OPOTA Practice Test | 63 Questions with 100% Correct Answers
$ 7

RN ATI Comprehensive Predictor 2025
$ 18

CCNA 1 EXAM 2023 WITH COMPLETE SOLUTION
$ 15

ACP Chemistry Exam: Chapters 5, 6,& 17
$ 30

Nursing Fundamentals: Essential Study Notes
$ 9

OCR GCSE (9–1) Combined Science B (Twenty First Century Science) J260/06 Chemistry (Higher Tier) General Certificate of Secondary Education Question Paper for June 2022
$ 5.5

Portage Learning Chem 210 Module 4 Problem Set | 100% Guaranteed Pass
$ 7.5

MATH 225N Applied Linear Algebra 2, questions and answers all 100% correct solution
$ 10
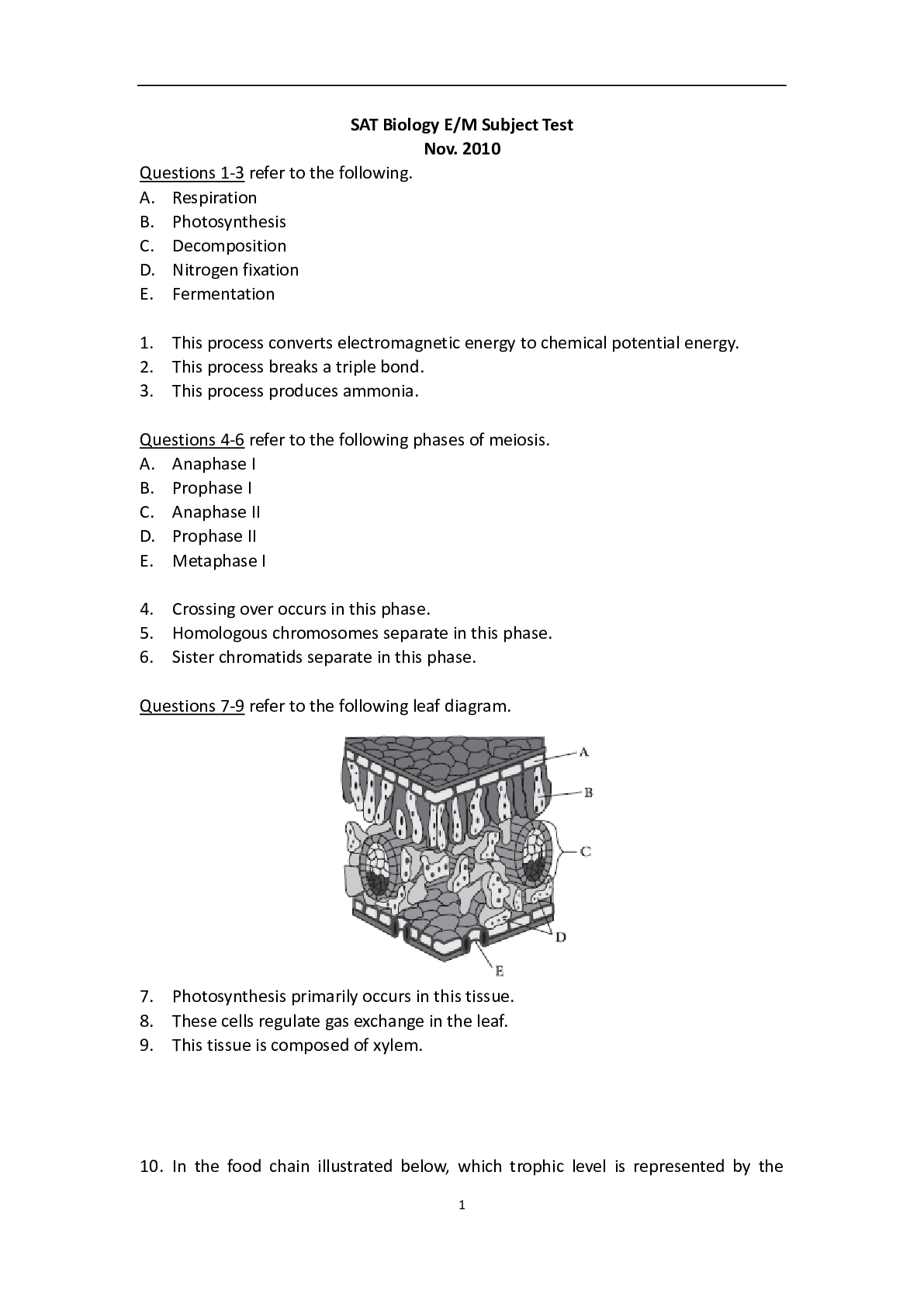
SAT Biology E/M Subject Test. 100 MCQ and Answer Key
$ 5

ANATOMY BSC 2346-Final Exam | 60 Q&A Correct Answers Highighted
$ 9

Accounting for decision makers C213 WGU Flashcards
$ 14

Stat 330: Module 4 Homework Solution | Download for quality grades | 100% correct answers |
$ 5
.png)
ATI Exit Practice Question Notes,
$ 5

ACLS: PROMED questions and answers Graded A+ complete solution 2025/2026
$ 21.5

NCLEX Review Questions-NG, Ostomy-Test your knowledge
$ 12

AZ 104 RENEWAL EXAM_Complete Q&A

![Preview image of Microbiology Study Questions[GRADED] document](https://scholarfriends.com/storage/MicroBiology_C453_Study_Guide_filled_out_and_modified.png)


.png)