MDC3 Exam 1 Review
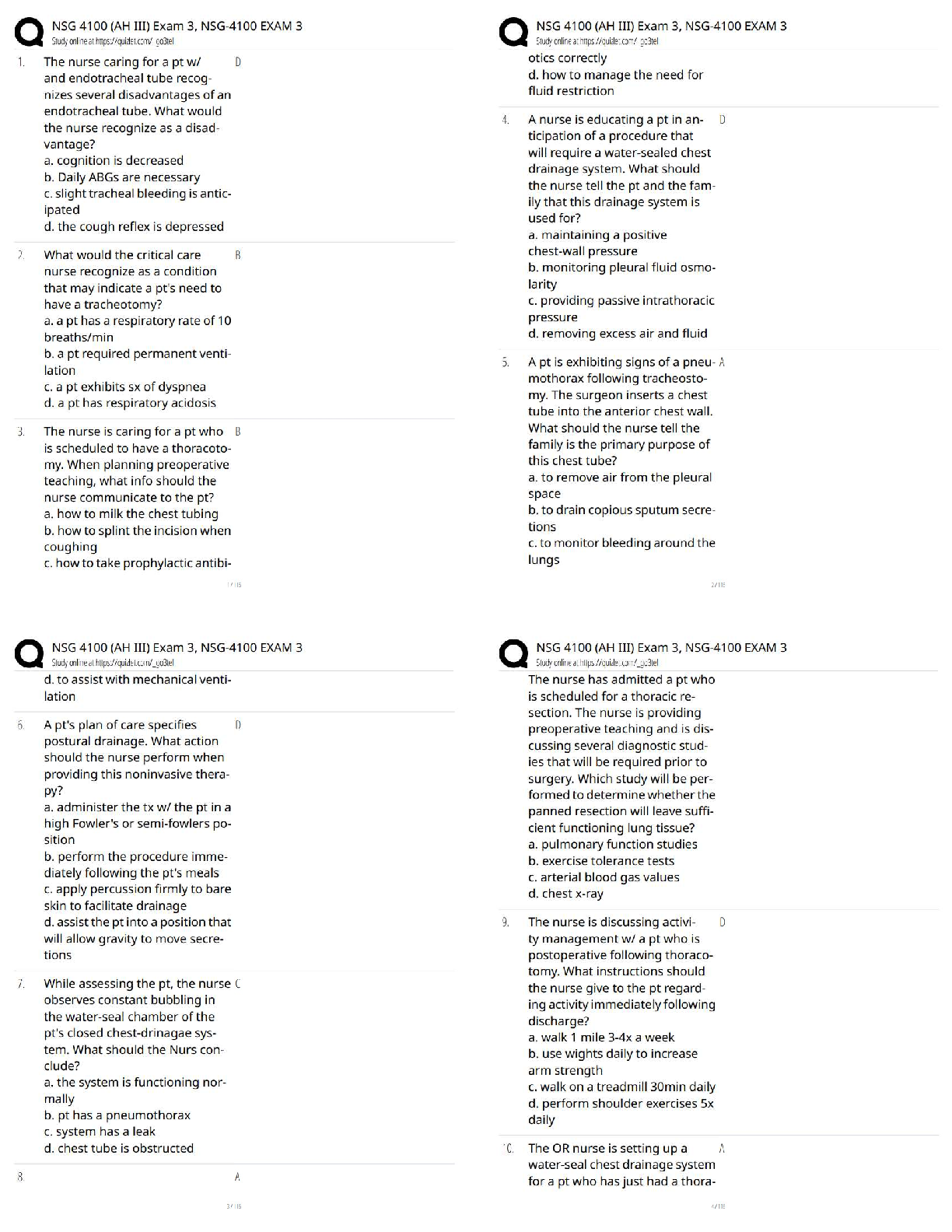
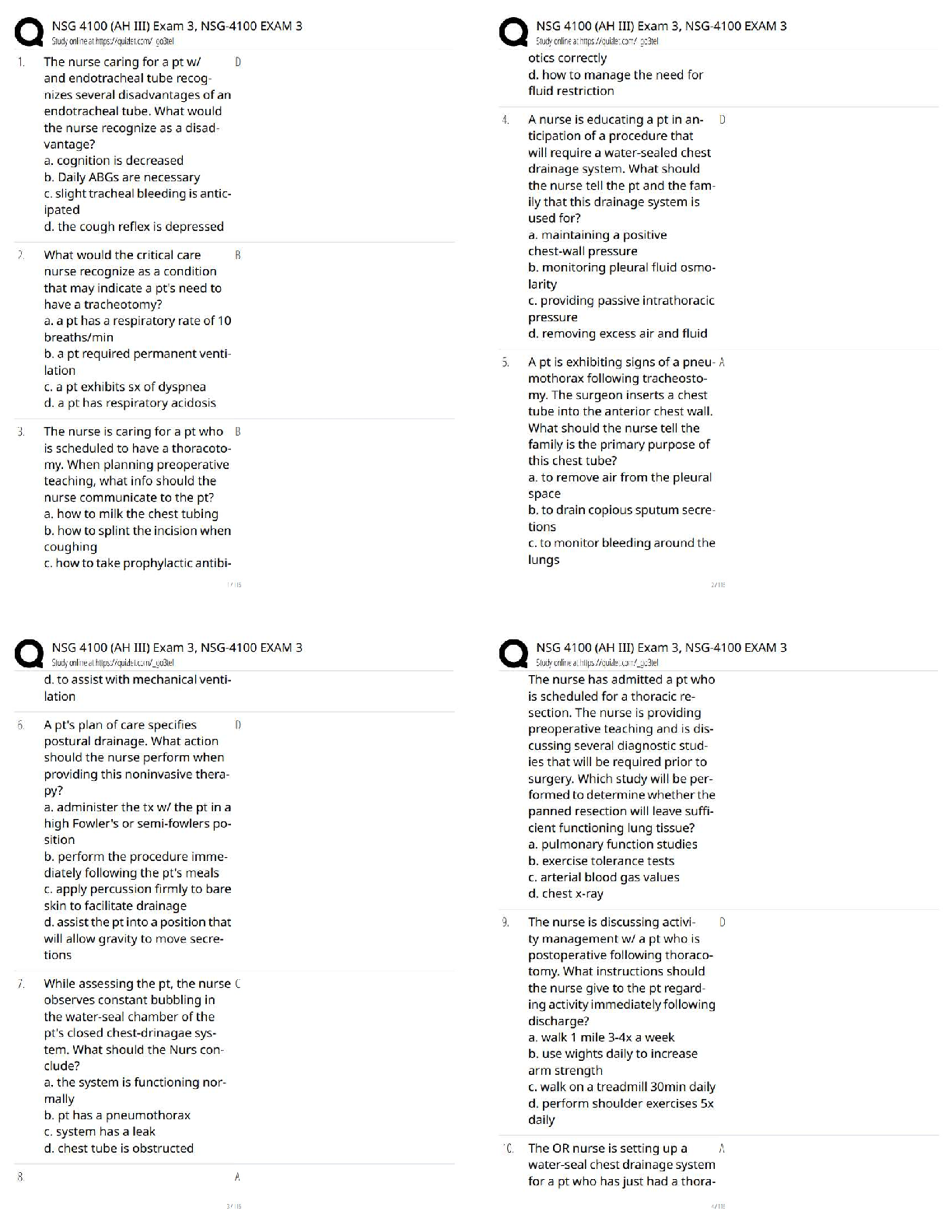
