. Following the evacuation of a subdural hematoma, an older adult develops an infection. The client is transferred to the neuro intensive care unit with a temperature of 102 Faxillary, pulse of 180 beats/minute, and a bl
...
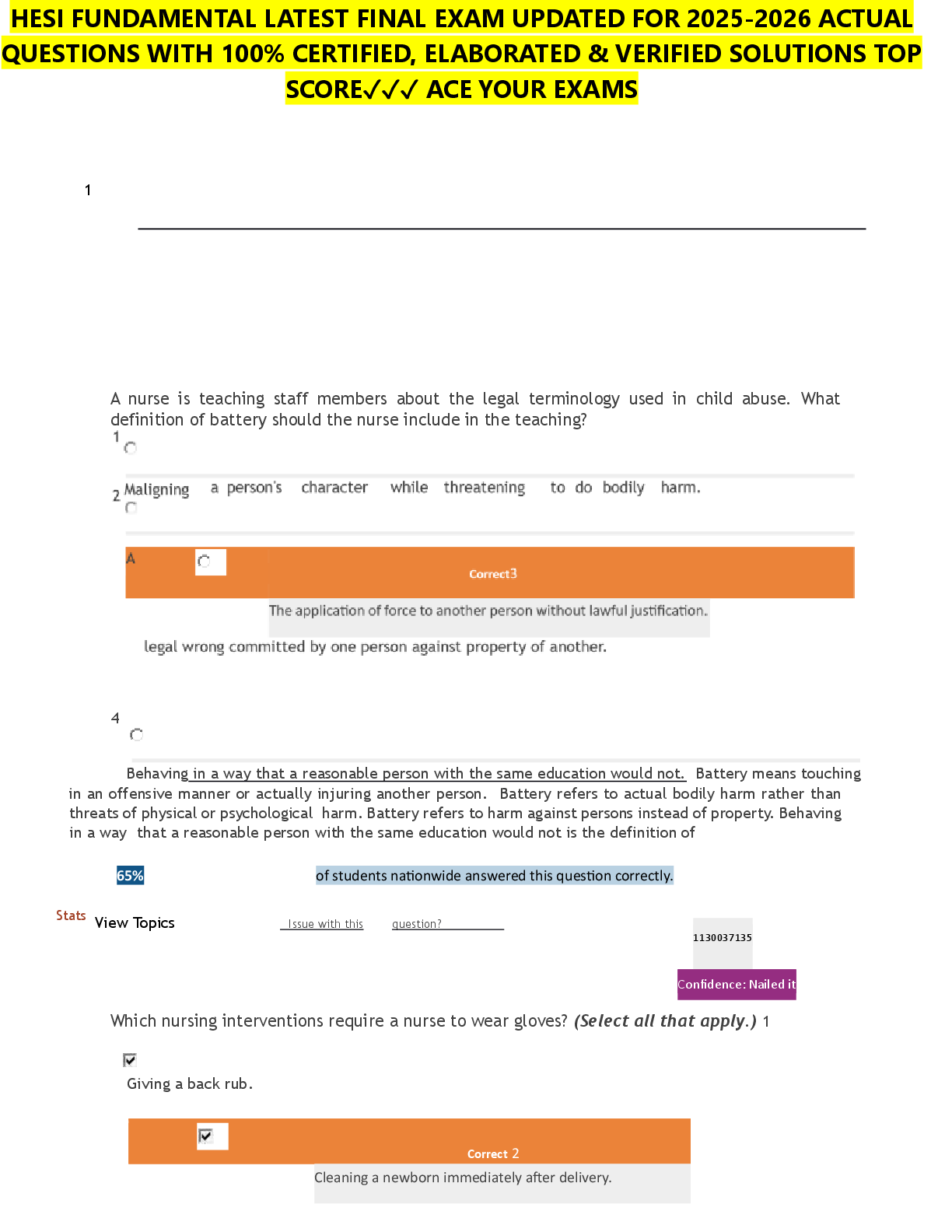
. Following the evacuation of a subdural hematoma, an older adult develops an infection. The client is transferred to the neuro intensive care unit with a temperature of 102 Faxillary, pulse of 180 beats/minute, and a blood pressure of 90/60 mmHg. Which is the priority intervention to include in this client’s plan of care?
A. Keep the suture line clean and dry.
B. Check neuro vital signs every 4 hours.
C. Maintain intravenous access.
D. Measure hourly urine output.
2. A client presents at the emergency department reporting a raspy voice, cold intolerance, and fatigue. Laboratory tests indicate an elevated thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and low T3 and T4 levels. After the client is admitted to the telemetry unit, which interventions is most important for the nurse to implement?
