FSA3e Test BankB Mod09 090612. Module 9 Intercorporate Entities
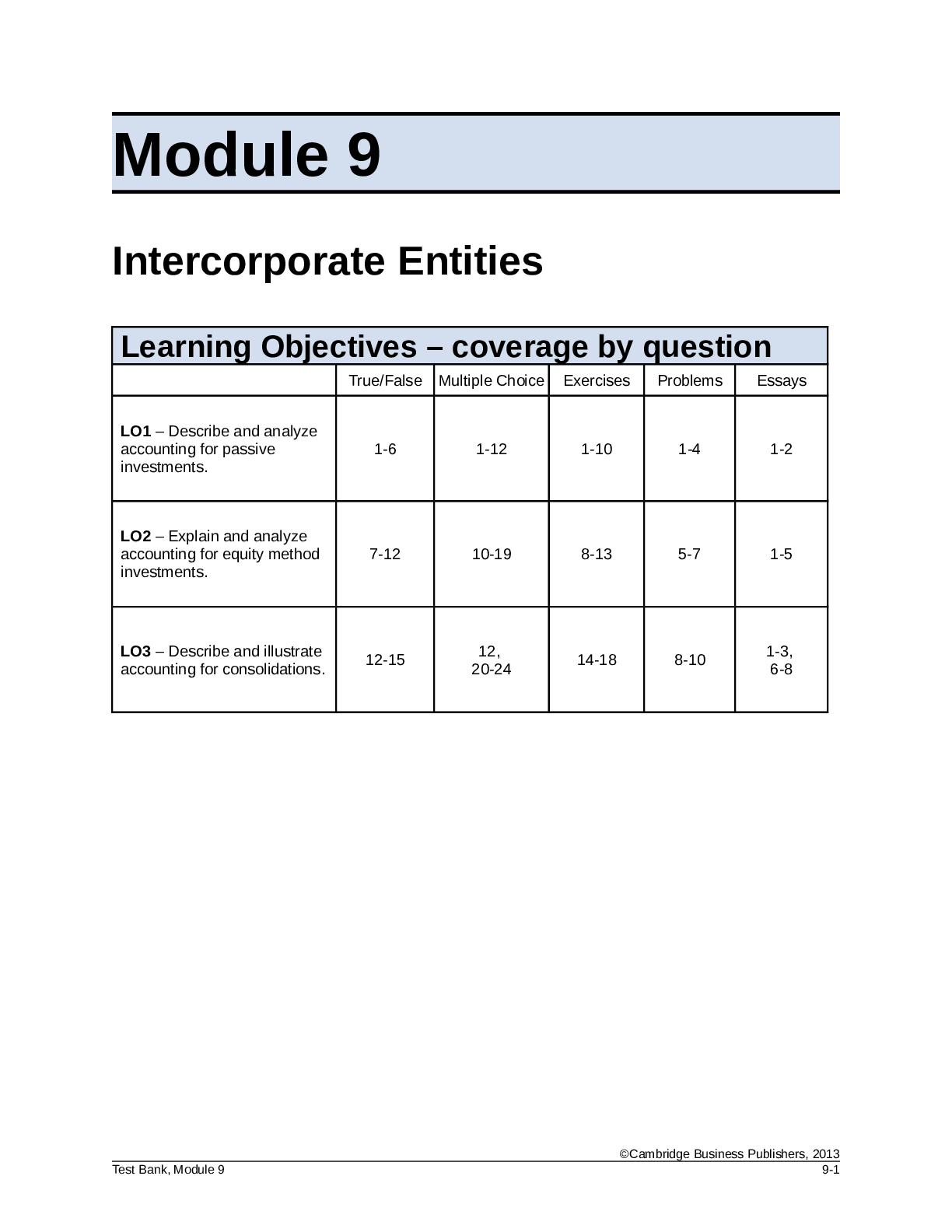
Learning Objectives – coverage by question
True/False Multiple Choice Exercises Problems Essays
LO1 – Describe and analyze
accounting for passive
inves
...
FSA3e Test BankB Mod09 090612. Module 9 Intercorporate Entities
Learning Objectives – coverage by question
True/False Multiple Choice Exercises Problems Essays
LO1 – Describe and analyze
accounting for passive
investments.
