremely low. 27) Which of the following is not one of the unique features of e-commerce technology? A) information density B) transparency C) richness D) social technology 28) The act of engaging consumers in a dialog that dynamically adjusts the experience to the individual describes which dimension of e-commerce technology? A) ubiquity B) personalization/customization C) richness D) interactivity 29) The integration of video, audio, and text marketing messages into a single marketing message and consumer experience describes which dimension of e-commerce technology? A) ubiquity B) personalization/customization C) richness D) interactivity 30) The effort required to locate a suitable product is called A) price discrimination. B) search costs. C) menu costs. D) shopping costs. 31) The lowered costs of information storage, processing, and communication, along with the improvement of data quality, has resulted in which unique quality of e-commerce? A) information density B) richness C) customization D) interactivity Answer: A 32) Information density refers to the A) richness complexity and content of a message. B) total amount and quantity of information delivered to consumers by merchants. C) total amount and quantity of information available to all market participants. D) amount of information available to reduce price transparency. 33) Selling the same goods to different targeted groups at different prices is called A) cost customization. B) cost optimization. C) price gouging. D) price discrimination. 34) Information exists when one party in a transaction has more information that is important for the transaction than the other party. A) transparency B) asymmetry C) complexity D) discrimination 35) Which of the following businesses uses the market creator business model? A) an online auction house B) an online newspaper C) a video-sharing site D) an online bookseller Answer: A 36) Varying a product's price according to the supply situation of the seller is called pricing. A) menu B) flexible C) dynamic D) asymmetric 37) Compared to digital markets, traditional markets have A) lower search costs. B) stronger network effects. C) higher delayed gratification effects. D) higher transaction costs. 38) Reducing the business process layers in a distribution channel is called A) disintermediation. B) BPR. C) market segmentation. D) network effects. Answer: A 39) Digital goods are goods that are A) produced digitally. B) sold over digital networks. C) delivered digitally. D) used with digital equipment. 40) Compared to traditional goods, digital goods have A) greater pricing flexibility. B) lower marketing costs. C) higher production costs. D) higher inventory costs. Answer: A 41) Compared to traditional markets, digital markets have A) lower distributed delivery costs. B) higher marginal costs per unit. C) equivalent copying costs. D) similar inventory costs. Answer: A 42) Selling products and services directly to individual consumers via the Internet best describes A) B2B e-commerce. B) C2C e-commerce. C) M-commerce. D) B2C e-commerce. 43) Consumers selling goods and services electronically to other consumers best describes A) disintermediation. B) C2C e-commerce. C) M-commerce. D) B2C e-commerce. 44) EBay is an example of A) C2C e-commerce. B) B2B e-commerce. C) B2C e-commerce. D) M-commerce. Answer: A 45) Your company provides online tax preparation software. Users can download forms and read tips online without paying, but a fee is charged for using the advanced tax form management services. This is an example of which type of revenue model? A) subscription B) affiliate C) transaction fee D) free/freemium 46) Which of the following businesses utilizes the content provider Internet business model? A) Amazon.com B) eBay.com C) CNN.com D) Motocross.com 47) In which of the following Internet business models does a merchant create an online digital environment that enables people with like interests to share information or buy and sell goods? A) community provider B) service provider C) market creator D) transaction broker Answer: A 48) Transaction brokers A) generate revenue from advertising or from directing buyers to sellers. B) save users money and time by processing online sales transactions. C) provide a digital environment where buyers and sellers can establish prices for products. D) sell physical products directly to consumers or individual businesses. 49) Market creators A) save users money and time by processing online sales transactions. B) provide a digital environment where buyers and sellers can establish prices for products. C) create revenue by providing digital content over the Web. D) sell physical products directly to consumers or individual businesses. 50) Which of the following best illustrates the sales revenue model? A) EBay receives a small fee from a seller if a seller is successful in selling an item. B) Epinions receives a fee after steering a customer to a participating Web site where he or she makes a purchase. C) Flickr provides basic services for free, but charges a premium for advanced services. D) Apple accepts micropayments for single music track downloads. 