A. Note the client’s most recent hemoglobin level.
B. Administer prescribed dose of levothyroxine.
C. Offer additional blankets and a warm drink.
D. Assess for presence of non-pitting edema.
3. The nurse observes an unlicensed assistive personnel (UAP) begin to remove exam gloves after emptying a bed pan containing feces. The UAP slides two fingers inside one of the gloves and begins to roll the glove off. Which actions should the nurse implement?
A. Instruct the UAP to use two pairs of gloves when fecal contamination is likely.
B. Remind the UAP to discard the gloves in the biohazard contain after removal.
C. Support that the UAP roll both of the gloves and inside out at the same time.
D. Advice the UAP that the technique being used will result in hand contamination.
4.A client with a liver abscess develops septic shock. A sepsis resuscitation bundle protocol is initiated, and the client receives a bolus of IV fluids. Which parameter should the nurse monitor to assess effectiveness of the fluid bolus?
A. Mean arterial pressure (MAP)
B. White blood cell count
C. Blood culture
D. Oxygen saturation
5.In monitoring tissue perfusion in a client following an above the knee amputation (aka), which action should the nurse include in the plan of care?
A. Evaluate closet proximal pulse.
B. Asses skin elasticity of the stump.
C. Observe for swelling around the stump.
D. Note amount color of wound drainage.
6. An older adult client is admitted to the intensive care unit unconscious after several days of vomiting and diarrhea. The nurse inserts a urinary catheter and obtains a scant amount of dark amber output. Which interventions should the nurse implement first? (Please scroll and view each tab’s information in the client’s medical record before selecting the answer.)
Flow Sheets
Vital Signs
Heart Rate – beats/minute 110
Respirations – breaths/minute 28
Blood Pressure – mmHG 80/60
Laboratory
Electrolytes
Sodium – 1.30 mEq/L
Potassium – 2.5 mEq/L
Chloride – 95 mEq/L
Diagnostics
Arterial blood gases (ABGs)
pH – 7.34
PaCO2 – 34 mmHg
HCO3 - 20 mEq/L
po2 – 90 mmHg
A. Initiate continuous dopamine infusion at2 mcg/kg/minute.
B. Give bolus of 0.9% sodium chloride 1,000 ml over 30 minutes.
C. Administer promethazine 2.5 mg slowly IV push q4.
D. Begin potassium chloride 10 mEq over 1 hour per secondary infusion.
7.The nurse is caring for a 17-year-old male who fell 20 feet 5 months ago while climbing the side of a cliff and has been in a sustained vegetative state since the accident. Which interventions should the nurse implement?
A. Initiate open communication with the teen’s parents.
B. Talk directly to the adolescent while providing care.
C. Inquire about food allergies and food likes and dislikes.
D. Monitor vital signs and neuro status every 2 hours.
8.A client with acute renal failure (ARF) is admitted for uncontrolled type 1 diabetes Mellitus and hyperkalemia. The nurse administers an IV dose of regular insulin per sliding scale. Which intervention is the most important for the nurse to include in this client’s plan of care?
A. Monitor the client’s cardiac activity via telemetry.
B. Maintain venous access with an infusion of normal saline.
C. Assess glucose via fingerstick q4 to 6 hours.
D. Evaluate hourly urine output for return of normal renal function.
9. A middle aged male client, admitted to a critical care unit several weeks ago because of serious injuries sustained in a motor vehicle accident, is currently in stable condition. Based on this client’s age and recent life-threatening crisis, which intervention is should the nurse implement?
A. Allow long periods of uninterrupted rest in order to reduce fatigue.
B. Encourage the client to reflect on personal goals and priorities.
C. Provide a routine schedule of activities to fascinate trust.
D. Discuss the cause of the accident with the client and his family.
10. A client is receiving the intravenous adrenergic agonist dobutamine. In evaluating the client’s reaction to the medication, which assessment findings indicates to the nurse that the medication is effective?
A. The client denies chest pain or discomfort.
B. The client had 160 ml urine output in 8 hours.
C. The client’s posterior tibial pulses are 1 +.
D. The client’s blood pressure is 110/70 mmHg.
11. The nurse is imitating IV fluid replacement for a child who has dry, sticky mucous membranes, flushed skin, and a fever of 103.6 F (39.7 C). Laboratory findings indicate that the child has a serum concentration of 156 mEq/L (156 mmol/L). Which physiologic mechanism contributes to this finding?
