Test Bank CHAPTER 24 FULL DISCLOSURE IN FINANCIAL REPORTING
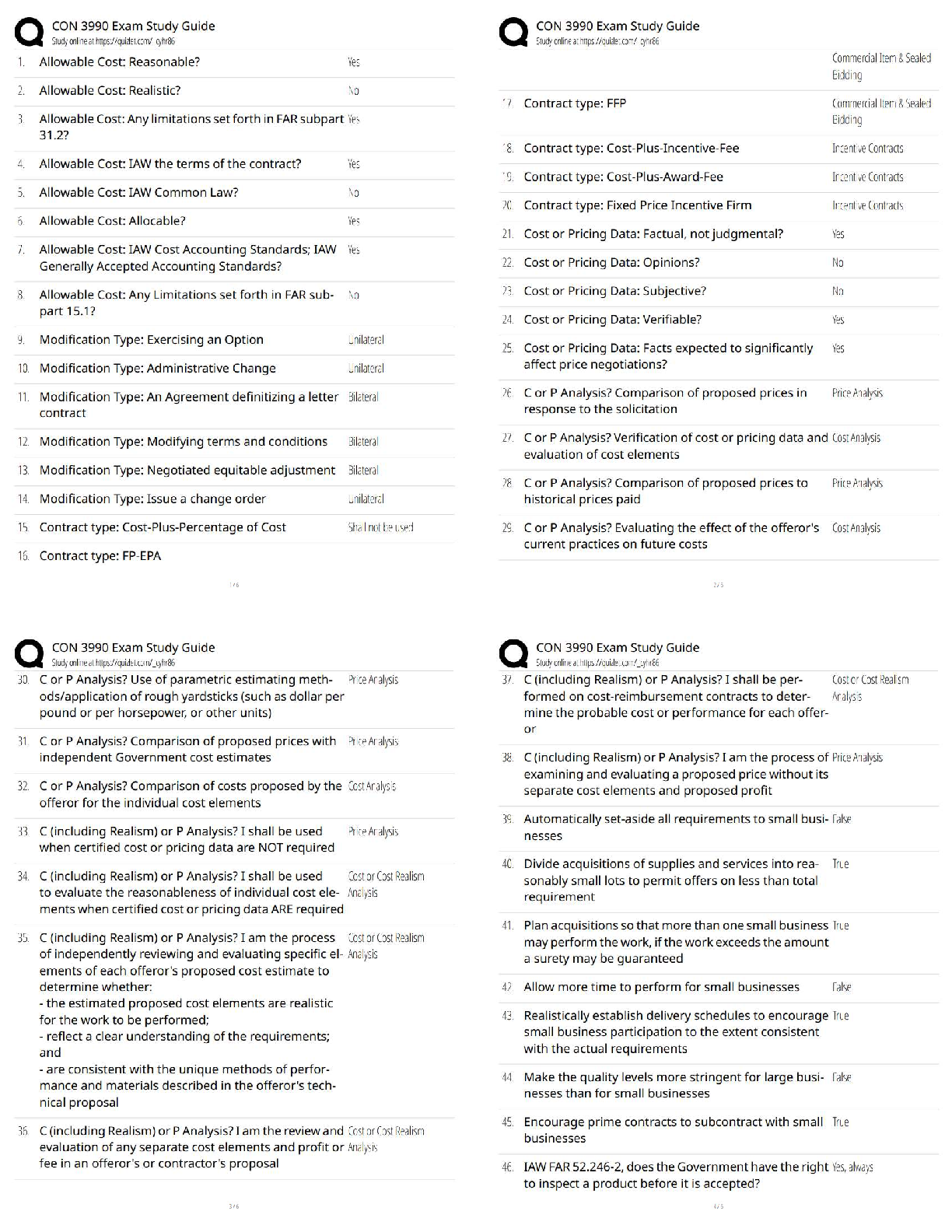
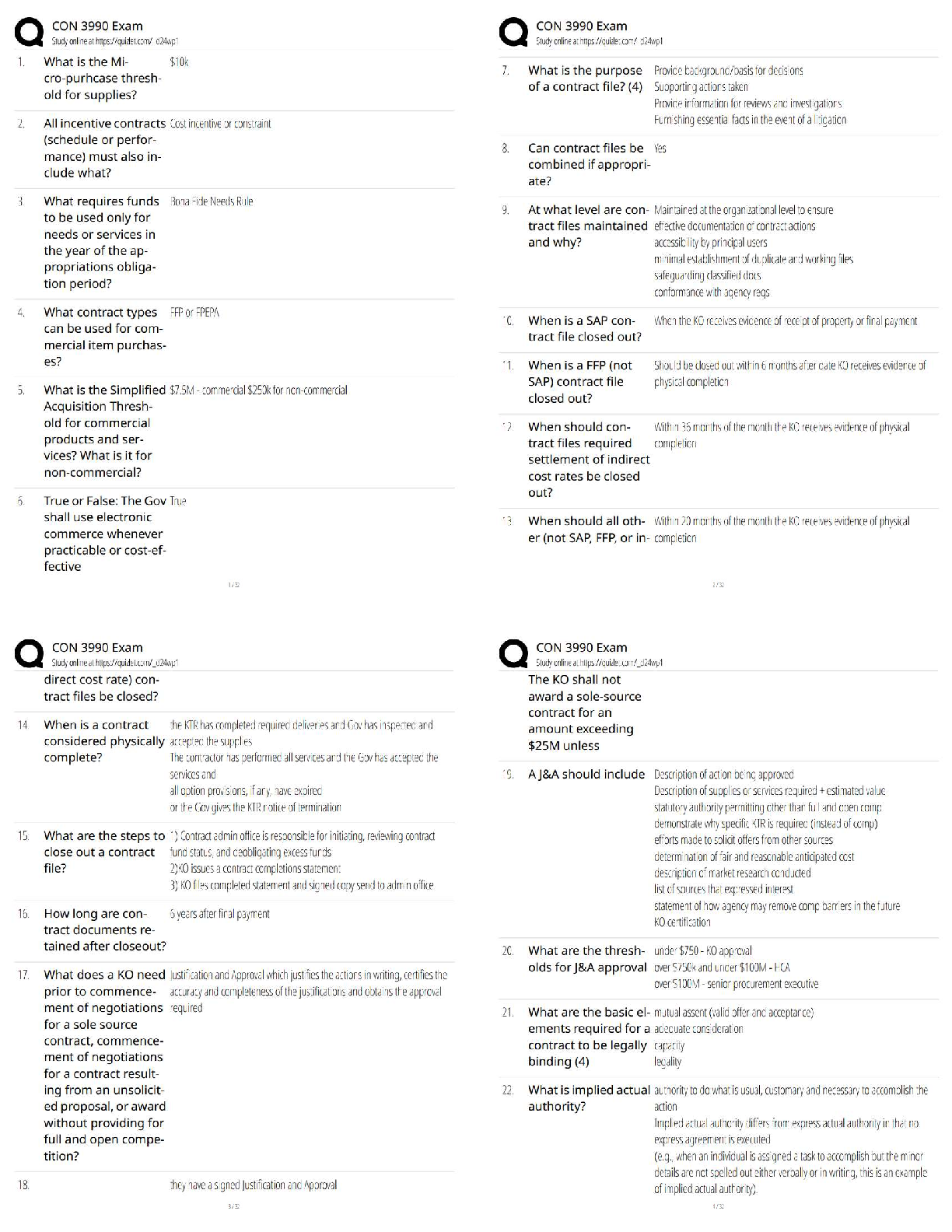
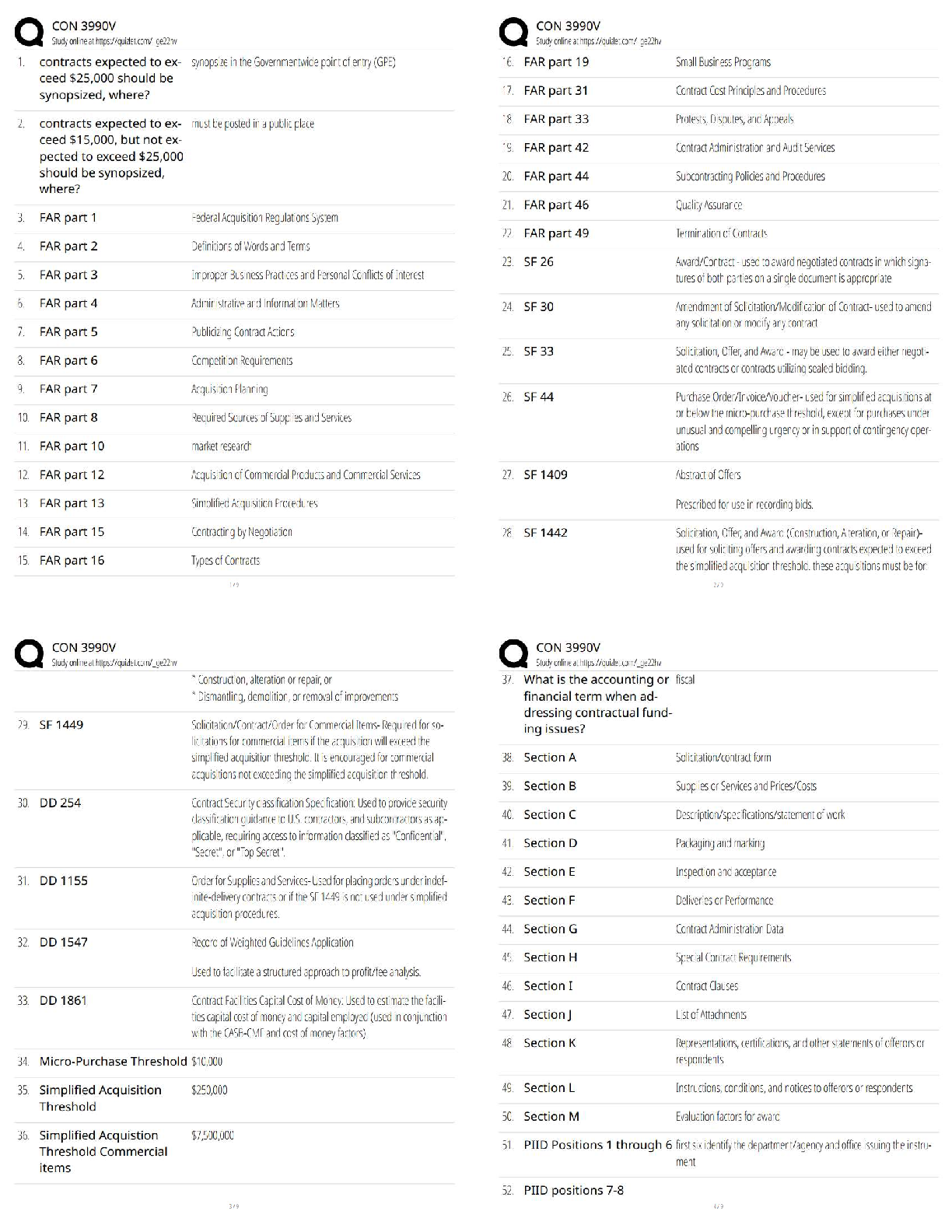
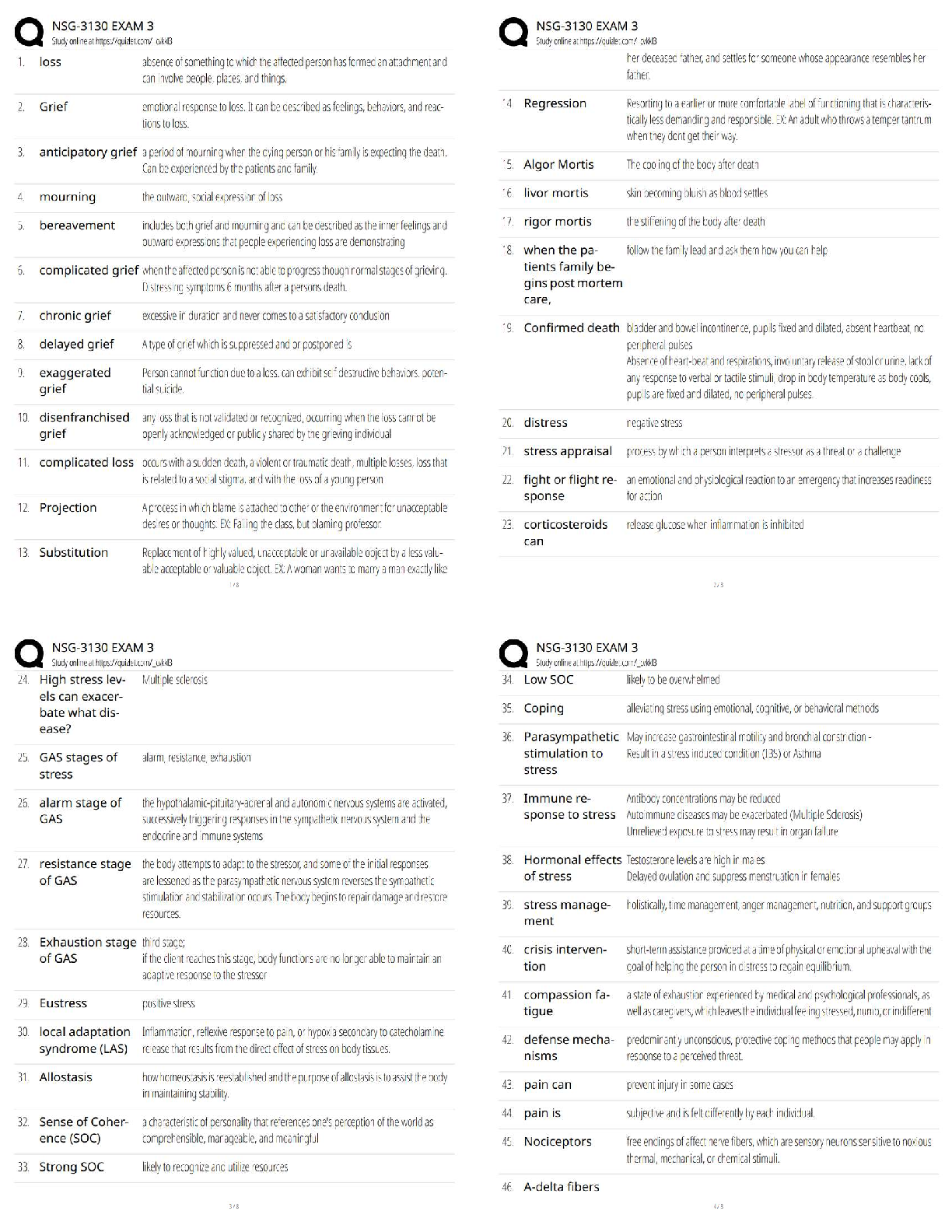
CHAPTER 24
FULL DISCLOSURE IN FINANCIAL REPORTING
IFRS questions are available at the end of this chapter.
TRUE-FALSe—Conceptual
...
Test Bank CHAPTER 24 FULL DISCLOSURE IN FINANCIAL REPORTING
CHAPTER 24
FULL DISCLOSURE IN FINANCIAL REPORTING
IFRS questions are available at the end of this chapter.
TRUE-FALSe—Conceptual
Answer No. Description
F 1. Items affected by FASB standards.
T 2. SEC reporting requirements.
T 3. Definition of accounting policies.
F 4. Related party transactions disclosure.
F 5. Post-balance-sheet disclosures.
T 6. FASB 131 requirements
F 7. Allocation of joint or common costs.
T 8. Disclosure of major customers.
F 9. Reporting under the integral approach.
T 10. Accounting principles in interim reports.
F 11. Reporting extraordinary items in interim reports.
T 12. Computing taxes in an interim period.
F 13. Opinions issued by auditor.
T 14. Definition of qualified opinion.
F 15. Management’s discussion and analysis section.
T 16. Information provided by MD&A section.
F 17. Definition of financial projection.
T 18. Financial forecast vs. financial projection.
T 19. Fraudulent financial reporting.
F 20. Internal environment influences.
