*NURSING > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > Chapter 46- Disorders of Skin Integrity and Function 2020 solution questions and answers (All)
Chapter 46- Disorders of Skin Integrity and Function 2020 solution questions and answers
Document Content and Description Below
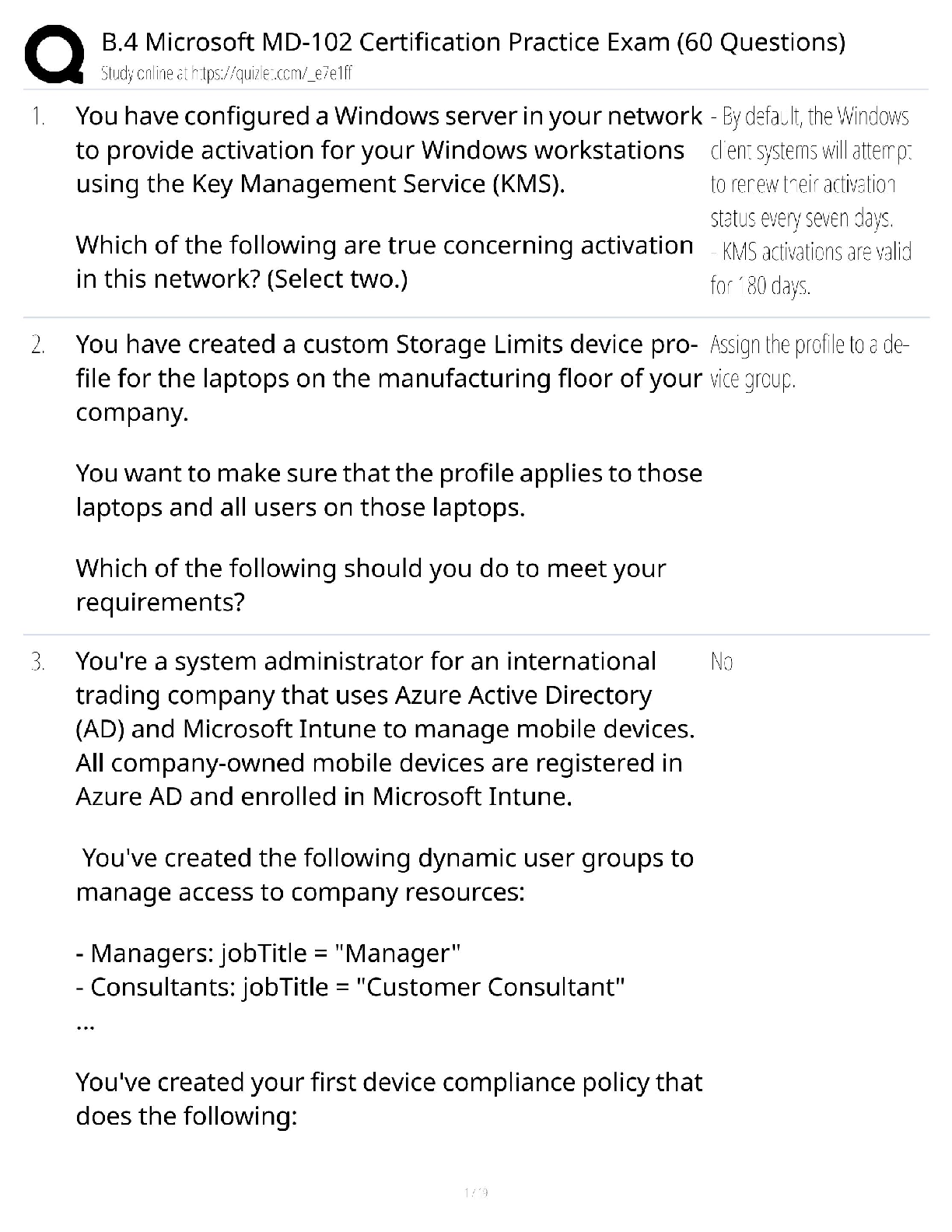
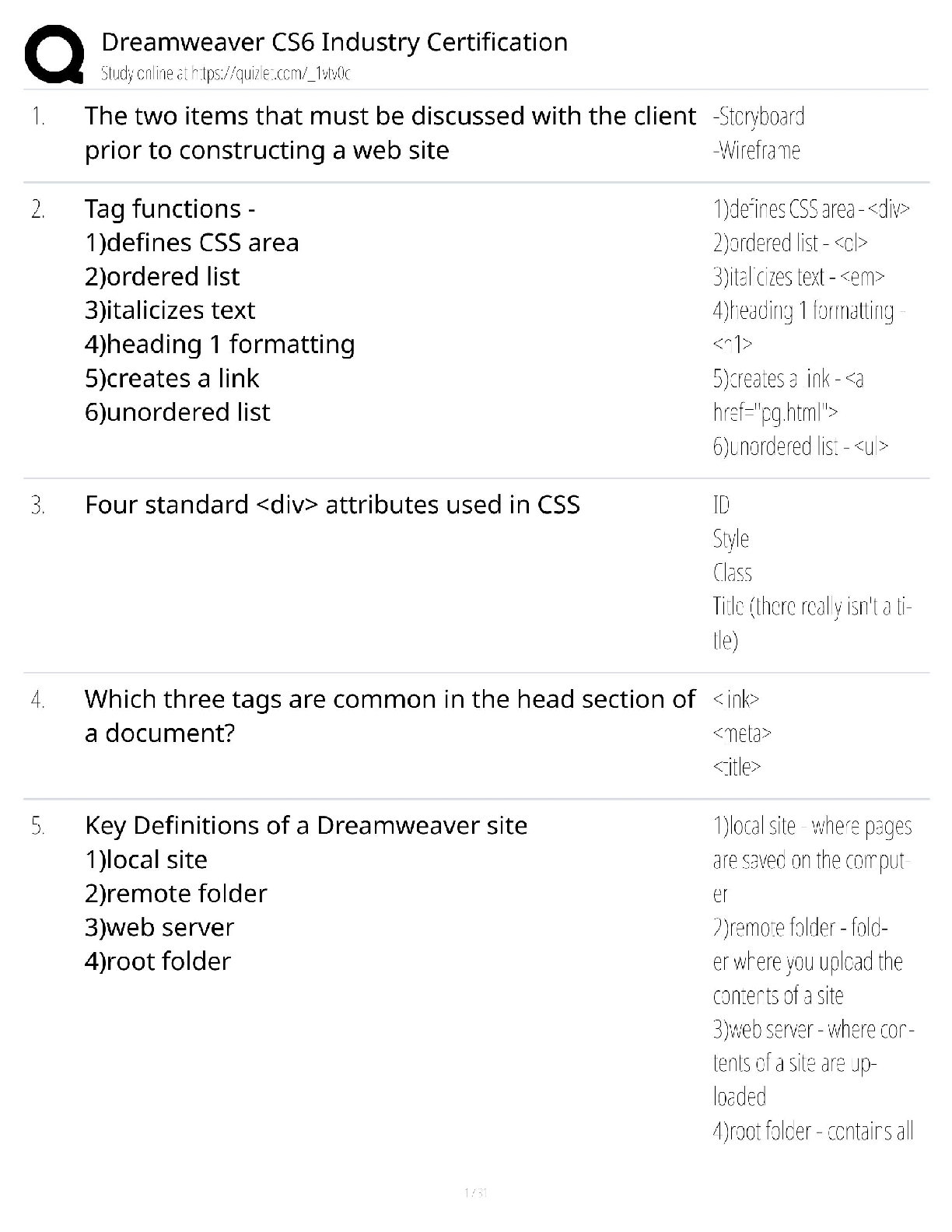
Chapter 46- Disorders of Skin Integrity and Function 2020 solution questions and answers 1. A client is exhibiting manifestations of superficial dermatophytosis of the skin with skin scaling and nai ... l disintegration. Based on these findings, the nurse can anticipate that the client will be prescribed: Select all that apply. A) An antifungal like ketoconazole B) An antibiotic like tetracycline C) Topical corticosteroid D) An antihistamine like Benadryl 2. The clinic health care worker notices that a client has a fungal infection on her nails that looks like the fungus is digesting the nail keratin. The nail appears opaque and white in color. The client states she has had this for years. The health care worker suspects the client has: A) Candidiasis B) Cellulitis C) Onychomycosis D) Tinea corporis 3. Which of the following clients would be predisposed to developing a yeast-like Candidaalbicans fungal infection? A) A diabetic male child with circular patches on the arms B) An immunosuppressed cancer client with maculopapular satellite lesions C) A high school football player with fungal spores cultured on the feet D) A dance instructor with a rash on the hands described as raised borders 4. A teenager reports ugly warts that have invaded her hands. She wants them gone before prom season. The nurse will likely be explaining which of the following treatment measures to this teenager? A) How to apply steroid creams and Band-Aids B) Applying a keratolytic agent like salicylic acid C) Taking a pair of tweezers and pulling the wart off D) How to safely use cryotherapy at home 5. Which of the following disorders of the skin is most likely to respond to treatment with systemic antibiotics? A) Acne vulgaris B) Urticaria C) Atopic dermatitis D) Verrucae 6. A teenager with rosacea should be educated that in addition to the “blush appearance” on the face, she should also assess for which of the following additional complications? Select all that apply. A) Inflamed and tender axillary lymph nodes B) Eye problems