*NURSING > STUDY GUIDE > PN_MANAGEMENT_STUDY_GUIDE (All)
PN_MANAGEMENT_STUDY_GUIDE
Document Content and Description Below
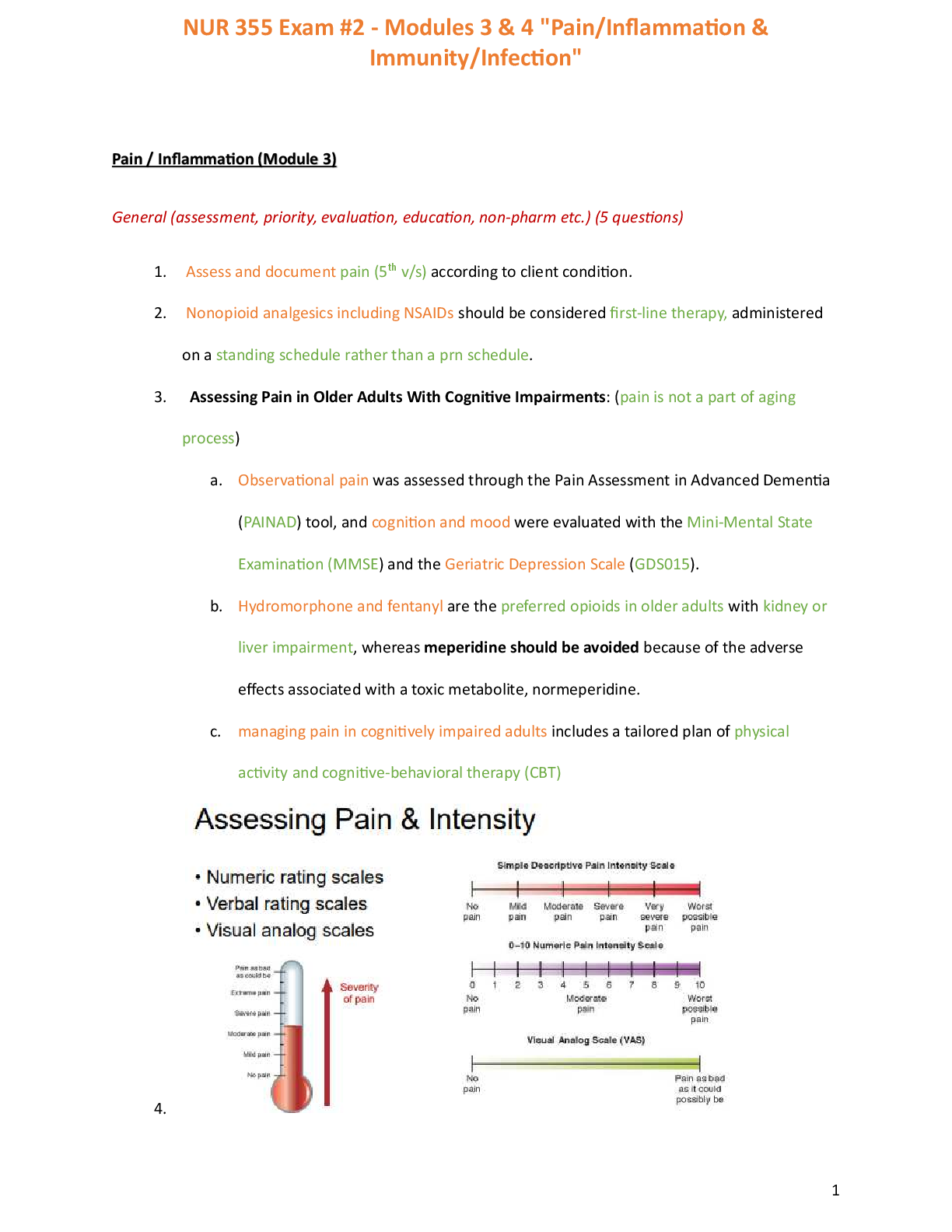
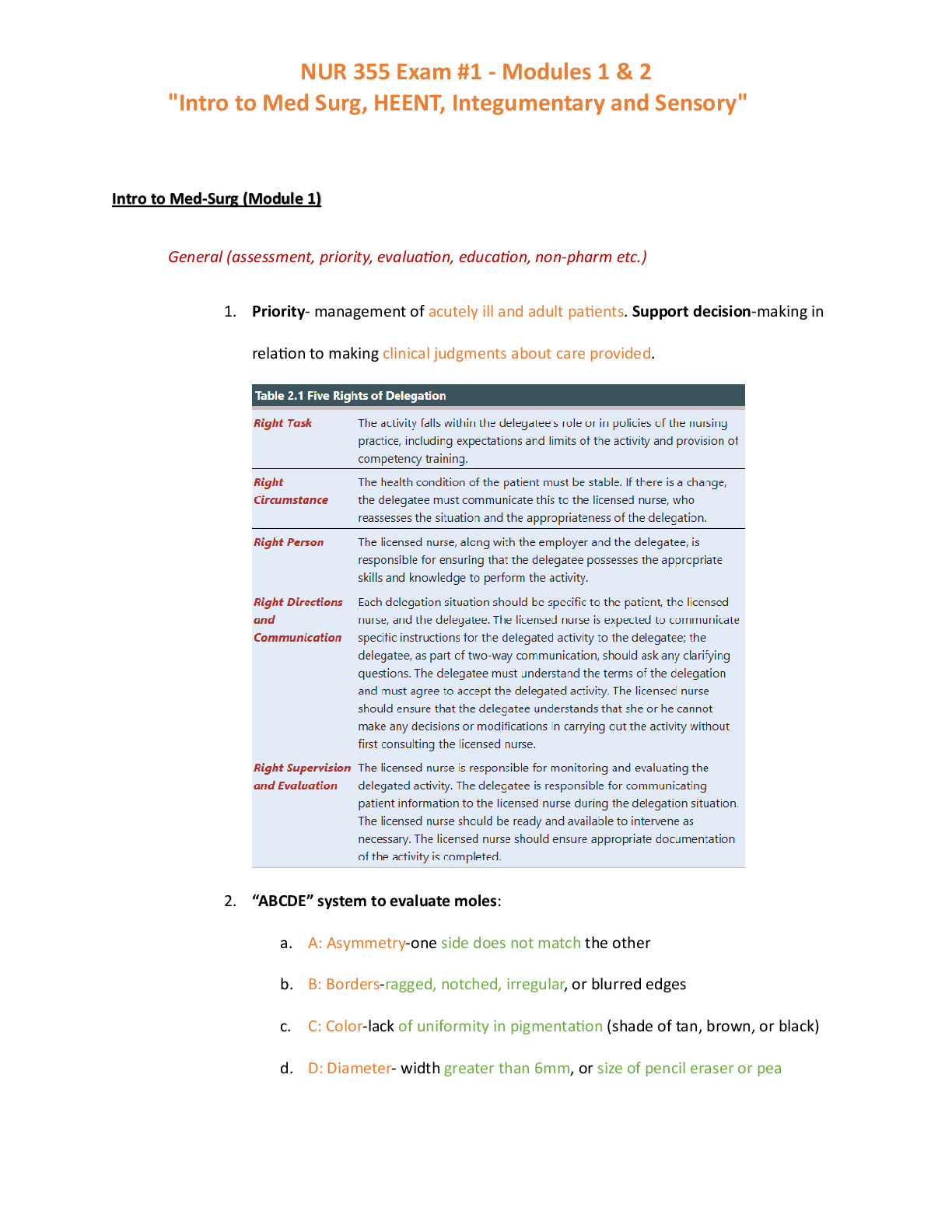
Leadership Study Guide MANAGEMENT OF CARE (47) 1) Managing Client Care: Prioritizing Postoperative Client Needs Prioritize systemic before local (“life before limb”). › Prioritizing int ... erventions for a client in shock over interventions for a client with a localized limb injury Prioritize acute (less opportunity for physical adaptation) before chronic (greater opportunity for physical adaptation). › Prioritizing the care of a client with a new injury/illness (e.g., mental confusion, chest pain) or an acute exacerbation of a previous illness over the care of a client with a long-term chronic illness Prioritize actual problems before potential future problems. › Prioritizing administration of medication to a client experiencing acute pain over ambulation of a client at risk for thrombophlebitis Listen carefully to clients and don’t assume. › Recognizing that a postoperative client’s report of pain could be due to pain in another location rather than expected surgical pain Recognize and respond to trends versus transient findings. › Recognizing a gradual deterioration in a client’s level of consciousness and/or Glasgow Coma Scale score Recognize signs of medical emergencies and complications versus “expected client findings.” › Recognizing signs of increasing intracranial pressure in a client newly diagnosed with a stroke versus the clinical findings expected following a stroke Apply clinical knowledge to procedural standards to determine the priority action. › Recognizing that the timing of administration of antidiabetic and antimicrobial medications is more important than administration of some other medications 2) Managing Client Care: Implementing Scheduling Change 3) Managing Client Care: Unsuccessful Attempts to Reach Provider 4) Professional Responsibilities: Impaired Coworker report the coworker to appropriate management personnel as specified by institutional policy. At the time of the infraction, the report may need to be made to the immediate supervisor, such as the charge nurse, to ensure client safety. 5) Professional Responsibilities: Client Advocacy ensuring that they are properly informed, that their rights are respected, and that they are receiving the proper level of care. Advocacy is one of the most important roles of the nurse, especially when clients are unable to speak or act for themselves. As an advocate, the nurse ensures that the client has the information he needs to make decisions about health care. Nurses must act as advocates even when they disagree with clients’ decisions The nursing