EMT Study Guide. Contains Over 200 Exam Questions and Answers.
Document Content and Description Below
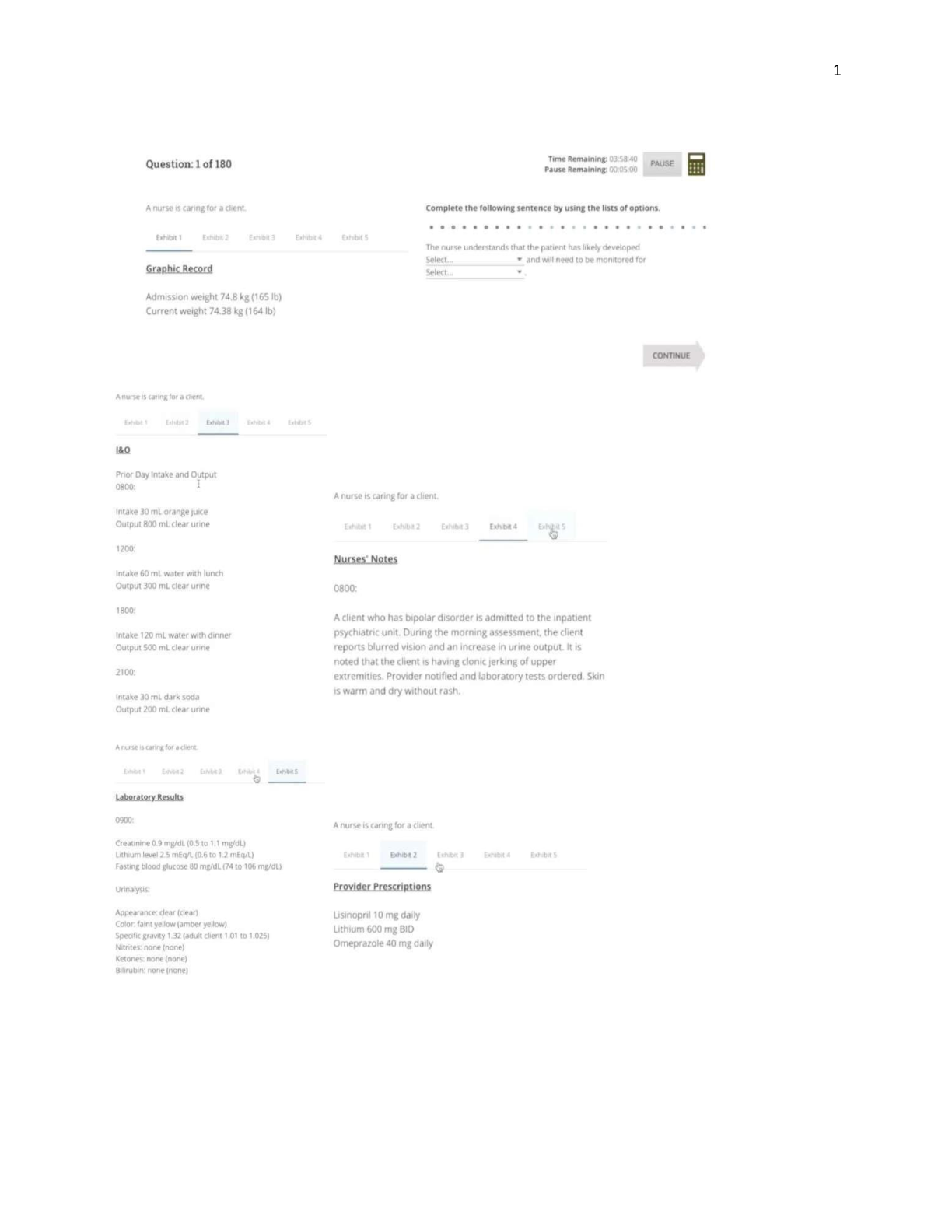
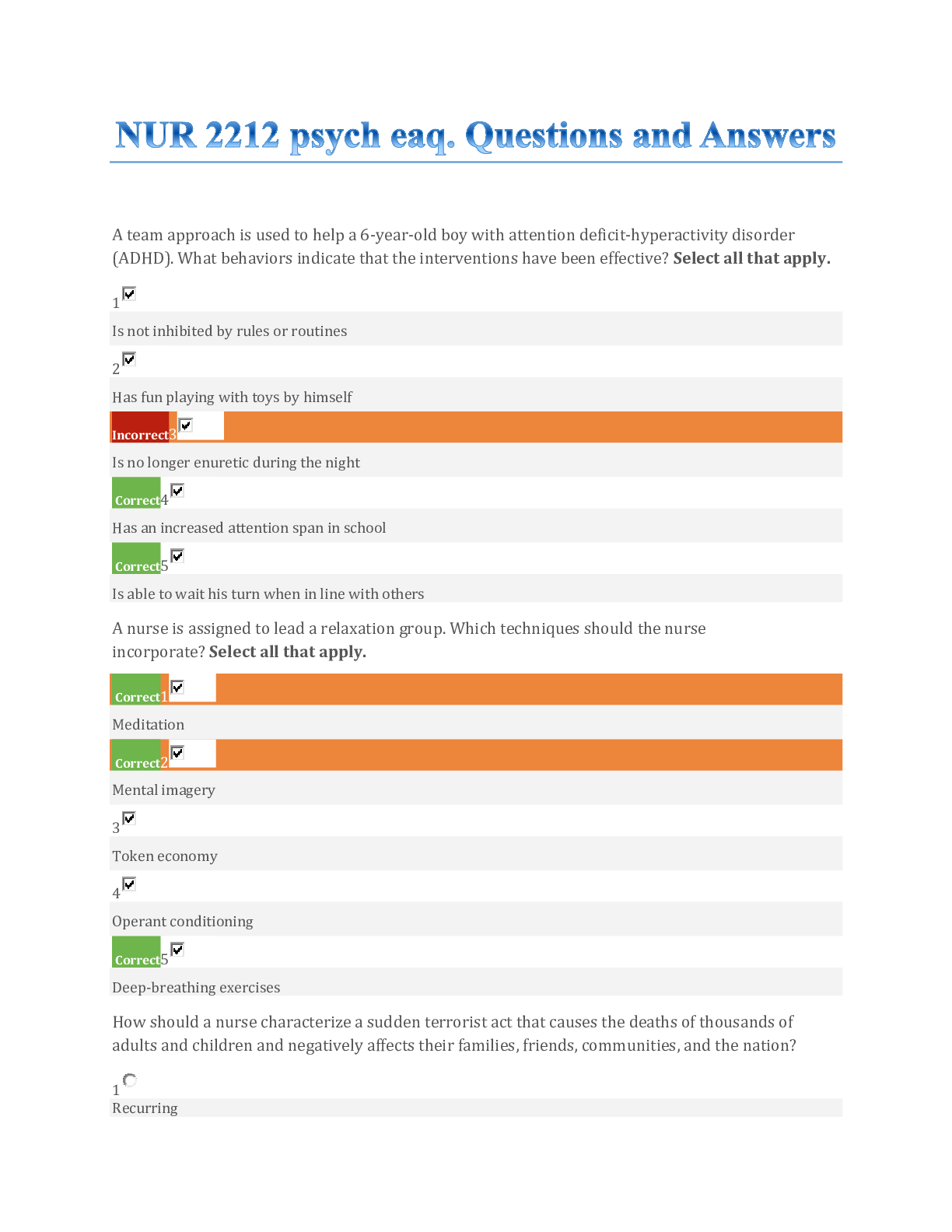
Explain medical direction as it relates to the EMS system at the EMT level. Online & Offline. What are the different levels of EMS Training that can be acquired? List the roles and respo ... nsibilities of an EMT. What is a Standing Order? Discuss the health concerns related to exposure to Hepatitis B, Hepatitis C, Tuberculosis, and AIDS. And PPE that an EMT should use to protect themselves from these disease processes. When would an N-95 or HEPA respirator need to be worn? List the different transmission routes that an EMT can be exposed to a pathogen. Name the three types of stress reactions that someone can experience. Describe the factors that must be considered prior to lifting any patient When would an "emergency move" of a patient be required? List the 6 types of patient carrying devices Scope of practice Abandonment Consent Assault Duty to act In loco parentis Describe the procedure that must take place in order for the patient to refuse treatment/transport. What must be identified from the patient and what must the EMT inform the patient of? What is the difference between a DNR and an Advanced Directive? What must the EMT be mindful of when involved with a patient care at a crime scene? List all of the body systems List the types of muscles in the body and where they're located List the three types of anatomical positions that we may find a patient in or place them in for treatment/transport. Define the different regions of the skull Define the different structures of blood and what they are responsible for Define the different structures between veins, arteries, and capillaries List the glands of the endocrine system List the sections of the spinal cord and how many vertebra are within each section Define blood pressure Describe how the respiratory and cardiac systems are connected. Think diffusion Describe why it is important that blood vessels have the capability to dilate and constrict. How does this impact the cardiovascular system as a whole. Define Cardiac Output Describe what happens to the following vital signs as a person ages from young to old: BP, pulse, and respiratory rate Age ranges for the following stages How would a child respond to an EMT assessing them, from birth through adolescence? What is the upper airway responsible for? What is the common obstruction of the airway? What are the two easiest methods in which an EMT can mitigate this? When would a basic airway adjunct be indicated? What dictates which device to use if it is indicated? List the Liter per minute rate for the following oxygen delivery devices Describe the difference between a patent airway and a maintainable airway What is the difference between respiratory distress and respiratory failure? What are the normal respiratory rates for the When assessing a patients respirations, what are the three things that an EMT should look for? 