C) Edema of the eyelids D) Large abscesses on the upper arms and neck 7. Atopic dermatitis can be described as: Select all that apply. A) Vesicle formation B) Oozing C) Round, erythematous papules that enlarge and coalesce D) Raised wheals with associated itching 8. A client has been admitted to the intensive care unit of the hospital after developing toxic epidermal necrolysis (TEN) consequent to the administration of a sulfonamide antibiotic. What pathophysiologic phenomenon is likely the greatest immediate threat to this client's health? A) The development of bacterial cellulitis on compromised skin surfaces B) Fluid and electrolyte imbalances resulting from the loss skin integrity C) A cascading autoimmune response that may result in shock D) The presence of diffuse lesions and skin sloughing on the client's mucous membranes 9. Papulosquamous dermatoses, such as psoriasis, are a group of skin disorders characterized by: A) Scaling papules B) Granular scabbing C) Raised red borders D) Nodular ulcerations 10. Dry, itchy plaques on her elbows and knees have prompted a 23-year-old woman to seek care. The clinician has subsequently diagnosed the client with psoriasis, a disorder that results from: A) Increased epidermal cell turnover B) An IgE-mediated immune reaction C) Hormonal influences on sebaceous gland activity D) Human papillomaviruses (HPV) 11. What process accounts for the damaging effects of the sun's radiation? A) Initiation of an autoimmune response B) Compensatory increases in melanin production C) Damage to epidermal cell DNA and free radical production D) Hyperkeratinization and the formation of microscopic, subcutaneous lesions 12. Which of the following clinical manifestations would lead the health care provider to diagnose the sunburn as severe? A) Skin is red and warm to touch. B) Some peeling and itching occur several days after the initial burn. C) There is blistering of the skin and associated fever and chills. D) There is a pruritic rash over the sunburned skin area. 13. A thermal burn described as involving the entire epidermis and dermis is classified as: A) Full third degree B) Deep first degree C) Partial second degree D) Full-thickness second degree 14. A 44-year-old man has been brought to the emergency department with severe electrical burns resulting from a workplace accident. The most immediate threat to this client's survival at