Test Bank Chapter 17 Investments.
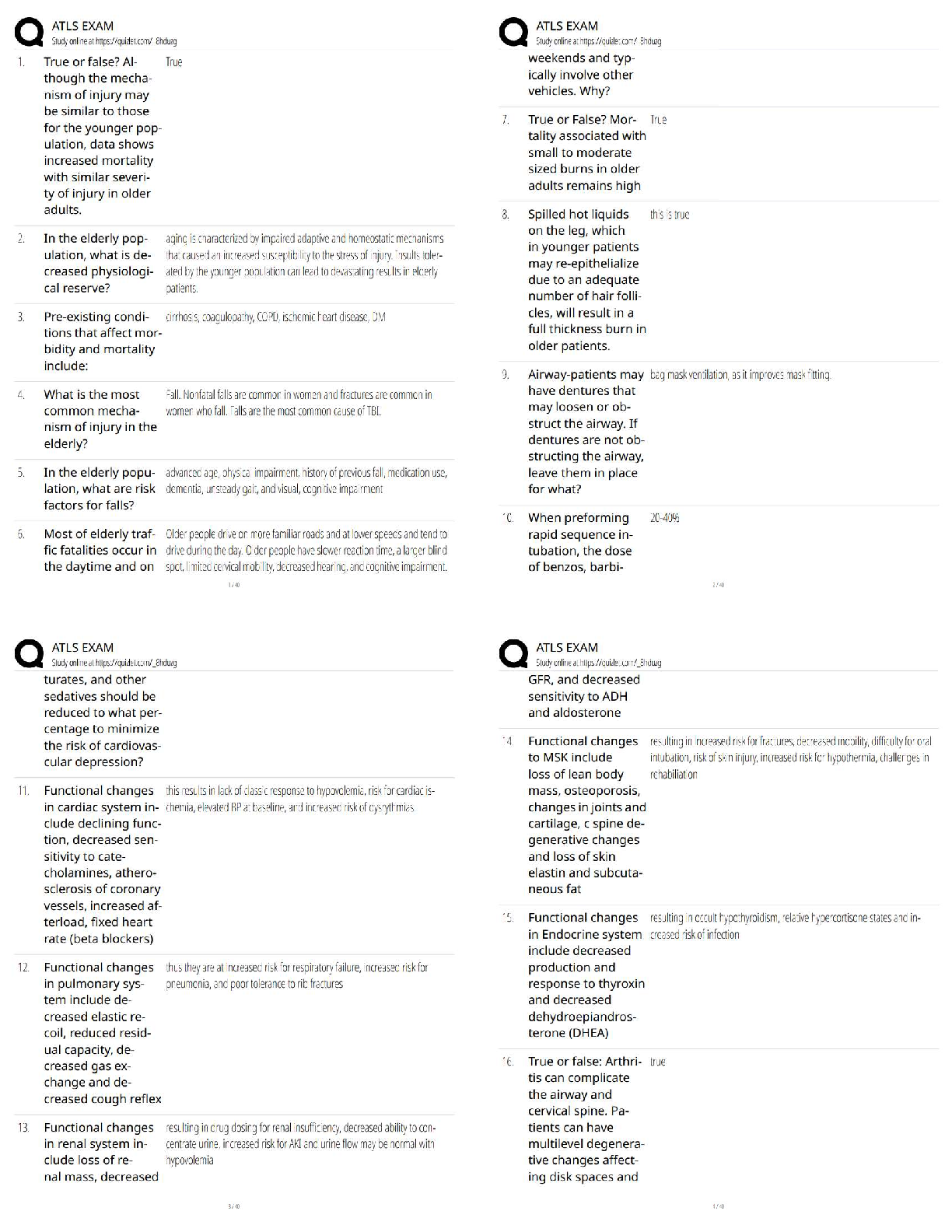
CHAPTER 17
INVESTMENTS
IFRS questions are available at the end of this chapter.
TRUE-FALSE—Conceptual
Description
F
...
Test Bank Chapter 17 Investments.
CHAPTER 17
INVESTMENTS
IFRS questions are available at the end of this chapter.
