ATI - Predictor Study Notes (updated 2020) – Rasmussen College
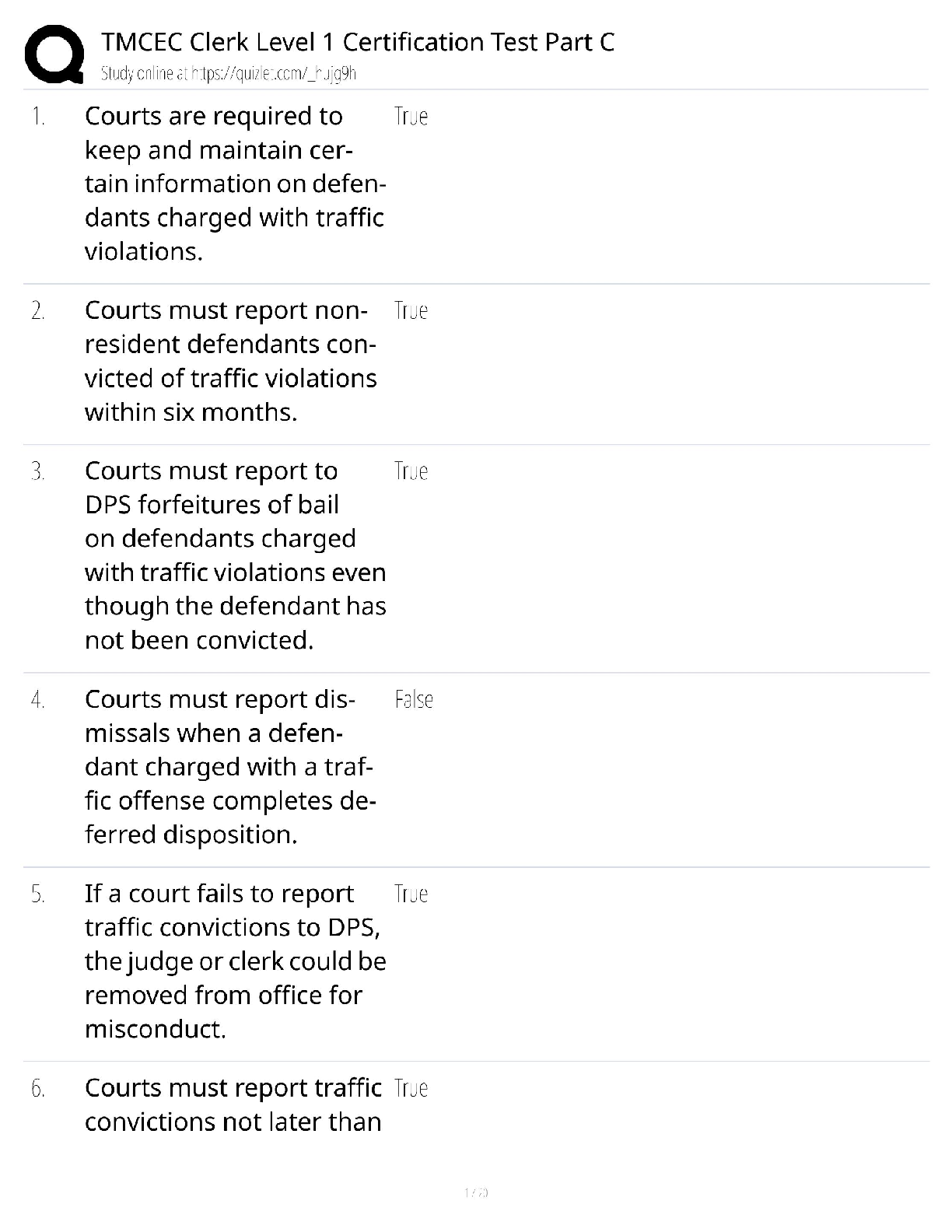
ATI – NCLEX Predictor Remediation Study Notes
Renal Calculi - Pain: Flank pain → Kidney or Ureter (if pain radiates → stones in ureter or bladder)
...