this time is: A) Infection B) Hemodynamic instability C) Acute pain D) Decreased protein synthesis and impaired healing 15. A child has been admitted to the burn unit after pulling a pan of hot water off the stove. Given the fact that there is primarily second- and third-degree burns, the health care worker should prioritize care to focus on which of the following? Select all that apply. A) Focus on replacing fluids that have been lost from the vascular, interstitial, and cellular compartments. B) Assess for indications that the child's airway has been compromised by assessing breath sounds and voice quality. C) Maintain sterile field when doing dressing changes and debridement. D) Withhold foods/nutrition since the GI tract may have slowed down in response to stress. E) Minimize pain medication administration to not compromise the child's respiratory effort. 16. Which of the following actions could result in pressure ulcer formation? A) Pulling a stroke client up in bed B) Turning a client from side to side every 2 hours C) Allowing a client to side up in a chair at mealtime D) Applying powder to buttocks area when diaphoresis has become a problem 17. Which of the following actions involves the greatest risk of skin shearing? A) Inserting a peripheral intravenous catheter B) Rolling the client from a supine to side-lying position C) Pulling the client up in bed D) Helping the client ambulate after surgery 18. A 79-year-old client has been confined to bed after a severe hemorrhagic stroke that has caused hemiplegia. Which of the following measures should his care team prioritize in the prevention of pressure ulcers? A) Prophylactic antibiotics B) Repositioning the client on a scheduled basis C) Applying protective dressings to vulnerable areas D) Parenteral nutrition 19. Dysplastic nevi are precursors of malignant melanoma that are: A) Larger than other nevi B) Oval epidermal nests C) Dermal cords of cells D) Brown, rounded papules 20. A client has just received the diagnosis of malignant melanoma, stage 3B. He asks the nurse what this means. The nurse should respond relaying which of the following information? Select all that apply. A) Malignant melanoma is a very rapid growing, aggressive cancer. B) This cancer usually extends wide and deep but rarely metastasize. C) This cancer is mainly contained to the head and neck area. D) Your cancer has grown into the deep tissues and quite likely into lymph nodes (stage 3B). 