1-6 1-12 1-10 1-4 1-2
LO2 – Explain and analyze
accounting for equity method
investments.
7-12 10-19 8-13 5-7 1-5
LO3 – Describe and illustrate
accounting for consolidations. 12-15 20-24 12, 14-18 8-10 1-3, 6-8
©Cambridge Business Publishers, 2013
Test Bank, Module 9 9-1Module 9: Intercorporate Entities
True/False
Topic: Available-for-Sale
LO: 1
1. When investments are classified as available-for-sale, fair-value changes are recognized in the
balance sheet as unrealized gains or losses that affect owners’ equity.
Answer: True
Rationale: Unrealized gains and losses on available-for-sale investments bypass the income
statement. Fair-value changes are recorded in the other comprehensive income (OCI) component of
stockholders’ equity.
Topic: Trading Securities
LO: 1
2. Realized gains and losses on investments classified as trading securities are reported in a company’s
net income in the period that they are realized.
Answer: True
Rationale: The “trading” classification implies that those investments are viewed as part of the
company’s operations; therefore, any gains/losses are presented as investment gain/loss on the
income statement, whether realized or unrealized.
Topic: Passive Investments
LO: 1
3. When a passive investment is sold, the gain (loss) is typically reported in “other” income
Answer: True
Rationale: The gain (loss) on sale is then reported as a component of “other” income, which is
commonly commingled with interest and dividend income.
Topic: Fair-value Accounting
LO: 1
4. Available-for-sale is the only classification that requires fair-value accounting.
Answer: False
Rationale: Two classifications require mark-to-market accounting: available-for-sale securities that
management intends to hold for capital gains and dividend income, and trading securities that
management intends to actively trade for profits as fair values fluctuate.
Topic: Available for Sale
LO: 1
5. Fair-value changes in available-for-sale investments are recognized in the income statement as
unrealized gains or losses.
Answer: False
Rationale: Fair value changes are only reported in the accumulated OCI section of equity until
realized.
©Cambridge Business Publishers, 2013
9-2 Financial Statement Analysis & Valuation, 3rd EditionTopic: Available for Sale
LO: 1
6. If marketable securities are classified in the current asset section, as “available for sale” securities,
then the assumption is that the shares will be sold during the current year.
Answer: False
Rationale: The available-for-sale classification means that the securities might be sold, not that they
will be.
Topic: Equity Method
LO: 2
7. If company A accounts for its investment in company B using the equity method, then a portion of
company B’s earnings are reported on company A’s income statement.
Answer: True
Rationale: The proportion of Company B’s stock that is owned by company A dictates the proportion
that A recognizes of B’s earnings as equity earnings.
Topic: Equity Method
LO: 2
8. Under the equity method, fair-value changes in the investee company’s stock are not reflected in the
investor’s accounting records.
Answer: True
Rationale: Unrealized gains on equity-method investments are not recognized until the investment is
sold.
Topic: Significant Influence
LO: 2
9. Regardless of the legal agreements, technology licensing, and the like between two companies,
significant influence is determined by ownership of a sufficient percentage of outstanding common
stock. This is called the significance influence test.
Answer: False
Rationale: Usually, the investor company can exert significant influence over the activities of the
investee company when it owns 20% - 50% of the voting stock of the investee company. An investor
company might also exert significant influence if it is the sole customer or supplier of the investee
customer, or has contractual rights, even if the investor owns less than 20%.
Topic: Equity Method
LO: 2
10. Under the equity method, the investment account is recorded at fair value but only if fair value
exceeds original cost.
Answer: False
Rationale: Fair-value accounting is not used for equity method investments.
©Cambridge Business Publishers, 2013
Test Bank, Module 9 9-3Topic: Equity Method
LO: 2
11. Dividends received from an investee company are reported as investment income by the investor
company when the investor does not control the investee.
Answer: False
Rationale: Under equity method accounting, the investor has no control. Yet, dividends are treated as
a return of investment, thereby reducing the investment account, not as income.
Topic: Equity Method vs. Consolidation
LO: 2 & 3
12. Shareholder equity of the investee company will be same using either equity method accounting or
the consolidation accounting method for an investment.