1. Rate 2. Depth/strength 3. Rhythm List the medical emergencies other than respiratory distress where oxygen therapy would be appropriate 1. COPD 2. CO poisoning 3. Chest pain associated with pulmonary edema: positive pressure ventilation What is the risk of a patient smoking a cigarette with a nasal cannula? Oxygen is highly combustible: Within the National Registry scope of practice, can an EMT insert an advanced airway such as an endotracheal tube? An EMT may assist an AEMT, but may not insert such an airway Describe how you would determine if you are delivering enough air when ventilating with a BVM Look for proper rise and fall of the chest List potential hazards that you would consider to be an unsafe scene 1. hazardous material 2. collision victims 3. smoke/fire 4. broken utility poles and downed wires 5. acts of violence Describe how you would position your ambulance safely at the scene of a motor vehicle accident If there is fuel spillage/ fire 100 ft in all directions, and upwind. Define the difference between a Mechanism of Injury and Nature of Illness 1. Mechanism of Injury: trauma accident: eg. vehicle collision 2. Nature of Illness: medical patient: chief complaint; chest pain What are some vehicle considerations to consider when approaching after it's been involved in a major vehicle accident, with a patient still inside, 1. Airbags deployed 2. Mechanism of collision 3. Law of inertia to determine extent of injuries 4. Possible spinal immobilization precautions 5. Hazardous material and scene safety List types of additional resources hat can be called upon. 1. Haz-mat team 2. Law enforcement 3. ALS 4. When doing the Primary assessment, when would you use the ABC format versus CAB? Use CAB when the patient appears lifeless and are not breathing, and may not have a pulse What are all of the components of the circulation category in the primary assessment? 1. Bleeding control 2. Pulse 3. Skin If a patient has a weak carotid pulse of 70 but is apneic, what should your initial treatment consist of? 1. Oxygen therapy List five patient scenarios in which rapid transport would be indicated 1. Spinal/brain injury 2. Chest pain consistent with acute myocardial infarction 3. Symptoms consistent with stroke 4. Major bleeding 5. Respiratory failure/arrest When assessing a patient's pupils, what are you looking for? 1. Equality 2. Reactive to light If a patient is responsive, where would you first check for a pulse? Check radial pulse, but for a child, check brachial pulse What are the three categories an EMT should assess when checking a patient's skin 1. Color 2. Condition 3. Temperature If your patient was altered for unknown reasons, how often should you attempt to reassess their vitals signs? Every five minutes What is a normal blood sugar level in the body? What is considered hypoglycemic? at least 60-80 mg/dL; no more than 120-140 mg/dL Hypoglycemic: less than 60 mg/dL What does SAMPLE stand for? What types of patients would you obtain a SAMPLE history from? 1. Signs/Symptoms, Allergies, Medications, Pertinent