Multiple Choice—Conceptual
Answer No. Description
d 21. Disclosure of significant accounting policies.
c 22. Disclosure of inventory accounting policy.
c 23. Definition of errors and irregularities.
d S24. Full disclosure principle description.
b S25. APB Opinion No. 22 disclosure.
b S26. Related party transactions.
c P27. Post-balance-sheet events.
d 28. Subsequent events disclosure.
d 29. Recognition of subsequent events.
b 30. Revenue of a segment.
d 31. Segment revenue test.
b 32. Segment revenue test.
c 33. Disclosure of operating segment information.
d 34. Bases of reporting disaggregated information.
a S35. Items reconciled in segment reporting.
d S36. Accounting principles used in interim reports.
a P37. Planned volume variance in interim period.
d 38. Interim financial reporting.
Multiple Choice—Conceptual (cont.)
Answer N/o. Description
d 39. Application of accounting principles on interim reporting.
b 40. Methods of inventory valuation—year end vs. interim.
a 41. Partial LIFO liquidation reported in interim statements.
c 42. Disclosing information in interim statements.
c 43. Extraordinary items in interim reports.
b S44. Issuing qualified opinion.
c P45. Items covered in MD&A section.
c S46. Difference between financial forecast and financial projection.
a 47. Disclosures in financial forecasts.
a *48. Acid-test ratio and current ratio.
b *49. Receivables turnover ratio.
b *50. Rate of return on common stock equity.
d *51. Payout ratio.
c *52. Measure of long-term solvency.
c *53. Number of times interest earned.
c *54. Using average amounts.
d *55. Limitations of ratio analysis.
P These questions also appear in the Problem-Solving Survival Guide.
S These questions also appear in the Study Guide.
* This topic is dealt with in an Appendix to the chapter.
Multiple Choice—Computational
Answer No. Description
b 56. Determine reportable operating segments.
c 57. Bonus expense in first quarter interim income statement.
a 58. Property taxes and plant repairs recognized in interim period.
c 59. Inventory loss reflected in interim statements.
d *60. Calculate the current ratio.
c *61. Calculate the number of times interest was earned.
d *62. Calculate book value per share of common stock.
c *63. Calculate rate of return on common stock equity.
c *64. Calculate receivables turnover.
d *65. Calculate inventory turnover.
b *66. Calculate the profit margin on sales.
c *67. Calculate the rate of return on common stock equity.
a *68. Determine book value per share.
a *69. Calculate the acid-test ratio.
c *70. Calculate the acid-test ratio.
c *71. Receivables turnover.
c *72. Calculate inventory turnover.
Multiple Choice—CPA Adapted
Answer No. Description
c 73. Significant accounting policies disclosed for plant assets.
c 74. Criteria for reporting disaggregated information.
b 75. Identification of reportable segments.
b 76. Identification of a reportable segment.
b 77. Advertising costs—year end vs. interim reporting.
c 78. Total expense to be reported in interim statements.
b 79. Extraordinary loss reported in interim statements.
c 80. Extraordinary gain reported in interim statements.
c *81. Acid-test ratio and inventory turnover ratio.
d *82. Acid-test ratio and debt to total assets ratio.
c *83. Receivables turnover and payout ratio.
Exercises
Item Description
E24-84 Notes to financial statements.
E24-85 Segment reporting.
E24-86 Segment reporting.
E24-87 Interim reports.
E24-88 Inventory and cost of goods sold at interim dates.
E24-89 Forecasts.
*E24-90 Financial statement analysis.
*E24-91 Selected financial ratios.
*E24-92 Computation of selected ratios.
PROBLEMS
Item Description
P24-93 Segment Reporting.
P24-94 Interim Reports.
CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES
1. Review the full disclosure principle and describe implementation problems.
2. Explain the use of notes in financial statement preparation.
3. Discuss the disclosure requirements for major business segments.
4. Describe the accounting problems associated with interim reporting.
5. Identify the major disclosures in the auditor's report.
6. Understand management’s responsibilities for financials.
7. Identify issues related to financial forecasts and projections.
8. Describe the profession's response to fraudulent financial reporting.
*9. Understand the approach to financial statement analysis.
*10. Identify major analytic ratios and describe their calculation.
*11. Explain the limitations of ratio analysis.
SUMMARY OF LEARNING OBJECTIVES BY QUESTIONS
Item
Type
Item
Type
Item
Type
Item
Type
Item
Type
Item
Type
Item
Type
Learning Objective 1
1.
TF
2.
TF
21.
MC
22.
MC
23.
MC
S24.
MC
Learning Objective 2
3.
