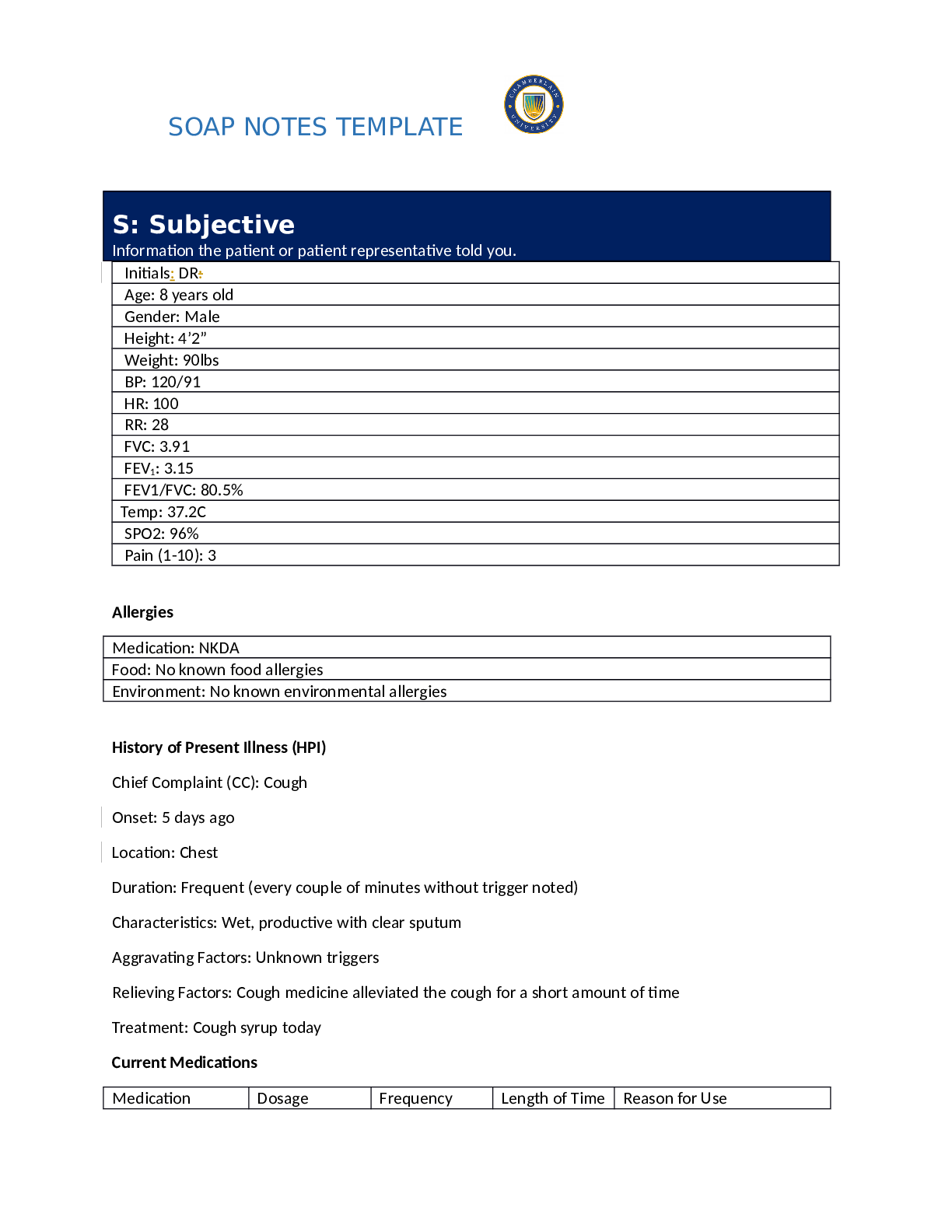
NR 509 Week 6 Pediatric SOAP Note LATEST
$ 15
.png)
WGU - C483 Principles of Management 2021/2022 (Full)
$ 10