A. Hypothalamic resetting of core body temperature causes vasodilation to reduce body heat.
B. Insensible loss of body fluids contributes to the hemoconcentration of serum solutes.
C. The intravenous fluid replacement contains a hypertonic solution of serum chloride.
D. Urinary and gastrointestinal fluid loss reduce blood viscosity and stimulate thirst.
12.A client with pneumonia has arterial blood gases levels at: PH 7.33; PaCO2 49 mm/hg; HCO3 25 mEq/L; PaO2 95. What intervention should the nurse implement based on these results?
A. Prepare to administer sodium chloride fluids.
B. Instruct the client to breath into a paper bag.
C. Institute coughing and deep breathing protocols
D. Initiate oxygen administration at 2 to 3/L per nasal cannula.
13.The nurse is assessing a client with a closed head injury sustained in a motor vehicle collision. Whichfinding indicates the lowest neurologic functioning?
A. Localization of a tactile stimulus.
B. Decorticate posturing during tracheal suctioning.
C. Withdrawal from painful stimuli
D.Decerebrate posturing during position changes.
14.The nurse is caring for a client who is in renal failure. In reviewing the client’s laboratory data, which results must be reported immediately to the healthcare provider?
A. Serum potassium 7 mEq/L or mmol (SI)
B. Serum sodium 140 mEq/L or mmol (SI)
C. Hematocrit 30% hemoglobin 10g/dl (100 g/L SI)
D. Increased blood urea nitrogen level.
15. A male client reports to the on-call nurse that he took tadafil 10 mg PO two hours ago and his skin now feels flushed. He reports a history of stable angina but denies experiencing any current chest pain. What action should the nurse take?
A. Reassure the client that skin flushing is a common side effect of the medication.
B. Advise the client to place one nitroglycerin tablet under his tongue as a precaution.
C. Instruct the client to increase his intake of oral fluids until the skin flushing is relieved.
D. Tell the client to have someone bring him to an emergency room.
16. A 9-year-old is receiving vancomycin 400 mg IV every 6 hours for a methicillin-resistant (Beta-lactam-resistant) Staphylococci aureus (MRSA) infection. The medication is diluted in a100-ml bag of saline with instructions to infuse over one and a half hours. How many ml/hours should the nurse program the infusion pump? (Enter numeric value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest whole number.)
17. After diagnosis and initial treatment of a 3-year-old with Cystic fibrosis, the nurse provides home care instructions to the mother, which statement by the child's mother indicates that she understands home care treatment to promote pulmonary functions?
A. “Chest physiotherapy should be performed twice a day before a meal.
B. “Energy should be conserved by scheduling minimally strenuous activities.”
C. “Maintain supplemental oxygen at 4 to 6L/minute.”
D. “Administer a cough suppressant every 8 hours”
18. An unconscious client is admitted to the intensive care unit and is placed on a ventilator. The ventilator alarms continuously and the client's oxygen saturation level is 62%. What action should the nurse take first?
A. Begin manual ventilation immediately.
B. Silence the alarm and call the technician.
C. Call respiratory therapy.
D. Monitor manual ventilation immediately.
19. The charge nurse is planning for the shift and has a registered nurse (RN) and a practical nurse (PN) on the team. Which client should the charge nurse assign to the RN?
A. A 75-yearold client with renal calculi who requires urine straining.
B. A 64-year-old client who had a total hip replacement the previous day.
C. A 30-year-old depressed client who admits to suicidal ideation.
D. An adolescent with multiple concussions due to a fall that occurred 2 days ago.
20. The nurse is planning care for a client who has a fourth-degree midline laceration that occurred during vaginal delivery of an 8-pound 10-ounce (3674 grams) infant. Which intervention has the highest priority for this client?
A. Administer prescribed stool softener.
B. Encourage use of prescribed analgesic perineal sprays.
C. Administer prescribed PRN sleep medications.
D. Encourage breastfeeding to promote uterine involution.
21. While caring for a client after a small bowel resection, the nurse is informed that the client has a history of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA). To reduce the riskof recurrence of the MRSA in the postoperative wound, which intervention is most important for the nurse to implement?
A. Report any increase in the white blood count.
B. Change the surgical dressing readily when soiled.
C. Wear a face mask while performing wound care.
D. Instruct the family to adhere to contact precautions.
22.A client with a history of dementia has become increasingly confused at night and is picking at an abdominal surgical dressing and the tape securing the intravenous (IV) line. The abdominal dressing is no longer occlusive, and the IV insertion site is pink. What intervention should the nurse implement?
