PANCE Practice Exam Questions
COMPLETE SOLUTION
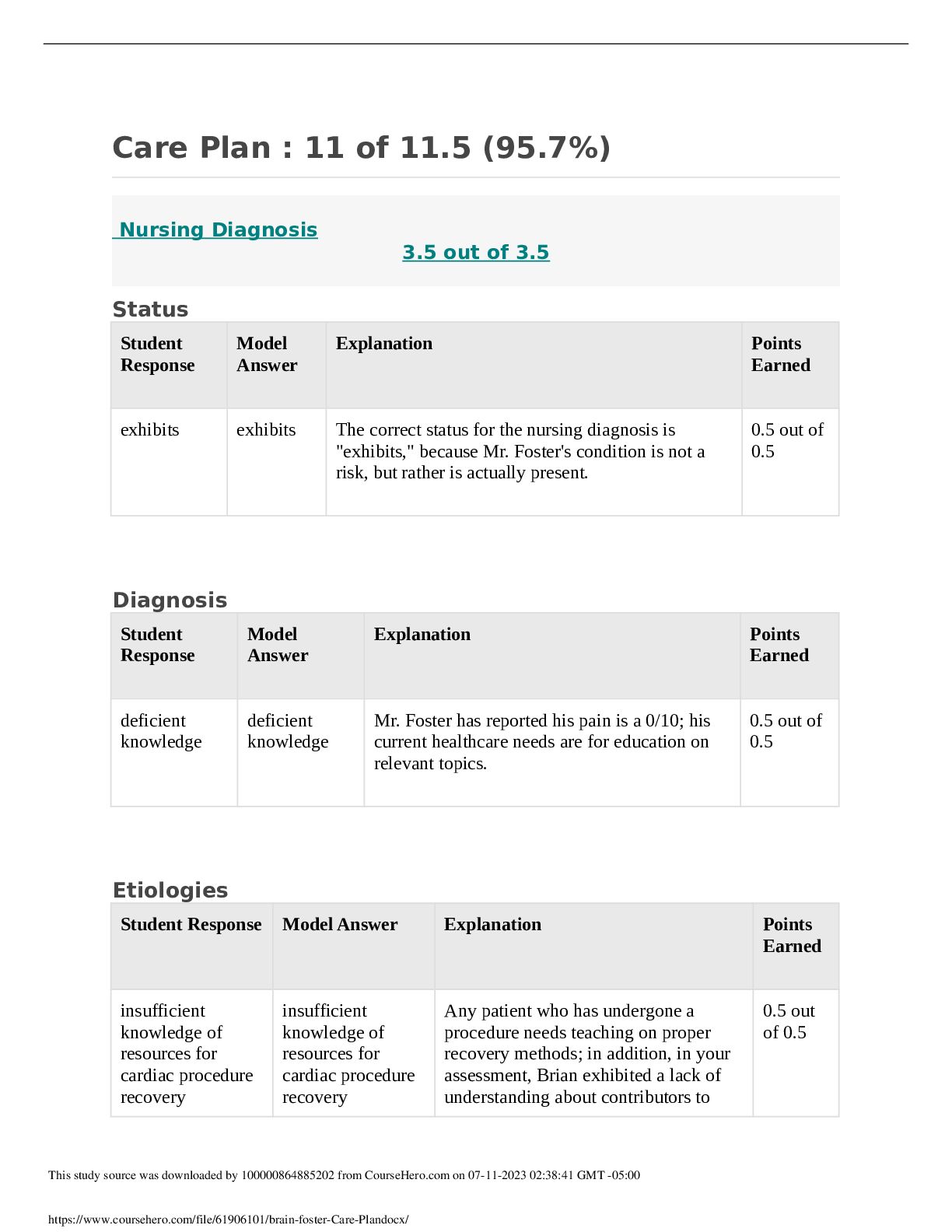
D. ALS - ✔✔A 58 year-old male presents complaining of weakness of his grip. Your examination reveals
that the problem is bilateral. During the next few office visits, yo
...
PANCE Practice Exam Questions
COMPLETE SOLUTION
D. ALS - ✔✔A 58 year-old male presents complaining of weakness of his grip. Your examination reveals
that the problem is bilateral. During the next few office visits, you note the development of
hyperactivity of his DTRs, extensor plantar reflexes and dysarthria. The patient's sensory system remains
normal and he denies any urinary symptomatology. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A. multiple sclerosis
B. Alzheimer's disease
C. Huntington's chorea
D. ALS
E. myasthenia gravis
C. inadequate dietary protein
Low dietary Calcium, not protein, is a risk factor for osteoporosis. All of the others are risk factors. -
✔✔Which of the following is NOT a risk factor for the development of osteoporosis?
A. low testosterone levels in men
B. low levels of physical activity
C. inadequate dietary protein
D. cigarette smoking
E. chronic corticosteroid use
B. metoprolol
Of these Beta-blockers (which are usually AVOIDED) in reactive airway disease - metoprolol is the most
"cardioselective", so theoretically could be used....although, on an exam, I would avoid beta-blockers in
general. - ✔✔Question 1 CORRECT
A patient presents complaining of severe pain and "burning" in an extremity. You note that the
extremity is pale and cool to the touch. You cannot appreciate a palpable pulsation. Which of the
following diagnostic modalities will identify the source of this patient's problem in approximately 95% of
cases?
A chest x-ray
B echocardiogram
aortic angiogram
D abdominal flat plate
E aortic ultrasound
Question 1 Explanation: Angiogram is the "gold standard" for occlusion of an arterial vessel.
Question 2 CORRECT
A 31 year-old pharmacist complaining of rectal pain. He describes the pain as "a severe tightness that
awakens him from sleep." His bowel activity is normal. He denies rectal bleeding and seepage. He adds
that sleep interruption is problematic, because with the number of hours he works, every minute of
sleep is important. What is the most likely diagnosis?
