Engineering > QUESTIONS & ANSWERS > ISYE-6501 – HOMEWORK WEEK #14 Graded A (All)
ISYE-6501 – HOMEWORK WEEK #14 Graded A
Document Content and Description Below
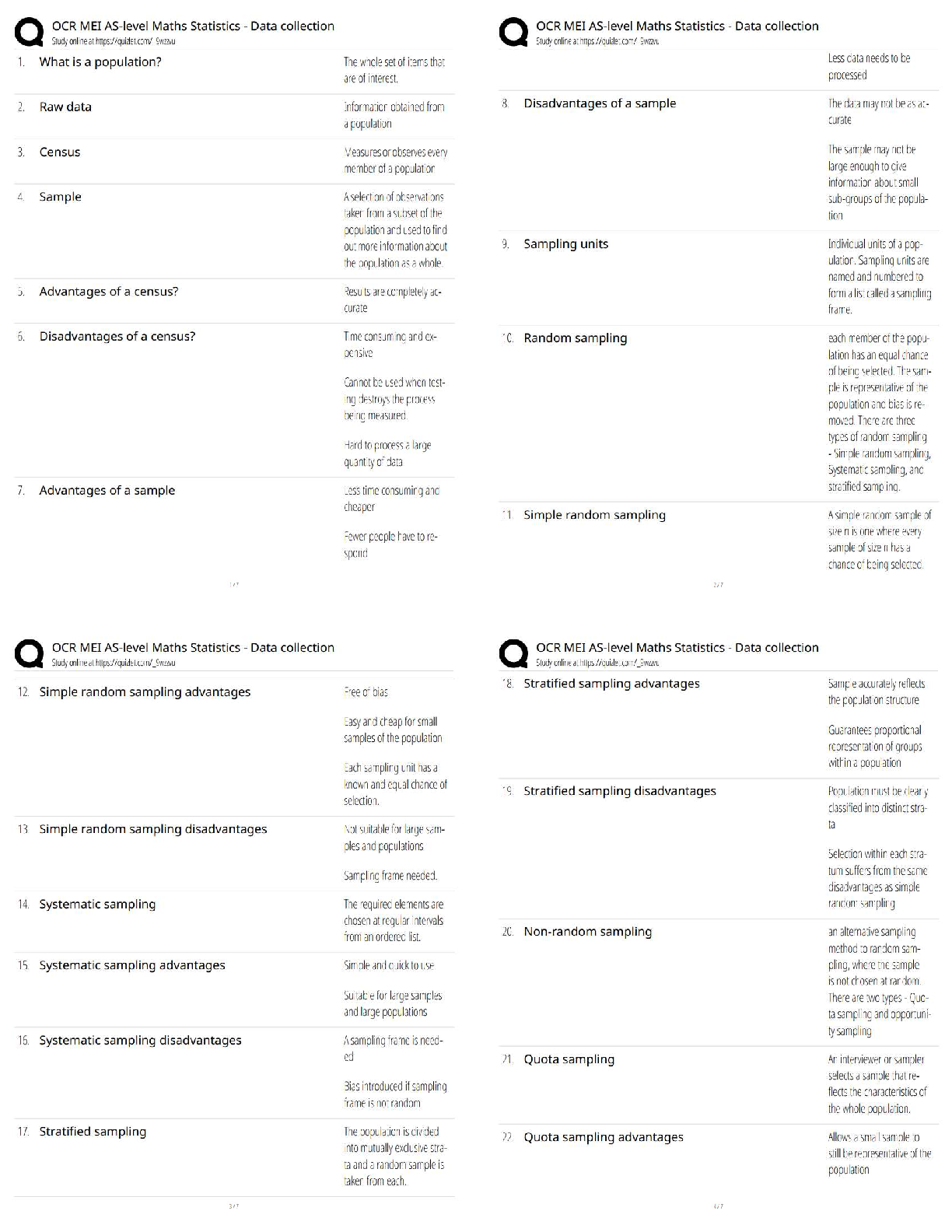
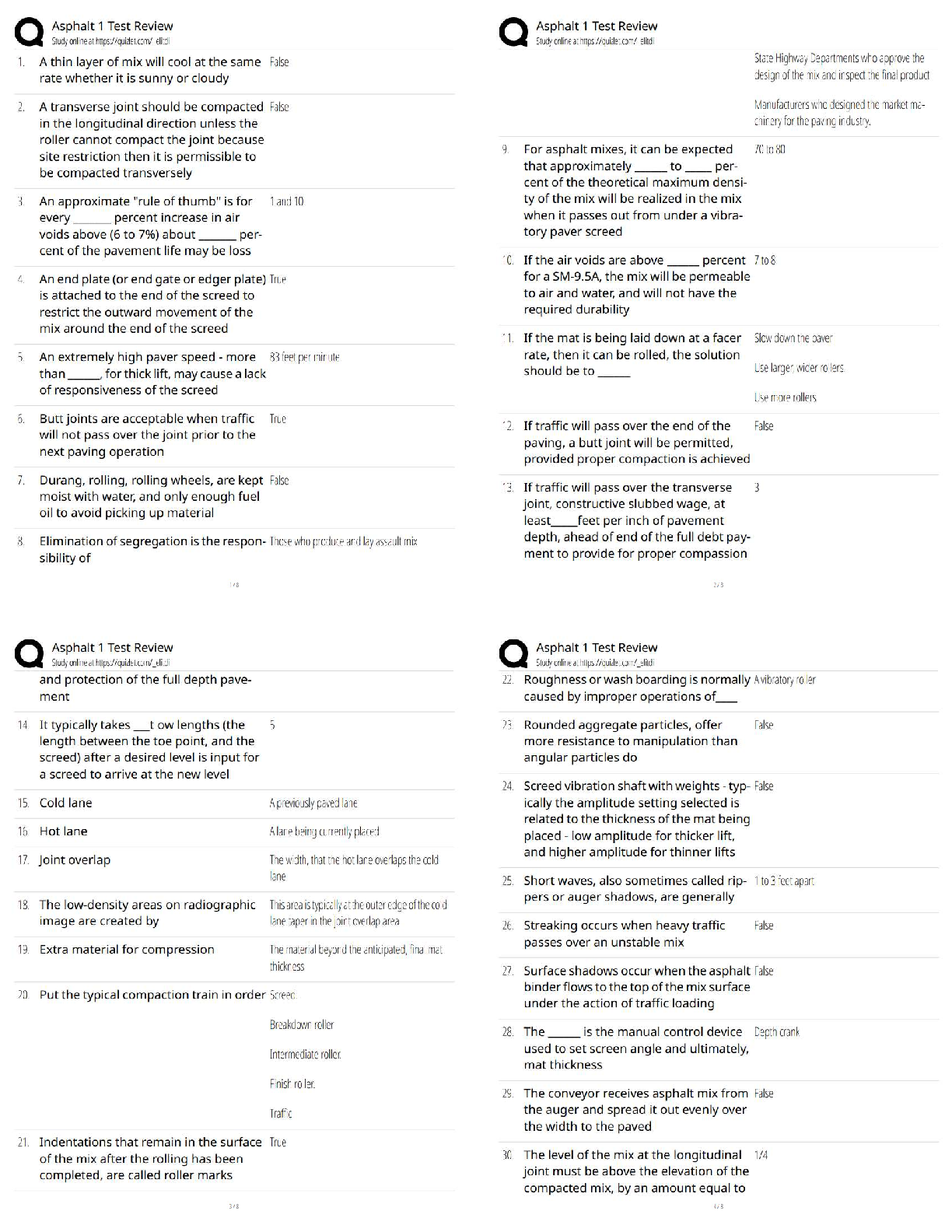
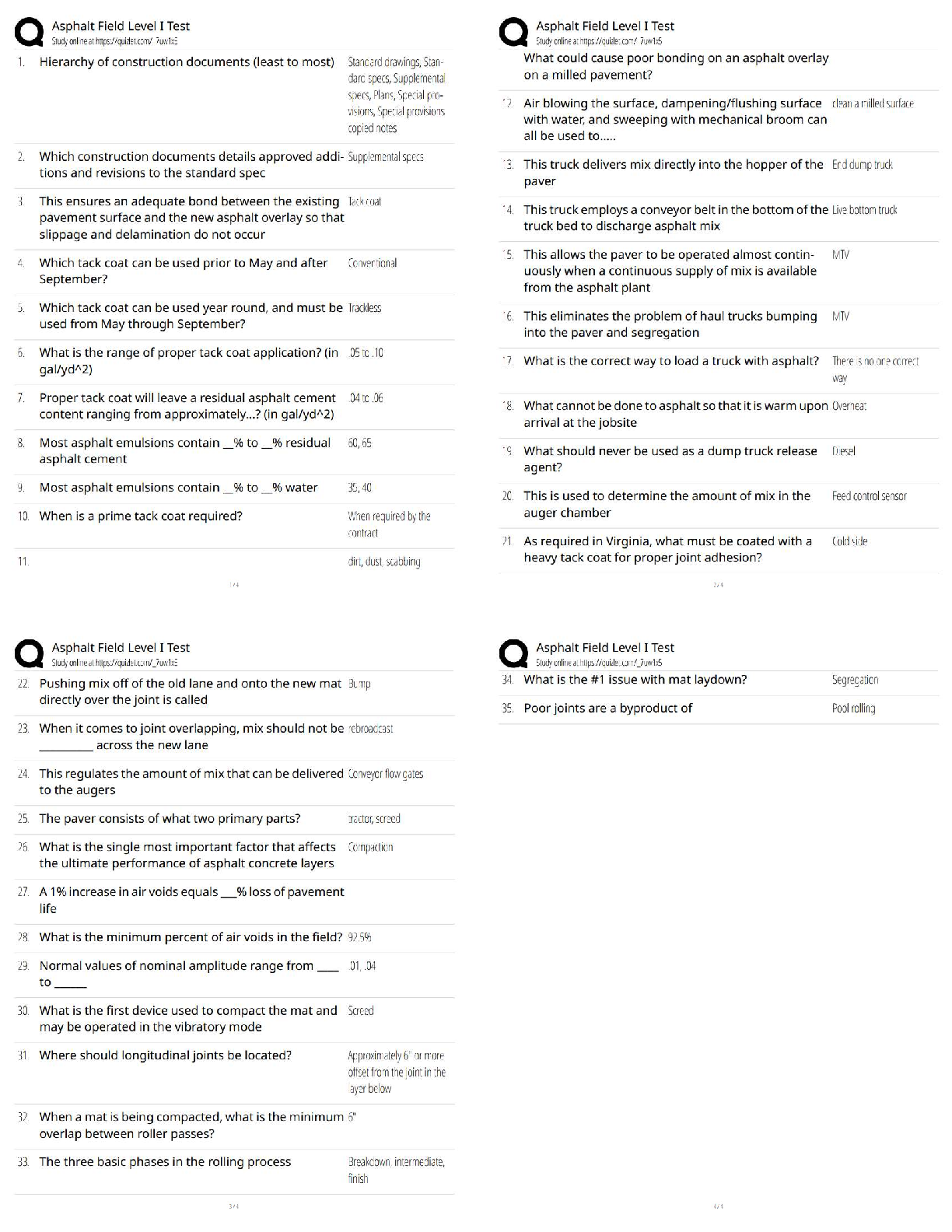
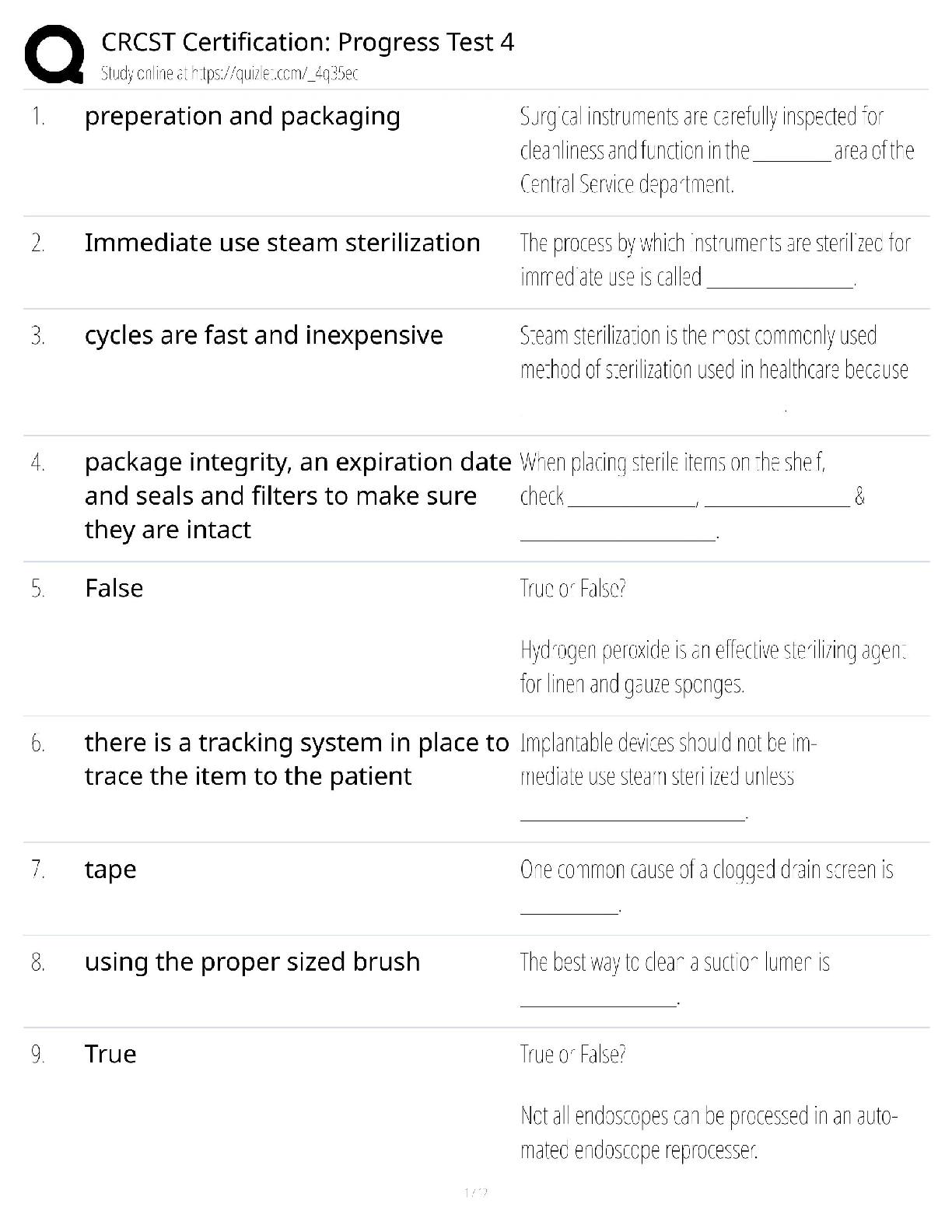
ISYE-6501 – HOMEWORK WEEK #14 Question 19.1 Describe analytics models and data that could be used to make good recommendations to the retailer. How much shelf space should the company have, to ma ... ximize their sales or their profit? Of course, there are some restrictions – for each product type, the retailer imposed a minimum amount of shelf space required, and a maximum amount that can be devoted; and of course, the physical size of each store means there’s a total amount of shelf space that has to be used. But the key is the division of that shelf space among the product types. For the purposes of this case, I want you to ignore other factors – for example, don’t worry about promotions for certain products, and don’t consider the fact that some companies pay stores to get more shelf space. Just