*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Fundamental Skills - Perioperative Care: 103 Questions and Answers on the Most commonly Tested Areas (All)
Fundamental Skills - Perioperative Care: 103 Questions and Answers on the Most commonly Tested Areas On Perioperative Care and Pain - Diagnostic Tests. All answers provided.
Document Content and Description Below
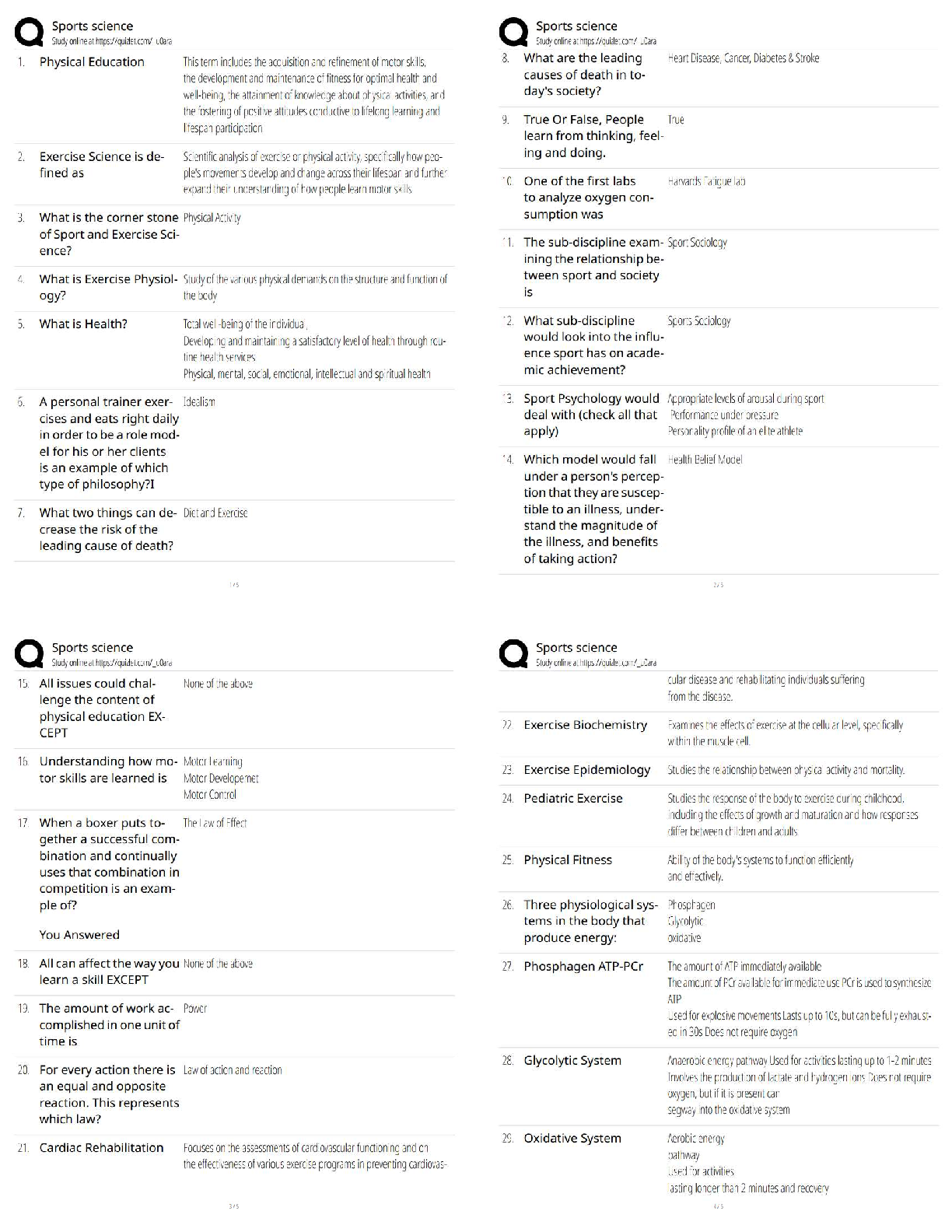
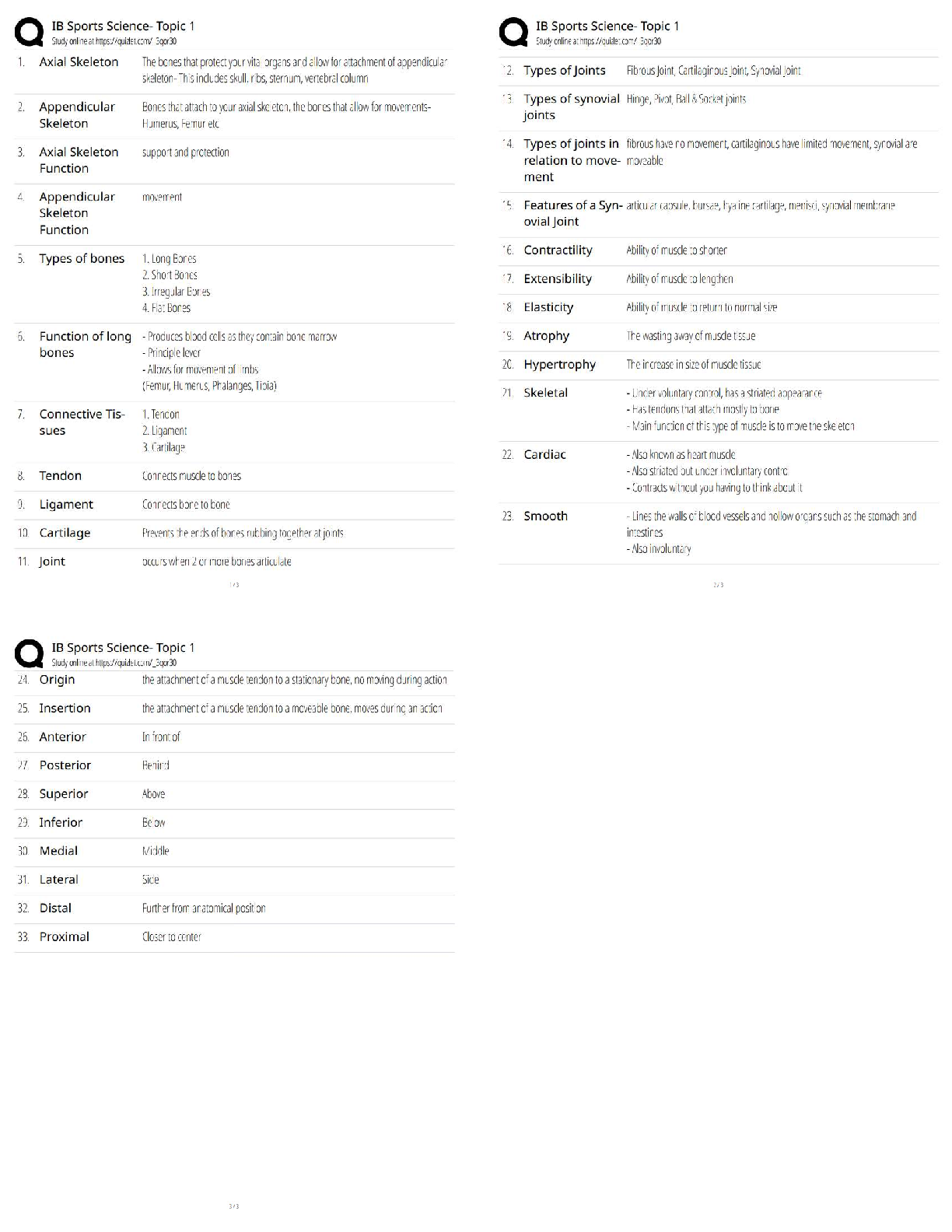
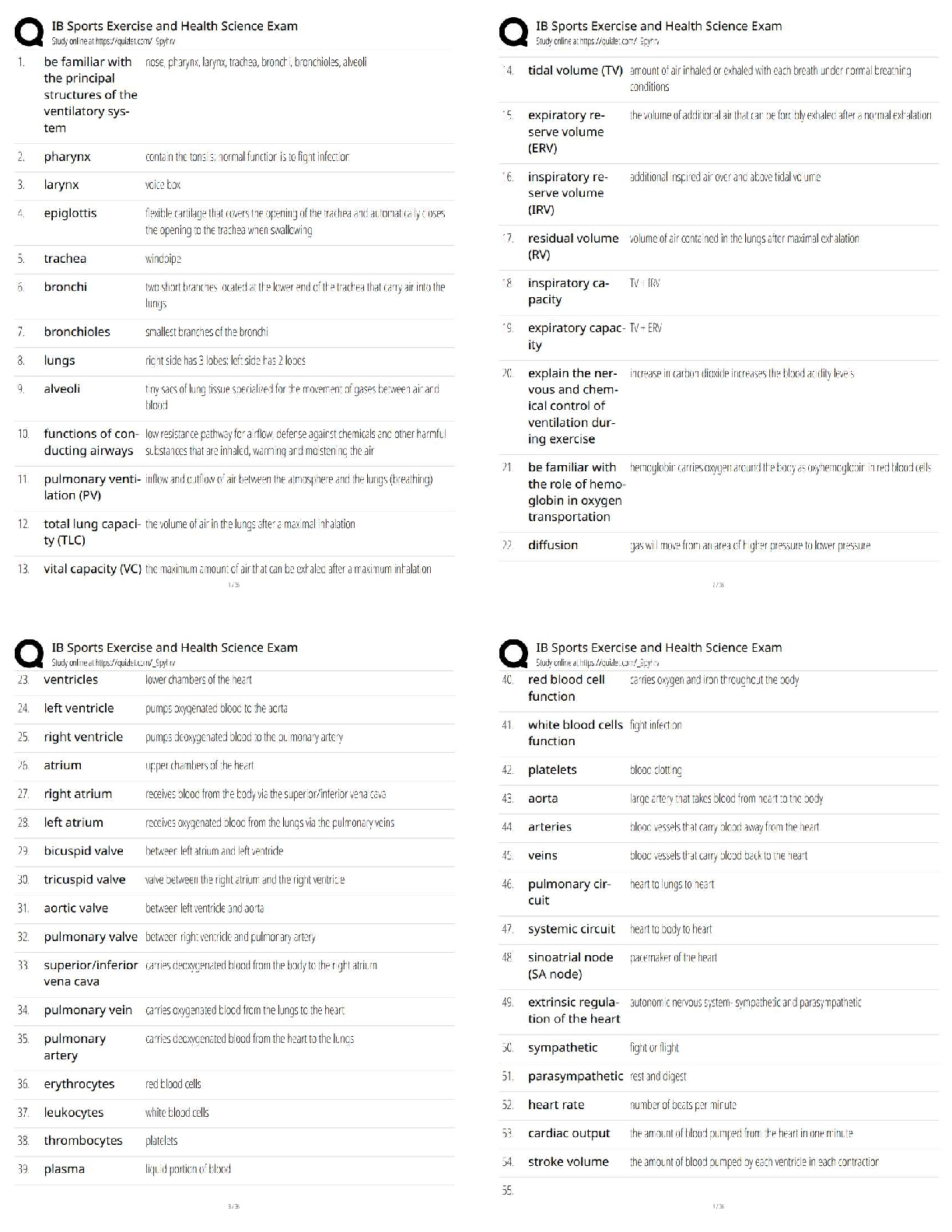
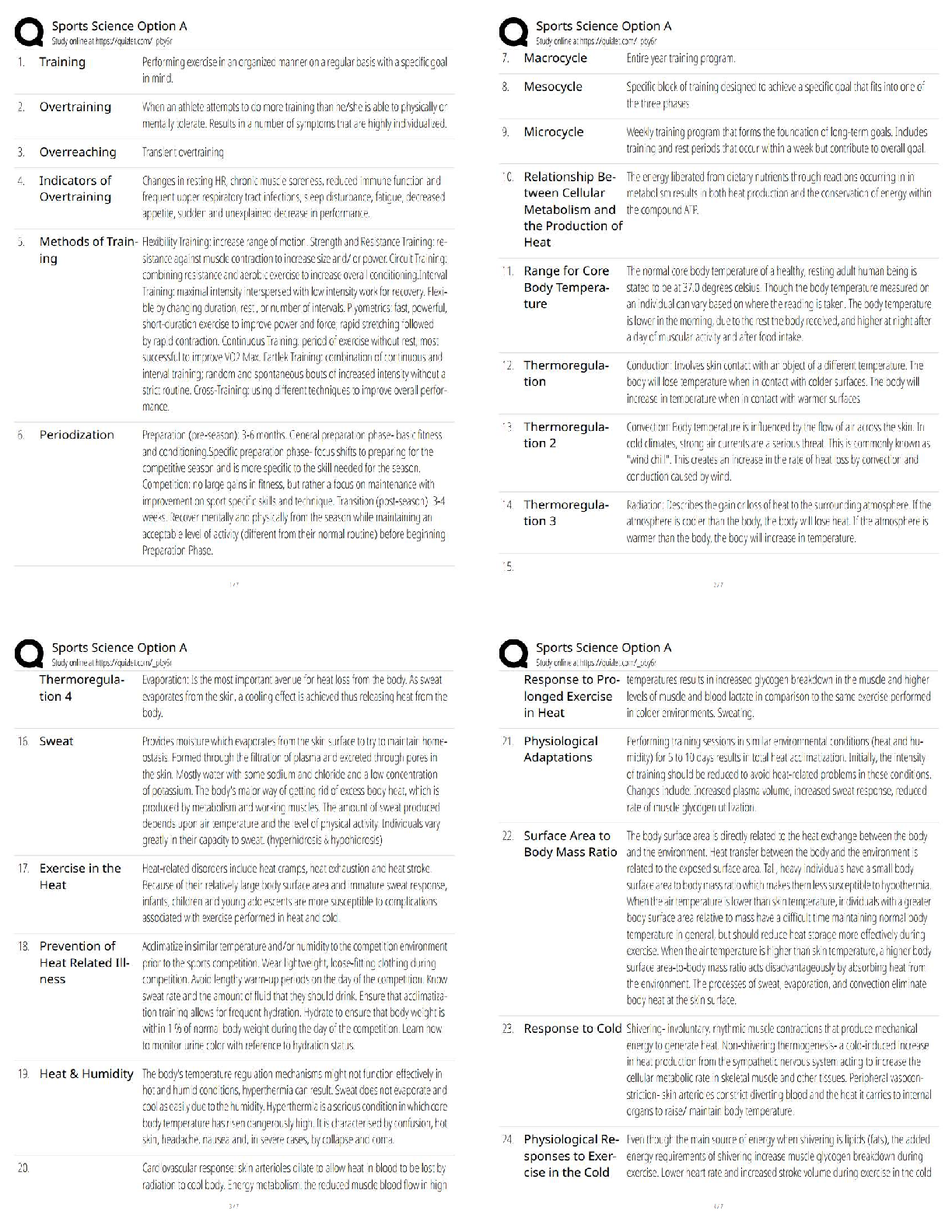
Fundamental Skills - Perioperative Care 1. The nurse has just reassessed the condition of a postoperative client who was admitted 1 hour ago to the surgical unit. The nurse plans to monitor which par ... ameter most carefully during the next hour? 1. Urinary output of 20 mL/hour 2. Temperature of 37.6° C (99.6° F) 3. Blood pressure of 100/70 mm Hg 4. Serous drainage on the surgical dressing 1. A postoperative client asks the nurse why it is so important to deep-breathe and cough after surgery. When formulating a response, the nurse incorporates the understanding that retained pulmonary secretions in a postoperative client can lead to which condition? 1. Pneumonia 2. Hypoxemia 3. Fluid imbalance 4. Pulmonary embolism 2. The nurse is developing a plan of care for a client scheduled for surgery. The nurse should include which activity in the nursing care plan for the client on the day of surgery? 1. Avoid oral hygiene and rinsing with mouthwash. 2. Verify that the client has not eaten for the last 24 hours. 3. Have the client void immediately before going into surgery. 4. Report immediately any slight increase in blood pressure or pulse. 3. A client with a perforated gastric ulcer is scheduled for surgery. The client cannot sign the operative consent form because of sedation from opioid analgesics that have been administered. The nurse should take which most appropriate action in the care of this client? 1. Obtain a court order for the surgery. 2. Have the charge nurse sign the informed consent immediately. 3. Send the client to surgery without the consent form being signed. 4. Obtain a telephone consent from a family member, following agency policy. 4. A preoperative client expresses anxiety to the nurse about upcoming surgery. Which response by the nurse is most likely to stimulate further discussion between the client and the nurse? 1. "If it's any help, everyone is nervous before surgery." 2. "I will be happy to explain the entire surgical procedure to you." 3. "Can you share with me what you've been told about your surgery?" 4. "Let me tell you about the care you'll receive after surgery and the amount of pain you can anticipate." 5. The nurse is conducting preoperative teaching with a client about the use of an incentive spirometer. The nurse should include which piece of information in discussions with the client? 1. Inhale as rapidly as possible. 2. Keep a loose seal between the lips and the mouthpiece. 3. After maximum inspiration, hold the breath for 15 seconds and exhale. 4. The best results are achieved when sitting up or with the head of the bed elevated 45 to 90 degrees. 6. The nurse has conducted preoperative teaching for a client scheduled for surgery in 1 week. The client has a history of arthritis and has been taking acetylsalicylic acid (aspirin). The nurse determines that the client needs additional teaching if the client makes which statement? 1. "Aspirin can cause bleeding after surgery." 2. "Aspirin can cause my ability to clot blood to be abnormal." 3. "I need to continue to take the aspirin until the day of surgery." 4. "I need to check with my health care provider about the need to stop the aspirin before the scheduled surgery." 7. The nurse assesses a client's surgical incision for signs of infection. Which finding by the nurse would be interpreted as a normal finding at the surgical site? 1. Red, hard skin 2. Serous drainage 3. Purulent drainage 4. Warm, tender skin 8. The nurse is monitoring the status of a postoperative client. The nurse would become most concerned with which sign that could indicate an evolving complication? 