ATI Predictor|ati Capstone test bank Latest Fall 2020
$ 12

BIS 155 Week 1 Quiz with Correct Answers DeVry University GradeAplus
$ 20

ATI: Enteral Tube Feeding Test 2022/2023 with complete solution
$ 6

Maternal Newborn Practice 2019 A ( A+ GRADED 100% VERIFIED)
$ 10

HESI MED SURG RETAKE EXAMS 2023 - UPDATED AND 100% VERIFIED QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 31.5

UNE Medical Biochemistry Midterm Review STUDY GUIDE 2025.
$ 18.5

ACC1002 Accounting II Finals Exam (Qns & Ans) 2025 SU
$ 12

Inderbir Singh’s Textbook of Human Neuroanatomy_ Fundamental and Clinical
$ 16

NR 603 Week 1 Comparison and Contrast Assignment: Migraines and Post-Concussive Syndrome
$ 15

PN3 Exam 1 Questions
$ 10

[Ebook][pdf] Digital SAT Study Guide 2024-2025: 3 Full-Length Exams, 200+ Online Video Tutorials, SAT Prep Book Secrets with Practice Tests for the Math, Reading and Writing Sections 9th Edition by Matthew Bowling
$ 14.5

eBook In Defiance of History 1st Edition By Victoria Leonard
$ 30

ATI TEAS TEST MATHEMATICS Questions with 100% verified solutions 2024
$ 9.5

NU 621 Advanced Pathophysiology Exam Herzing University
$ 11

Individual Assignment 3: What is the Rationale for Investing in a New BrewPub. The Presentation.
$ 9.5

eBook Receptive Music Therapy 2nd Edition By Katrina McFerran, Denise Grocke
$ 30

ATI MED SURG PROCTORED EXAM 2020/2021 EXAM - STUDY GUIDE
$ 8

Bloomberg Market Concepts -BMC- Equities- Introducing the stock market - Questions and Answers. Score100%
$ 9

AHIP FINAL EXAM TEST QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS RATED A+ LATEST UPDATE 2023
$ 17
.png)
Strayer BUS 430 Week 3 Quiz 2 Answers (2021) (A Grade), Questions and Answers, All Correct Study Guide, Download to Score A
$ 12.5

NU 216 Adult Health 1- FINAL EXAM. Herzing University REVISED and ANSWERED 100%.
$ 13
.png)
FINANCE 100:PRINCIPLES OF FINANCE WEEK 7 Exam (elaborations)
$ 10