51) Which of the following best illustrates the transaction fee revenue model? A) EBay receives a small fee from a seller if a seller is successful in selling an item. B) Epinions receives a fee after steering a customer to a participating Web site where he or she makes a purchase. C) Flickr provides basic services for free, but charges a premium for advanced services. D) Apple accepts micropayments for single music track downloads. Answer: A 52) In which of the following revenue models does a Web site charge a fee for access to some or all of its offerings on a continual, regular basis? A) subscription B) free/freemium C) transaction fee D) sales Answer: A 53) Which of the following best illustrates the affiliate revenue model? A) EBay receives a small fee from a seller if a seller is successful in selling an item. B) Epinions receives a fee after steering a customer to a participating Web site where he or she makes a purchase. C) Flickr provides basic services for free, but charges a premium for advanced services. D) Apple accepts micropayments for single music track downloads. 54) In a phenomenon called , some argue that large numbers of people can make better decisions about a wide range of topics or products than a single person or even a small committee of experts. A) the wisdom of crowds B) outsourcing C) crowdsourcing D) social networking Answer: A 55) Netflix's public announcement of a reward for a technology solution to its movie recommendation system is an example of A) prediction markets. B) behavioral targeting. C) long-tail marketing. D) crowdsourcing. 56) Exposing an individual to ads that are chosen and based on the recorded and analyzed online behavior of the individual is referred to as A) clickstream advertising. B) behavioral targeting. C) online profiling. D) long-tail marketing. 57) Which of the following was the leading marketing format in 2010? A) display ads B) e-mail C) classifieds D) search engine 58) Which of the following statements about B2B commerce is not true? A) Eighty percent of online B2B e-commerce is still based on EDI. B) B2B e-commerce represents approximately three-quarters of the overall B2B marketplace. C) B2B e-commerce only includes commercial transactions between firms. D) B2B e-commerce revenues in 2009 were over $3 trillion. 59) Which of the following describes long-tail marketing? A) The unexpected growth of sales of a product long after its initial release. B) The yearly sales of one or two copies each of thousands of obscure films. C) The dwindling sales of a once-popular book. D) The continued successful sales of a product over years. 60) Which of the following statements about m-commerce is not true? A) In 2010, m-commerce represented less than 10 percent of all e-commerce. B) M-commerce is the fastest growing form of e-commerce. C) M-commerce applications are especially popular in Europe, Japan, and South Korea. D) In 2010, the top-grossing category of m-commerce was e-book sales. 61) The system functionalities of an e-commerce site are best described as the A) general capabilities wanted. B) information systems capabilities wanted. C) information elements needed. D) software and hardware required. 62) EDI is A) the use of Internet technologies for electronic data transactions. B) the exchange between two organizations of standard transactions through a network. C) electronic data invoicing. D) electronic delivery infrastructure. 63) The process of sourcing goods and materials, negotiating with suppliers, paying for goods, and making delivery arrangements is called A) procurement. B) e-procurement. C) SCM. D) sourcing. Answer: A 64) An extranet that links a large firm to its suppliers and other key business partners is called a(n) A) e-hub. B) marketspace. C) exchange. D) private industrial network. 65) E-hubs are more than private industrial networks. A) transaction-oriented B) collaborative C) independent D) supply-chain oriented Answer: A 66) Net marketplaces A) focus on continuous business process coordination between companies for supply chain management. B) are industry owned or operate as independent intermediaries between buyers and sellers. C) are geared towards short-term spot purchasing. D) are more relationship oriented than private industrial networks. 67) A third-party Net marketplace that connects many buyers and suppliers for spot purchasing is called a(n) A) exchange. B) vertical market. C) private exchange. D) e-hub. Answer: A 68) Which of the following is not one of the categories of services that are popular for m-commerce? A) location-based services B) financial services C) games and entertainment D) retail shopping 69) In the United States, m-commerce A) has become widely adopted. B) is still in its infancy. C) now represents a major fraction of total e-commerce transactions. D) is growing slowly. 70) You are planning the requirements for a site tracking and reporting system for your company Web site. Which of the following information requirements would not be essential for this function? A) number of unique visitors B) pages visited C) products purchased D) secure credit card clearing MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 21) What is the primary driving factor in firms to select domestic outsourcing firms to build system solutions? A) to take advantage of technical skills the firm does not have B) to save labor costs C) to avoid change management issues D) all of the above Answer: A 22) The four kinds of structural organizational change enabled by IT, in order from least to most risky, are A) rationalization, automation, reengineering, and redesigning. B) rationalization, automation, reengineering, and paradigm shift. C) automation, rationalization, reengineering, and paradigm shift. D) automation, redesigning, restructuring, and paradigm shift. 