A. Replace the IV site with a smaller gauge.
B. Redress the abdominal incision
C. Leave the lights on in the room at night.
D. Apply soft bilateral wrist restraints.
23. When caring for an older male client with urinary frequency, which measure is most important for the nurse to implement to help the client prepare to go to bed for the night?
A. Offer the client an evening snack before providing oral care.
B. Place fresh water and a glass within reach on the bedside table.
C. Ensure that the call bell is easily accessible to the client.
D. Reassure the client someone will check on him hourly.
24.When obtaining a throat culture from a 6-year-old with possible streptococcal infection, which action is most important for the nurse to implement?
A. Encourage the parent to hold their child during the procedure.
B. Instruct the child to look at the ceiling and open mouth widely.
C. Allow the child to hold the tongue depressor and practice saying “Ah”
D. Swab the child’s erythematous oropharyngeal surfaces or tonsillar pustules.
25. During a return demonstration of teaching provided by the nurse, the daughter of a client administers the mother’s eye drops by resting her dominant hand on her mother’s forehead and dropping the medication into the conjunctival sac. Which action should the nurse take in response to this demonstration?
A. Remind the client to gently close her eyes after the eye drops are instilled.
B. Instruct the mother to gently rub the affected eye to distribute the drops.
C. Advice the daughter to keep her hand farther from her mother’s eye.
D. Offer to demonstrate the eye drop procedure to the daughter one more time.
26.The nurse is ready to insert an indwelling urinary catheter as seen in the picture. At this point in the procedure, what actions should the nurse take before inserting the catheter? (Select all that apply)
A. Ask the client to bear down as if voiding to relax the sphincter
B. Complete perianal care with soap and water
C. Gently palpate the client’s bladder for distention
D. Hold the catheter 3 – 4 inches (7.5 – 10 cm) from its tip
E. Secure the urinary drainage bag to the bed frame
27. A mother brings her 3-week-old son to the clinic because he is vomiting “all the time.” In performing a physical assessment, the nurse notes that the infant has poor skin turgor, has lost 20% of his birth weight, and has a small palpable oval-shaped mass in his abdomen. What intervention should the nurse implement first?
A. Give the infant 5% dextrose in water orally
B. Insert a nasogastric tube for feeding
C. Initiate a prescribed IV for parental fluid
D. Feed the infant 3 ounces of Isomil
28.A client is currently receiving an infusion labeled Heparin Sodium 25,000 Units in 5% Dextrose Injection 500 ml at 14 ml/hour. A prescription is received to change the rate of the infusion to 900 units of Heparin per hour. The nurse should set the infusion pump to deliver how many ml/hr.? (Enter numeric value only)
29. A client with type 2 diabetes mellitus presents to the emergency roomwith signs of hyperosmolar hyperglycemic state (HHS). Which of the client’s serum laboratory values requires intervention by the nurse?
A. Positive urinary ketones.
B. Elevated white blood cells.
C. Decreased serum potassium.
D. Low serum phosphate level.
30. Which assessment should the home health nurse include during a routine home visit for a client who was discharged home with a suprapubic catheter?
A. Assess the perineal area.
B. Palpate flank area.
C. Observe insertion site.
D. Measure abdominal girth.
31.A 3-year-old boy with a congenital heart defect is brought to the clinic by his mother because he has a fever and an earache. During the assessment, the mother asks the nurse why her child is at the 5th percentile for weight and height for his age. Which response is best for the nurse to provide?
A. “Haven’t you been feeding him according to recommended daily allowances for children”
B. “His smaller size is probably due to the heart disease”
C. “You should not worry about the growth tables. They are only averages for children.”
D. “Does your child seem mentally slower than his peers also?”
32.While administering a continuous insulin infusion to a client with diabetic ketoacidosis, it is essential for the nurse to monitor which serum lab values?
A. Calcium.
B. Potassium.
C. Protein.
D. Hemoglobin.
33. When is it most important for the nurse to assess a pregnant client’s deep tendon reflexes (DTRs)?
A. Within the first trimester.
B. During admission to labor and delivery.
C. If the client has an elevated blood pressure.
D. When the client has ankle edema.
34. A client is admitted following a motor vehicle collision. When assessing the client’s level of consciousness, the nurse notes that the client no longer responds to commands. The nurse initiates a painful stimulus and the client responds by pulling the arms inward with elbows and wrists flexed and extending the legs with the toes pointed downward. Which action should the nurse implement?
