Test Bank Chapter 7 Cash and Receivables.
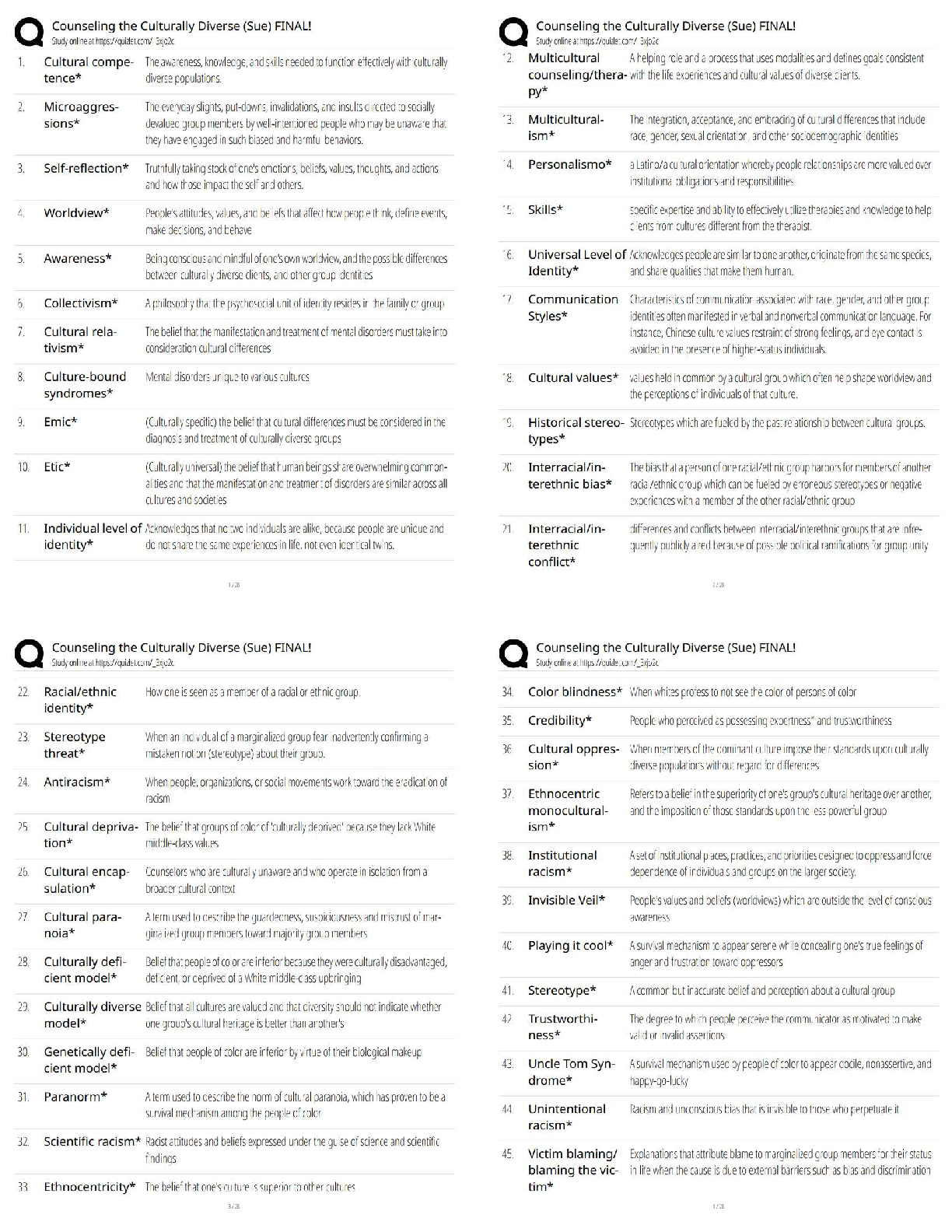
CHAPTER 7
CASH AND RECEIVABLES
IFRS questions are available at the end of this chapter.
TRUE-FALSE—Conceptual
Description
...