past history, Last oral intake, Events leading up to episode 2. Obtain SAMPLE from conscious and oriented patients Define DCAP-BTLS Secondary assessment acronym 1. Deformities 2. Contusions 3. Abrasions 4. Punctures 5. Penetrations - 6. Burns 7. Tenderness 8. Lacerations 9. Swelling List the standard to be considered a significant M.O.I for the following Falls, Motor Vehicle Collisions, Pedestrian vs. Vehicle 1. Falls: over 20 ft for adults, or if under 15, fall > 10 ft or 2-3 X their child's age. 2. Motor Vehicle collision: When is an EMT permitted to remove a penetrating object from a patient's body? Do not remove impaled object. If the object is perforating the cheek, and is at risk for occluding the airway, and you can see both ends of the object, pull it out in the direction that it entered. What are the specific signs of a basilar skull fracture 1. headache 2. confusion 3. leakage of clear fluid from nose or ears/ blood 4. deep lacerations or severe bruises 5. depressions or deformities of the skull with large swellings 6. battle sign: bruise behind the ear 7. pupils are unequal and unresponsive to light 8. raccoon or black eyes, and one may appear sunken Flail segment 1. characterized by paradoxical motion 2. fracture of two or more adjacent ribs opposite of the direction of movement 3. Patient career: maintain positive thoracic pressure with NPPV Sucking Chest Wound 1. chest cavity is open to the atmosphere 2. maintain open airway and seal the chest wound with an occlusive dressing at least 2 inches wider than wound over entrance and exit wound. Administer O2, and care for shock Tension Pneumothorax 1. closed chest injury where air enters the chest cavity, and positive pressure equillibriates, causing lung collapse and reduced cardiac output 2. administer high concentration o2 and care for shock If pedal pulses cannot be felt when assessing Pulse, Motor, and sensory checks on the lower extremities, what is the alternative? posterior tibial pulse Priapism persistent erection indicative of spinal injury What is the difference between a rapid trauma assessment and a detailed trauma? Rapid trauma assessment is performed on a patient that is not responsive or has a significant injury or unknown mechanism. After critical interventions are performed, a detailed trauma assessment is performed on a more stable patient What are the 5 rights that should be checked prior to administering medication? 1. Patient 2. Medication 3. Dose 4. Route 5. Time What does OPQRST stand for and when should it be used? 1. Onset 2. Provocation 3. Quality 4. Region/radiation/relief 5. Severity 6. Time Should be used to assess history of a conscious/responsive and oriented patient If a patients chief complaint is chest pain, what should the EMT's secondary assessment consist of? 1. palpate the chest and evaluate for crepitation or flail chest. 