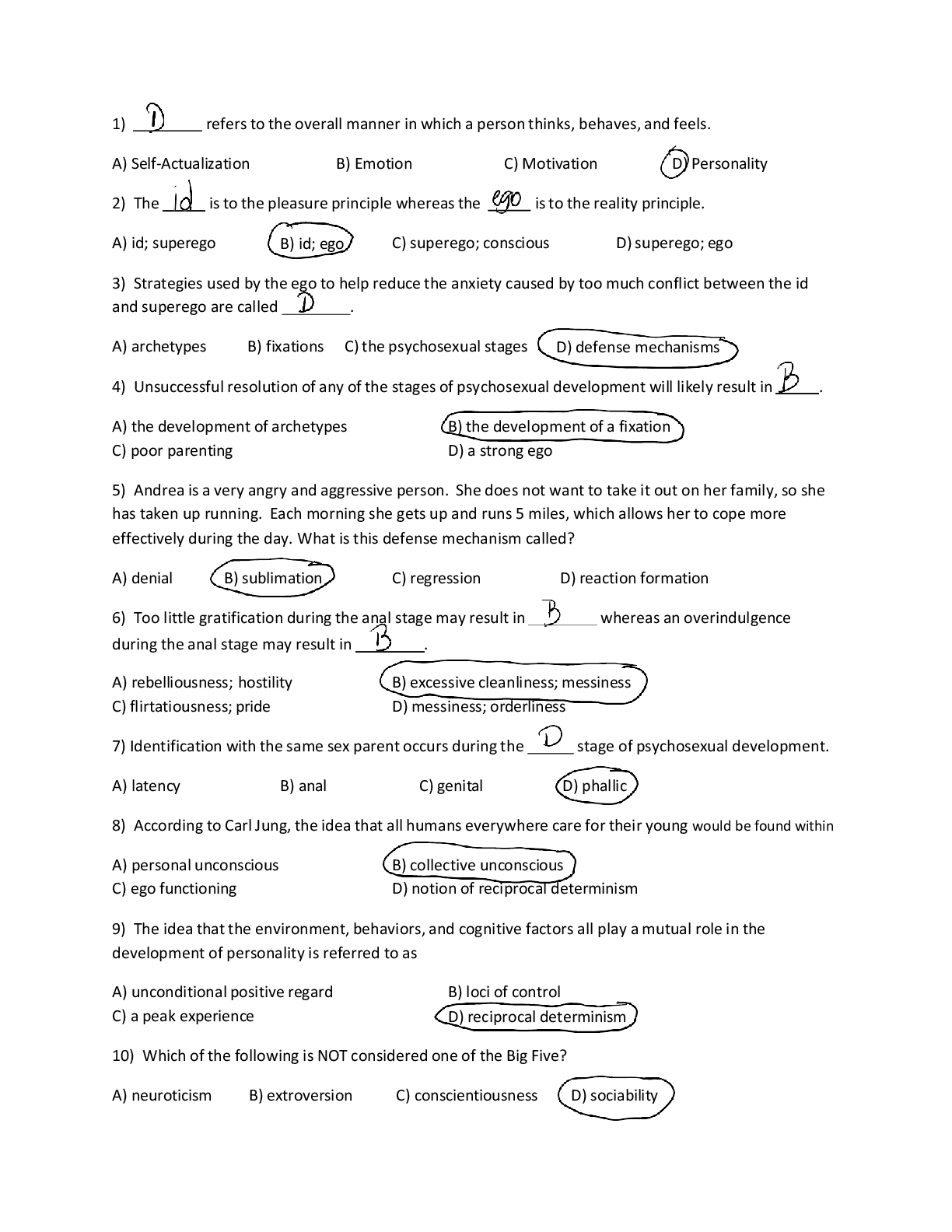
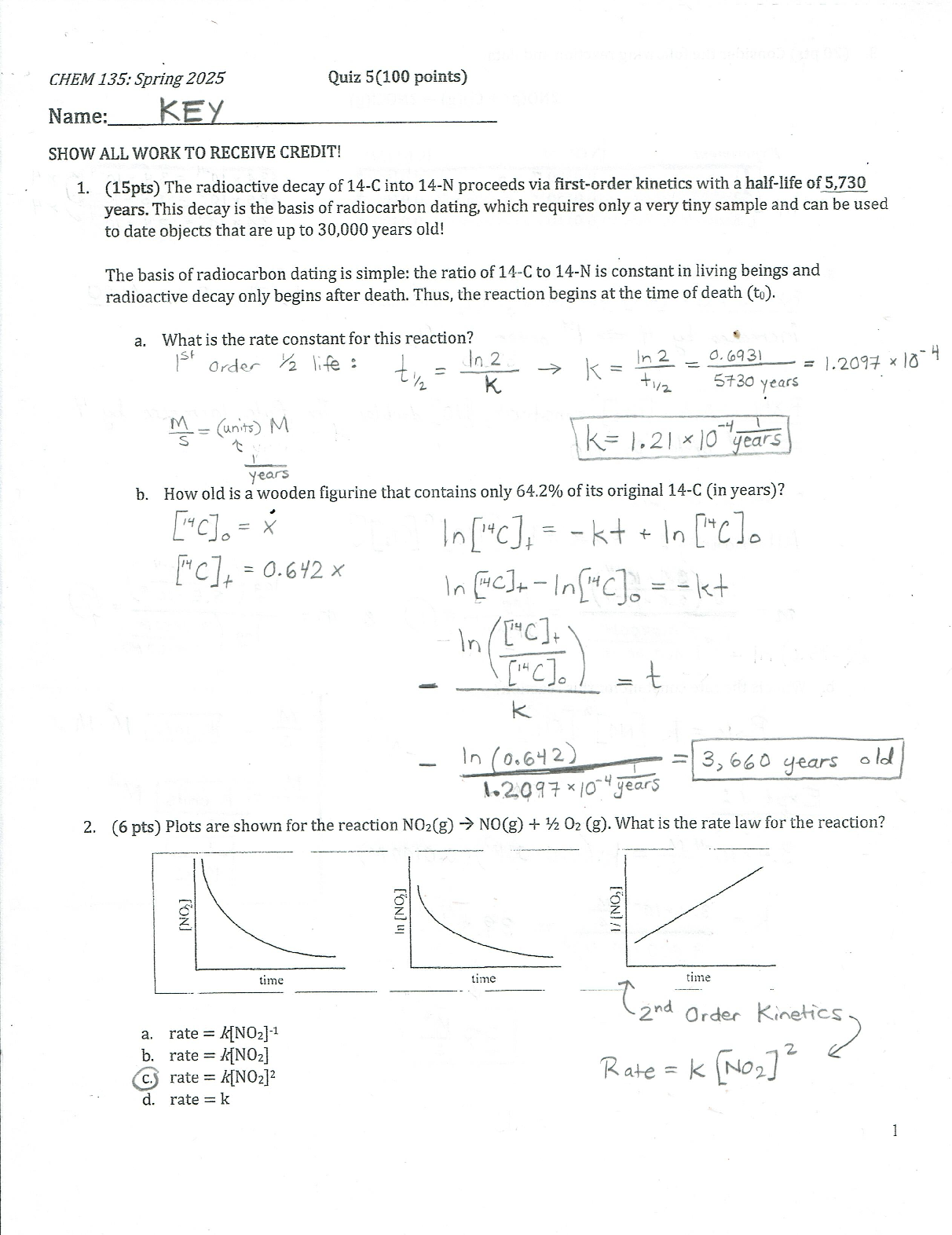
NURSING 6521N-51 - PHARM MIDTERM
Document Content and Description Below
Chapter 1: Prescriptive Authority
1. An APRN works in a urology clinic under the supervision of a physician who does not restrict the types of medications the APRN is allowed to prescribe. State law does not require th
...
Chapter 1: Prescriptive Authority
1. An APRN works in a urology clinic under the supervision of a physician who does not restrict the types of medications the APRN is allowed to prescribe. State law does not require the APRN to practice under physician supervision. How would the APRN’s prescriptive authority be described?
1. Which factors increase the need for APRNs to have full prescriptive authority?
Which factors could be attributed to limited prescriptive authority for APRNs? Select all that apply
2. Which aspects support the APRN’s provision for full prescriptive authority? Select all that apply.
3. Which aspects support the APRN’s provision for full prescriptive authority? Select all that apply.
4. A family nurse practitioner practicing in Maine is hired at a practice across state lines in Virginia. Which aspect of practice may change for the APRN?
Chapter 2: Rational Drug Selection and Prescription Writing
5. How can collaboration with a pharmacist improve positive outcomes for patients? Select all that apply.
6. A patient presents with delirium tremens requiring Ativan administration. The provider of care is not in the facility. Which action by the nurse is most appropriate?
7. A patient with chronic pain calls the provider’s office to request a refill on their oxycontin. Which action is most appropriate?
8. A patient prescribed amoxicillin for streptococcal pharyngitis reports new onset of a flat, itchy red rash on the chest and neck. Which action is most important?
9. A patient taking three medications for hypertension is diagnosed with COPD. Which action should be taken prior to prescribing medications to treat COPD?
10. A patient with diabetes reports losing their job and an inability to purchase required medications. Which action is most appropriate?