21. The nurse caring for a client with a malignant melanoma should prepare the client for which of the following treatments? Select all that apply. A) Cosmetic surgery to remove the mole without leaving a scar B) Immediate radiation therapy to shrink the tumors C) Surgical excision with lymph node biopsy D) Biologic therapy with interferon alfa-2B 22. A woman has just delivered a child with a hemangioma on his right cheek area. The mother clutches the nurse and asks, “What is that thing on his face?” The nurse will respond with which of the following facts? Select all that apply. A) “This is usually called a strawberry 'birth mark' and pretty common in newborns.” B) “These hemangiomas may grow larger early on followed by a period where the growth is reversed.” C) “Most of these hemangiomas will remain with the infant for the rest of his life. However, they are not cancerous.” D) “If this birth mark develops ulceration, we will need to keep a close eye on it to prevent any infections.” E) “We will keep a close watch on your infant's vision since they can develop malformation of the eye that could develop into glaucoma.” 23. A 5-year-old girl has been presented for care by her father due to her recent development of macules on her trunk, extremities, and mucous membranes. The child is mildly febrile, but her primary symptom is extreme pruritus. What disorder of the skin should the clinician who is assessing the child first suspect? A) Varicella B) Lichen planus C) Rosacea D) Impetigo. 24. Which of the following changes are normal in the elderly population? Select all that apply. A) The dermis and epidermis thin as one ages. B) An increase in the amount of subcutaneous tissue. C) A thickening of blood vessels. D) Increased amount of padding on the buttocks. E) Skin may become dry, rough, and scaly. 25. Which one of the following skin disorders seen in elderly persons is considered a premalignant lesion? A) Cherry angiomas B) Actinic keratosis C) Solar lentigines D) Telangiectases [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages
 ans (1).png)
Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$11.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 06, 2020
Number of pages
12
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 06, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
132

 answers.png)