BioChemistry > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > WGU BioChem OA Review with complete solution (Graded A) (All)
WGU BioChem OA Review with complete solution (Graded A)
Document Content and Description Below
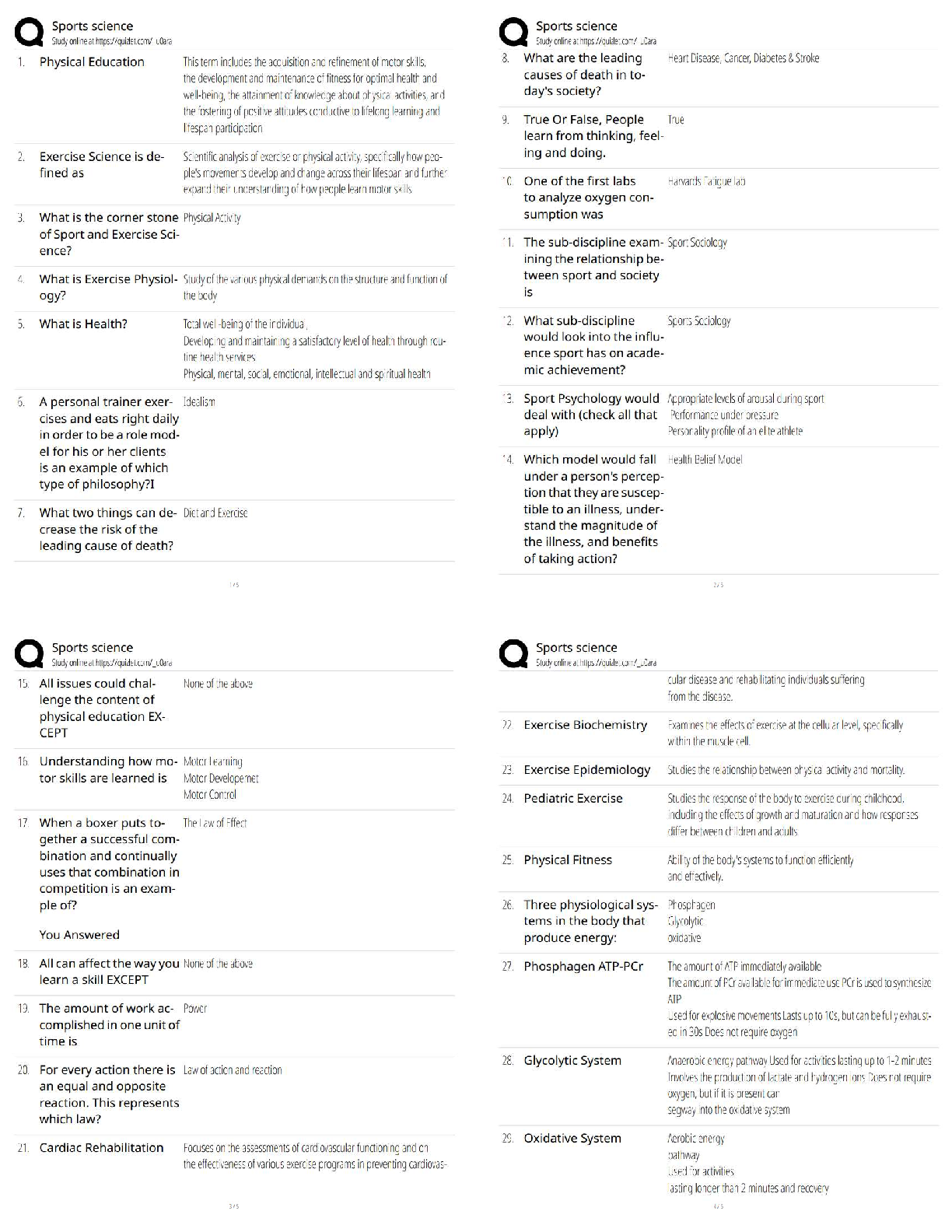
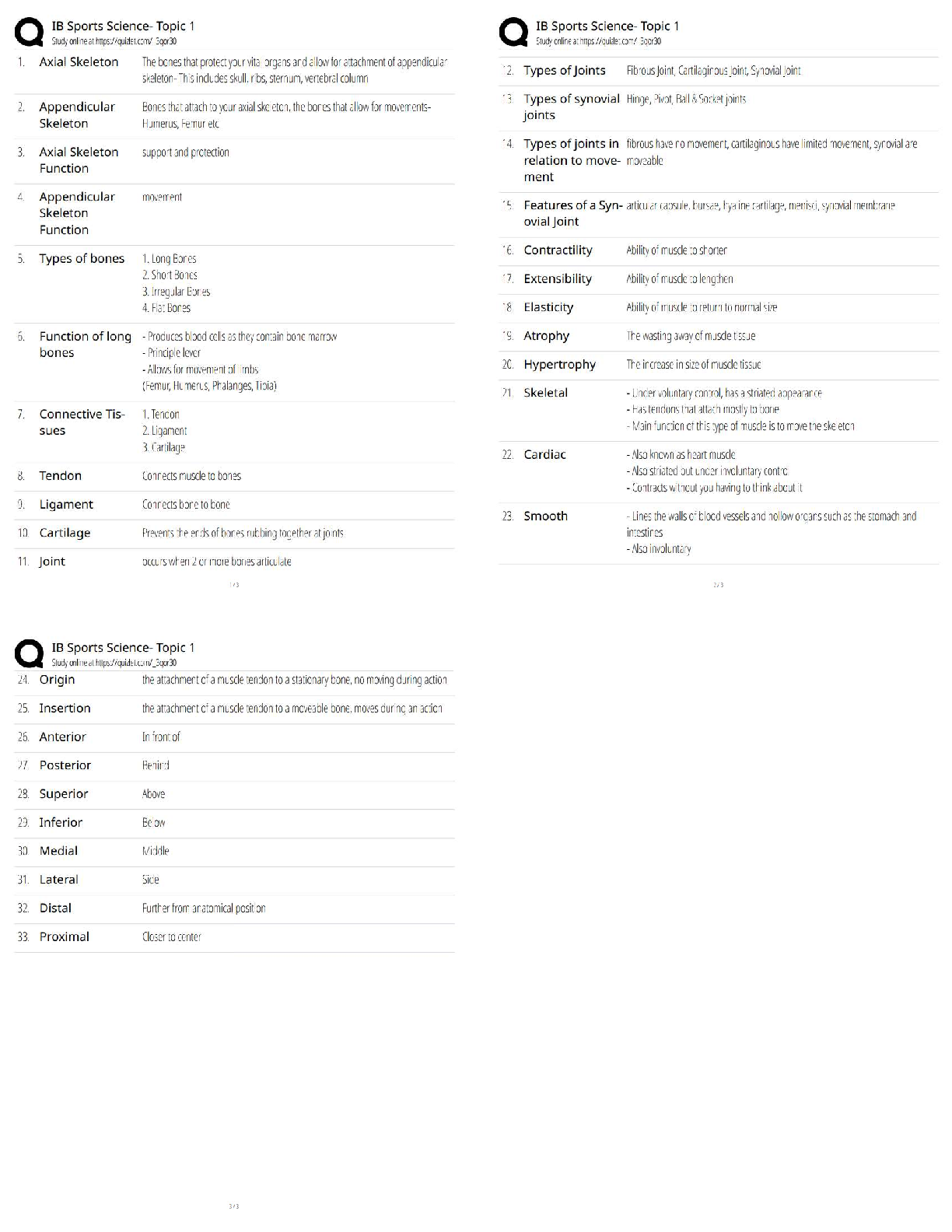
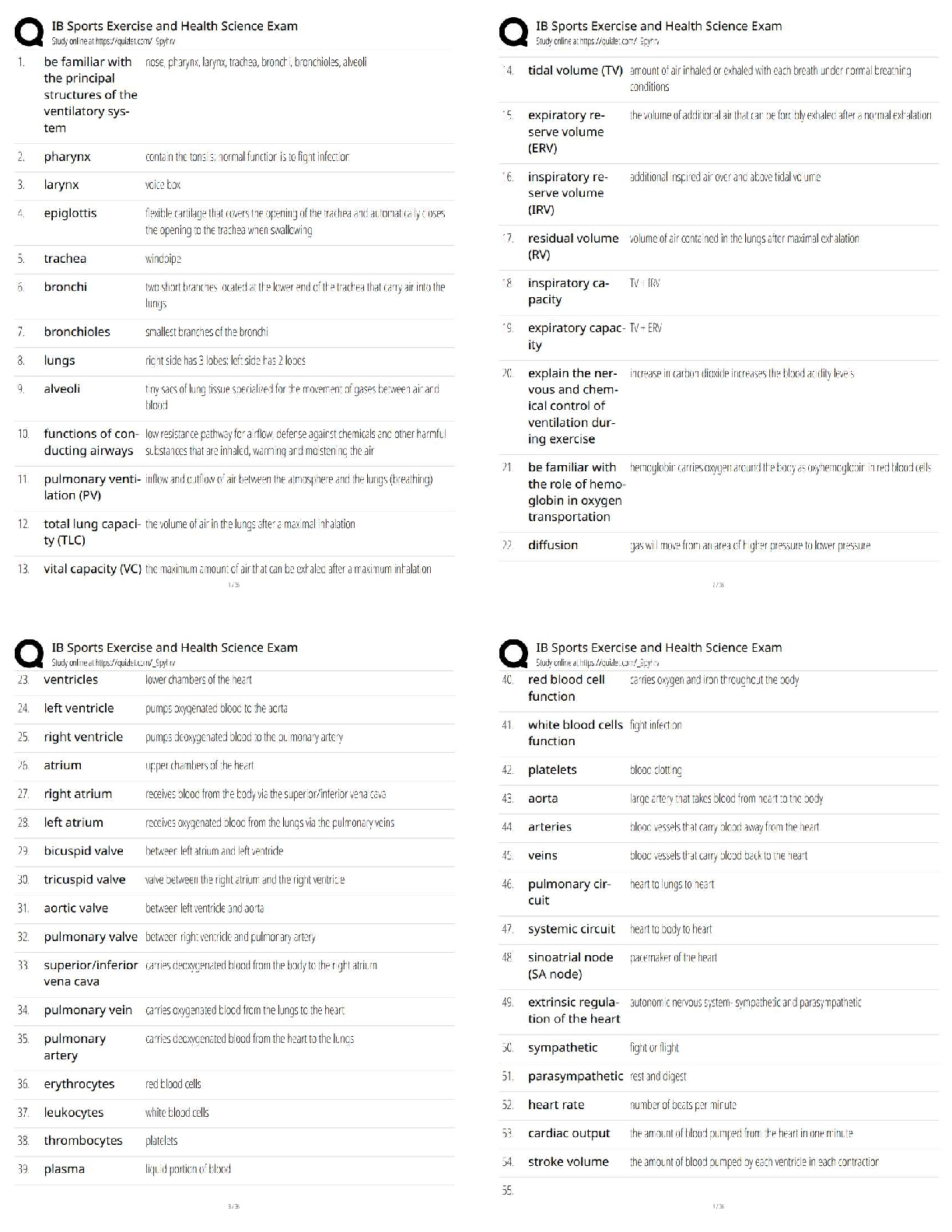
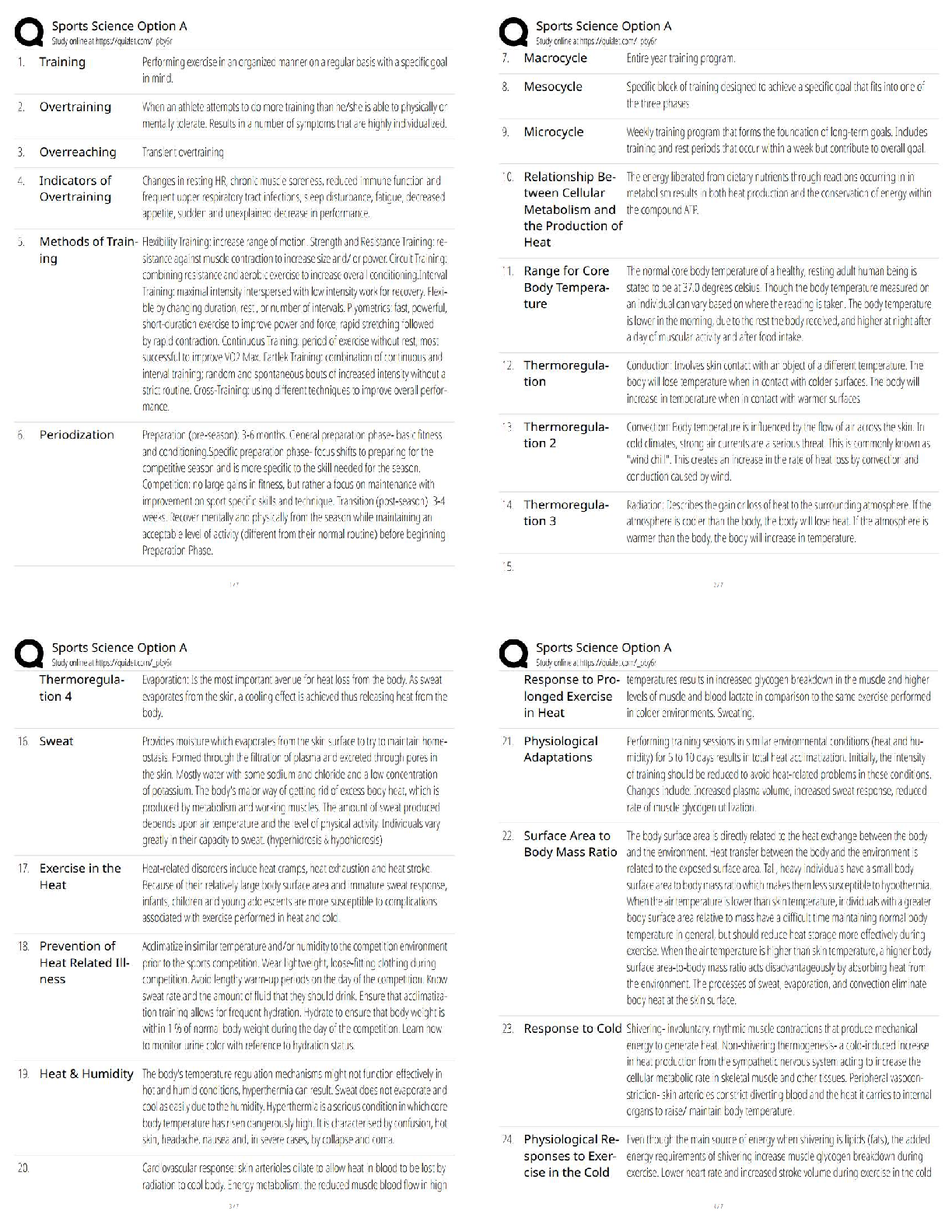
WGU BioChem OA Review with complete solution Males and Females are equally affected Correct Answer-Autosomal The process of copying DNA in the lab. Correct Answer-Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Tem ... plate DNA, Nucleotides (dNTPS), DNA Polymerase, and DNA Primers. Correct Answer-What is needed for Polymerase Chain Reaction? Denaturing, Annealing, Elongating Correct Answer-What are the three steps of a Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR)? Denaturing (DNA is heated up to separate it) Correct Answer-What is the first step of a Polymerase Chain Reaction? Cooling the Polymerase Chain Reaction. Primers stick to the DNA that you want to copy and ADD DNA Polymerase Correct Answer-What is Annealing? The Polymerase Chain Reaction is heated and DNA Polymerase adds nucleotides to build a new DNA strand. Correct Answer-What is elongating? Ligase Correct Answer-What is NOT involved in PCR? It is used to repair damage to bases caused by harmful molecules by removing the base that is damaged and replacing it. #1 GLYCOSYLASES see the damaged DNA. #2 DNA Polymerase puts the right one back #3 DNA Ligase seals it. Correct Answer-What is base excision repair (BER)? DNA Glycolysase sees the damage and removes it, DNA polymerase puts the tight base back, DNA ligase seals it back up. Correct Answer-What are the 3 steps in base excision repair? 