11. A patient recently prescribed hydrocodone calls to report they are unable to fill the prescription. Which factors could contribute to the inability to fill the prescription?
Select all that apply.
Chapter 3: Promoting Positive Outcomes of Drug Therapy
12. A patient reports that a medication prescribed for recurrent migraine headaches is not working. Which action should be taken first?
13. A patient is prescribed metronidazole for bacterial vaginosis. Which patient history finding would be most concerning?
14. A patient is using a metered-dose inhaler containing albuterol for asthma. The medication label instructs the patient to administer “two puffs every 4 hours as needed for coughing or wheezing.” The patient reports feeling jittery sometimes when taking the medication, and she doesn’t feel that the medication is always effective. Which action is most appropriate?
15. A patient newly diagnosed with diabetes is to be discharged from the hospital. Which action should be taken first during medication education?
16. The drug manual states that older adult patients are at increased risk for hepatic side effects. Which action is most important when prescribing this medication to an 80-year-old patient?
17. A patient recently diagnosed with HIV is prescribed several medications to treat the condition. Which factors could impact the patient’s adherence to the treatment regimen?
Select all that apply.
18. A patient diagnosed with bipolar disorder is prescribed daily lithium. Which action is most important to determine if the therapeutic level is maintained?
Chapter 4: Pharmacokinetics, Pharmacodynamics, and Drug Interactions
19. The nurse administers naloxone [Narcan] to a patient who has received a toxic dose of morphine sulfate. The nurse understands that the naloxone is effective because of which action?
20. A patient is taking drug X and receives a new prescription for drug Y, which is listed as an inducing agent. The nurse caring for this patient understands that this patient may require doses of drug
21. The nurse is preparing to administer penicillin G intramuscularly to a child. The child’s parents ask why the drug cannot be given in an oral liquid form. What is the nurse’s reply?
22. Which statement about food and drug interactions is true?
23. A nurse is teaching a patient about a drug that induces P-glycoprotein. The nurse will explain that this drug may cause which effect on other drugs?
24. A patient claims to get better effects with a tablet of Brand X of a drug than with a tablet of Brand Y of the same drug. Both brands contain the same amount of the active ingredient. What does the nurse know to be most likely?
25. Two nurses are discussing theories of drug-receptor interaction. Which statements are true regarding the affinity of a drug and its receptor?
Select all that apply.
26. A patient receives a drug that has a narrow therapeutic range. The nurse administering this medication will expect to do what?
27. What occurs when a drug binds to a receptor in the body?
28. A patient is receiving intravenous gentamicin. A serum drug test reveals toxic levels. The dosing is correct, and this medication has been tolerated by this patient in the past. Which could be a probable cause of the test result?
29. A patient reports becoming “immune” to a medication because it no longer works to alleviate symptoms. The nurse recognizes that this decreased effectiveness is likely caused by:
30. A patient who is taking morphine for pain asks the nurse how a pain medication can also cause constipation. What does the nurse know about morphine?
31. The nurse is administering morning medications. The nurse gives a patient multiple medications, two of which compete for plasma albumin receptor sites. As a result of this concurrent administration, the nurse can anticipate that what might occur?
Select all that apply.
32. When administering medications to infants, it is important to remember which of the following?
Select all that apply.
Chapter 5: Adverse Drug Reactions and Medication Errors
33. A nursing student is preparing to give a medication that has a boxed warning. The student asksthe nurse what this means. What will the nurse explain about boxed warnings?
34. A nurse is preparing to administer a drug. Upon reading the medication guide, the nurse notes that the drug has been linked to symptoms of Parkinson disease in some patients. What will the nurse do?
35. Which patients are at increased risk for adverse drug events? Select all that apply.
36. A nurse provides teaching to a patient who will begin taking a drug with a known risk of hepatotoxicity. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
37. A nurse is reviewing a medication administration record before administering medications. Which order will the nurse implement?
38. A patient is given a new medication and reports nausea within an hour after taking the drug. The nurse consults the drug information manual and learns that nausea is not an expected adverse effect of this drug. When the next dose is due, what will the nurse do?
39. A nurse is preparing to give an antibiotic to a patient who reports being allergic to antibiotics. Before giving the medication, what will the nurse do first?
40. A patient is taking sertraline [Zoloft] for depression, and the provider orders azithromycin [Zithromax] to treat an infection. What will the nurse do?
41. A patient is given a drug for the first time and develops shortness of breath. The patient’s heart rate is 76 beats/minute, the respiratory rate is 20 breaths/minute, and the blood pressure is 120/70 mm Hg. The nurse checks a drug administration manual to make sure the correct dose was given and learns that some patients taking the drug experience shortness of breath. The nurse will contact the provider to report what?