1. Increasing restlessness 2. A pulse of 86 beats/minute 3. Blood pressure of 110/70 mm Hg 4. Hypoactive bowel sounds in all four quadrants 9. A client who has had abdominal surgery complains of feeling as though "something gave way" in the incisional site. The nurse removes the dressing and notes the presence of a loop of bowel protruding through the incision. Which nursing interventions should the nurse take? Select all that apply. 1. Contact the surgeon. 2. Instruct the client to remain quiet. 3. Prepare the client for wound closure. 4. Document the findings and actions taken 5. Place a sterile saline dressing and ice packs over the wound. 6. Place the client in a supine position without a pillow under the head. o 1. Contact the surgeon. o 2. Instruct the client to remain quiet. o 3. Prepare the client for wound closure. o 4. Document the findings and actions taken 10. A client who has undergone preadmission testing has had blood drawn for serum laboratory studies, including a complete blood count, coagulation studies, and electrolytes and creatinine levels. Which laboratory result should be reported to the surgeon's office by the nurse, knowing that it could cause surgery to be postponed? 1. Sodium, 141 mEq/L 2. Hemoglobin, 8.0 g/dL 3. Platelets, 210,000 cells/mm3 4. Serum creatinine, 0.8 mg/dL 11. The nurse receives a telephone call from the postanesthesia care unit stating that a client is being transferred to the surgical unit. The nurse plans to take which action first on arrival of the client? 1. Assess the patency of the airway. 2. Check tubes or drains for patency. 3. Check the dressing to assess for bleeding. 4. Assess the vital signs to compare with preoperative measurements. 12. The nurse is reviewing a health care provider's (HCP's) prescription sheet for a preoperative client that states that the client must be NPO after midnight. The nurse would telephone the HCP to clarify that which medication should be given to the client and not withheld? 1. Prednisone 2. Ferrous sulfate 3. Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) 4. Conjugated estrogen (Premarin) 13. The nurse is caring for a client who is postoperative following a pelvic exenteration and the health care provider changes the client's diet from NPO status to clear liquids. The nurse should check which priority item before administering the diet? 1. Bowel sounds 2. Ability to ambulate 3. Incision appearance 4. Urine specific gravity 14. A gastrectomy is performed on a client with gastric cancer. In the immediate postoperative period, the nurse notes bloody drainage from the nasogastric tube. The nurse should take which most appropriate action? 1. Measure abdominal girth. 2. Irrigate the nasogastric tube. 3. Continue to monitor the drainage. 4. Notify the health care provider (HCP). 15. The nurse is assessing the colostomy of a client who has had an abdominal perineal resection for a bowel tumor. Which assessment finding indicates that the colostomy is beginning to function? 1. The passage of flatus 2. Absent bowel sounds 3. The client's ability to tolerate food 4. Bloody drainage from the colostomy 16. The nurse in a surgical unit receives a postoperative client from the postanesthesia care unit. After the initial assessment of the client, the nurse should plan to continue with postoperative assessment activities how often? 1. Every hour for 2 hours, and then every 4 hours as needed 2. Every 30 minutes for the first hour, every hour for 2 hours, and then every 4 hours as needed 3. Every 15 minutes for the first hour, every 30 minutes for 2 hours, every hour for 4 hours, and then every 4 hours as needed 4. Every 5 minutes for the first half-hour, every 15 minutes for 2 hours, every 30 minutes for 4 hours, and then every hour as needed 17. A client is admitted to a surgical unit postoperatively with a wound drain in place. Which actions should the nurse take in the care of the drain? Select all that apply. 1. Check the drain for patency. 2. Observe for bright red bloody drainage. 3. Clamp the drain for 15 minutes every hour. 4. Curl the drain tightly, and tape it firmly to the body. 5. Maintain aseptic technique when emptying the drain. o . 18. The nurse is developing a plan of care for a preoperative client who has a latex allergy. Which intervention should be included in the plan? 1. Avoid using medications from glass ampules. 2. Use medications that are from ampules with rubber stoppers. 