Understanding Normal Distribution: week #5
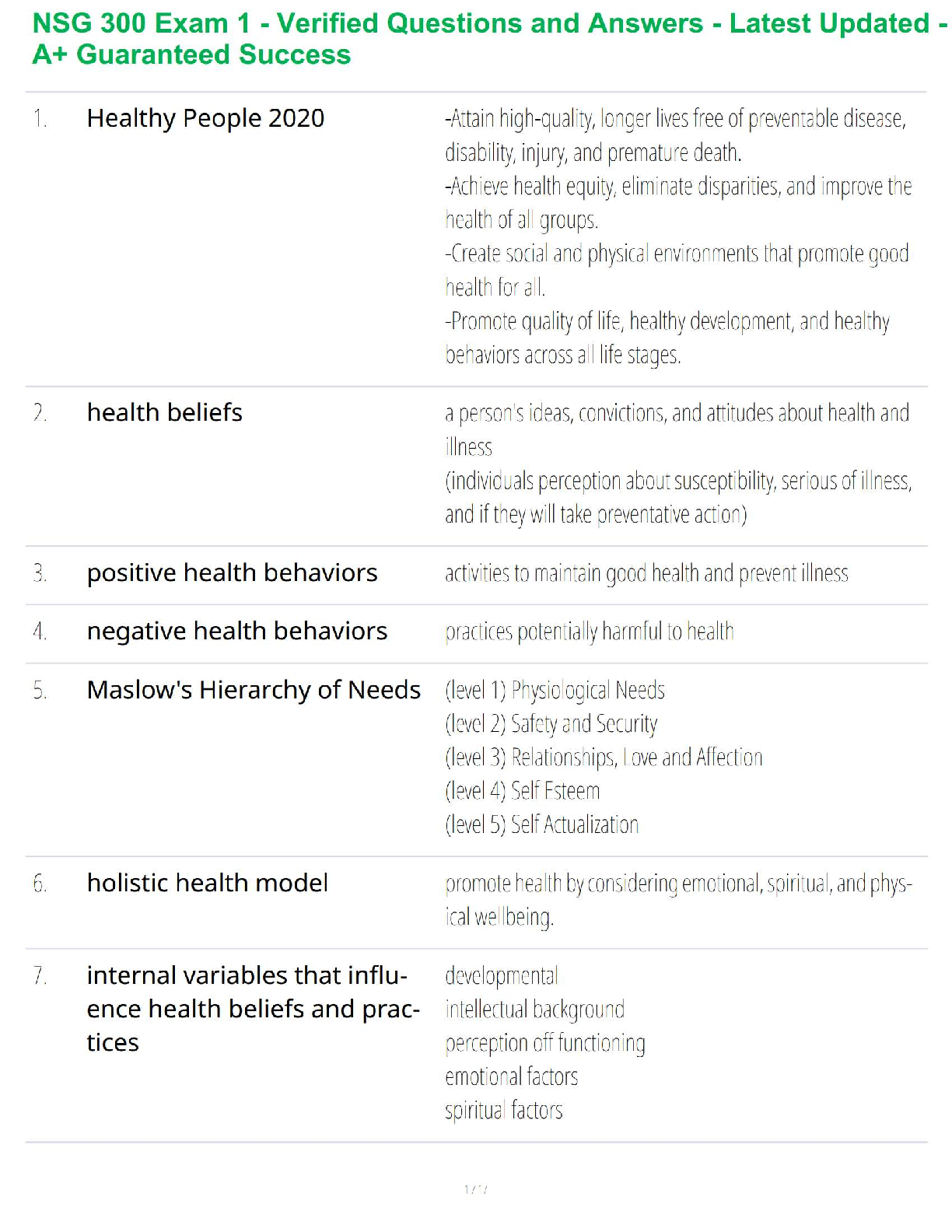
1. Lexie averages 149 points per bowling game with a standard deviation of 14 points.
Suppose Lexie's points per bowling game are normally distributed. Let X= the number of
p
...
Understanding Normal Distribution: week #5
1. Lexie averages 149 points per bowling game with a standard deviation of 14 points.
Suppose Lexie's points per bowling game are normally distributed. Let X= the number of
points per bowling game. Then X∼N(149,14).
Suppose Lexie scores 186 points in the game on Tuesday. The z-score
when x = 186 is 2.643 - no response given. The mean is 149 - no
response given.
This z-score tells you that x = 186 is 2.643- no response given standard
deviations to the right of the mean.
The z-score can be found using this formula:
z=x−μσ=186−149/14=3714≈2.643
The z-score tells you how many standard deviations the value x is above (to
the right of) or below (to the left of) the mean, μ. So, scoring 186 points is
2.643 standard deviations away from the mean. A positive value of z
means that that the value is above (or to the right of) the mean, which was
given in the problem: μ=149 points in the game.