TRUE-FALSE—Conceptual
Description
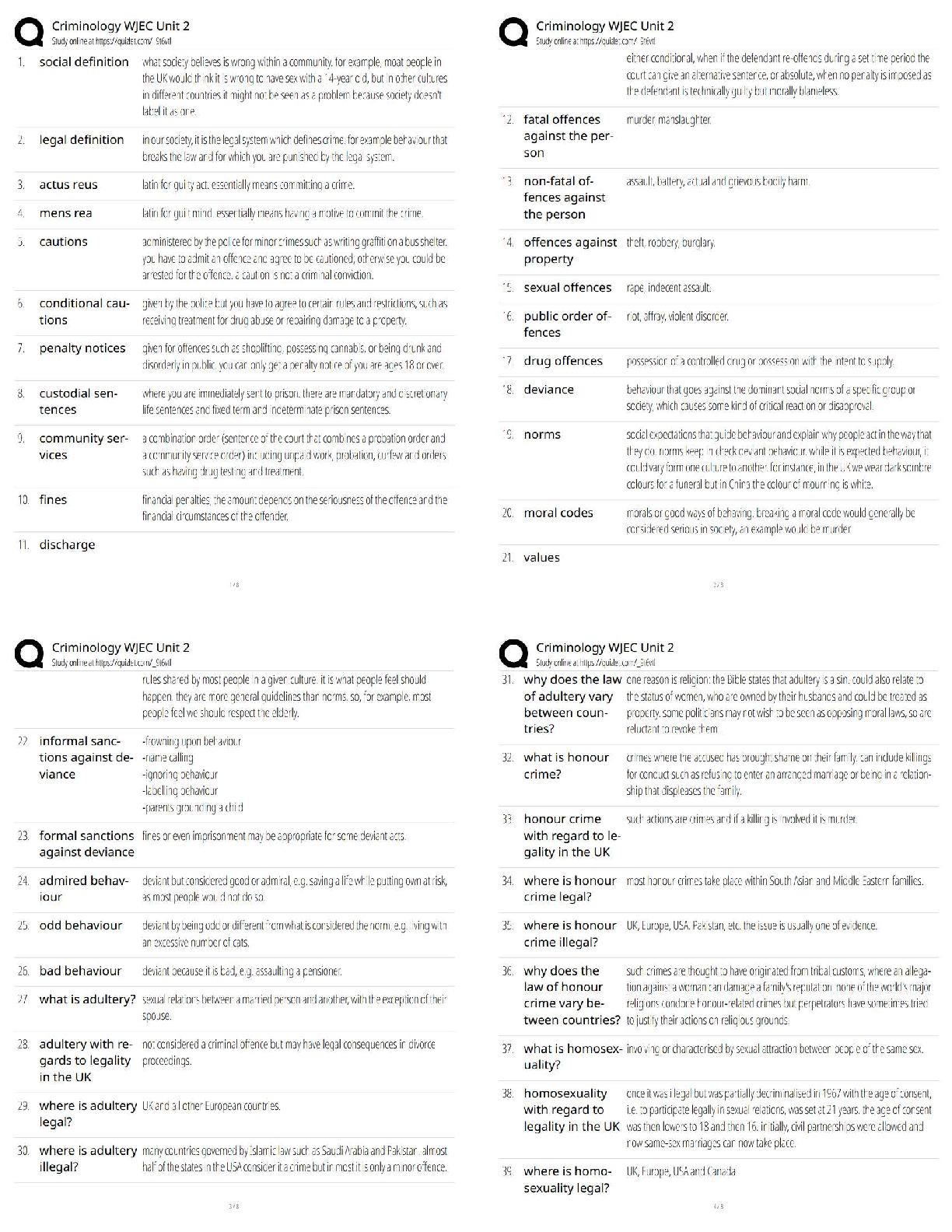
F 1. Examples of debt securities.
T 2. Definition of trading securities.
F 3. Available-for-sale unrealized gains/losses.
F 4. Classifying held-to-maturity securities.
T 5. Fair value changes in AFS securities.
F 6. Securities Fair Value Adjustment account.