23) Business processes are analyzed, simplified, and redesigned in A) business process redesign. B) rationalization of procedures. C) automation. D) paradigm shifts. Answer: A 24) In automation A) business processes are simplified. B) business processes are reorganized to cut waste and eliminate repetitive, paper-intensive tasks. C) standard operating procedures are streamlined to remove bottlenecks. D) employees are enabled to perform their tasks more efficiently. 25) A bank has reworked its mortgage application process so that several steps are handled by computer software, and some steps are combined to reduce bottlenecks in processing. The goal is to gradually improve its efficiency over time. This is an example of A) automation. B) rationalization of procedures. C) paradigm shift. D) business process redesign. 26) An upscale organic foods grocery chain is implementing an information system that will enable it to add same-day home delivery of groceries to its customers. This is an example of A) automation. B) rationalization of procedures. C) paradigm shift. D) business process redesign. 27) In order, what are the first three steps in BPM? A) (1) identifying processes for change, (2) analyzing existing processes, (3) designing the new process B) (1) analyzing existing processes, (2) identifying processes for change, (3) designing the new process C) (1) identifying processes for change, (2) designing the new process, (3) implementing the new process D) (1) analyzing processes to change (2) designing the new process, (3) measuring the optimized process Answer: A 28) provide(s) a methodology and tools for dealing with the organization's ongoing need to revise and optimize its numerous business processes. A) Business process redesign B) Business process management C) CASE tools D) TQM 29) The idea that the achievement of quality control is an end in itself describes a main concept of A) BPM. B) BPR. C) six sigma. D) TQM. 30) Which process develops a detailed description of the functions that a new information system must perform? A) feasibility study B) requirements analysis C) systems design D) test plan development 31) The entire system-building effort is driven by A) organizational change. B) feasibility studies. C) the information value chain. D) user information requirements. 32) Systems design A) describes what a system should do to meet information requirements. B) shows how the new system will fulfill the information requirements. C) identifies which users need what information, where, when and how. D) is concerned with the logical view of the system solution. 33) System design specifications that address the category of database design issues will include specifications for A) transaction volume and speed requirements. B) data entry. C) job design. D) program logic and computations. Answer: A 34) Enabling organizations to make continual improvements to many business processes and to use processes as the fundamental building blocks of corporate information systems is the goal of A) business process management. B) business process redesign. C) workflow engineering. D) workflow management. Answer: A 35) Transferring data from a legacy system to the new system would be defined by which category of system design specifications? A) input B) database C) manual procedures D) conversion 36) Determining methods for feedback and error handling would be defined by which category of system design specifications? A) training and documentation B) user interface C) manual procedures D) security and controls 37) Unit testing A) includes all the preparations for the series of tests to be performed on the system. B) tests the functioning of the system as a whole in order to determine if discrete modules will function together as planned. C) tests each program separately. D) provides the final certification that the system is ready to be used in a production setting. 38) System testing A) includes all the preparations for the series of tests to be performed on the system. B) tests the functioning of the system as a whole in order to determine if discrete modules will function together as planned. C) tests each program separately. D) provides the final certification that the system is ready to be used in a production setting. 39) Acceptance testing A) includes all the preparations for the series of tests to be performed on the system. B) tests the functioning of the system as a whole in order to determine if discrete modules will function together as planned. C) tests each program separately. D) provides the final certification that the system is ready to be used in a production setting. 40) In a parallel conversion strategy, the new system A) is tested by an outsourced company. B) replaces the old one at an appointed time. C) and the old are run together. D) is introduced in stages. 41) In the direct cutover conversion strategy, the new system A) is tested by an outsourced company. B) replaces the old one at an appointed time. C) and the old are run together. D) is introduced in stages. 42) Changes in hardware, software, documentation, or production to a production system to correct errors, meet new requirements, or improve processing efficiencies are termed A) compliance. B) production. C) maintenance. D) acceptance. 