A. Document the purposeful response to pain.
B. Initiate seizure precautions immediately.
C. Report the finding to the healthcare provider.
D. Administer a prescribed PRN analgesic.
35.A client who underwent an uncomplicated gastric bypass surgery is having difficult with diet management. What dietary instruction is most important for the nurse to explain to the client?
A. Chew food slowly and thoroughly before attempting to swallow
B. Plan volume-controlled evenly-space meal thorough the day
C. Sip fluid slowly with each meal and between meals
D. Eliminate or reduce intake fatty and gas forming food
36.A client with a history of using illicit drugs intravenously is admitted with Kaposi’s sarcoma. Which intervention should the nurse include in this client’s admission plan of care?
A. Identify local support HIV support groups.
B. Assess for symptoms of AIDS dementia.
C. Observe for adverse drug reaction.
D. Monitor for secondary infections.
37.The nurse reviews the laboratory findings of a client with an open fracture of the tibia. The white blood cell (WBC) count and erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) are elevated. Before reporting this information to the healthcare provider, what assessment should the nurse obtain?
A. Degree of skin elasticity
B. Appearance of wound
C. Bilateral pedal pulse force
D. Onset of any bleeding
38. A client with deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is receiving a continuous intravenous heparin infusion. The client now has tarry, black diarrhea and reports abdominal pain. Which action should the nurse implement? (Select all that apply.)
A. Auscultate bowel sounds in all quadrants.
B. Assess characteristics of pain.
C. Monitor stools for presence of blood.
D. Review last partial thromboplastin time results.
E. Prepare to administer warfarin.
39. Which laboratory finding for an adult client is most critical to report to the healthcare provider? (Click on the correct location on the chart. To change, click on a new location.)
40. A male client with multiple myeloma is admitted with pneumonia and pancytopenia. The nurse reviews the complete blood cell count findings and identifies a platelet count of 20,000 cells/mm3. Which intervention should the nurse include in the client’s plan of care?
A. Monitor intake and output.
B. Limit exposure to visitors with respiratory infections.
C. Pace activities between planned rest periods.
D. Avoid intramuscular injections.
41.A male client is admitted for the removal of an internal fixation that was inserted for the fracture ankle. During the admission history, he tells the nurse he recently received vancomycin (vancomycin) for a methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) wound infection. Which action should the nurse take? (Select all that apply.)
A. Collect multiple site screening culture for MRSA
B. Call healthcare provider for a prescription for linezolid (Zyrovix)
C. Place the client on contact transmission precautions
D. Obtain sputum specimen for culture and sensitivity
E. Continue to monitor for client sign of infection
42. When administering brompheniramine maleate, an extended release antihistamine tablet, the nurse is told by the male client that he cannot swallow tablets. Which intervention should the nurse implement?
A. Document that the client cannot take the prescription.
B. Document the client’s refusal to take the medication.
C. Crush tablet and mix with small amount of pudding.
D. Ask the pharmacist to send it in liquid form.
43. The nurse identifies the presence of clear fluid on the surgical dressing of a client who just returned the unit following lumbar surgery. Which action should the nurse implement immediately?
A. Test the fluid on the dressing for glucose.
B. Mark the drainage area with a pen and continue to monitor.
C. Document the findings in the electronic medical record.
D. Change the dressing using a compression bandage.
44.Dopamine hydrochloride 2 mcg/kg/minute is prescribed to promote renal perfusion for a client weighing 198 lbs. The pharmacy sends a pre-mixed bag of dopamine containing 400 mg in 250ml D5W. An IV pump is available that provides a precision infusion rate to a tenth of a ml. (Therounding is required, round to the nearest tenth)
45. A client is admitted with hypoparathyroidism. Which laboratory value indicates that the nurse should place a client on a telemetry monitor?
A. Calcium 6.5 mg/dl or 0.25 mmol/L.
B. Potassium 5.0 mEq/L or mmol/L.
C. Magnesium 2.0 mEq/L or 0.85 mmol/L.
D. Sodium 132 mEq/L or mmol/L.
46. In preparing a nursing care plan for a client admitted with diagnosis of Guillain-Barre syndrome, which nursing problem has the highest priority.
A. Impaired physical mobility related to asymmetrical descending paralysis.
B. Imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to impaired swallowing reflex.
C. Ineffective coping related to uncertainly of disease progression.
D. Ineffective breathing pattern related to ascending paralysis.
47. The nurse is providing discharge teaching to a male client who underwent pneumonectomy. The client wants to resume social activities with family. How should the nurse respond?