profession also has a responsibility to support and advocate for legislation that promotes public policies that protect clients as consumers and create a safe environment for their care. As advocates, nurses must ensure that clients are informed of their rights and have adequate information on which to base health care decisions. Nurses must be careful to assist clients with making health care decisions and not direct or control their decisions. Nurses may need to mediate on the client’s behalf when the actions of others are not in the client’s best interest or changes need to be made in the plan of care. Situations in which nurses may need to advocate for clients or assist them to advocate for themselves include: ◯ End-of-life decisions ◯ Access to health care ◯ Protection of client privacy ◯ Informed consent ◯ Substandard practice 6) Professional Responsibilities: Responding to Client Fears Educate patient, provide information, and make referrals as needed 7) Coordinating Client Care: Findings to Report to Provider Assessment data integral to changes in client status Recommendations for changes in the plan of care Clarification of orders 8) Managing Client Care: Appropriate Resources for Staff Development 9) Professional Responsibilities: HIPAA Violation Become familiar with facility policies about the use of social media, and adhere to them. Avoid disclosing any client health information online. Be sure no one can overhear conversations about a client when speaking on the telephone. Do not take or share photos or videos of a client. Remember to maintain professional boundaries when interacting with clients online. Never post a belittling or offensive remark about a client, employer, or coworker. Report any violations of facility social media policies to the nurse manager 10) Managing Client Care: Recognizing Appropriate LPN Delegation LPNS CAN: monitoring client findings reinforcement of client teaching from a standard care plan trach care suctioning checking NG tube patency administering enteral feeds urinary catheterization medication administration (excluding IV) LPNS CANNOT: maintain blood or blood components, hang solution for TPN -cancer therapeutic meds like chemo or anti-neoplastic agents -experimental meds -solutions in a line that does not terminate in a peripheral vein -iv piggyback -D/C a central venous, arterial or any other line that does not terminate in a peripheral vein -do anything with PCA -Change arterial tubing, venous line or any line that does not terminal in peripheral vein 11) Professional Responsibilities: Risk for Breach of Client Confidentiality 12) Professional Responsibilities: Reporting Abuse nurses are mandated to report any suspicion of abuse following facility policy 13) Maintaining a