1 Correct Answer-How many nucleotides does base excision repair remove? Mismatch Repair (MMR). It is the only one to occur during REPLICATION - DURING THE PROOFREADING Correct Answer-What is it called when a large section of the nucleotide is removed from the DNA so that DNA polymerase can try again? (This corrects DNA damage) Mismatch Repair (MMR) repairs errors such as G with T instead of G with C. DNA Polymerase fixes it. This happens during replication and MMR removes a large section of the nucleotide from the DNA and DNA Polymerase tries again. Correct Answer-What repairs a base mismatch? When DNA polymerase takes an individual nucleotide and matches them to the parental sequences to ensure a correct pair. (it must bind with RNA primer to work). ie: DNA Polymerase binds to DNA to make RNA Correct Answer-What is DNA Transcription? CLEANS damage caused by things such as UV rays and repairs it. A large section of nucleotides are removed, including the damaged portion, along with a few on each side. It is then replaced by DNA polymerase. Correct Answer-What is NecleoTIDE repair It repairs double stranded breaks (last effort) by copying another strand of DNA and replacing it completely. Correct Answer-What is Homologous Recombination? Another last effort to repair a double strand break by putting the ends back together before making sure they are correctly copied. This can lead to deletions/insertions (frameshift mutations). Correct Answer-What is Non-Homologous Recombintaion? It must bind to RNA primer Correct Answer-What does DNA Polymerase bind to in order to make RNA TRANSCRIPTION DNA take the individual nucleotide and match them to the PARENTAL sequences to ensure a correct