43) In what stage of systems development are design specifications created? A) systems analysis B) systems design C) testing D) conversion 44) The primary tool for representing a system's component processes and the flow of data between them is the A) data dictionary. B) process specifications diagram. C) user documentation. D) data flow diagram. 45) To understand and define the contents of data flows and data store, system builders use A) a data dictionary. B) process specifications diagrams. C) user documentation. D) data flow diagrams. Answer: A 46) To show each level of a system's design, its relationship to other levels, and its place in the overall design structure, structured methodologies use A) structure charts. B) Gantt and PERT charts. C) process specifications. D) data flow diagrams. Answer: A 47) An entire information system is broken down into its subsystems by using A) high-level data flow diagrams. B) low-level data flow diagrams. C) process specifications. D) structured diagrams. Answer: A 48) In object-oriented development A) the class is used as the basic unit of systems analysis and design. B) an object is a collection of data that is acted on by external processes. C) processing logic resides within objects. D) a strict, step-by-step development process is essential. 49) In an object-oriented development framework for a university, how would the classes Degree, Mathematics, and Physics be related? A) Degree would be a sister class to Mathematics and Physics. B) Degree is a superclass to Mathematics and Physics. C) Mathematics and Physics would be ancestors to Degree. D) Degree would be a subclass to Mathematics and Physics. 50) Object-oriented modeling is based on the concepts of A) objects and relationships. B) classes and objects. C) class and inheritance. D) objects and inheritance. 51) Object-oriented development could potentially reduce the time and cost of writing software because A) object-oriented programming requires less training. B) iterative prototyping is not required. C) objects are reusable. D) a single user interface object can be used for the entire application. 52) CASE tools automate A) documentation. B) code generation. C) creating data dictionaries. D) all of the above. 53) The oldest method for building information systems is A) component-baseddevelopment. B) prototyping. C) object-oriented development. D) the systems development lifecycle. 54) In the traditional systems development lifecycle, end users A) are important and ongoing members of the team from the original analysis phase through maintenance. B) are important only in the testing phases. C) have no input. D) are limited to providing information requirements and reviewing the technical staff's work. Answer: D 55) In which type of systems building are the development stages organized so that tasks in one stage are completed before the tasks in the next stage begun? A) traditional B) prototyping C) RAD D) all of the above Answer: A 56) As a technical project manager you have decided to propose implementing a prototyping methodology for a small Web-based design project. What is the order of steps you will follow in this project? A) Develop the prototype; use the prototype; revise and enhance the prototype. B) Identify user requirements, develop the prototype, use the prototype, revise and enhance the prototype. C) Define the requirements, develop solutions, select the best prototype, and implement the prototype. D) Define the requirements, develop the prototype, revise and enhance the prototype. 57) A systems building approach in which the system is developed as successive versions, each version reflecting requirements more accurately, is described to be A) end-user oriented. B) iterative. C) object-oriented. D) agile. 58) Which type of fourth-generation language tools are end-users most likely to work with? A) report generators and query languages B) report generators and application generators C) PC software tools and query languages D) PC software tools and report generators 59) Which type of fourth-generation language tool contains preprogrammed modules that can be used to create entire applications? A) PC software tools B) report generators C) application generators D) application software packages 60) When systems are created rapidly, without a formal development methodology A) end users can take over the work of IT specialists. B) the organization quickly outgrows the new system. C) hardware, software, and quality standards are less important. D) testing and documentation may be inadequate. 61) Management should control the development of end-user applications by A) developing a formal development methodology. B) requiring cost justification for end-user IS projects. C) establishing standards for user-developed applications. D) both B and C E) both A and B 62) Fourth-generation tools cannot replace conventional development tools because they A) cannot handle large numbers of transactions or extensive procedural logic. B) are not designed to integrate with legacy systems. C) do not incorporate methods for documentation. D) do not incorporate methods for testing. Answer: A 63) Categories of tools for BPM include all of the following except A) tools to integrate existing systems to support business processes improvements. B) tools to automate business processes. C) tools to identify and document business processes. D) tools to test the security of business processes. 