Safe Environment: Strategies for Cost Containment Using all levels of personnel to their fullest when making assignments. Providing necessary equipment and properly charging clients. Returning uncontaminated, unused equipment to the appropriate department for credit. Using equipment properly to prevent wastage. Providing training to staff unfamiliar with equipment. Returning equipment (IV, kangaroo pumps) to the proper department (central service, central distribution) as soon as it is no longer needed. This action will prevent further cost to clients 14) Managing Client Care: Responding to Staff Complaint Typical steps of the grievance process include: Formal presentation of the complaint(s) using the proper chain of command, Formal hearing if the issue is not resolved at a lower level, Professional mediation if a solution is not reached during a formal hearing 15) Managing Client Care: Using Time Appropriately What must be done immediately (administration of analgesic or antiemetic, assessment of unstable client)? What must be done by a specific time to ensure client safety, quality care, and compliance with facility policies and procedures (medication administration, vital signs, blood glucose monitoring)? What must be done by the end of the shift (ambulation of the client, discharge and/or discharge teaching, dressing change)? ◯ What can be delegated? Time management involves using time-saving strategies and avoiding time wasters › Documenting nursing interventions as soon as possible after completion to facilitate accurate and thorough documentation › Grouping activities that are to be performed on the same client or are in close physical proximity to prevent unnecessary walking › Estimating how long each activity will take and planning accordingly › Mentally envisioning the procedure to be performed and ensuring that all equipment has been gathered prior to entering the client’s room › Taking time to plan care and taking priorities into consideration › Delegating activities to other staff when client care workload is beyond what can be handled by one nurse › Enlisting the aid of other staff when a team approach would be more efficient than an individual approach › Completing more difficult or strenuous tasks when energy level is high › Avoiding interruptions and graciously but assertively saying “no” to unreasonable or poorly timed requests for help › Setting a realistic standard for completion of care and level of performance within the constraints of assignment and resources Time initially spent developing a plan will save time later and help to avoid management by crisis. ◯ Set goals and plan care based on established priorities and thoughtful utilization of resources. ◯ Complete one client care task before beginning the next, starting with the highest priority task. ◯ Reprioritize remaining tasks based on continual reassessment of client care needs. ◯ At the end of the day, perform a time analysis and determine if time was used wisely. 