3. Avoid using intravenous (IV) tubing that is made of polyvinyl chloride. 4. Apply a cloth barrier to the client's arm under a blood pressure cuff when taking the blood pressure. 19. A client is admitted to the ambulatory surgery center for elective surgery. The nurse asks the client whether any food, fluid, or medication was taken today. Which medication, if taken by the client, should indicate to the nurse the need to contact the health care provider (HCP)? 1. A β-blocker 2. An antibiotic 3. An anticoagulant 4. A calcium-channel blocker 20. The home care nurse visits a client to perform a dressing change on a leg ulcer. The client has diabetes mellitus and a history of cardiac disease and is taking one aspirin daily in addition to other medications as prescribed. The client tells the nurse that dental surgery is scheduled and asks the nurse whether the aspirin should be discontinued. The nurse should most appropriately make which statement to the client? 1. "The pharmacist should be called." 2. "There is no risk to having such a minor surgery while taking aspirin." 3. "Aspirin has no effect on the surgical procedure and may minimize discomfort." 4. "Dental surgery can safely be done usually 10 days after stopping the aspirin, depending on the health care provider's (HCP) preference." 21. A nurse is providing preoperative teaching to a client scheduled for a cholecystectomy. Which intervention would be of highest priority in the preoperative teaching plan? 1. Teaching leg exercises 2. Teaching coughing and deep breathing exercises 3. Providing instructions regarding fluid restrictions 4. Assessing the client's understanding of the surgical procedure 22. A client who has undergone radical neck dissection is experiencing problems with verbal communication related to postoperative hoarseness. The nurse should formulate which outcome as the most appropriate goal for this client problem? 1. Uses nonverbal communication only 2. Describes that hoarseness will be permanent 3. Initiates communication only when necessary 4. Incorporates nonverbal forms of communication as needed 23. A preoperative client has received a dose of scopolamine as prescribed by the anesthesiologist. The nurse should assess the client for which anticipated side effect of this medication? 1. Diaphoresis 2. Pupillary constriction 3. Increased urinary output 4. Dry oral mucous membranes 24. A client arrives at the surgical unit after nasal surgery. The client has nasal packing in place. The nurse reviews the health care provider's prescriptions and understands that it is essential that the client be placed in which position to reduce swelling? 1. Sims 2. Prone 3. Supine 4. Semi-Fowler's position 25. A client scheduled for surgery receives a dose of scopolamine. The nurse expects to note which side effects of the medication? Select all that apply. 1. Dry mouth 2. Diaphoresis 3. Profuse diarrhea 4. Pupillary dilation 5. Excessive urination 26. The nurse is providing discharge instructions to the client who has had a pneumonectomy and prepares a list of postoperative instructions for the client. Which intervention should the nurse include in the list? 1. Contact the HCP if any feelings of weakness and fatigue occur. 2. Avoid breathing exercises to allow the diaphragm to strengthen. 3. Avoid lifting any objects greater than 30 pounds for at least 3 weeks. 4. Report any signs of respiratory infection to the health care provider (HCP). 27. A postoperative client with a large abdominal wound requiring frequent dressing changes is starting to develop skin irritation in the area where the dressing tape is applied to the skin. The nurse determines that the client would benefit most from which measure? 1. Obtaining a wound culture 2. The use of Montgomery straps 3. The use of hypoallergenic tape 4. Cleansing the irritated area with povidone-iodine 28. A client is recovering well 24 hours after cranial surgery but is fatigued. The neurosurgeon advances the client from NPO status to clear liquids. The nurse knows that which information is least reliable in determining the client's readiness to take in fluids? 