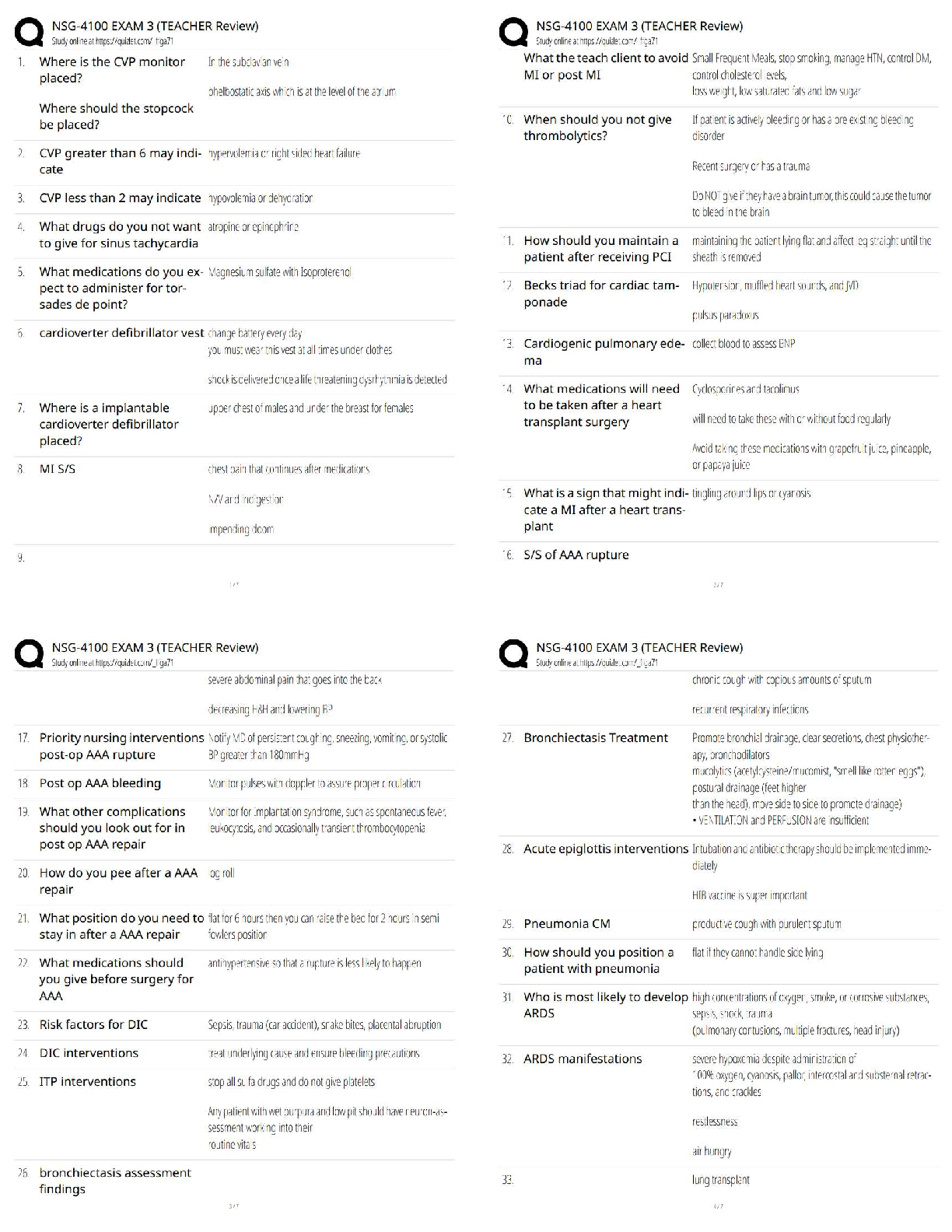
ABCs
A - airway
B - breathing
C – circulation
Uterine Leiomyoma
Benign, slow growing solid tumors of the muscle layer of the uterus (fibroids)
Excessive local growth of smooth muscle t
...