ATI - Predictor Study Notes (updated 2020) – Rasmussen College
ATI – NCLEX Predictor Remediation Study Notes
Renal Calculi - Pain: Flank pain → Kidney or Ureter (if pain radiates → stones in ureter or bladder)
Performing Ear Irrigation: Sterile technique, warm meds, pull up & back, tilt toward affected ear
Thrombolytic Therapy (Stroke): Reteplase recombinant (rTPA – clot buster) w/ in 4.5 hours of initial symptoms
Trach care: Dressing ∆, inner cannula ½ hydrogen peroxide, & stoma □ knot
Head injury (changes in LOC): Length of time unconscious & GCS
General anesthesia (post-op): ABC’s – full body assessment, Vitals every 15 minutes, Lateral position (if unresponsive or unconscious - monitor LOC), Fluids/Electrolytes
Superficial Burns: Painful, pink, red, mild edema (3-6 day healing), damage to epidermis
Dialysis (reporting unexpected findings): Temp of 100 degrees, ↓ BP, bleeding, 1 L of fluid = 1Kg, clotting, H/A, Nausea, Disequilibrium syndrome (rapid ↓ BUN & Fluid volume), anemia, peritonitis, ↑ BG, ↑ cholesterol
Pacemaker (complications): Infection, hematoma, pneumothorax, hemo-thorax, arrhythmias, pacer spikes before P or QRS, hiccups / muscle twitching
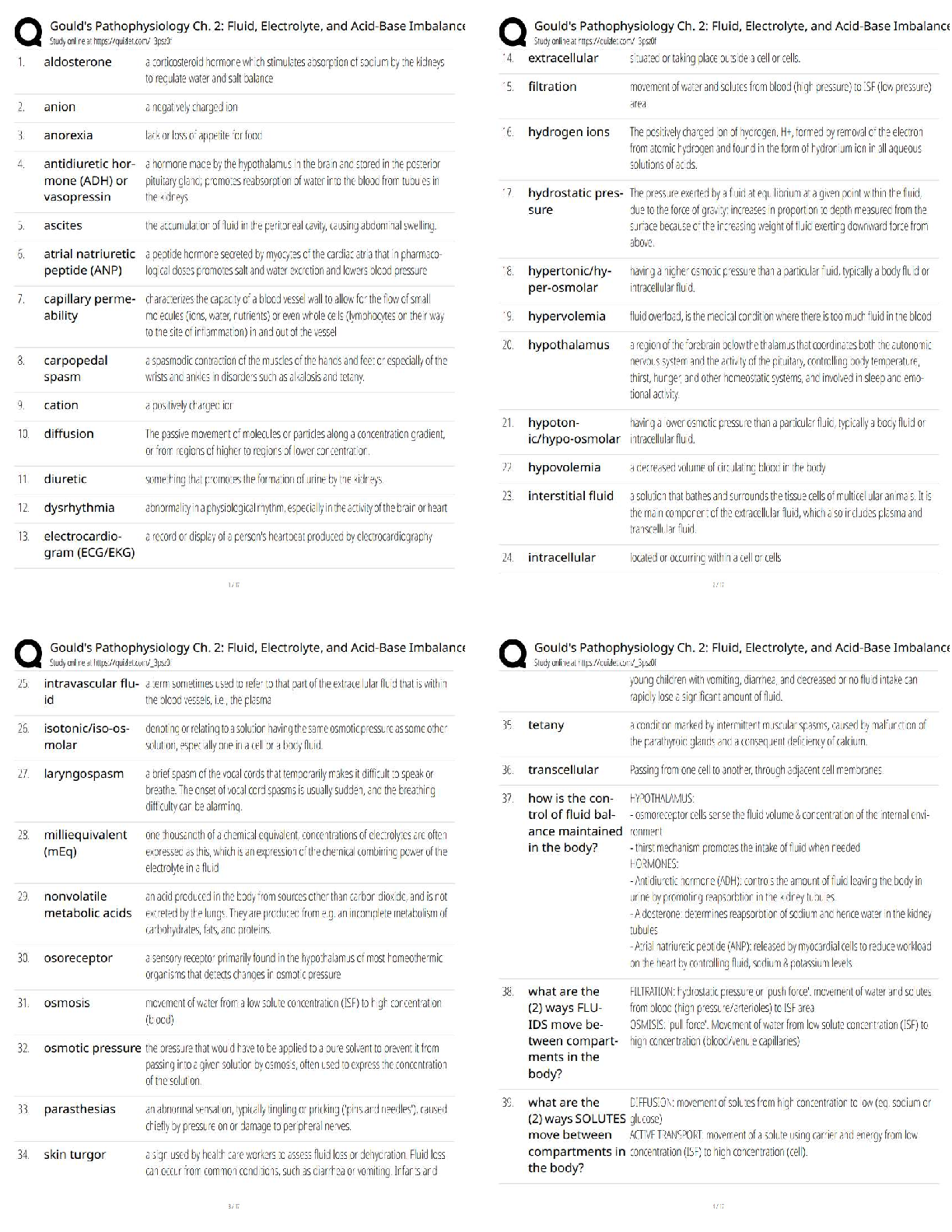
Magnesium (Mg) Sulfate → Increase Mg+ > 1.3 Mg/dL
↑ Mg foods = (Dairy, dark leafy greens veges)
↓ Mg causes → Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes
* Paresthesia’s, muscle tetany, positive chvostek’s & Trousseau’s sign, hypoactive bowels, constipation, abdominal distention, paralytic Ileus.