1. Appetite 2. Absence of nausea 3. Presence of bowel sounds 4. Presence of a swallow reflex 1 29. The nurse is caring for a 25-year-old client who will undergo bilateral orchidectomy for testicular cancer. Which statement by the nurse would be helpful in exploring the client's concerns about loss of reproductive ability? 1. "You must be sad that you won't be able to have children after surgery." 2. "Has the health care provider told you that you will not be able to have children?" 3. "Can you share with me any concerns about how this surgery will affect you in the future?" 4. "Do you feel that the health care provider has told you all you need to know about the upcoming surgery?" 30. The nurse has a prescription to remove the nasogastric (NG) tube from a client on the first postoperative day after cardiac surgery. The nurse should question the prescription if which finding was noted on assessment of the client? 1. The client is drowsy. 2. Bowel sounds are absent. 3. The abdomen is slightly distended. 4. NG tube drainage is Hematest negative. 31. A nurse is assigned to change the surgical dressing on a client who has undergone abdominal surgery. After removing the old dressing, the nurse assesses the surgical site. Which should be the nurse's initialaction if the appearance shown in the figure is observed? 1. Document the findings. 2. Apply a sterile nonadherent dressing. 3. Redress the wound with a dry sterile dressing. 4. Ask the client to cough to assess for protrusion of the internal structures. 32. A client arrives at the surgical unit after undergoing rhinoplasty and has a nose splint and gauze drip (moustache dressing) in place. The nurse reviews the health care provider's prescriptions and anticipates that which client position will be prescribed? 1. Sims 2. Prone 3. Supine 4. Semi-Fowler's 33. The nurse has instructed a preoperative client using an incentive spirometer to sustain the inhaled breath for 3 seconds. When the client asks about the rationale for this action, the nurse explains that this action achieves which function? 1. Dilates the major bronchi 2. Increases surfactant production 3. Maintains inflation of the alveoli 4. Enhances ciliary action in the tracheobronchial tree 34. A client has a risk for infection following radical vulvectomy. Therefore, the nurse should avoid which action when giving perineal care to this client? 1. Cleansing with warm tap water 2. Intermittently exposing the wound to air 3. Providing prescribed sitz baths after the sutures are removed 4. Providing perineal care after each voiding and bowel movement (BM) 35. In preparation for ambulation, the nurse is planning to assist a postoperative client to progress from a lying position to a sitting position. Which nursing action is most appropriate to maintain the safety of the client? 1. Assess the client for signs of dizziness and hypotension. 2. Allow the client to rise from the bed to a standing position unassisted. 3. Elevate the head of the bed quickly to assist the client to a sitting position. 4. Assist the client to move quickly from the lying position to the sitting position. 36. A client has returned to the nursing unit after an abdominal hysterectomy. The client is lying supine. To thoroughly assess the client for postoperative bleeding what is the primary nursing action? 1. Check the heart rate. 2. Check the blood pressure. 3. Roll the client to one side and check her perineal pad. 4. Ask the client about sensation of moistness on her perineal pad. 37. A client has received atropine sulfate intravenously during a surgical procedure. The nurse should monitor the client for which side effect of the medication in the immediate postoperative period? 1. Diarrhea 2. Bradycardia 3. Urinary retention 4. Excessive salivation 38. The nurse is providing home care instructions to the parents of an infant who had a surgical repair of an inguinal hernia. What instruction should the nurse include to prevent infection at the surgical site? 1. Report a fever immediately. 2. Restrict the infant's physical activity. 3. Change the diapers as soon as they become damp. 4. Soak the infant in a tub bath twice a day for the next 5 days. 39. The nurse is assessing a client who had abdominal surgery earlier in the day. Which preexisting medical condition would place the client at most risk for postoperative complications? 