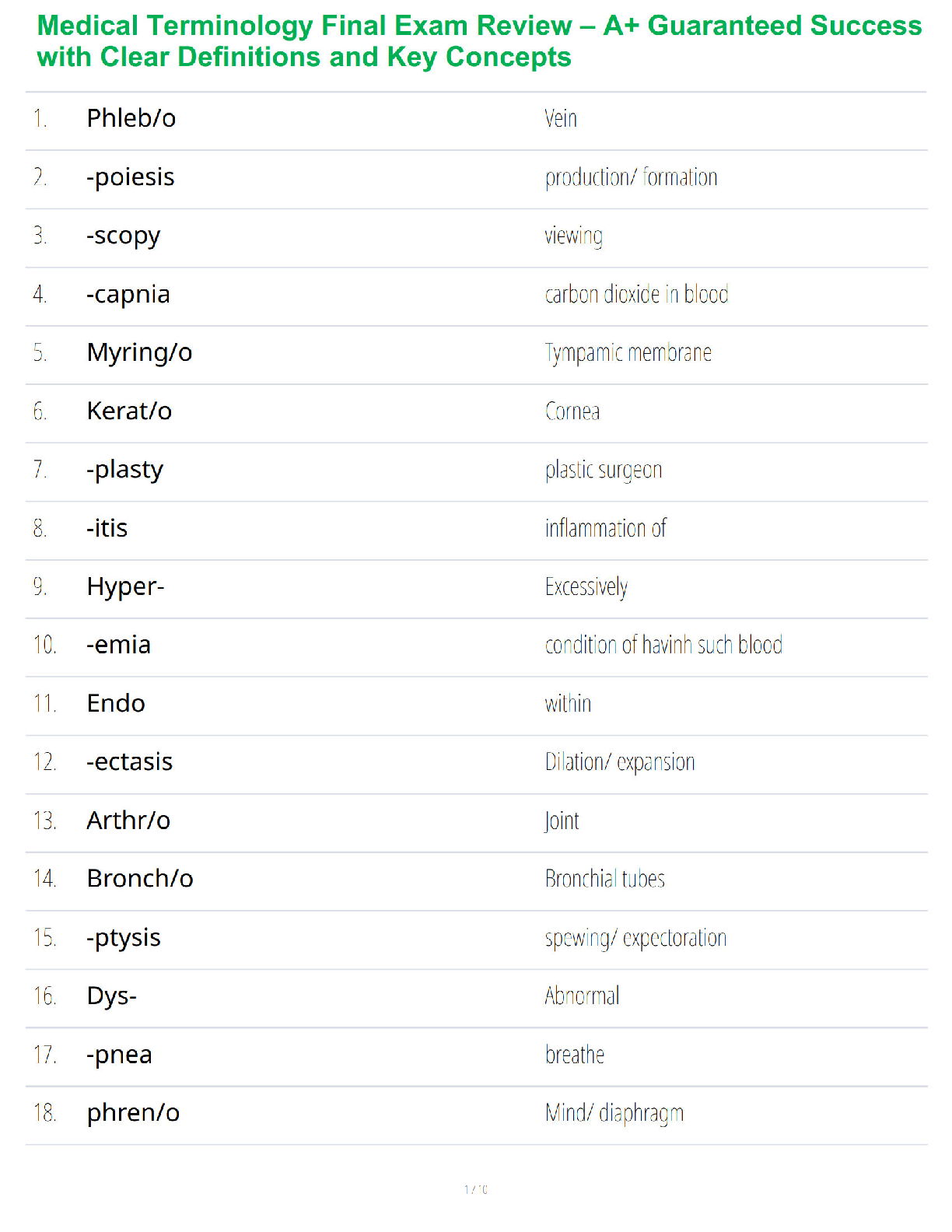
2. Suppose X∼N(18,2), and x=22. Find and interpret the z-score of the
standardized normal random variable.
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 01-19-2022 14:25:38 GMT -06:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/58202586/Understanding-Normal-Distribution-week-5docx/
The z-score when x=22 is . The mean
is .
This z-score tells you that x=22 is standard
deviations to the right of the mean.
3. Suppose X∼N(12.5,1.5), and x=11. Find and interpret the z-score of the
standardized normal random variable.
X is a normally distributed random variable with μ=12.5 (mean) and σ=1.5
(standard deviation). To calculate the z-score,
z=x−μσ=11−12.51.5=−1.51.5=−1
This means that x=11 is one standard deviation (1σ) below or to the left of the
mean. This makes sense because the standard deviation is 1.5. So, one standard
deviation would be (1)(1.5)=1.5, which is the distance between the mean
(μ=12.5) and the value of x (11).