64) What is the greatest barrier to successful business process change? A) ineffective project management B) usability of implemented solution C) selecting the correct process to change D) organizational change 65) The process of creating workable information systems in a very short period of time is called A) RAD. B) JAD. C) prototyping. D) B and C. Answer: A 66) Which type of systems development is characterized by significantly speeding up the design phase and the generation of information requirements and involving users at an intense level? A) RAD B) JAD C) prototyping D) end-user development 67) You are an IT project manager for an advertising firm. The firm wishes to create an online tool that will be used to survey focus group reactions to products in development. The most important consideration for the firm is being able to offer the tool as soon as possible as a new corporate service. However, you know that many of the senior managers that are business owners of this project have difficulty in understanding technical or software development issues, and are likely to change their requirements during the course of development. What development method would be most successful for this project? A) RAD B) JAD C) end-user development D) prototyping 68) Groups of objects are assembled into software components for common functions, which can be combined into large-scale business applications, in which type of software development? A) object-oriented development B) component-baseddevelopment C) structured methodologies D) RAD 69) Compared to the use of proprietary components, Web services promise to be less expensive and less difficult to implement because of A) their ability to integrate seamlessly with legacy systems. B) the use of universal standards. C) the ubiquity of the Internet. D) the ability to reuse Web services components. 70) development focuses on rapid delivery of working software by breaking a large project into a series of small sub-projects that are completed in short periods of time using iteration and continuous feedback. A) Agile B) Rapid application C) Joint application D) Object-oriented Answer: A MULTIPLE CHOICE. Choose the one alternative that best completes the statement or answers the question. 21) On average, private sector IT projects underestimated budget and delivery time of systems by percent A) 30 B) 40 C) 50 D) 60 22) The major variables in project management are A) scope, time, cost, and performance. B) scope, time, cost, quality, and risk. C) time, cost, quality, performance, and risk. D) time, cost, scope, and performance. 23) At the top of the management structure for information systems projects in a large company is A) project management. B) the CIO. C) the corporate strategic planning group. D) the IS steering committee. 24) The is directly responsible for the individual systems project. A) project management group B) project team C) IS steering committee D) corporate strategic planning committee 25) The reviews and approves plans for systems in all divisions. A) project management group B) project team C) IS steering committee D) corporate strategic planning committee 26) The consists of systems analysts, specialists from the relevant end-user business areas, application programmers, and perhaps database specialists. A) project management group B) project team C) IS steering committee D) corporate strategic planning committee 27) A road map indicating the direction of systems development, the rationale, the current systems, new developments to consider, the management strategy, the implementation plan, and the budget is called a(n) A) project plan. B) portfolio analysis. C) information systems plan. D) enterprise analysis. 28) A CSF approach to establishing an enterprise's information requirements is especially suitable for A) distinguishing between individual and organizational objectives. B) identifying the key entities and attributes of the organization's data. C) understanding how organizational units define critical data. D) the development of DSSs and ESSs. 29) The principal method used in CFS analysis is to A) inventory all of the organization's information systems projects and assets and assign risk levels. B) perform a weighted comparison of the criteria used to evaluate a system. C) survey a large sample of managers on their objectives, decision-making process, and uses and needs for data and information. D) interview a small number of top managers to identify their goals and criteria for achieving success. 30) In CFS analysis, it is important to A) interview as many employees from different levels of the company as possible. B) create a broad inquiry into the various types of information used in the company. C) distinguish between organizational and individual CSFs. D) identify operational managers that can accurately portray the day-to-day information needs of the firm. 31) The central method used in a portfolio analysis is to A) inventory all of the organization's information systems projects and assets. B) perform a weighted comparison of the criteria used to evaluate a system. C) survey a large sample of managers on their objectives, decision-making process, and uses and needs for data and information. D) interview a small number of top managers to identify their goals and criteria for achieving success. Answer: A 32) In using a portfolio analysis to determine which IT projects to pursue, you would A) select the most low-risk projects from the inventory. B) limit work to those projects with great rewards. C) select only low-risk, high-reward projects. D) balance high-risk, high reward projects with lower-risk projects. 