T 7. Accounting for trading securities.
F 8. Definition of significant influence.
T 9. Reporting Unrealized Holding Gain/Loss—Equity account.
T 10. Examples of significant influence.
F 11. Definition of controlling interest.
T 12. Effect of dividends on investment under equity.
F 13. Reporting revenue under fair value method.
T 14. Definition of controlling interest.
F 15. Using fair value option.
T 16. Accounting for changes in fair value.
F 17. Temporary declines and write downs.
T 18. Necessary of reclassification adjustment.
F 19. Transfer of held-to-maturity securities.
T 20. Transfers from trading to available-for-sale.
MULTIPLE CHOICE—Conceptual
Description
c 21. Debt securities.
b 22. Valuation of debt securities.
c 23. Held-to-maturity securities.
c 24. Unrealized gain/loss recognition for securities.
a P25. Accounting for accrued interest.
a S26. Identifying securities accounted for at amortized cost.
c S27. Accounting for available-for-sale securities.
b S28. Using effective-interest method of amortization.
a S29. Identifying available-for-sale securities.
d 30. Classification as held-to-maturity.
b 31. Reporting held-to-maturity securities.
c 32. Acquisition of held-to-maturity securities.
d 33. Accounting for trading securities.
c 34. Accounting for trading debt securities.
c 35. Recording investments in debt securities.
d 36. Calculating the issue price of bonds.
c 37. Valuation of investments in debt securities.
a 38. Recording amortization of bond discount.
c 39. Amortization of premium/discount on investment in a debt security.
MULTIPLE CHOICE—Conceptual (cont.)
Description
d 40. Effective-interest rate method.
c 41. Debt securities purchased between interest dates.
c 42. Sale of debt security prior to maturity.
b S43. Passive interest investment.
a S44. Fair value vs. equity method.
c P45. Fair value vs. equity method.
b 46. Conditions for using the equity method.
d 47. Ownership interest required for using the equity method.
a 48. Recording of dividends received under the equity method.
d 49. Recognition of earnings of investee using the equity method.
d 50. Effect of using the fair value method in error.
d 51. Determine value of investment.
a 52. Fair value option.
d 53. Accounting for impairments.
c 54. Reclassification adjustment in comprehensive income.
b 55. Reclassification of securities.
b 56. Reclassification of securities.
d P57. Transfer of a debt security.
c 58. Definition of “gains trading” or “cherry picking”.
b 59. Accounting for transfers between Categories.
a *60. Accounting for derivatives.
c *61. Characteristics of a derivative instrument.
b *62. Identifying companies that are arbitrageurs.
d *63. Identifying equity securities.
c *64. Accounting for fair value hedges.
b *65. Gains/losses on cash flow hedges.
a *66. Identifying an embedded derivative.
c *67. Requirements for financial instrument disclosures.
a *68. Variable-interest entity.
d *69. Risk-and-reward model and voting-interest approach.
P These questions also appear in the Problem-Solving Survival Guide.
S These questions also appear in the Study Guide.
*This topic is dealt with in an Appendix to the chapter.
MULTIPLE CHOICE—Computational
Description
c 70. Recording the purchase of debt securities.
b 71. Computing cost of bond investment.
d 72. Calculation of discount amortization.
b 73. Calculation of revenue from HTM securities.
a 74. Computation of other comprehensive income.
c 75. Computation of gain/loss on sale of bonds.
a 76. Acquisition of held-to-maturity securities.
b 77. Carrying value of held-to-maturity securities.
c 78. Carrying value of available-for-sale debt securities.
a 79. Calculation of income from available-for-sale debt securities.
b 80. Calculation of income from HTM securities.
MULTIPLE CHOICE—Computational (cont.)