A. Reinforce the need to avoid social contract for several weeks.
B. Recommend the use of a face mask during family events.
C. Explain the need to avoid persons with respiratory infections.
D. Encourage family gatherings to reduce feelings of isolation.
48. Two days after admission for a fractured wrist from a fall while intoxicated, a male client with a history of mental illness and alcohol abuse become anxious, agitated, and diaphoretic. His vital signs are temperature 99.6 F (37.6 C), heart rate 112 beats/minute, respirations 26 breaths/minute, and blood pressure 190/108. He tells the nurse that bugs are crawling in his bed. Which prescription should the nurse administer?
A. Codeine.
B. Risperidone.
C. Buspirone.
D. Chlordiazepoxide.
49. When addressing a client, the nurse should establish which findings as objective? (Select all that apply.)
A. Urticaria.
B. Edema.
C. Anxiety.
D. Nausea.
E. Hypertension.
F. Diaphoresis.
50. The nurse is providing care for a child who is brought to the emergency department a few days after a laceration to the leg from a barbed wire fence. The child has not received any tetanus immunizations and is manifestation early signs of muscular rigidity with spasms and jaw clenching or trismus. Which intervention should the nurse’s highest priority for this child?
A. Monitor IV infusions.
B. Suction oropharyngeal secretions.
C. Prepare for intubation with mechanical ventilation.
D. Minimize stimulation from sound, light, and touch.
51. The nurse provides sliding scale insulin administration instructions to an adult who was recently diagnosed with diabetes mellitus. The client demonstrates an understanding of the instructions provided by performing the procedure in which order? (Arrange with the first on top and the last on the bottom.)
1. Obtain blood glucose level.
2. Verify insulin prescription.
3. Draw insulin into insulin syringe.
4. Cleanse the selected site.
52. The nurse receives report on four clients who are complaining of increased pain. Which clientrequires immediate intervention by the nurse?
A. Sharp pain related to a crushed femur.
B. Paresthesia of finger due to carpal tunnel syndrome.
C. Stinging pain related to plantar fasciitis.
D. Burning pain due to Morton’s neuroma.
53. A client with bleeding esophageal varices receives vasopressin (Pitressin) IV. What should the nurse monitor for during the IV infusion of this medication?
A. Decreasing GI cramping and nausea.
B. Chest pain and dysrhythmia.
C. Hypotension and tachycardia.
D. Vasodilation of the extremities.
54. An older adult male is brought to the Emergency department (ED) by ambulance after a neighbor found him confused and unable to walk. The client is hypotensive, tachycardia, febrile, and incontinent of foul-smelling urine. After the client is admitted to the intensive care unit for septic shock, his daughter arrives and tells the nurse that his father does not want to be resuscitated. To include a “do not resuscitate” (DNR) form in the client’s record, which information should the nurse obtain?
A. Other family members support of the daughter’s report regarding the client’s end-of-life wishes.
B. The daughter is the client’s durable power of attorney for health care.
C. A DNR form, signed by the client during a previous hospitalization is available from Medical Records.
D. The healthcare provider verifies the client’s DNR status.
55. A native-American male client diagnosed with pneumonia, states that in addition to his prescribed medical treatment of IV antibiotics he wishes to have a spiritual cleaning performed. Which outcome statement indicates that the best plan of care was followed?
A. Identifies his ethnocentric values and behaviors
B. States an understanding of the medical treatment
C. Participated actively in all treatment’s regimens
D. Expresses a desire for cultural assimilation
56. While transferring a client with a chest tube from bed to stretcher, the chest tube becomes disconnected from the water-seal drainage container. The nurse immediately immerses the end of the tube in a container of sterile water. Which action should the nurse implement next?
A. Apply pressure to the chest tube site using petroleum gauze.
B. Clamp the chest tube and maintain distal end in the water.
C. Begin manual ventilation while retuning the client to the bed.
D. Prepare a new water-seal system and reattach the chest tube.
57. An older male client who was successfully treated for herpes zoster (shingles) with an antiviral medication reports that he is now experiencing pain on his trunk where the lesions were located. Which action should the nurse take?
A. Review the medication record to determine when the last analgesic was administered.
B. Teach the client about the importance of completing the full course of antiviral medication.
C. Reassure the client that the infection is resolved, and the pain should soon disappear.
D. Contact the healthcare provider about the need to resume the client’s antiviral medication.
58. The healthcare provider prescribes ondansetron oral solution 6 mg PO for an adult client before receiving chemotherapy. The available solution is labeled 4 mg/5ml. How many ml should the nurse administer? (Enter numeric value only. If rounding is required, round to the nearest whole number.)