TPN Admin: (Total parenteral nutrition) -feeding that bypasses the GI tract. Fluids are given into a vein to provide most of the nutrients the body needs. Given when person cannot/ should not receive feedings or fluids by mouth.
Hypertonic (20-50% dextrose), Used in chronic pain, peritonitis, burns, Infection, etc
No more than 10% hourly, ↑ in rate for body adjustment, check BG
Hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, vitamin deficiencies, air embolism (clamp, place in Trendelenburg pos., O2)
Fluid imbalance → Fluid volume excess
Wound Culture specimen: Sterile field, press / rotate over wound surface inside the wound (center) in drainage
Diabetes Mellitus (Nephropathy): Kidney damage d/t prolonged ↑ BG & dehydration
Monitor I & O, Creatinine, BP
Avoid Soda, alcohol, acetaminophen/NSAIDS / 2 – 3 L fluid from food / beverages
Kidney Biopsy (Post op):
Monitor VS → Client receives sedation
Assess dressings & urinary output (hematuria-blood in urine)
Labs: HgB & Hct values, Admin PRN pain meds, Complications hemorrhage / infection
Thyroidectomy (Post Op): Needs Thyroid hormone replacement
Client in high fowler’s position, Respiratory (trach supplies) present, Check for laryngeal nerve damage
Pain management, Hypocalcemia / Tetany can occur
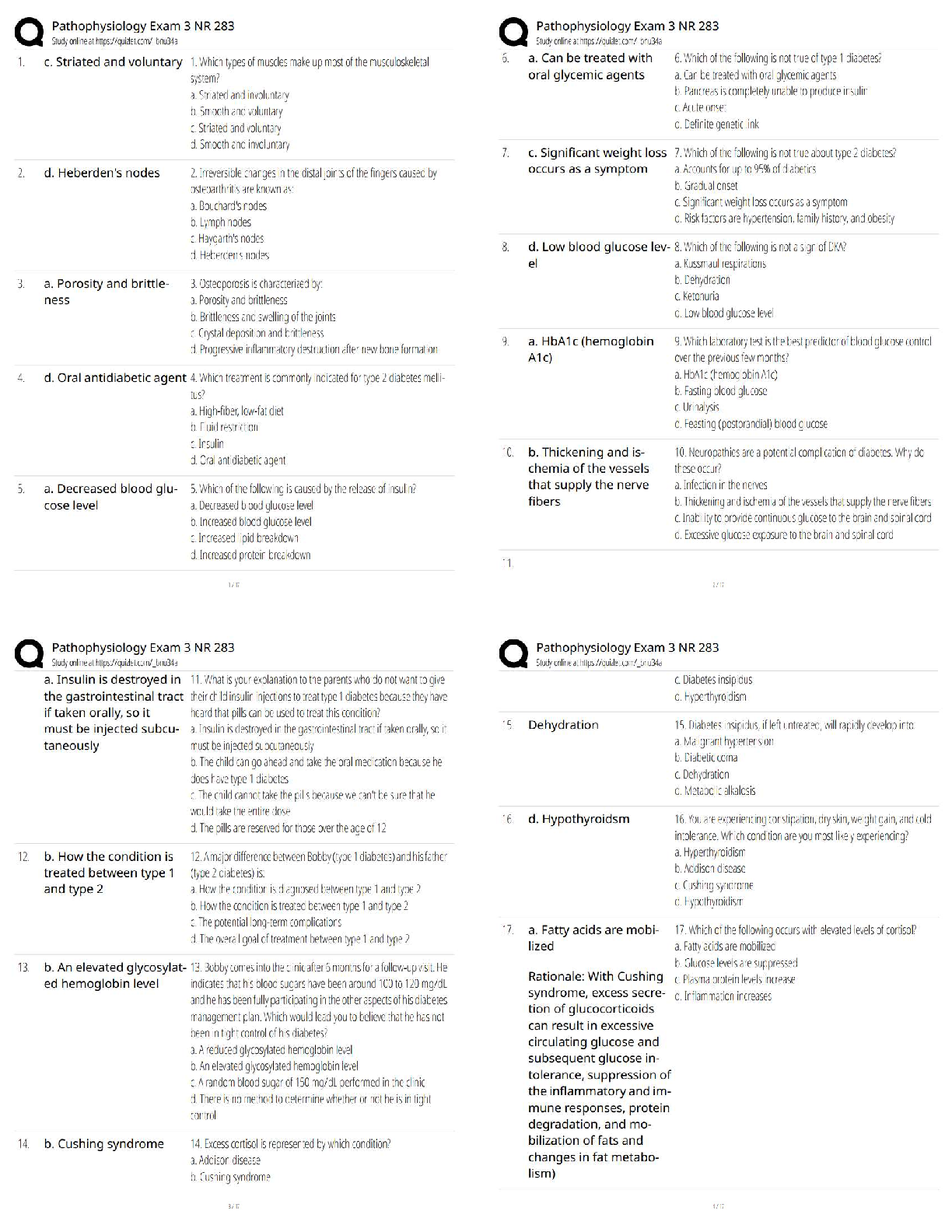
Prioritization: Apply knowledge to Standards to determine priority action
Systemic before Local – “Life before Limb”
Acute before Chronic
Actual Problems before Potential Future
Listen carefully to clients & Don’t Assume
Recognize & Respond - Trends vs. Transient findings
Recognize indications - Emergencies vs. Expected
Delegate to LPN: Monitoring Findings, Reinforcing teaching, performing trach care, suctioning, checking NG tube patency, administer tube feedings, inserting urinary catheter, administering meds (No IV)
Delegate to AP: ADLs, Bathing, Grooming, Dressing, toileting, Ambulating, feeding w/out swallowing precautions, positioning, routine tasks, bed making, specimen collection, I & O, VS for stable clients, monitoring clinical manifestations after initial RN assess/eval.
Paracentesis (prep) - take out fluid from belly (peritoneal fluid) Have client VOID