Answer: True
Rationale: Shareholder equity will be same using either equity method accounting or consolidation
accounting for an investment.
Topic: Control
LO: 3
13. The investor company cannot be considered to have control over the investee company if it owns less
than 50% of the outstanding voting stock of the investee company.
Answer: False
Rationale: Circumstances may point to control even if stock ownership is less than 50%. Examples
include contracts and licenses that confer control in the absence of majority stock ownership.
Topic: Consolidation
LO: 3
14. Financial statements of investee and investor companies can only be consolidated if both companies
use the same accounting principles.
Answer: False
Rationale: Consolidation does not require consistent accounting policies among the consolidated
group.
Topic: Goodwill
LO: 3
15. Goodwill is recorded when the fair value of the assets acquired in a merger exceeds the net book
value of those same assets.
Answer: False
Rationale: Goodwill is recorded when the purchase price of the assets acquired exceeds the fair
value of the individual assets and liabilities acquired.
©Cambridge Business Publishers, 2013
9-4 Financial Statement Analysis & Valuation, 3rd EditionMultiple Choice
Topic: Unrealized Gains
LO: 1
1. For which of the following types of intercorporate investments are unrealized gains reflected in the
shareholders’ equity section of the investor’s balance sheet?
A) Equity Method
B) Trading Securities
C) Available-for-Sale Securities
D) B and C only
E) A, B and C
Answer: D
Rationale: Unrealized gains for trading securities are reflected in the income statement of the investor
company which flows to retained earnings on the balance sheet. Unrealized gains on available-forsale securities are recorded in shareholders’ equity in the Accumulated Other Comprehensive Income
account.
Topic: Understanding Fair-Value Method of Accounting
LO: 1
2. Which of the following statements does not accurately describe the fair-value method of accounting?
A) Investments for which current, reliable fair values exist are accounted for using this method.
B) Held-to-maturity investments are not accounted for using this method.
C) Dividends and interest received are recognized in current income.
D) The investment is recorded on the balance sheet at its fair value.
E) None of the above
Answer: A
Rationale: Fair values exist for any marketable security but this does not mean that the fair-value
method is appropriate. If the investor controls an entity with traded equity securities, the investment is
consolidated and thus, the fair-value method is not used.
Topic: Available-for-Sale
LO: 1
3. When the fair value of a company’s portfolio of available-for-sale equity securities exceeds its book
value, the difference should be:
A) Written off as an impairment
B) Added to stockholders’ equity of the investee
C) Recorded on the company’s income statement
D) Added to the investment account
E) None of the above
Answer: D
Rationale: Available-for-sale securities are accounted for on a fair-value basis; therefore, an increase
in fair value would result in an increase in both of the investment account and the stockholders’ equity
(through accumulated other comprehensive income/loss). Note that answer b is incorrect because the
unrealized gain is added to the investor’s equity and not the investee’s equity.
©Cambridge Business Publishers, 2013
Test Bank, Module 9 9-5Topic: Effect of Fair Value Changes (Numerical calculations required)
LO: 1
4. On its 2011 balance sheet, Bank of America Corporation reports marketable debt securities of
$311,416 million. The footnotes disclose that these securities have an amortized cost of $306,437
million. Which of the following is true?
A) These are available-for-sale securities.
B) These are trading securities.
C) There are net unrealized gains of $4,979 on these securities.
D) Both A and C
E) Both B and C
Answer: C
Rationale: The fair value of the securities is more than cost; this is a net unrealized gain. We do not
know if these are trading or available for sale from the information provided.
Topic: Fair-Value Method of Accounting (Numerical calculations required)
LO: 1
5. Following is a portion of the investments footnote from Homer Corp. 2012 10-K.
(in millions) 2012
Amortized cost of available-for-sale securities $231,312
Gross unrealized gains 7,635
Gross unrealized losses $33,123
What amount does Homer report for available-for-sale securities on its 2012 balance sheet?
A) $25,488 million
B) $205,824 million
C) $231,312 million
D) $256,800 million
E) None of the above
Answer: B
Rationale: Available-for-sale investments are reported at fair value on the balance sheet. Thus,
Homer’s securities are reported as $231,312 + $7,635 - $33,123 =$205,824 million as of 2012.