Test Bank Chapter 7 Cash and Receivables.
CHAPTER 7
CASH AND RECEIVABLES
IFRS questions are available at the end of this chapter.
TRUE-FALSE—Conceptual
Description
T 1. Items considered cash.
F 2. Items considered cash.
F 3. Items considered cash.
F 4. Cash equivalents definition.
F 5. Bank overdrafts.
T 6. Cash equivalents.
F 7. Classification of receivables.
F 8. Items considered trade receivables.
T 9. Trade discount uses.
T 10. Sales discounts.
T 11. Valuation of receivables.
F 12. Percentage-of-receivables approach.
F 13. Percentage-of-sales method.
T 14. Reporting notes receivable.
F 15. Stated interest rate vs. effective rate.
F 16. Classification of notes receivable.
T 17. Recourse liability.
F 18. Buying receivables with recourse.
T 19. Selling receivables with recourse.
F 20. Computing receivables turnover.
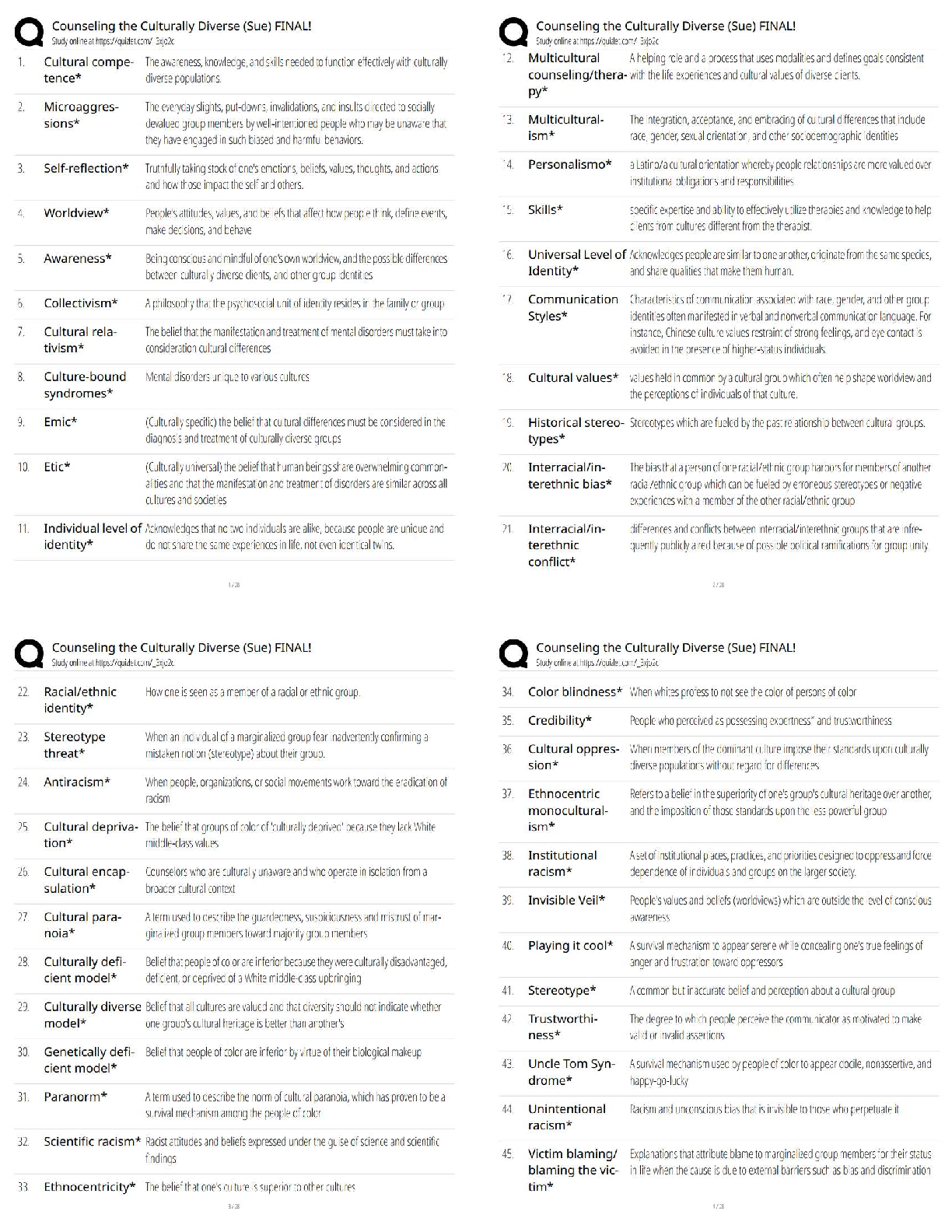
MULTIPLE CHOICE—Conceptual
Description
d 21. Identification of cash items.