A anal abseess
B perianal fistula
proctalgia fugax
D ulcerative colitis
E internal hemorrhoids.
Question 2 Explanation: proctalgia (rectal pain) fugax (comes and goes) is the best description. Abscess
would be constant, fistula would drain, UC would cause bloody mucousy diarrhea, hemorrhoids would
cause no pain, but bleeding.
Question 3 CORRECT
A 38 year-old chronic smoker presents with shortness of breath and wheezing. He has had several
similar episodes in the past. He states that each previous episode began after developing a "cold that
moved into his chest." Usually, after treatment with albuterol (VENTOLIN) and several days, the
wheezing stops. He adds that he has a chronic cough, productive of mucous, most mornings during the
past several years. Which of the following best describes this patient's condition?
A chronic emphysema
B chronic bronchitis
chronic bronchitis with hypersensitive airways (asthmatic bronchitis)
D cor pulmonale
E bronchiectasis
Question 3 Explanation: This is the best descriptor.
Question 4 CORRECT
A patient is being treated for Tuberculosis. She is experiencing central scotomata, a loss of green-red
color perception and decreased visual acuity. Which agent is most likely responsible?
A rifampin
B isoniazid
C streptomycin
ethambutol
E para-aminosalicylic acid
Question 4 Explanation: Ethambutol is the TB drug that causes "E"ye symptoms. I remember it because
it begins with an E.
Question 5 CORRECT
Secondary to a traumatic event, a child complains of pain in the index finger. An x-ray of the digit
demonstrates a fracture line through the metaphysis of the proximal aspect of the middle phalanx,
ending at the epiphyseal plate. What type of fracture does this child have?
A Salter Harris Type I
Salter Harris Type II
C Salter Harris Type III
D Salter Harris Type IV
E Salter Harris Type V
Question 5 Explanation: Salter I = slight increase in Space between epiphyseal plate and metaphysis
Salter II = fx Above the plate (in the metaphysis) Salter III = fx Lower (in the epiphyseal plate) Salter IV =
fit Through (both the metaphysic and epiphysis) Salter V = Really bad (comminuted fx compressing the
epiphysis) This spells SALTR and may help you remember. 7365546_orig About Jorge Muniz PA-C
(Creator of Medcomic)
Question 6 CORRECT
A 24 year-old male presents complaining of chest pain. He states that it is worse with swallowing and
taking a deep breath. It is improved by sitting up and leaning forward. He denies trauma, a cough and
shortness of breath. Which of the following tests would be most compatible with your suspected
diagnosis?
A a hiatal hernia visualized on chest x-ray
B a normal erythrocyte sedimentation rate
C calcified "popcorn" lesions in the lung fields bilaterally
diffuse ST segment elevation on his electrocardiograph
E a widened A-a gradient on his arterial blood gas
Question 6 Explanation: This is pericarditis (by clinical presentation) which causes diffuse ST segment
elevation on ECG (there can be notching of the R wave as well)
Question 7 CORRECT
A 2 month-old febrile male is brought to your facility to be evaluated for loss of appetite, irritability, and
an acute petechial rash. Rectal temperature is 102.8F. Which of the following diagnostic studies is the
most important in this child's evaluation?
A white blood cell count and differential
B urinalysis
CSF analysis
D serum glucose
E chest X-ray (CXR)
Question 7 Explanation: Any infant (neonate) with fever and rash should have a lumbar puncture (LP).
While I would certainly do a CBC, even if it was normal, I would want the LP.
Question 8 CORRECT
Your 27 year-old sister is visiting and requests you to provide refills of dexamethasone and homatropine
ophthalmic drops for her. What condition is most likely being treated?
A conjunctivitis
B glaucoma
iritis
D Herpes keratitis
E blepharitis
Question 8 Explanation: Iritis is treated with steroid drops (dexamethasone) and miotic drops
*homatropine, like atropine (to constrict and fix the pupil to help the pain and open the angle until the
iritis is resolved)
Question 9 PARTIAL-CREDIT
A 58 year-old male presents complaining of weakness of his grip. Your examination reveals that the
problem is bilateral. During the next few office visits, you note the development of hyperactivity of his
DTRs, extensor plantar reflexes and dysarthria. The patient's sensory system remains normal and he
denies any urinary symptomatology. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
A multiple sclerosis
B Alzheimer's disease
Huntington's choreaHint: Huntington's causes a movement disorder with writhing choreiform
movements of the body
amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
E myasthenia gravisHint: Myasthenia causes fatigue of the ocular muscles typically worsening at the end
of the day.
Question 9 Explanation: ALS (Lou Gehrig's disease) is a progressive bilateral muscle disease which causes
fasciculations (lower motor neuron), and hyper-reflexia, plantar reflexes (upper motor neuron) and
dysarthria. Sensation is normal as is bladder function. MS may have dysarthria, but reflexes are normal,
sensation is impaired and bladder function is frequently affected. Alzheimer's has normal neuro exam
with cognitive disability. Huntington's causes a movement disorder with writhing choreiform
movements of the body. Myasthenia causes fatigue of the ocular muscles typically worsening at the end
of the day.
Question 10 CORRECT
Which of the following is NOT a characteristic feature of multiple myeloma?
A elevated serum calcium
B osteoporosis
C "punched out" osseous lesions
D plasma cell infiltration of bone marrow
hypogammaglobulinemia
Question 10 Explanation: MM is a HYPERgammaglobulinemia - all of the other findings occur in MM.
Question 11 PARTIAL-CREDIT
Which of the following is NOT a risk factor f
[Show More]


 (1).png)