TF
5.
TF
S26.
MC
28.
MC
73.
MC
4.
TF
S25.
MC
P27.
MC
29.
MC
84.
E
Learning Objective 3
6.
TF
30.
MC
33.
MC
56.
MC
76.
MC
93.
P
7.
TF
31.
MC
34.
MC
74.
MC
85.
E
8.
TF
32.
MC
S35.
MC
75.
MC
86.
E
Learning Objective 4
9.
TF
S36.
MC
40.
MC
57.
MC
78.
MC
88.
E
10.
TF
P37.
MC
41.
MC
58.
MC
79.
MC
94.
P
11.
TF
38.
MC
42.
MC
59.
MC
80.
MC
12.
TF
39.
MC
43.
MC
77.
MC
87.
E
Learning Objective 5
13.
TF
14.
TF
15.
TF
16.
TF
S44.
MC
Learning Objective 6
P45.
MC
Learning Objective 7
17.
TF
18.
TF
S46.
MC
47.
MC
89.
E
Learning Objective 8
19.
TF
20.
TF
Learning Objective 10
48.
MC
52.
MC
61.
MC
65.
MC
69.
MC
81.
MC
91.
E
49.
MC
53.
MC
62.
MC
66.
MC
70.
MC
82.
MC
92.
E
50.
MC
54.
MC
63.
MC
67.
MC
71.
MC
83.
MC
51.
MC
60.
MC
64.
MC
68.
MC
72.
MC
90.
E
Learning Objective 11
55.
MC
Note: TF = True-False
MC = Multiple Choice
E = Exercise
P = Problem
TRUE-FALSE—Conceptual
1. FASB standards directly affect financial statements, notes to the financial statements, and management’s discussion and analysis.
2. The SEC requires that companies report to it certain substantive information that is not found in their annual reports.
3. Accounting policies are the specific accounting principles and methods a company uses and considers most appropriate to present fairly its financial statements.
4. In order to make adequate disclosure of related party transactions, companies should report the legal form, rather than the economic substance, of these transactions.
5. If the loss on an account receivable results from a customer’s bankruptcy after the balance sheet date, the company only discloses this information in the notes to the financial statements.
6. FASB Statement 131 requires that general purpose financial statements include selected information on a single basis of segmentation.
7. The FASB requires allocations of joint, common, or company-wide costs for external reporting purposes.
8. If 10 percent or more of company revenue is derived from a single customer, the company must disclose the total amount of revenue from each such customer by segment.
9. Companies should report accounting transactions as they occur, and expense recognition should not change with the period of time covered under the integral approach.
10. Companies should generally use the same accounting principles for interim reports and for annual reports.
11. Companies report extraordinary items in interim reports by prorating them over the four quarters.
12. To compute the year-to-date tax, companies apply the estimated annual effective tax rate to the year-to-date ordinary income at the end of each interim period.
13. In most situations, an auditor issues a qualified opinion or disclaims an opinion.
14. A qualified opinion is issued when the exception to the standard opinion is not of sufficient magnitude to invalidate the statements as a whole.
15. Management’s discussion and analysis section covers three financial aspects of an enterprise’s business-liquidity, profitability, and solvency.
16. The MD&A section must provide information about the effects of inflation and changing prices, if they are material to financial statement trends.
17. A financial projection is a set of prospective financial statements that present a company’s expected financial position and results of operations.
18. The difference between a financial forecast and a financial projection is that a forecast provides information on what is expected to happen, while a projection provides information on what might take place.
19. Fraudulent financial reporting is intentional or reckless conduct, whether act or omission, that results in materially misleading financial statements.
20. Influences in a company’s internal environment may relate to industry conditions, poor internal control systems, or legal and regulatory considerations.
True-False Answers—Conceptual
Item
Ans.
Item
Ans.
Item
Ans.
Item
Ans.
1.
F
6.
T
11.
F
16.
T
2.
T
7.
F
12.
T
17.
F
3.
T
8.
T
13.
F
18.
T
4.
F
9.
F
14.
T
19.
T
5.
F
10.
T
15.
F
20.