Topic: Fair-Value Method of Accounting
LO: 1
6. Which of the following statements is not true of the fair-value method of accounting for marketable
securities?
A) The investment account is recorded at current fair value on the balance sheet.
B) Interim changes in the investments’ fair value may or may not affect income depending on the
securities’ classification.
C) This method is used when the reporting company generally owns less than 20% of the investee
company.
D) Dividends are treated as a return of the capital invested.
E) None of the above.
Answer: D
Rationale: Dividends are reported as income, rather than a return of the capital invested, which is the
case for equity method investments.
©Cambridge Business Publishers, 2013
9-6 Financial Statement Analysis & Valuation, 3rd EditionTopic: Fair-Value Method of Accounting (Numerical calculations required)
LO: 1
7. Following is a portion of the investments footnote from Allstate’s 2011 10-K.
(in millions) 2011
Amortized cost of available-for-sale securities $73,379
Gross unrealized gains 4,404
Gross unrealized losses 1,670
What amount does Allstate report for available-for-sale securities on its 2011 balance sheet?
A) $2,734 million
B) $71,709 million
C) $76,113 million
D) $77,783 million
E) None of the above
Answer: C
Rationale: Available-for-sale investments are reported at fair value on the balance sheet. Thus,
Allstate’s bond investments are reported as $73,379 + $4,404 - $1,670 =$76,113 million as of 2011.
Topic: Held-to-Maturity Securities and Fair Value (Numerical calculations required)
LO: 1
8. In footnotes to its 2011 annual report, Bancfirst Corp. reported that held-to-maturity securities with an
amortized cost of $22,477 thousand had an estimated fair value of $22,958 thousand. The balance
sheet reported:
A) Held-to-maturity assets of $22,477 thousand
B) Held-to-maturity assets of $22,958 thousand
C) Accumulated other comprehensive income of $481 thousand related to held-to-maturity assets
D) Both A and C
E) Both B and C
Answer: A
Rationale: Held-to-maturity securities are recorded at amortized cost, which is $22,477. The
unrealized gains of $481 thousand are not reported on the balance sheet, but disclosed in the
footnotes only.
©Cambridge Business Publishers, 2013
Test Bank, Module 9 9-7Topic: Fair-Value Method of Accounting (Numerical calculations required)
LO: 1
9. Starbucks, Inc. reported that short-term investments consisted of the following (in millions):
Amortized cost Fair value
October 3, 2010
Short-term investments — available-for-sale securities $236.4 $236.5
Short-term investments — trading securities 58.8 49.2
Total short-term investments $295.2 $285.7
Which of the following is true?
A) Starbuck’s 2010 balance sheet includes short-term investments of $295.2 million.
B) Unrealized losses of $9.6 million on trading securities are included in 2010 income.
C) There are no net unrealized gains on available-for-sale securities.
D) Accumulated other comprehensive income included no unrealized gains or losses.
E) None of the above
Answer: B
Rationale: Unrealized gains and losses for trading securities are included in current-year income.
Answer A is not correct because the investments are recorded at fair value of $285.7 million on the
balance sheet. Answer C and D are not correct since a net unrealized gain of 0.1 million on
available-for-sale securities is included in accumulated other comprehensive income.
Topic: Dividends
LO: 1 & 2
10. Roger Corp. holds a 10% equity investment in Access Inc. Sarasota Investments holds 40% of
Access Inc. stock. On April 1, 2012, Access Inc. declares and pays dividends to its stockholders.
How will the dividend affect each company’s balance sheet account: Access Inc. investment?
Roger
Corp.
Sarasota
Investments
A) No effect Decrease
B) No effect No effect
C) Decrease No effect
D) Decrease Decrease
E) None of the above
Answer: A
Rationale: Roger Corp. should use the fair-value method to account for its investment in Access Inc.;
therefore, a dividend would not affect its investment account. Sarasota Investments should use the
equity method to account for its investment in Access Inc. Therefore, a dividend will be deducted from
its investment account and added to cash.
[Show More]