b 22. Identification of cash items.
d 23. Classification of travel advance.
d P24. Items included as cash.
b 25. Identification of cash items.
a 26. Classification of post-dated checks.
b 27. Classification of postage stamps.
d 28. Compensating balance definition.
b 29. Classification of cash restricted for plant expansion.
d S30. Cash equivalent definition.
d 31. Classification of bank overdraft.
d 32. Classification of compensating balances.
d 33. Definition of trade receivables.
d 34. Identification of trade receivables.
c S35. Presentation of nontrade receivables.
d S36. Cash discount definition.
MULTIPLE CHOICE—Conceptual (cont.)
Description
d P37. Trade discount uses.
a 38. Classification of sales discounts.
d 39. Reasons for trade discounts.
c 40. Accounting for cash discounts and trade discounts.
a 41. Theoretically correct approach for cash discounts.
c 42. Accounts receivable valuation problems.
d 43. Reason allowance method is preferable.
a 44. Allowance method concept.
b 45. Accounting for bad debts and earnings management.
c 46. Recording bad debt expense.
a 47. Journal entry for writing off an account.
d 48. Journal entry for collection of an account previously written off.
c 49. Valuation of short-term receivables.
d 50. Bad debt provision and the matching concept.
a 51. Bad debts as a percentage of sales.
b 52. Bad debts as a percentage of sales.
a 53. Bad debts as a percentage of receivables.
d 54. Financial statement effect of a note recorded incorrectly.
b 55. Imputed interest description.
c 56. Reason a company sells receivables.
d 57. Transfer of receivables as a sale.
a 58. Definition of selling receivables with recourse.
c 59. Factoring accounts receivable without recourse.
c S60. Classification of accounts and notes receivable.
a S61. Transfer of receivables with recourse.
a P62. Accounts receivable turnover ratio.
d 63. Accounts receivable turnover ratio.
c 64. Items included in accounts receivable on balance sheet.
a 65. Days to collect accounts receivable calculation.
d 66. Reason for accounts receivable turnover increase.
b *67. Balance per bank reconciling item.
c *68. Entry to replenish Petty Cash.
c *69. Purpose of Cash Over & Short account.
b *70. Classification of bank service charges.
c *71. Treatment of bank credits on bank reconciliation.
P These questions also appear in the Problem-Solving Survival Guide.
S These questions also appear in the Study Guide.
* This topic is dealt with in an Appendix to the chapter.