A.
59. A preschool-aged boy is admitted to the pediatric unit following successful resuscitation from a near-drowning incident. While providing care to child, the nurse begins talking with his preadolescent brother who rescued the child from the swimming pool and initiated resuscitation. The nurse notices the older boy becomes withdrawn when asked about what happened. What action should the nurse take?
A. Tell the older brother that he seems depressed.
B. Ask the older brother how he felt during the incident.
C. Commended the older brother for his heroic actions.
D. Develop a water safety teaching plan for the family
60. In providing nursing care for a client after a gastric endoscopy, which commonly occurring problem should the nurse include interventions for in the post-procedure plan of care?
A. Sore throat.
B. Headache.
C. Nausea.
D. Aching leg.
61. The nurse is providing intermittent gavage feedings for a 33-week gestational age newborn. The nurse positions the newborn in a right side-lying position with the head slightly elevated and passes the feeding tube through the mouth. Prior to administrating the bolus feeding, it is most important for the nurse to obtain which assessment?
A. Nasal breathing obstruction.
B. Gag reflex and vomiting.
C. Intake and output.
D. Volume of gastric residual.
62.A client is admitted with acute pancreatitis. The client admits to drinking a pint of bourbon daily. The nurse medicates the client for pain and monitors vital signs q2 hours. Which finding should the nurse report immediately to the healthcare provider?
A. Confusion and tremors
B. Yellowing and itching of skin.
C. Abdominal pain and vomiting
D. Anorexia and abdominal distention
63. A male client with terminal cancer is brought to the Emergency Department manifesting a Cheyne-Stokes respiratory pattern. His wife tells the nurse that her husband has an advance directive that indicates a “Do not resuscitate” (DNR) status, but the documents are at home. When the client becomes apneic and pulseless, which actions should the nurse take?
A. Begin cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR).
B. Call the healthcare provider for a DNR prescription.
C. Determine if the family wants hospice care.
D. Ask the wife if her husband’s wishes ever changed?
64.When assessing a recently delivered, multigravida client, the nurse finds that her vaginal bleeding is more than expected. Which factor in the client’s history is likely to be most related to this finding?
A. She is gravida 6, para 5.
B. The second stage of labor lasted 10 minutes.
C. She is receiving butorphanol 2 mg IVP during labor.
D. She is over 35 years of age.
65. An adolescent client on a drug treatment unit becomes angry and pulls the refrigerator from the wall and then throws the microwave. After the client fails to respond to redirection, the healthcare provider prescribes restraints. Which assessment should the nurse include in the client’s record while the client is in restraints?
A. Speech patterns and processes.
B. Range-of-motion and circulation.
C. Responsiveness to painful stimuli.
D. Pupils equal, round and reactive to light.
66. A client is admitted with the diagnosis of peripheral arterial disease (PAD). During the assessment, the nurse is unable to palpate the pedal pulses. Which action should the nurse perform next?
A. Document that the pedal pulses are not palpable.
B. Use a stethoscope to auscultate the pedal pulses.
C. Attempt to palpate bilateral pulses in the posterior tibial arteries.
D. Palpate the femoral artery pulses.
67. Prior to surgery, written consent must be obtained. Which is the nurse’s legal responsibility with regard to obtaining written consent?
A. Ask the client or a family member to sign the surgical consent form.
B. Validate the client’s understanding of the surgical procedure to be conducted.
C. Explain the surgical procedure to the client and ask the client to sign the consent form.
D. Determine that the surgical consent form has been signed and is included in the client’s record.
68. The nurse is planning to assist a client with pneumonia from the bed to a chair for the first time after four days of bedrest. The nurse determines that the client’s ability to help during the transfer is limited. Which is the priority action?
A. Use a gait belt.
B. Provide non-slip footwear.
C. Request assistance.
D. Position the chair at 45 degrees.
69. The nurse is planning care for a client with chronic kidney disease who is a resident at a long-term nursing facility. The client is anuric and has hemodialysis 3 times a week. Which intervention should the nurse include in the client’s plan of care?
A. Monitor for signs of anemia.
B. Encourage intake of high potassium foods.
C. Provide perineal skin barrier cream.
D. Initiate toileting schedule.
70. A client with history of schizophrenia is admitted with diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). Which nursing interventions should the nurse implement during the admission process for this client? (Select all that apply.)