16) Suicide: Priority Action for Client who is Depressed Assess for thought or feelings of harming himself or others 17) Managing Client Care: Appropriate AP Delegation activities of daily living (ADLs) Bathing Grooming Dressing Toileting Ambulating Feeding (without swallowing precautions) Positioning Bed making Specimen collection Intake and output (I&O) Vital signs (on stable clients 18) Managing Client Care: Appropriate Assignment for an LPN Monitoring client findings (as input to the RN’s ongoing assessment of the client) › Reinforcement of client teaching from a standard care plan › Tracheostomy care › Suctioning › Checking nasogastric tube patency › Administration of enteral feedings › Insertion of a urinary catheter › Medication administration (excluding intravenous medications in several states) 19) Professional Responsibilities: Identifying Battery Intentional and wrongful physical contact with a person that involves an injury or offensive contact (restraining a client and administering an injection against his wishes) physical contact without a person’s consent 20) Managing Client Care: Appropriate Task for Assistive Personnel activities of daily living (ADLs) Bathing Grooming Dressing Toileting Ambulating Feeding (without swallowing precautions) Positioning Bed making Specimen collection Intake and output (I&O) Vital signs (on stable clients 21) Coordinating Client Care: Client who has Anorexia Nervosa 22) Managing Client Care: Appropriate Tasks for LPN Monitoring client findings (as input to the RN’s ongoing assessment of the client) › Reinforcement of client teaching from a standard care plan › Tracheostomy care › Suctioning › Checking nasogastric tube patency › Administration of enteral feedings › Insertion of a urinary catheter › Medication administration (excluding intravenous medications in several states) 23) Professional Responsibilities: Priority Intervention as Client Advocate As advocates, nurses must e [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 12 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

LPN EXAM PACK ALL RATED A
PN Mental Health Online Practice 2017 A 1-50 1.A nurse is collecting data from a client who is experiencing alcohol withdrawal. Which of the manifestation should the nurse expect? Answer: Diaphores...
By Nutmegs 3 years ago
$40
10
Reviews( 0 )
$13.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 01, 2022
Number of pages
12
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 01, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
147