pair. introns (non-coding region) are removed and exons (coding region) joined to form a contiguous coding sequence. Correct Answer-What happens during RNA splicing to generate a mature RNA molecule? The ability to turn genes on and off Correct Answer-What is Gene Expression? The study of changes in organisms caused by modification of gene expression NOT alternation of the gene code. Correct Answer-What is epigenetics? Where a DNA molecule wraps around histone proteins to form tight loops called nucleosomes. These nucleosomes coil and stack together to form fibers called chromatin. (genes are ON if the nucleosomes are wide spread and OFF if the genes are tightly packed) Correct Answer-What is packaging of DNA? Polymerase Correct Answer-What is needed for DNA replication? A point mutation in a sequence of DNA (change in one nucleotide) that results in a premature STOP codon Correct Answer-What is NonSense Mutation A mutations in DNA that do not have an observable effect on the organism's phenotype. (1 neucleotide changes but it codes for the same amino acid) Correct Answer-What is a Silent Mutation? A point mutation in which a single nucleotide change results in a codon that codes for a DIFFERENT amino acid. Correct Answer-What is a Missense Mutation? It is typically not seen in every generation of an affected family. X-linked dominant disorders are caused by mutations in genes on the X chromosome, one of the two sex chromosomes in each cell. (males and females are equally affected) Correct Answer-What is Autosomal Dominate? It becomes Ionized Alanine. (Alanine is HYDROPHOBIC and has CH3 as its weak interaction. Ionized means it has a + or -. Correct Answer-Alanine is an amino acid with an amino group, a carboxyl