A. Review the list of home medications and dosages.
B. Prepare the client for involuntary commitment admission.
C. Hold psychotropic medications until glucose is regulated.
D. Interview client about reasons for admission to hospital.
E. Obtain psychiatric and medical admission records.
71. After an older client receives treatment for drug toxicity, the healthcare provider prescribes a 24-hour creatinine clearance test. Prior to starting the urine collection, the nurse notes that the client’s serum creatine is 0.3 mg/dl (22.9 micromol/L). Which action should the nurse implement?
A. Evaluate the client’s serum BUN level.
B. Initiate the urine collection as prescribed.
C. Notify the healthcare provider of the results.
D. Assess the client for signs of hypokalemia.
72. An adult client is admitted to the critical care unit with systemic inflammatory response syndrome (SIRS) as a result of a postburn infection. The client has a long line peripherally inserted IV catheter for fluid and medication administration and current vital signs include temperature 102.8 F or 39.3 C, heart rate 108 beats/minute, respiratory32 breaths/minute. Which action should the nurse implement first?
A. Evaluate daily serum electrolytes and hydration status.
B. Culture sputum, urine, burn wound, and all intravenous access sites.
C. Implement central line-associated bloodstream infection (CLBSI)
D.Provide bedside equipment for transmission and protective precautions.
73. The nurse is caring for a client after a thoracentesis that drained 50 mL of clear fluid from the left lung. Which assessment finding should the nurse report to the healthcare provider immediately?
A. Serosanguinous drainage from the chest tube.
B. Mediastinal shift to the right
C. Dullness bilaterally on precaution.
D. Diminished breath sounds in the left lower lobe.
74. After receiving IV fluids in the emergency department, an elderly client is admitted to the acute care unit with a medical diagnosis of dehydration. The client is receiving 0.9% normal saline at 125 ml/hour via saline lock and has a bounding pulse, tachycardia, and pedal edema. When contacting the healthcare provider, the nurse anticipates a prescription what intervention?
A. Decrease the rate of the normal saline infusion.
B. Increase the rate of the normal saline infusion.
C. Remove the saline lock from the client’s arm.
D. Change the IV solution to 0.45% saline solution.
75. The nurse plans to collect to a 24-hour urine specimen for a creatinine clearance test. Which instructions should the nurse provide to the adult male client?
A. Urinate immediately into a urinal, and the lab will collect the specimen every 6 hours, for the next 24 hours.
B. For the next 24 hours, notify the nurse when the bladder is full, and the nurse will collect catharized specimens.
C. Urinate at a specified time, discard this urine and collect all the subsequent urine during the next 24 hours.
D. Cleanse around the meatus discard first portion of voiding and collect the rest in a sterile bottle.
76. Which self-care measure is most important for the nurse to include in the plan of care of a client recently diagnosed with type 2 diabetes mellitus?
A. A realistic exercise plan.
B. Blood glucose monitoring.
C. Self-injection techniques.
D. Diabetic diet meal planning.
77. The nurse notices that a male client is particularly delusional one afternoon. He begins to pace floor and appears to be losing control of himself. Which intervention is best for the nurse to implement?
A. Use firmness and direct the client to sit for a while.
B. Suggest to the client that he take a walk.
C. Encourage the client to use the punching bag.
D. Move the client to a quiet place on the unit.
78. A client with gestational diabetes is being induced for labor. Which assessment is most important for the nurse to perform prior to increasing oxytocin rate?
A. Vaginal exam.
B. Blood pressure.
C. Fingerstick glucose.
D. Contraction pattern.
ANS: D
79. The nurse is assessing a middle-aged adult who is diagnosed with osteoarthritis. Which factor in the client’s history is a contributor to the osteoarthritis?
A. Recently treated for deep vein thrombosis.
B. Lactose intolerance since childhood.
C. Long distance runner since high school.
D. Photosensitivity to a drug currently taking.
80. A young adult female client arrives at the emergency department with severe lower abdominal pain, vaginal bleeding, and right shoulder pain. The healthcare provider suspects an ectopic pregnancy and prescribes an abdominal ultrasound. Which additional diagnostics test results should the nurse report to the healthcare provider?
A. Positive human chronic gonadotropin blood test.
B. Hemoglobin 12 grams/dl (120 mmol/L)
C. Urinalysis with white blood cells, too many to count.
D. White blood cell count (WBC) 8,000/MM3 (8 x 10^9/L (SI units)
[Show More]




.png)




.png)