1. Pacemaker 2. Osteoporosis 3. Alcohol abuse 4. Peptic ulcer disease 40. An 85-year-old client is hospitalized for a fractured right hip. During the postoperative period, the client's appetite is poor and the client refuses to get out of bed. Which nursing statement would be most appropriate to make to the client? 1. "We need to give you iodine so to help in hemoglobin synthesis." 2. "It is important for you to get out of bed so that calcium will go back into the bone." 3. "We need to increase your calcium intake because you are spending too much time in bed." 4. "You need to remember to turn yourself in bed every 2 hours to keep from getting so stiff." 41. The nurse is obtaining a pulse oximetry reading from a postoperative client who appears short of breath. The client has dark fingernail polish on top of artificial nails. What is the most appropriate action? 1. Take the pulse oximetry reading from any finger. 2. Remove one of the artificial nails and then obtain the reading from the finger. 3. Obtain a pulse oximetry reading from another appropriate area, such as an earlobe. 4. Obtain fingernail polish remover, remove the polish, and then obtain the pulse oximetry reading from a finger. 42. A client returns to the nursing unit following a pyelolithotomy for removal of a kidney stone. A Penrose drain is in place. Which action should the nurse include in the client's postoperative plan of care? 1. Positioning the client on the affected side 2. Irrigating the Penrose drain using sterile procedure 3. Changing dressings frequently around the Penrose drain 4. Weighing dressings and adding the amount to the output 43. Which assessment finding indicates that a client who had a mastectomy is experiencing a complication related to the surgery? 1. Pain at the incisional site 2. Arm edema on the operative side 3. Sanguineous drainage in the Jackson-Pratt drain 4. Complaints of decreased sensation near the operative site 44. An operating room nurse is positioning a client on the operating room table to prevent the client's extremities from dangling over the sides of the table. A nursing student who is observing for the day asks the nurse why this is so important. The nurse responds that this is done primarily to prevent which condition? 1. An increase in pulse rate 2. A drop in blood pressure 3. Nerve and muscle damage 4. Muscle fatigue in the extremities 45. The nurse is preparing a preoperative client for transfer to the operating room. The nurse should take which action in the care of this client at this time? 1. Ensure that the client has voided. 2. Administer all the daily medications. 3. Verify that the client has not eaten for the last 24 hours. 4. Have the client practice postoperative breathing exercises. 46. When performing a surgical dressing change on a client's abdominal dressing, the nurse notes an increased amount of drainage and separation of the incision line. The underlying tissue is visible to the nurse. The nurse should take which action in the initial care of this wound? 1. Leave the incision open to the air to dry the area. 2. Irrigate the wound and apply a sterile dry dressing. 3. Apply a sterile dressing soaked with normal saline. 4. Apply a sterile dressing soaked in povidone-iodine (Betadine). 47. The nurse is developing a list of home care instructions for a client being discharged after a laparoscopic cholecystectomy. Which instruction would be least appropriate to include in the postoperative discharge plan of care? 1. Wound care 2. Follow-up care 3. Activity restrictions 4. Deep-breathing exercises 48. A man has had an invasive abdominal surgery to relieve an obstruction in his common bile duct. The man's surgery is completed and he has been transferred to the postanesthesia care unit (PACU). The PACU nurse observes that the man suddenly appears red in the face and appears to be coughing despite the presence of an endotracheal tube and ventilator support. What action should the PACU nurse take first? 1. Suction the client through the endotracheal tube. 2. Instruct the client in the use of an incentive spirometer. 3. Turn the client from a 30-degree lateral position to a supine position. 4. Instruct the client to use a communication board to tell the nurse what is wrong. 