MDC3 Exam 1 Review
ABCs
A - airway
B - breathing
C – circulation
Uterine Leiomyoma
Benign, slow growing solid tumors of the muscle layer of the uterus (fibroids)
Excessive local growth of smooth muscle tissues
o Growth may be stimulated by estrogen, progesterone, and growth
hormone
Assessment: asymptomatic or symptomatic (heavy prolonged vaginal bleeding)**
Assess pelvic pressure, elimination pattern, abdomen size, dyspareunia,
infertility
Painful menses
Elimination patterns (due to enlarged fibroid pressing on organs)
Ask how many pads/tampons used in a day
S/S: Heavy periods or periods that last a long time & abd distention, urinary
frequency
Psychosocial assessment:
Quality of life from dyspareunia
Fear that symptoms could be cancerous
Anxiety
Significance of loss of uterus for patient and partner if want to conceive
Diagnostic assessment:
CBC – iron deficiency anemia from heavy bleeding
WBC would be normal
HGB and HCT – low
Pregnancy test to rule out uterine enlargement
Transvaginal US – able to see if fibroid is protruding into uterine cavity
Biopsy: gold standard
Pelvic exam
Planning and Implementation
Manage bleeding
o Non-surgical management: oral contraceptive**
o Surgical management:
MRI focused ultrasound-heat to tumor
Uterine artery embolization – starves tumor of circulation
allowing it to shrink
Myomectomy- laser removal
Hysterectomy
Erectile Dysfunction: causes & treatment
Common as one ages: reduced blood flow to penis
Causes
Medical causes: change in blood pressure
Non-organic: increased stressor, illnesses
Treatment
Medications that increase perfusion to penis (PDE- 5 inhibitors)
Vacuum pump
Pineal implant
Managing stress
Education related to treatment for HPV/Cervical Cancer
Caused by HPV
s/s of cervical cancer:
o heavy bleeding in later stages
o bleeding after sex
o Most of the time asymptomatic
Bleeding between periods
Preventive screening: PAP smear, surgical biopsy (gold standard) to determine
staging
Treatment:
Early- ablation, laser
Late- chemotherapy/radiation
Education:
No sticking anything up the vagina (tampons, douches)
May have bleeding
No sexual intercourse
No tub baths
Breast cancer- preventative screenings, risk factors, diagnostic tests
Preventative screenings
Mammography
o Recommended to start screening at 45
o Women over 55 may switch to every 2 years
Breast self-awareness/self-examinations
o >90% detected by patient
Clinical breast clinical
o At least every 3 years for women in their 20s and 30s and every year for
asymptomatic women at least 40 years old
Risk Factors
Increased age
Family history
Early menarche, late menopause
Lack of breastfeeding
Postmenopausal obesity
Alcohol consumption
Mutations in BRCA1 or BRCA2
Diagnostic tests
Lab assessment: study of breast mass tissue and lymph nodes, liver enzymes,
calcium, and alkaline phosphatase
Imaging assessment:
o Mammogram
o Ultrasound
o MRI
o Chest x-ray, CT for metastasis
o Breast biopsy*
Endometrial cancer- symptoms, risk factors, diagnostic testing
Most common gynecologic malignancy
Cancer of inner uterine lining
Grows slowly but vaginal bleeding usually leads to prompt evaluation and
treatment = good prognosis
Most commonly associated with prolonged exposure to estrogen without its
protective effects of progesterone
Risk Factors:
Women in reproductive years
Family History
Diabetes Mellitus
HTN
Obesity
Uterine polyps
Late menopause
Nulliparity (no childbirths)
Smoking
Tamoxifen – given for breast cancer
Symptoms:
Postmenopausal bleeding (how many pads/tampons a day)**
Watery, bloody vaginal discharge
Low back or abdominal pain
Low pelvic impaired comfort (describe exact location and intensity)
Pelvic exam may reveal palpable uterine mass**
Diagnostic testing:
o Transvaginal ultrasound*
o Endometrial biopsy – gold standard “determine presence of endometrial
thickening/cancer”**
Interventions
o Pelvic exam
Hysterectomies- what they are, who gets th
[Show More]