group, and a methyl group (side chain). What happens if it looses an electron. Amino Acids whose side chains prefer water. (NH, OH, SH) Correct Answer-What is a Polar Amino Acid? Amino Acids that Can't Have (CH) water (hydrophobic) Correct Answer-What is a Non Polar Amino Acid? There is a charge (+/-) attached to the amino acid Correct Answer-What is Ionized Amino Acid? It is caused by tangles inside the cell and plaques outside the cell (senile plaques) caused by abnormal protein aggregation (APA). Correct Answer-What is the misfolding of protein structure in Alzhiemers disease? It is a fibrous, toxic material inside of cells. When its connections are lost, it becomes defective and forms filaments in the neuron. Its accumulation is triggered by a buildup of Amyloid protein, which disrupts the functioning of brain cells. Correct Answer-What roll does the protein TAU play in Alzhiemers disease? It is a buildup of excess Amyloid protein between nerve cells. It starts in the hippocampus and moves up, creating senile plaques in the brain. Correct Answer-How is Amyloid-beta protein linked to Alzhiemers Disease? Protein aggregates usually consist of fibers containing misfolded protein with a β-sheet conformation, termed amyloid. Neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease (AD), Parkinson's disease (PD), Huntington's disease (HD), amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) and prion diseases have these protein aggregations. Neurodegeneration and memory loss can be detected before Amyloid fibers accumulate in the brain. Correct Answer-What is Neurodegenerative protein aggregation? Proteins that bind to denatured proteins and assist in the PROPER folding or unfolding and the assembly or