Description
b 81. Determine gain on sale of debt securities.
d 82. Computation of revenue from HTM securities.
a 83. Calculation of premium amortization.
d 84. Calculation of other comprehensive income.
b 85. Calculation of loss on sale of bonds.
d 86. Calculation of loss on sale of trading security.
b 87. Determination of unrealized loss on trading security.
c 88. Determination of accumulated other comprehensive income.
b 89. Entry to record unrealized gain on AFS securities.
c 90. Fair value for trading securities.
a 91. Unrealized gain on available-for-sale securities.
a 92. Calculation of gain on sale of equity security.
b 93. Determination of unrealized loss on AFS securities.
a 94. Calculation of unrealized loss included in comprehensive income.
b 95. Computation of purchase price of equity method investment.
c 96. Computation of revenue from investment.
c 97. Computation of investment account balance.
a 98. Calculation of investment revenue.
c 99. Accounting for stock investments/fair value method.
b 100. Accounting for stock investments/equity method.
b 101. Accounting for stock investments/fair value method.
b 102. Equity method of accounting.
c 103. Fair value method of accounting for stock investment.
c 104. Equity method of accounting for stock investment.
c 105. Balance of investment account using the equity method.
b 106. Investment income recognized under the equity method.
c 107. Balance of investment account using the equity method.
b 108. Balance of investment account using the equity method.
d 109. Investment income recognized under the equity method.
b 110. Other comprehensive income.
MULTIPLE CHOICE—CPA Adapted
Description
d 111. Carrying value of AFS debt securities.
d 112. Unrealized loss on trading and AFS securities.
c 113. Unrealized loss on trading and AFS securities.
d 114. Classification of an equity security.
c 115. Investment income recognized under the equity method.
b 116. Balance of investment account using the equity method.
c 117. Sale of stock investment.
a 118. Calculate the acquisition price of a stock investment.
b 119. Transfer of securities from trading to AFS.
EXERCISES
Item Description
E17-120 Investment in debt securities at a premium.
E17-121 Investment in debt securities at a discount.
E17-122 Investments in equity securities (essay).
E17-123 Investment in equity securities.
E17-124 Fair value and equity methods (essay).
E17-125 Fair value and equity methods.
E17-126 Comprehensive income calculation.
*E17-127 Fair value hedge.
*E17-128 Cash flow hedge.
PROBLEMS
Item Description
P17-129 Trading equity securities.
P17-130 Trading securities.
P17-131 Available-for-sale securities.
*P17-132 Derivative financial instrument.
*P17-133 Free-standing derivative.
CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES
1. Identify the three categories of debt securities and describe the accounting and reporting treatment for each category.
2. Understand the procedures for discount and premium amortization on bond investments.
3. Identify the categories of equity securities and describe the accounting and reporting treatment for each category.
4. Explain the equity method of accounting and compare it to the fair value method for equity securities.
5. Describe the accounting for the fair value option.
6. Discuss the accounting for impairments of debt and equity investments.
7. Explain why companies report reclassification adjustments.
8. Describe the accounting for transfer of investment securities between categories.
*9. Explain who uses derivatives and why.
*10. Understand the basic guidelines for accounting for derivatives.
*11. Describe the accounting for derivative financial instruments.
*12. Explain how to account for a fair value hedge.
*13. Explain how to account for a cash flow hedge.
*14. Identify special reporting issues related to derivative financial instruments that cause unique accounting problems.
*15. Describe the accounting for variable-interest entities.
SUMMARY OF LEARNING OBJECTIVES BY QUESTIONS
Item Type Item Type Item Type Item Type Item Type Item Type Item Type
Learning Objective 1
1. TF 3. TF 22. MC 24. MC S26. MC 70. MC
2. TF 21. MC 23. MC P25. MC S27. MC 71. MC
Learning Objective 2
4. TF 30. MC 36. MC 42. MC 77. MC 83. MC
5. TF 31. MC 37. MC 72. MC 78. MC 84. MC
6. TF 32. MC 38. MC 73. MC 79. MC 85. MC
7. TF 33. MC 39. MC 74. MC 80. MC 111. MC
S28. MC 34. MC 40. MC 75. MC 81. MC 120. E
S29. MC 35. MC 41. MC 76. MC 82. MC 121. E
Learning Objective 3
8. TF 11. TF 87. MC 90. MC 93. MC 113. MC 129. P
9. TF S43. MC 88. MC 91. MC 94. MC 114. MC 130. P
10. &n
[Show More]













.png)