Bariatric Surgery: (weight loss surgery) – Semi fowlers, 6 small meals/day, liquid/pureed food for first 6 weeks (not to exceed 1cup), Vitamin / mineral supplements, & 2 servings of protein daily.
Ostomy (in small intestine) Avoid odorous & gas foods (dark green veges, dairy, fish, eggs, beans, corn), yogurt ↓ gas
Avoid ↑ fiber foods for first 2 months, ↑ fluid intake
Dumping Syndrome: Happens within 15mins of eating.
Sx: cramps, diarrhea, tachycardia, dizziness, fatigue, hypoglycemia
Interventions: small frequent meals, drink liquids 1hr b4/after
Parkinson’s disease: Tremor, muscle rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness in movement), postural instability
Stages:
1. Unilateral shaking / tremor of one limb
2. Bilateral limb involvement, difficulty walking/balance
3. Slowed physical movements
4. Akinesia & Rigidity make ADL’s difficult
5. Unable to stand/walk, dependent of cares, dementia
Assault: threat Battery: touching
Hypoglycemia Sx: Shakiness, confusion, sweating, tachycardia, diaphoresis, palpitations, H/A, lack of coordination, blurred vision, seizures, coma
Oral Hypoglycemic Agents: promote insulin release from pancreas (Type2 DM)
Glipizide (Glucotrol), Chlorpropamide (Diabines), Glyburide (Diabinese), Metformin (Glucophage).
* Med for insulin overdose = Glucagon
Radiation Adverse Effects: Skin changes, hair loss, debilitating fatigue, 30 minute visits / stays 6ft away / private room
Infection control in clients home: good hygiene, avoid crowded areas, avoid raw foods (veges/meats), avoid cleaning litter boxes, clean home and avoid sick family.
Client evacuation in response to fire: greatest good for the greatest amount of people
Client in seclusion: 18 yo+ → 4 hours, 9 – 17 yo →2 hours, 8 yo & younger →1 hour
Conduct Disorders: lack of remorse, bullies, threatens, low self-esteem, tempers, physical cruelty, destroys property, truant, and shoplifts
Manic Phase: ↑ mood, irritable, lasts at least a week, euphoria, agitation, restless, ↑ in talking, flight of ideas, grandiose view of self, impulsive, manipulative, poor judgement, attention seeking.