33) Which method would you use is used to develop risk profiles for a firm's information system projects and assets? A) information systems plan B) scoring model C) portfolio analysis D) CSF 34) The central method used in a scoring model is to A) inventory all of the organization's information systems projects and assets. B) perform a weighted comparison of the criteria used to evaluate a system. C) survey a large sample of managers on their objectives, decision-making process, and uses and needs for data and information. D) interview a small number of top managers to identify their goals and criteria for achieving success. 35) You have been hired by a pharmaceutical company to evaluate its inventory of systems and IT projects. Which types of projects would be best avoided? A) any high risk projects B) any low-benefit projects C) all high-risk, low benefit projects D) none, any project might be beneficial 36) Which method is used to assign weights to various features of a system? A) information systems plan B) scoring model C) portfolio analysis D) CSF 37) The criteria used for evaluation in a scoring model are usually determined by A) lengthy discussions among the decision-making group. B) a CSF analysis. C) the IS steering committee. D) systems analysts. Answer: A 38) All of the following are intangible benefits of information systems except A) improved asset utilization. B) increased organizational learning. C) improved operations. D) reduced workforce. 39) Which of the following is not a tangible benefit of information systems? A) reduced rate of growth in expenses B) lower computer expenses C) improved resource control D) increased productivity 40) The worth of systems from a financial perspective essentially revolves around the issue of A) CSFs. B) adherence to information requirements. C) asset utilization. D) return on invested capital. 41) You are using a capital budgeting method to assess the worth of your company's new information system. Which of the following costs would you include in measuring the cash outflow? A) increased sales of products B) hardware and software expenditures C) labor expenditures D) reduced costs in production and operation E) both A and D F) both B and C G) A, B, C and D 42) In working with ROPMs and options valuation, a call option is a(n) A) obligation to purchase an asset at a later date at a fixed price. B) obligation to either purchase or sell an asset at a later date at a strike price. C) right to purchase an asset a later date at a strike price. D) right to purchase or sell an asset a later date at a fixed price. 43) The principal capital budgeting models for evaluating information technology projects are the payback method, the accounting rate of return on investment (ROI), the net present value, and the A) future present value. B) internal rate of return. C) external rate of return. D) ROPM. 44) ROPMs value information systems similar to stock options, in that A) ROPMs can be bought and sold like stocks. B) a company's worth can be evaluated by the worth of their ROPMs. C) initial expenditures on IT projects are seen as creating the right to pursue and obtain benefits from the system at a later date. D) expenditures and benefits from IT projects are seen as inflows and outflows of cash that can be treated themselves like options. 45) To best evaluate, from a financial standpoint, an IT investment whose benefits cannot be firmly established in advance, you would use A) capital budgeting. B) the real option pricing model. C) a scoring model. D) the net present value. 46) The level of a project's risk is influenced primarily by A) project size, project structure, and the level of technical expertise. B) project cost, project scope, and the implementation plan. C) project scope, project schedule, and project budget. D) project size, project scope, and the level of technical expertise. Answer: A 47) The project risk will rise if the project team and the IS staff lack A) legacy applications as a starting point. B) good equipment. C) the required technical expertise. D) financial studies and plans. 48) The organizational activities working toward the adoption, management, and routinization of a new information system are called A) production. B) maintenance. C) implementation. D) acceptance. 49) Which of the following is not one of the activities of the systems analyst? A) acting as a change agent B) communication with users C) mediating between competing interest groups D) formulation of capital budgeting models 50) One example of an implementation problem is A) poor user interface. B) inadequate user training. C) project running over budget. D) changes in job activities and responsibilities. 51) According to your reading of the chapter, change management is a process that A) should be addressed before a project is developed. B) begins when a project is implemented. C) is used primarily to mandate user acceptance. D) must be addressed in all systems development. Answer: A 52) Users prefer systems that A) are oriented to facilitating organizational tasks and solving business problems. B) work with existing DBMS. C) are able to provide optimum hardware and software efficiency. D) are capable of storing much more data than they need. Answer: A 53) The communications gap between users and systems designers is created by their differences in A) backgrounds. B) interests. C) priorities. D) A and B. E) B and C. F) all of the above. 