F
MULTIPLE CHOICE—Conceptual
21. Which of the following should be disclosed in a Summary of Significant Accounting Policies?
a. Types of executory contracts
b. Amount for cumulative effect of change in accounting principle
c. Claims of equity holders
d. Depreciation method followed
22. An example of an inventory accounting policy that should be disclosed in a Summary of Significant Accounting Policies is the
a. amount of income resulting from the involuntary liquidation of LIFO.
b. major backlogs of inventory orders.
c. method used for pricing inventory.
d. composition of inventory into raw materials, work-in-process, and finished goods.
23. Errors and irregularities are defined as intentional distortions of facts.
Errors Irregularities
a. Yes Yes
b. Yes No
c. No Yes
d. No No
S24. The full disclosure principle, as adopted by the accounting profession, is best described by which of the following?
a. All information related to an entity's business and operating objectives is required to be disclosed in the financial statements.
b. Information about each account balance appearing in the financial statements is to be included in the notes to the financial statements.
c. Enough information should be disclosed in the financial statements so a person wishing to invest in the stock of the company can make a profitable decision.
d. Disclosure of any financial facts significant enough to influence the judgment of an informed reader.
S25. The focus of APB Opinion No. 22 is on the disclosure of accounting policies. This information is important to financial statement readers in determining
a. net income for the year.
b. whether accounting policies are consistently applied from year to year.
c. the value of obsolete items included in ending inventory.
d. whether the working capital position is adequate for future operations.
S26. If a business entity entered into certain related party transactions, it would be required to disclose all of the following information except the
a. nature of the relationship between the parties to the transactions.
b. nature of any future transactions planned between the parties and the terms involved.
c. dollar amount of the transactions for each of the periods for which an income state-ment is presented.
d. amounts due from or to related parties as of the date of each balance sheet presented.
P27. Events that occur after the December 31, 2013 balance sheet date (but before the balance sheet is issued) and provide additional evidence about conditions that existed at the balance sheet date and affect the realizability of accounts receivable should be
a. discussed only in the MD&A (Management's Discussion and Analysis) section of the annual report.
b. disclosed only in the Notes to the Financial Statements.
c. used to record an adjustment to Bad Debt Expense for the year ending December 31, 2013
d. used to record an adjustment directly to the Retained Earnings account
28. Which of the following post-balance-sheet events would generally require disclosure, but no adjustment of the financial statements?
a. Retirement of the company president
b. Settlement of litigation when the event that gave rise to the litigation occurred prior to the balance sheet date.
c. Employee strikes
d. Issue of a large amount of capital stock
29. Which of the following subsequent events (post-balance-sheet events) would require adjustment of the accounts before issuance of the financial statements?
a. Loss of plant as a result of fire
b. Changes in the quoted market prices of securities held as an investment
c. Loss on an uncollectible account receivable resulting from a customer’s major flood loss
d. Loss on a lawsuit, the outcome of which was deemed uncertain at year end.
30. Revenue of a segment includes
a. only sales to unaffiliated customers.
b. sales to unaffiliated customers and intersegment sales.
c. sales to unaffiliated customers and interest revenue.
d. sales to unaffiliated customers and other revenue and gains.
31. An operating segment is a reportable segment if
a. its operating profit is 10% or more of the combined operating profit of profitable segments.
b. its operating loss is 10% or more of the combined operating losses of segments that incurred an operating loss.
c. the absolute amount of its operating profit or loss is 10% or more of the company's combined operating profit or loss.
d. none of these.
32. A segment of a business enterprise is to be reported separately when the revenues of the segment exceed 10 percent of the
a. total combined revenues of all segments reporting profits.
b. total revenues of all the enterprise's industry segments.
c. total export and foreign sales.
d. combined net income of all segments reporting profits.
33. All of the following information about each operating segment must be reported except
a. unusual items.
b. interest revenue.
c. cost of goods sold.
d. depreciation and amortization expense.
34. The profession requires disaggregated information in the following ways:
a. products or services.
b. geographic areas.
c. major customers.
d. all of these.
S35. In presenting segment information, which of the following items must be reconciled to the entity's consolidated financial statements?