think about the basic question asked by the retailer, and how you could use analytics to address it. As part of your answer, I’d like you to think about how to measure the effects. How will you estimate the extra sales the company might get with different amounts of shelf space – and, for that matter, how will you determine whether the effect really exists at all? Maybe the retailer’s hypotheses are not all true – can you use analytics to check? Think about the problem and your approach. Then talk about it with other learners, and share and combine your ideas. And then, put your approaches up on the discussion forum, and give feedback and suggestions to each other. You can use the {given, use, to} format to guide the discussions: Given {data}, use {model} to {result}. One of the key issues in this case will be data – in this case, thinking about the data might be harder than thinking about the models. Solution: Here is a list of potential useful data needed to solve the task: 1. Amount of shelf space required per product a. Minimum b. Maximum 2. Total daily revenue 3. Daily revenue (gross profit margin) generated by individual products 4. Daily revenue (gross profit margin) per square foot 5. Market basket (list of items in each customer’s basket) 6. Retail space 7. Number of products available 8. Daily total sales 9. Food category 10. Inventory 11. Number of items per basket 12. Pay-to-stay fees 13. Weekday (Y,N) 14. Weekday (Monday through Sunday) Hypotheses: This study source was downloaded by 100000834091502 from CourseHero.com on 05-16-2022 07:00:03 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/40909739/Homework-14-Answerpdf/ 2 | P a g e ISYE-6501 – HOMEWORK WEEK #14 1. More self-space results into more sales 2. More sales result into more complementary sales 3. Larger effect if complementary products are placed in adjacent selves Hypothesis testing - • Using sales data to confirm Hypothesis 2 and 3 • As limited data was available for 1, o Used A/B testing o Change detection ▪ Seasonality ▪ Trend ▪ External factors o Use exponential smoothing if multi-year data is available ▪ This showed correlation, but not causation New data set • Tracking Cameras o Use logistic regression to match images (visual data) and