49. When a client is transferred from the post-anesthesia care unit (PACU) and arrives on the surgical unit, which should be the first action taken by the nurse? 1. Assess the client's pain. 2. Obtain the client's vital signs. 3. Administer oxygen to the client. 4. Check the rate of the intravenous infusion. 50. A nurse provides instructions to a preoperative client about the use of an incentive spirometer. The nurse determines that the client needs further instruction if the client indicates that he or she will take which action? 1. Sit upright when using the device. 2. Inhale slowly, maintaining a constant flow. 3. Place the lips completely over the mouthpiece. 4. After maximal inspiration, hold the breath for 10 seconds and then exhale. 51. A client has a prescription for continuous monitoring of oxygen saturation by pulse oximetry for a preoperative client. The nurse should perform whichbest action to ensure accurate readings on the oximeter? 1. Apply the sensor to a finger that is cool to the touch. 2. Apply the sensor to a finger with very dark nail polish. 3. Ask the client to limit motion in the hand attached to the pulse oximeter. 4. Place the sensor distal to an intravenous (IV) site with a continuous IV infusion. 52. The preoperative client expresses anxiety to the nurse about the upcoming surgery. Which statement by the nurse is most likely to stimulate further discussion between the client and the nurse? 1. "If it's any help, everyone is very nervous before surgery." 2. "I will be happy to explain the entire surgical procedure to you." 3. "Let me tell you about the amount of pain you can anticipate." 4. "Can you share with me what you've been told about your surgery?" 53. A nurse is preparing the client for transfer to the operating room. The nurse should take which action first? 1. Ensure that the client has voided. 2. Administer all the daily medications. 3. Verify the client has not eaten for the last 24 hours. 4. Teach and practice postoperative breathing exercises. 54. The nurse is caring for a client who recently returned from the operating room. On data collection, the nurse notes that the client's vital signs are blood pressure (BP), 118/70 mm Hg; pulse, 91 beats/minute; and respirations, 16 breaths/minute. Preoperative vital signs were BP, 132/88 mm Hg; pulse, 74 beats/minute; and respirations, 20 breaths/minute. Which action should the nurse plan to take first? 1. Call the surgeon immediately. 2. Shake the client gently to arouse. 3. Cover the client with a warm blanket. 4. Recheck the vital signs in 15 minutes. 55. The nurse has just reassessed the condition of the postoperative client who was admitted 1 hour ago to the surgical unit. Which parameter should the nurse carefully monitor during the next hour? 1. Urinary output of 20 mL/hr 2. Temperature of 37.6° C (99.6° F) 3. Blood pressure of 116/78 mm Hg 4. Serous drainage on the surgical dressing 56. The nurse is caring for a client who was admitted to the surgical unit postoperatively with a wound drain (Jackson-Pratt) in place. What is the primary purpose of a Jackson-Pratt drain? 1. It decreases the risk of evisceration and dehiscence. 2. It provides an accurate measurement of wound drainage. 3. It reduces the risk of infection and helps the wound heal faster. 4. It assists in the evacuation of fluid and blood from the surgical wound. 57. A nurse is reviewing the health care provider's prescription sheet for a preoperative client, which states that the client must be NPO after midnight. Which medication should the nurse clarify to be given and not withheld? 1. Atenolol (Tenormin) 2. Atorvastatin (Lipitor) 3. Cyclobenzaprine (Flexeril) 4. Conjugated estrogen (Premarin) Fundamental Skills - Pain 1. The home health care nurse is caring for a client with cancer who is complaining of acute pain. The most appropriate determination of the client's pain should include which assessment? 1. The client's pain rating 2. Nonverbal cues from the client 3. The nurse's impression of the client's pain 4. Pain relief after appropriate nursing intervention 1. A nurse is caring for a client who is receiving morphine sulfate by the intravenous route for acute pain. The nurse ensures that which medication is available in the event that the client's respiratory status and level of consciousness deteriorate? 