Operating Identifiable
Revenues Profit (Loss) Assets
a. Yes Yes Yes
b. No Yes Yes
c. Yes No Yes
d. Yes Yes No
S36. APB Opinion No. 28 indicates that
a. all companies that issue an annual report should issue interim financial reports.
b. the discrete view is the most appropriate approach to take in preparing interim financial reports.
c. the three basic financial statements should be presented each time an interim period is reported upon.
d. the same accounting principles used for the annual report should be employed for interim reports.
P37. Rondelli Manufacturing Company employs a standard cost system. A planned volume variance in the first quarter of 2011, which is expected to be absorbed by the end of the fiscal year, ordinarily should
a. be deferred at the end of the first quarter, regardless of whether it is favorable or unfavorable.
b. never be deferred beyond the quarter in which it occurs.
c. be deferred at the end of the first quarter if it is favorable; unfavorable variances are to be recognized in the period incurred.
d. be deferred at the end of the first quarter if it is unfavorable; favorable variances are to be recognized in the period incurred.
38. In considering interim financial reporting, how does the profession conclude that such reporting should be viewed?
a. As a "special" type of reporting that need not follow generally accepted accounting principles.
b. As useful only if activity is evenly spread throughout the year so that estimates are unnecessary.
c. As reporting for a basic accounting period.
d. As reporting for an integral part of an annual period.
39. Accounting principles are modified for the following at interim dates.
Revenue Losses
a. Yes Yes
b. Yes No
c. No Yes
d. No No
40. The following methods of estimating inventory can be used at interim dates for inventory pricing. May they also be used at year end?
Gross Profit Method Retail Inventory Method
a. No No
b. No Yes
c. Yes No
d. Yes Yes
41. A company that uses the last-in, first-out (LIFO) method of inventory pricing finds at an interim reporting date that there has been a partial liquidation of the base period inventory level. The decline is considered temporary and the partial liquidation is expected to be replaced prior to year end. The amount shown as inventory at the interim reporting date should
a. be shown at the actual level, and cost of sales for the interim reporting period should include the expected cost of replacement of the liquidated LIFO base.
b. be shown at the actual level, and cost of sales for the interim reporting period should reflect the historical cost of the liquidated LIFO base.
c. not give effect to the LIFO liquidation, and cost of sales for the interim reporting period should reflect the historical cost of the liquidated LIFO base.
d. be shown at the actual level, and the decrease in inventory level should not be reflected in the cost of sales for the interim reporting period.
42. Companies should disclose all of the following in interim reports except
a. basic and diluted earnings per share.
b. changes in accounting principles.
c. post-balance-sheet events.
d. seasonal revenue, cost, or expenses.
43. The required approach for handling extraordinary items in interim reports is to
a. prorate them over all four quarters.
b. prorate them over the current and remaining quarters.
c. charge or credit the loss or gain in the quarter that it occurs.
d. disclose them only in the notes.
S44. If the financial statements examined by an auditor lead the auditor to issue an opinion that contains an exception that is not of sufficient magnitude to invalidate the statement as a whole, the opinion is said to be
a. unqualified.
b. qualified.
c. adverse.
d. exceptional.
P45. The MD&A section of a company's annual report is to cover the following three items:
a. income statement, balance sheet, and statement of owners' equity.
b. income statement, balance sheet, and statement of cash flows.
c. liquidity, capital resources, and results of operations.
d. changes in the stock price, mergers, and acquisitions.
S46. Which of the following best characterizes the difference between a financial forecast and a financial projection?
a. Forecasts include a complete set of financial statements, while projections include only summary financial data.
b. A forecast is normally for a full year or more and a projection presents data for less than a year.
c. A forecast attempts to provide information on what is expected to happen, whereas a projection may provide information on what is not necessarily expected to happen.
d. A forecast includes data which can be verified about future expectations, while the data in a projection is not susceptible to verification.
47. A financial forecast per professional pronouncements presents to the best of the responsible party's knowledge and belief,
a. an entity's expected financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
b. an assessment of the company's ability to be successful in the future.
c. given one or more hypothetical assumptions, an entity's expected financial position, results of operations, and cash flows.
d. an assessment of the company's ability to be successful in the future under a number of different assumptions.
*48. Cash, short-term investments, and net receivables are the numerator for
Acid-Test Ratio Current Ratio
a. Yes No
b. Yes Yes
c. No No
d No &nbs
[Show More]





.png)