then, o Use optimization for maximum probability matching based on logistic regression output • Analytics VS Privacy o Camera tracking and associating that data with credit card etc. Will open privacy concerns o Keep ethical issues in mind Approach: 1. Clustering Model - Distance between two products in the store is inversely proportional to their sales together (more distance = less sales) Given... Use... To... Sales and store Data Clustering models Correlate sale of complementary products 2. Community Finding Model (Louvain) - The first step is a "greedy" assignment of nodes to communities, favoring local optimizations of modularity between complementary products. The second step is the definition of a new coarse-grained network of products and shelf spaces, based on the communities found in the first step. These two steps are repeated until no further modularity-increasing reassignments of communities are possible. Given... Use... To... Cluster information from above Louvain Finding product and shelf space correlations and confirming the hypothesis earlier This study source was downloaded by 100000834091502 from CourseHero.com on 05-16-2022 07:00:03 GMT -05:00 https://www.coursehero.com/file/40909739/Homework-14-Answerpdf/ 3 | P a g e ISYE-6501 – HOMEWORK WEEK #14 3. Optimization model Given... Use... To... Sales and store Data Discrete stochastic simulation model in ARENA [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 3 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Also available in bundle (1)
Click Below to Access Bundle(s)

BUNDLED PAPERS (Multiple versions) FOR Georgia Institute Of Technology ISYE 6501 Homeworks 1 - 15, Midterm 1 & 2 + FINAL EXAM | ISYE6501x Courseware | edX - Complete Solutions - Introduction To Analytics Modeling - GTX ISYE 6501
GTx: ISYE6501x Introduction to Analytics Modeling Midterm Quiz 2 - GT Students and Verified MM Learners latest 2021 Midterm Quiz 1 - GT Students (Launch Proctortrack first before taking the Midterm Qu...
By Nutmegs 3 years ago
$15
66
Reviews( 0 )
$7.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
May 17, 2022
Number of pages
3
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
May 17, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
343










.png)