disassembly of molecular structures. (they can help newly formed proteins and help misfolded proteins) Correct Answer-What is a molecular chaperone? Primary, (formed by peptid bonds) Secondary, (held together by hydrogen bonds, formed from two polar amino acids) Tertiary, (side chain interaction) Quaternary (more than one polypeptide) Correct Answer-What are the levels of a protein structure? The folding and intramolecular bonding of the linear amino acid chain. Folded proteins are stabilized by thousands of noncovalent bonds between amino acids. THE AMINO ACID SEQUENCE OF A PROTEIN DETERMINES ITS 3D SHAPE. Correct Answer-What determines the 3D shape of a protein? Folded structures that form within a polypeptide. Stabilized by HYDROGEN BONDS between atoms in the polypeptide backbone. How the chains on amino acids interact with each other to form BETA SHEETS and ALPHA HELIXES. Correct Answer-What is the Secondary level of protein structure? AcetylCoA starts the citric acid cycle. It produces NADH and FADH2 Correct Answer-What starts the citric acid cycle and what does it produce? [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 13 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

WGU Biochemistry 785 Full Solution Pack(Bundled exams 100% verified)
BioChem C785 module 2 quiz with complete solution WGU Biochemistry Final Review WGU 785 Final Exam With Complete Solution WGU BioChem OA Review with complete solution C785 Biochemistry preassessment w...
By Nutmegs 3 years ago
$22
21
Reviews( 0 )
$10.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 10, 2022
Number of pages
13
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 10, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
202








.png)