HESI A2 2020 LATEST VERSION
$ 20

Instructor Manual For America's Courts and the Criminal Justice System 9th Edition By David Neubauer (Lecture Notes Only)
$ 15
.png)
NURS 225 Med Surg Exam 5 completed A
$ 7.5
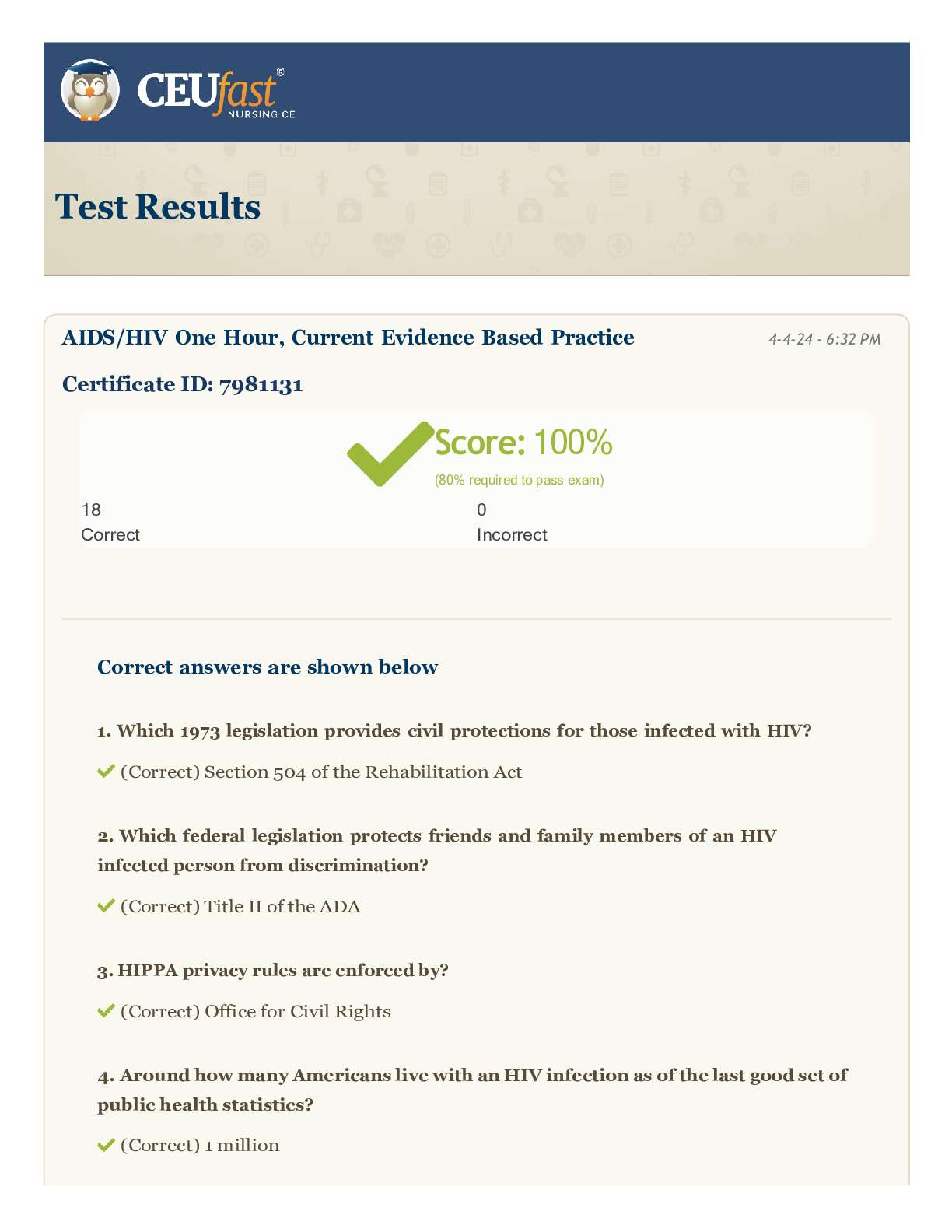
CEUFast - Test Results_ AIDS_HIV One Hour, Current Evidence Based Practice
$ 9.5

eBook (EPUB) Suicide Among Gifted Children and Adolescents 2nd Edition By Tracy L. Cross, Jennifer Riedl Cross
$ 30