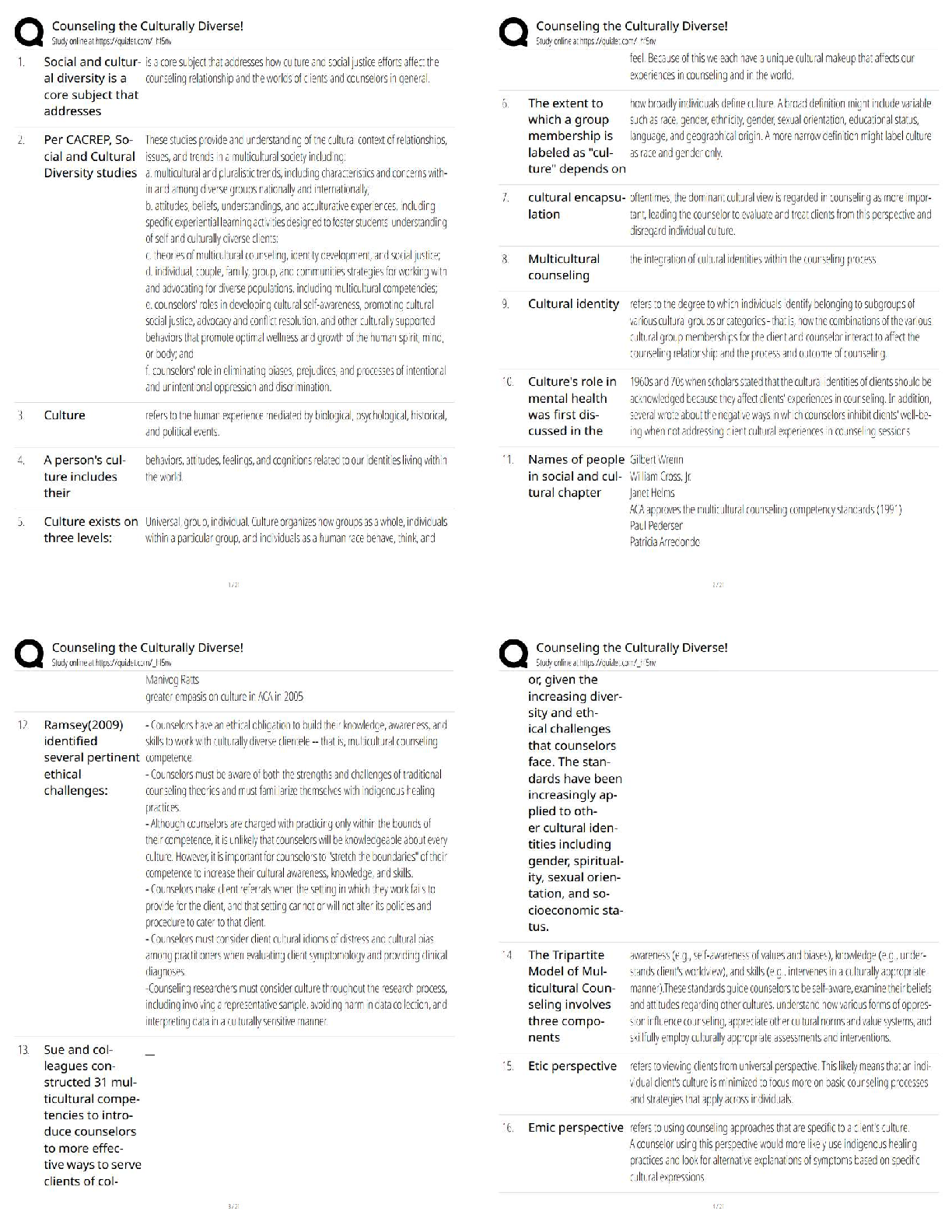
MULTIPLE CHOICE—Computational
Description
b 72 Calculate cash balance.
d 73. Calculate effective interest on loan with required compensatory balance.
b 74. Reporting cash.
c 75. Cash and cash equivalents.
b 76. Reporting cash.
c 77. Cash and cash equivalents.
c 78. Determine effective annual interest rate of sales discount.
b 79. Calculate sales revenue using net method.
c 80. Entry for credit sale using gross method.
a 81. Entry for credit sale using net method.
c 82. Calculate ending allowance for doubtful accounts balance.
d 83. Calculate bad debt expense.
c 84. Calculate ending allowance for doubtful accounts balance.
b 85. Calculate balance of accounts receivable.
b 86. Calculate net realizable value of accounts receivable.
d 87. Calculate net realizable value of accounts receivable.
c 88. Calculate bad debt expense using aging of receivables.
b 89. Calculate bad debt expense using percent of sales.
a 90. Calculate bad debt expense using percent of receivables.
b 91. Valuation of accounts receivable.
b 92. Calculation of bad debt expense.