1. Atropine sulfate 2. Protamine sulfate 3. Naloxone (Narcan) 4. Promethazine (Phenergan) 2. The nurse is setting up a transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) unit on a client with chronic pain. As the nurse turns up the level of stimulation, the client complains of discomfort. Based on this finding, the nurse should make which interpretation? 1. The maximal stimulation has been reached, and it should be decreased slightly. 2. This is a temporary effect, and the stimulation should continue to be increased. 3. The maximal stimulation has been far exceeded, and it should be decreased by half. 4. This is a complication of the device's use, and it should be discontinued immediately. 3. The nurse is assessing the status of pain in a client who was recently admitted to the hospital with a diagnosis of chronic back pain. The nurse plans care, knowing that physiological responses to chronic pain include which finding? 1. Dry skin 2. Perspiration 3. Dilated pupils 4. Increased pulse rate 5. The nurse is caring for a client who had a cholecystectomy 1 day ago. The nurse plans pain-management techniques, knowing that the severity of the client's pain can be related to which factor? 1. Positioning of the client during surgery 2. How long the client had pain before surgery 3. The type of general anesthesia used during surgery 4. The use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) before surgery 6. The nurse is assessing the status of pain in a cognitively impaired older adult. The nurse understands which information about pain in the older adult? 1. Clients in this age group are less sensitive to pain and have a greater pain tolerance. 2. The prevalence of pain in this age group is about the same as among clients younger than 60 years of age. 3. Mental images of pain are a more effective means to assess pain in this group than visual representations. 4. Pain in the cognitively impaired older adult may require more frequent assessments than in clients who are not impaired. 7. Parenteral meperidine hydrochloride (Demerol) is prescribed postoperatively for an older adult who has just had a right hip repair. The nurse questions the prescription before administering the medication because of which factor? 1. It is just as effective as parenteral morphine sulfate. 2. It may accumulate with repeated dosing, leading to seizures. 3. It is recommended for use because of the medication's short half-life. 4. It is excreted more rapidly in older adults, thus necessitating more frequent dosing. 8. The nurse is caring for a postoperative client who had a small bowel repair 1 day earlier. Because the client is a known opioid substance abuser, the nurse plans care, knowing which piece of information? 1. Opioid substance abusers are less tolerant to opioids and require decreased doses. 2. These clients should be allowed to choose their pain medications and dosing regimen. 3. Nonopioid therapies such as cutaneous stimulation are generally effective if used alone. 4. These clients are at an increased risk for abrupt physiological withdrawal when opioid agonists are abruptly withdrawn. 9. A patient-controlled analgesia (PCA) system is prescribed for a postoperative client to control pain. The nurse understands that this method of pain relief alleviates pain and increases client satisfaction because of which factor? 1. Overdosing is totally eliminated because the PCA machine has a lockout system. 2. The need for naloxone to reverse the effects of the opioid analgesic is eliminated. 3. Compared with intermittent dosing, pain is relieved more effectively by increasing the amount of opioid consumption per day. 4. Clients are empowered to initiate administration of the medication, thereby eliminating the delay in waiting for the nurse to administer the medication. 10. The nurse plans care for an older client admitted with a fractured hip. Which analgesic, prescribed by the health care provider at standard doses and frequencies, would the nurse question? 1. Ibuprofen (Motrin IB) by oral route 2. Morphine sulfate by intravenous (IV) route 3. Tramadol hydrochloride (Ultram) by oral route 4. Meperidine hydrochloride (Demerol) by intramuscular route 11. A client who had abdominal surgery is receiving epidural analgesia. The nurse monitors the client closely, knowing that which is a potential complication of this therapy? 