2. auscultate for the presence of equal breath sounds 3. Vital signs What are the contraindications of Nitroglycerin? What is a single dose? 1. Patient has low blood pressure, >90mgHg 2. Patient has taken sexual enhancing drugs within the last 48-72 hours 3. Patient has taken the maximum dose" 0.4 mg 4.Patient has a head injury Patient is an infant or child Define Differential diagnoses A list of potential diagnoses compiled early in the assessment of the patient What is the difference between a sign and a symptom> 1. Sign: something that the EMT can subjectively observe about the patient 2. Symptom: what the patient feels and verbalizes If an error occurs when writing your narrative, how should you correct it? Draw a single line through the mistake and initial the corner Explain the difference between subjective and objective information in the narrative portion of the prehospital care report 1. Subjective: information from an individual point of view, eg, symptom/opinion 2. objective: observable, measurable, or verifiable statements. What are the different types of radios used in EMS? 1. Base Station 2. Portable radio 3. Mobile radio 4. Repeater 5. Telemetry 6. Cell phones What form is activated charcoal supplied? 1. premixed in water: susended 2. powder When would assisting a patient with their Epi-pen be indicated? Can you assist with it for any kind of allergic reaction? 1. Assist patient if they are unable to do so themselves. 2. Assist for an allergic reactions to which they know they are allergic to List all routes in which medications can be administered 1. Oral intake 2. Sublingual 3. Intramuscular injection 4. Intravenous injection 5. Inhalation 6. Intranasal 7. Intraosseous 8. Subcutaneous 9. Endotracheal What is the difference between enteral and parenteral when referring the route of a medication? 1. Enteral route utilizes the GI tract, such as oral intake. 2. Parenteral bypasses the GI tract, eg, auto-injector List the differences from an infant airway anatomy to adult anatomy 1. Infant's tongue takes up proportionally more space in the mouth 2. Infant has a smaller trachea 3. Infant has a more flexible trachea 4. Infant do not utilize accessory muscles: primarily diaphragm What does COPD stand for? What are the two subcategories of COPD? 1. Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease 2. Chronic bronchitis: involves long term cough with mucous 3. Emphysema: Damage to the lungs overtime What signs/symptoms might you see with a patient experiencing a congestive heart failure exacerbation? 1. tachycardia [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 30 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

13 EMT Final Exam Study Guides AND Multiple Exam Questions and Answers. Most Comprehensive content for EMT Basic and Advanced Course and Exam Preparation.
EMT Final Exam Study Guide. Most Comprehensive Content for a quick read right before EXAM EMT Final Exam Study Guide. Best for quick exam preping NREMT Study Guide. Comprehensive Content. Medical,...
By Kirsch 4 years ago
$35
13
Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 22, 2021
Number of pages
30
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 22, 2021
Downloads
0
Views
294