54) Which of the following types of projects is most likely to fail? A) integration of an third-party automated payment system B) replacement of middleware with Web services for legacy application integration C) a business process redesign project that restructures workflow and responsibilities D) redesigning a user interface to an online investment site 55) Which of the following is not a responsibility of effective change management? A) integrating legacy systems B) dealing with fear and anxiety about new systems C) training users of the new system D) enforcing user participation at all stages of system development Answer: A 56) Which of the following tools would you use to control risk factors in an information systems project? A) internal integration tools B) external integration tools C) formal planning tools and formal control tools D) A and B E) A and C F) all of the above 57) Internal integration tools A) enable a project to have sufficient technical support for project management and development. B) enable a project manager to properly document and monitor project plans. C) portray a project as a network diagram with numbered nodes representing project tasks. D) consist of ways to link the work of the implementation team with users at all organization levels. Answer: A 58) An example of using an internal integration tool would be to A) define task dependencies. B) include user representatives as active members of the project team. C) create a PERT chart. D) hold frequent project team meetings. 59) Formal planning and control tools A) enable a project to have sufficient technical support for project management and development. B) enable a project manager to properly document and monitor project plans. C) portray a project as a network diagram with numbered nodes representing project tasks. D) consist of ways to link the work of the implementation team with users at all organization levels. 60) External integration tools A) enable a project to have sufficient technical support for project management and development. B) enable a project manager to properly document and monitor project plans. C) portray a project as a network diagram with numbered nodes representing project tasks. D) consist of ways to link the work of the implementation team with users at all organization levels. 61) An example of using an external integration tool would be to A) define task dependencies. B) include user representatives as active members of the project team. C) create a PERT chart. D) hold frequent project team meetings. 62) Which type of planning tool shows each task as a horizontal bar whose length is proportional to the time required to complete it? A) PERT chart B) Gantt chart C) both A and B D) neither A nor B 63) To review a project's tasks and their interrelationships, you would use a A) PERT chart. B) Gantt chart. C) either A or B. D) neither A nor B. Answer: A 64) Which type of tool helps project managers identify bottlenecks in project development? A) internal integration tools B) external integration tools C) formal planning and control tools D) both B and C 65) Which of the following is a limitation of using a financial approach to evaluate information systems? A) inability to measure ROI B) inability to control vendor costs C) inability to assess risk D) inability to assess costs from organizational disruption 66) Which of the following statements best describes the effect of project structure on overall project risk? A) Highly structured projects are more complex, and run a higher risk of programmers and users misunderstanding the ultimate goals. B) Projects with relatively undefined goals are more likely to be subjected to users changing requirements and run a higher risk of not satisfying project goals. C) Highly structured projects tend to be larger, affecting more organizational units, and run both the risk of out-of-control costs and becoming too difficult to control. D) Less structured projects are more able to be quickly developed, tested, and implemented using cuttingedge RAD and JAD development techniques, and pose less risk of running up unforeseen costs. 67) Which of the following is not an organizational factor in systems planning and implementation? A) standards and performance monitoring B) government regulatory compliance C) health and safety D) user interface 68) In sociotechnical design A) separate sets of technical and social design solutions are developed and compared. B) ergonomic features of a system and the system's technical design are given equal importance. C) systems analysts with proven backgrounds in sociological concerns rate and compare a system's social and technical aspects. D) all of the above. Answer: A 69) The most widely used project management software today is A) Vertabase. B) IBM Project Guide. C) Microsoft Project. D) Microsoft Excel. 70) As discussed in the chapter, which of the following is not one of the immediate consequences of inadequate software project management? A) cost overruns B) organizational conflict C) time slippage D) technical shortfalls [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 83 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 02, 2021
Number of pages
83
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 02, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
226