1. Constipation because of the location of the epidural catheter 2. Dislodgement of the epidural catheter because the catheter is not sutured in place 3. Permanent lower motor weakness because of the proximity of the catheter to the sciatic nerve 4. Chronic addiction to the epidural medication because epidural analgesia is a more powerful means of pain relief than patient-controlled analgesia therapy 12. A nurse works in a long-term care facility, caring for older clients. The nurse should make which interpretation when an older client complains of pain? 1. Pain is a natural and expected outcome of aging. 2. Something is wrong and an assessment should be made. 3. Nonpharmacological relief measures are not effective in older clients. 4. It is best to treat the symptom of pain immediately rather than focus on identifying the cause. 13. The health care provider (HCP) writes a prescription for acetylsalicylic acid (ASA), or aspirin, for a client who was admitted to the hospital with joint pain from rheumatoid arthritis. The nurse contacts the HCP to verify the prescription if which finding is noted in the assessment data? 1. Renal colic 2. Hypertension 3. Diabetes mellitus 4. Gastric ulceration 14. To prevent postoperative atelectasis in a client recovering from an open cholecystectomy, what should the nurse do first? 1. Request a cardiopulmonary consult. 2. Teach the client to splint the incision. 3. Teach the proper technique for huff coughing. 4. Ensure that the client is experiencing adequate pain control. 15. A client with a fractured femur who has had an open reduction–internal fixation is receiving ketorolac. Which assessment measurement will assist the nurse in determining the effectiveness of this medication? 1. Pain rating 2. Temperature 3. Serum calcium level 4. White blood cell count 16. The nurse is caring for a client with a back injury sustained 1 year ago. To obtain the most complete assessment data about the client's chronic pain pattern, what should the nurse ask the client? 1. "Can you describe what makes your pain worse?" 2. "What is the intensity of your pain on a scale of 0 to 10?" 3. "Can you describe your daily activities in relation to your pain?" 4. "Would you describe your pain as aching, throbbing, or stabbing?" 17. A child is seen in the school nurse's office with complaints of pain in his right forearm. In reviewing the child's record the nurse notes that he has a history of being physically abused by the mother. Which would be the initial intervention with this child? 1. Assess the child's physical status. 2. Ask the child how the injury occurred. 3. Report the case as suspected child abuse. 4. Observe the interactions between the child and his friends. 18. A client is being started on tramadol (Ultram) therapy for pain management after a back injury. When educating this client on tramadol therapy, what is the priority? 1. The client cannot drink alcohol while taking tramadol. 2. The client cannot smoke cigarettes while taking tramadol. 3. The client should increase the intake of calcium-rich foods. 4. The client should avoid additional over-the-counter cough syrups. 19. The nurse is assessing a client's postoperative pain using the PQRSTU method. Using this method, which questions would the nurse ask the client? 1. "Where is the pain located?" 2. "Does pain medication help?" 3. "What does the pain feel like?" 4. "How does the pain affect you?" 5. "Do you have the pain when you sleep?" 6. "What makes your pain better or worse?" 20. A nurse is making initial rounds on the nursing unit to check the condition of assigned clients. The client complains of discomfort at the intravenous (IV) and the nurse notes that the site is cool, pale, and swollen, and the solution is not infusing. What IV therapy complication has the client most likely experienced? 1. Phlebitis 2. Infection 3. Infiltration 4. Thrombosis [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 31 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$8.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Oct 22, 2020
Number of pages
31
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Oct 22, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
143