NRS-434VN Topic 3 Discussion Question 2/RATED A
$ 10.5

BUSI 352 final exam Liberty University answers complete solutions Already Graded A
$ 10
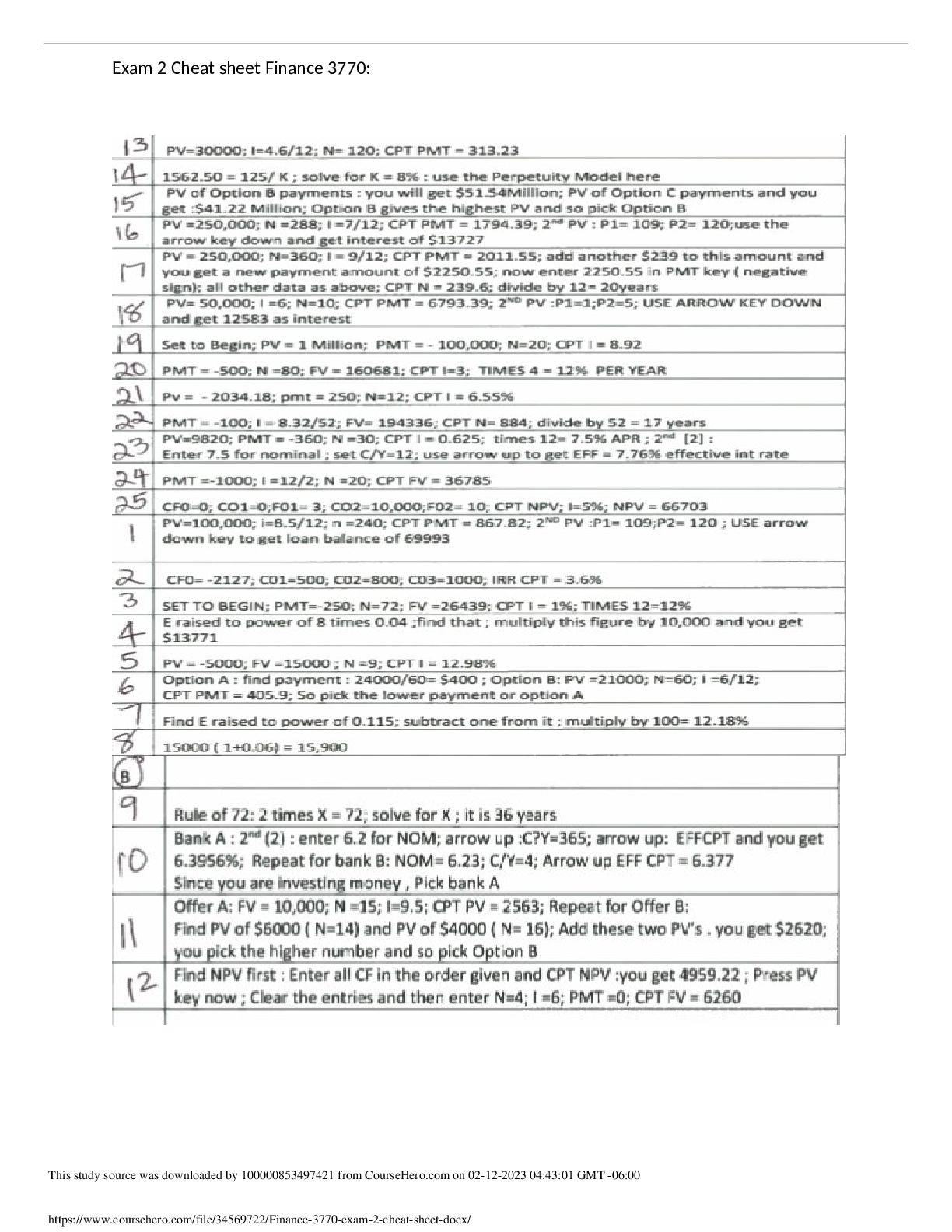
Exam 2 Cheat sheet Finance 3770: | Download for quality grades |
$ 2

Understanding Pathophysiology 7th Edition Test Bank 2021
$ 20

AP Biology Final Exam Review Graded A+ Latest Updates
$ 11

SOCS 185N Week 1 - Assignment; Sociological Imagination
$ 5

TNCC open exam test 2023 with correct answers .
$ 14

Chapter 13: Cancer Epidemiology TESTBANK
$ 11

C16 - Business of Insurance
$ 8.5

Test Bank for Adolescence 13th Edition By Laurence Steinberg Chapter 1-13
$ 19

Esther Park Focused Exam: Abdominal Pain and Care Plan: Shadow Health Physical Assessment NUR 3010
$ 11
.png)
WGU C202 Pre-Assessment Questions and Answers 100% Pass
$ 5

Nutrition Therapy and Pathophysiology 3rd Edition Test Bank solution
$ 10

Florida Atlantic University - MAE 4310MAE4310 Ch9 Quiz. Chapter 9 Quiz. All Answers
$ 8

J10 Criminal investigation-Lessons 6&7 Exam
$ 12

2021 HESI EXIT V2
$ 18

Questions And Answers>Human Resources Management (BZ420) Exam 1:100/100 - 100 %
$ 8
-LATEST-2021.png)
ATI PN COMPREHENSIVE EXIT EXAM (14 VERSIONS) (NEW-2021)| VERIFIED, 100% CORRECT DOCUMENT
$ 45

Evergreen Valley CollegeNURS 101NCSBN question bank.UPDATED
$ 28

Leadership - Proctored (COMPLETED and Grade A Guaranteed) INCLUDING 2020/2021




 (1).png)