2
18
2
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 01-19-2022 14:25:38 GMT -06:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/58202586/Understanding-Normal-Distribution-week-5docx/
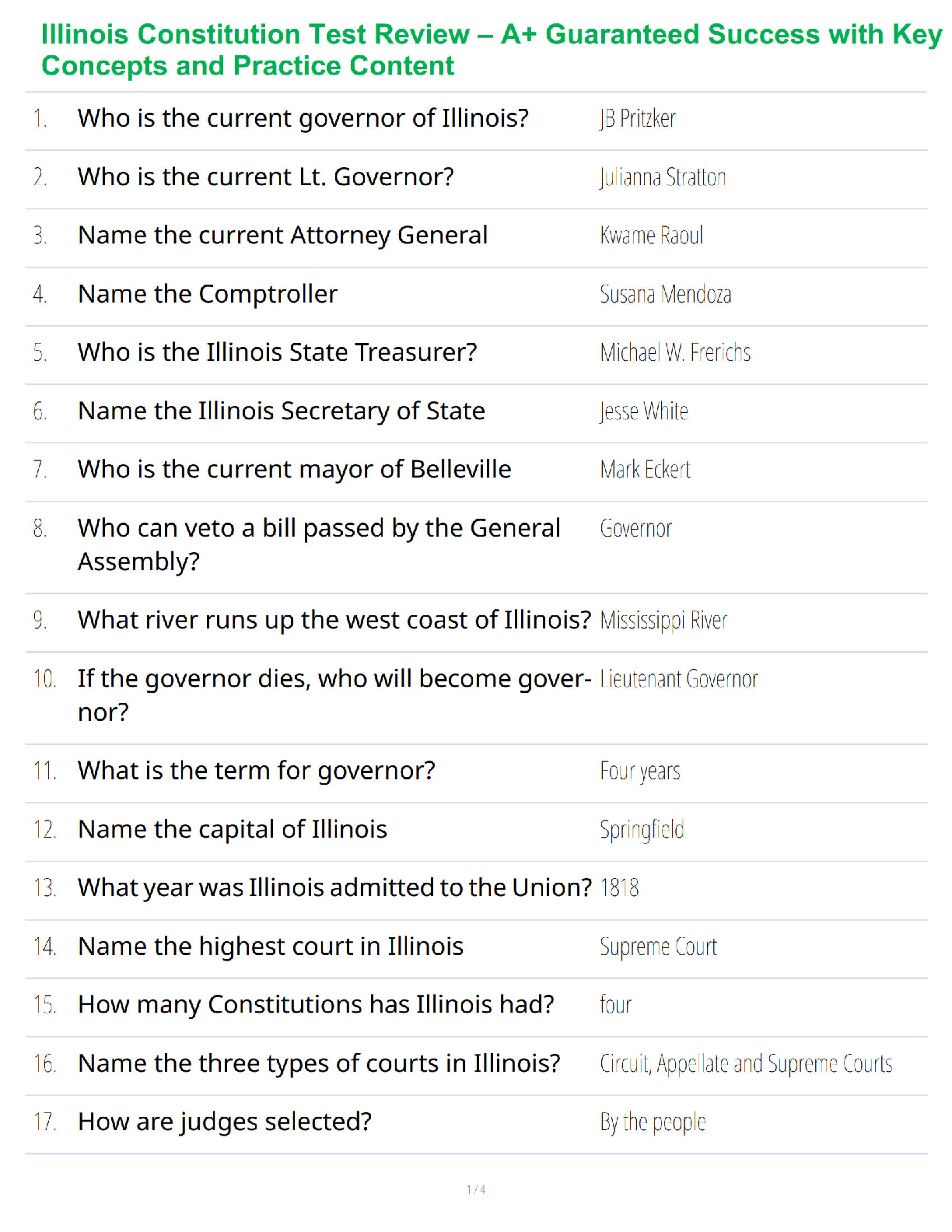
5. Isabella averages 17 points per basketball game with a standard deviation of 4 points.
Suppose Isabella's points per basketball game are normally distributed. Let X= the
number of points per basketball game. Then X∼N(17,4).
3,17,3
6. Suppose X∼N(13.5,1.5), and x=9. Find and interpret the z-score of the
standardized normal random variable.-3,13.5,3
7.
Suppose X∼N(10,0.5), and x=11.5. Find and interpret the z-score of the
standardized normal random variable.
3,10,3
This means that x=11.5 is three standard deviations (3σ) above or to the right of the
mean. This makes sense because the standard deviation is 0.5. So, three standard
deviations would be (3)(0.5)=1.5, which is the distance between the mean (μ=10)
and the value of x (11.5).
8. Annie averages 23 points per basketball game with a standard deviation of 4 points.
Suppose Annie's points per basketball game are normally distributed. Let X= the number
of points per basketball game. Then X∼N(23,4).
2.75,23,2.75
9. Suppose X∼N(9,1.5), and x=13.5. Find and interpret the z-score of the
standardized normal random variable.
3,9,3
10. Rosetta averages 148 points per bowling game with a standard deviation of 14
points. Suppose Rosetta's points per bowling game are normally distributed. Let X= the
number of points per bowling game. Then X∼N(148,14).
2.714,148,2.714
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 01-19-2022 14:25:38 GMT -06:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/58202586/Understanding-Normal-Distribution-week-5docx/
11. Suppose X∼N(5.5,2), and x=7.5.
This means that x=7.5 is one standard deviation (1σ) above or to the right of the mean,
μ=5.5.
12. Jerome averages 16 points a game with a standard deviation of 4 points.
Suppose Jerome's points per game are normally distributed. Let X = the
number of points per game. Then X∼N(16,4).
Suppose Jerome scores 10 points in the game on Monday. The z-score when
x=10 is _______. This z-score tells you that x=10 is _______ standard
deviations to the _______(right /left) of the mean, _______.
[Show More]