d 93. Calculate Allowance for Doubtful Accounts balance.
b 94. Valuation of accounts receivable.
b 95. Calculation of bad debt expense.
d 96. Calculate Allowance for Doubtful Accounts balance.
b 97. Determine appropriate interest rate for a zero-interest-bearing note.
a 98. Calculate present value of a zero-interest-bearing note.
a 99. Calculation of sales revenue.
b 100. Entry for exchange of goods for note receivable.
c 101. Calculate amount of interest.
c 102. Calculate interest revenue on a zero-interest-bearing note.
d 103. Calculate note payable amount.
a 104. Calculate gain (loss) on transfer of receivables.
b 105. Calculate gain (loss) on transfer of receivables.
d 106. Calculation of gain (loss) on transfer of receivables.
c 107. Calculate proceeds from transfer of receivables with recourse.
a 108. Record assignment of accounts receivables.
c 109. Calculate cash proceeds from transfer of receivables.
c 110. Entry to record collection of assigned receivables.
b 111. Factoring receivables without recourse.
b 112. Factoring receivables with recourse.
c 113. Calculate loss on sale of receivables.
c 114. Calculate loss on sale of receivables.
c 115. Calculate accounts receivable turnover.
c 116. Calculate accounts receivable turnover.
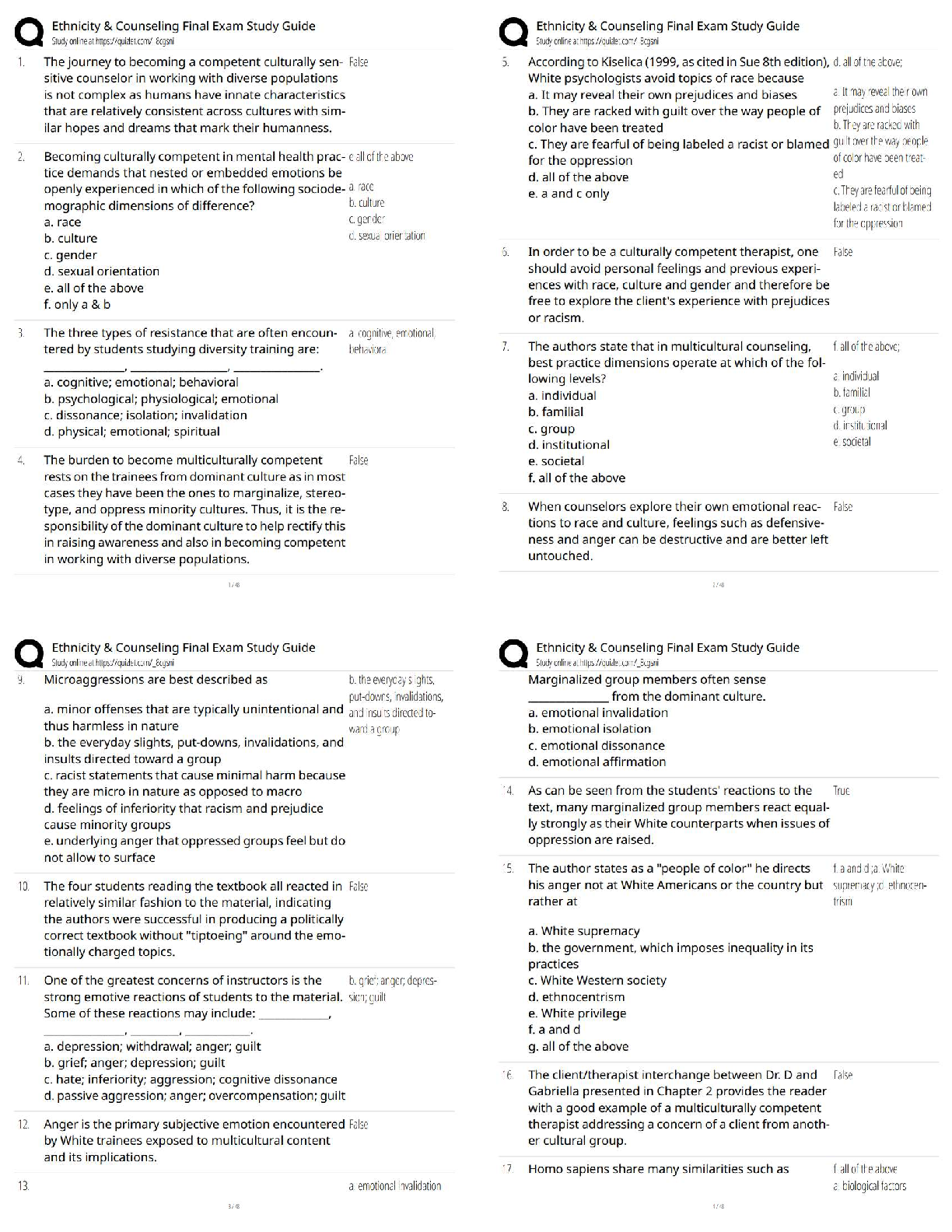
MULTIPLE CHOICE—Computational (cont.)