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-Hazards of immobility on CV system & interventions DVT: elastic stockings, SCD's, Orthostatic BP: give pt time between position changes
Hazards of immobility on pulmonary system & interventions PE: TED host, Inadequate expansion of the chest: place pt in orthopneic position Pneumonia: clean/sterile technique, pneumovax
Intervention for each: early and frequent ambulation
Hazards of immobility on renal system & interventions-UTI, problems with continence, altered BP: monitor I/O's, assist w/ voiding as needed
Hazards of immobility on integumentary system & interventions
Skin breakdown: repositioning, monitor nutrition status, reduce moisture, and provide hygiene care
Hazards of immobility on musculoskeletal system & interventions
Stiff joints: ROMs/ambulation
Muscle atrophy: ROMs/ambulation
Ca2+ imbalance: nutrition measures
Risk factors for skin breakdown
Poor nutrition, bedrest, obesity, using an SPM machine, increased friction and shear
4 areas prone to skin breakdown-Tailbone, Heels, Elbows, Hips
Intervention most effective in preventing flaccidity in a hospitalized patient? Early ambulation after surgery
After application of sequential compression devices (SCDs) on a patient, what assessment finding is essential for the nurse to include in documentation? Lower extremity circulatory status
Components of Morse Fall Scale- History of falls, secondary diagnosis, ambulatory aid, IV/hep lock, gait/transferring, mental status
Scores:
45+ = high risk 25-44 = moderate risk 0-24 = low risk
TB Injection - Max amt: 0.1 cc, site: forearm, Angle: 15-20 degrees, Length: 1/4 - 1/2 in, Aspiration? No
SQ injections - Max amt: 2 cc, Usual site: Upper arm, stomach, Angle: 45 degrees, Length: 1/2 - 1 in, Aspiration? Yes
IM injections - Max amt: 5 cc Usual site: deltoid (1 cc), gluteus med/max or vastus lateralis (5 cc), Angle: 90 degrees, Length: 1 - 1.5 in, Aspiration? Yes
What factors affect a BG result? Having fasted or eaten, time of day, level of activity, stress, illness, menstruation
client most at risk for hypoglycemia? In the morning before breakfast
Considerations for pt's on blood thinners such as warfarin, asprin, heparin, coumadin, etc?
Monitor platelet levels (labs)
Watch for bleeding/reduce risks of bleeding
Monitor vitals (esp. BP)
Assess skin
Monitor mobility status
benzodiazepines to older adults? No, benzo's increase the risk of accidents and mental deficits
FUO - fever of unknown origin
qhs - at bedtime
ac - before meals
Contraindications for opening capsules and mixing with food? EC: enteric coated & ER: extended release
Rapid acting insulin
Generic & brand names: Inslin aspart (NovoLog), insulin glulisine (Apidra), insulin lispro (Humalog)
Onset: 15 min
Peak: 30 - 90 min
Duration: 3-5 hr
Short acting insulin - Insulin regular (Humulin R, Novolin R)
Onset: 30 - 60 min
Peak: 2 - 4 hr
Duration: 5 - 8 hr
Intermediate-acting insulin- Insulin NPH (Humulin/Novolin N)
Onset: 1 - 3 hr
Peak: 8 hr
Duration: 12 - 16 hr
Long-acting insulin- insulin glargine (lantus), insulin detemir (levemir)
Onset: 1 hr
Peak: no clear peak
Duration: 20 - 26 hr
Signs of infiltration -Edema, pallor, decreased skin temperature around the site, and pain
Signs of phlebitis - Pain, increased skin temperature, and redness along the vein
Signs of extravasation (infiltration w/ dislodged IV catheter) - Pain, stinging or burning at the site, swelling, and redness
Nursing interventions for infiltration, phlebitis, and extravasation
Infiltration: D/C IV, elevate extremity, apply warm compress
Phlebitis: D/C IV, apply warm/moist compress
Extravasation: D/C IV, apply cool compress, administer antidote if needed, document degree of extravasation
INT -intermittent (catheter)
The 6 rights of medication administration
1. Right drug
2. Right dose
3. Right route
4. Right pt
5. Right time
6. Right documentation
3 nursing interventions r/t routine care of peripheral IV
1. Check insertion site frequently
2. Change tubing every 96 hr
3. Use good hand hygiene + standard precautions
Factors to consider when choosing the best IV location Age, condition of veins, circulation status, length of IV therapy
What is the smallest gauge IV catheter used to infuse blood? 20-22: RBS' might get crushed when using a smaller cath.
4 techniques to improve the chances of good IV access
1. Trim hair around the area
2. Gently stroke the area from the distal to proximal end
3. Place a warm blanket over the extremity
4. Palpate gently
[Show More]
 – Rasmussen College.png)






 – Concorde career College.png)