Description
d *117. Entry to replenish petty cash.
b *118. Calculate correct balance in bank account.
b *119. Calculate correct cash balance.
c *120. Calculate correct cash balance.
b *121. Calculate correct cash balance.
c *122. Calculate correct cash balance.
MULTIPLE CHOICE—CPA Adapted
Description
a 123. Determine current net receivables.
d 124. Calculate adjustment for bad debts.
d 125. Calculate bad debt expense.
b 126. Calculate adjustment to write off bad debts.
c 127. Effect of a write-off under the allowance method.
d 128. Determine balance in the Allowance for Doubtful Accounts.
c 129. Determine interest revenue of a zero-interest-bearing note.
c 130. Determine interest receivable at year end.
b 131. Assignment and factoring of accounts receivable.
a *132. Calculate correct cash balance.
a *133. Calculate the cash balance per books.
EXERCISES
Item Description
E7-134 Asset classification.
E7-135 Allowance for doubtful accounts.
E7-136 Entries for bad debt expense.
E7-137 Fair value option.
E7-138 Accounts receivable assigned.
PROBLEMS
Item Description
P7-139 Entries for bad debt expense.
P7-140 Amortization of discount on note.
P7-141 Accounts receivable assigned.
*P7-142 Factoring accounts receivable.
*P7-143 Bank reconciliation.
CHAPTER LEARNING OBJECTIVES'
1. Identify items considered as cash.
2. Indicate how to report cash and related items.
3. Define receivables and identify the different types of receivables.
4. Explain accounting issues related to recognition of accounts receivable.
5. Explain accounting issues related to valuation of accounts receivable.
6. Explain accounting issues related to recognition and valuation of notes receivable.
7. Explain the fair value option.
8. Explain accounting issues related to disposition of accounts and notes receivable.
9. Explain how to report and analyze receivables.
*10. Explain common techniques employed to control cash.
SUMMARY OF LEARNING OBJECTIVES BY QUESTIONS
Item Type Item Type Item Type Item Type Item Type Item Type Item Type
Learning Objective 1
1. TF 3. TF 22. MC P24. MC 26. MC 72. MC
2. TF 21. MC 23. MC 25. MC 27. MC
Learning Objective 2
4. TF 6. TF 29. MC 31. MC 73. MC 75. MC 77. MC
5. TF 28. MC S30. MC 32. MC 74. MC 76. MC 134. E
Learning Objective 3
7. TF 8. TF 33. MC 34. MC S35. MC
Learning Objective 4
9. TF S36. MC 38. MC 40. MC 78. MC 80. MC 123. MC
10. TF P37. MC 39. MC 41. MC 79. MC 81. MC
Learning Objective 5
11. TF 45. MC 51. MC 85. MC 91. MC 124. MC 136. E
12. TF 46. MC 52. MC 86. MC 92. MC 125. MC 139. P
13. TF 47. MC 53. MC 87. MC 93. &nbs
[Show More]





.png)