42. Which are effective ways to help prevent medication errors? Select all that apply.
43. A patient is taking a drug that has known toxic side effects. What will the nurse do?
44. A patient is being discharged after surgery. During the admission history, the nurse learned that the patient normally consumes two or three glasses of wine each day. The prescriber has ordered hydrocodone with acetaminophen [Lortab] for pain. What will the nurse do?
45. Which actions occur in 90% of fatal medication errors? Select all that apply.
Chapter 6: Individual Variation in Drug Responses
46. A nurse is caring for a woman with breast cancer who is receiving tamoxifen. A review of this patient’s chart reveals a deficiency of the CYP2D6 gene. The nurse will contact the provider to suggest:
47. Which groups of people are especially sensitive to medication effects? Select all that apply.
48. A post-operative patient who is worried about pain control will be discharged several days after surgery. The nurse providing discharge teaching tells the patient that the prescribed Lortab is not as strong as the morphine the patient was given in the immediate post-operative period. Which response is the patient likely to experience?
49. A patient has been taking narcotic analgesics for chronic pain for several months. The nurse caring for this patient notes that the prescribed dose is higher than the recommended dose. The patient has normal vital signs, is awake and alert, and reports mild pain. What does the nurse recognize about this patient?
50. A patient asks a nurse why a friend who is taking the same drug responds differently to that drug. The nurse knows that the most common variation in drug response is due to differences in each patient’s:
51. The nurse is assessing a newly admitted older patient who has recently lost 15 pounds. The nurse notes that the patient is taking warfarin (Coumadin). Which laboratory tests will the nurse discuss with this patient’s provider?
52. A nurse is preparing to care for a patient who is receiving digoxin. When screening for potential adverse effects from this drug, the nurse will review which of this patient’s laboratory results?
53. A nurse administers the same medication in the same preparation in the same dose to several patients and notes that some patients have a better response to the drug than others. What is the most likely explanation for this phenomenon?
54. A nurse is teaching a group of women about medications. The women want to know why so many drugs have unpredictable effects in women. The nurse will tell them that:
55. The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) recommends genetic testing of patients receiving certain medications. Genetic testing helps prescribers:
Chapter 10: Basic Principles of Neuropharmacology
1. A nursing student asks about drugs that interfere with the termination of transmitter action. Which statement by the nurse is correct?
2. A nurse is teaching a group of nursing students about neuropharmacology. Which statement by a student about peripheral nervous system (PNS) drugs indicates a need for further teaching?
3. A nurse is preparing to administer a medication and learns that it is a nonselective agonist drug. What does the nurse understand about this drug?
4. A patient has allergies and takes an antihistamine. The patient wants to know how the drug works. The nurse understands that antihistamines work because they are what?
5. A patient receiving botulinum toxin injections to control muscle spasticity asks how the drug works. The nurse knows that this drug affects the transmitter acetylcholine by:
6. A nurse is administering drug X to a patient. The drug information states that the drug acts by activating receptors in the peripheral nervous system by increasing transmitter synthesis. The nurse understands that the effect of this drug is to:
7. A patient receives morphine and shows signs of toxicity. The prescriber orders naloxone [Narcan] to reverse the effects of the morphine. The nurse understands that the naloxone reverses morphine toxicity by which action on morphine receptor sites?
8. A nurse learns about a drug that interferes with transmitter storage in the PNS. The transmitter affected by this drug causes an increased heart rate. What response will the nurse expect to see when this drug is administered?
Chapter 11: Physiology of the Peripheral Nervous System
9. What is the target organ when a beta1 agonist is administered?
10. A nurse is teaching a group of nursing students about neurotransmitters. Which statement by a student about acetylcholine indicates a need for further teaching?
11. A nurse is administering an agonist drug that acts on postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system. Which response will the nurse expect to see?
12. A nurse is teaching a patient about a medication that alters sympathetic nervous system functions. To evaluate understanding, the nurse asks the patient to describe which functions the sympathetic nervous system regulates. Which answer indicates the need for further teaching?
13. A patient is wheezing and short of breath. The nurse assesses a heart rate of 88 beats/minute, a respiratory rate of 24 breaths/minute, and a blood pressure of 124/78 mm Hg. The prescriber orders a nonspecific beta agonist medication. Besides evaluating the patient for a reduction in respiratory distress, the nurse will monitor for which side effect?
14. Many medications list side effects that include dry mouth, constipation, and urinary retention. What kinds of effects are these?
15. A patient is to receive a beta agonist. Before administration of this medication, which assessment finding would most concern the nurse?
16. A nurse is explaining activation of beta2 receptors to nursing students during a clinical rotation at the hospital. Which statement by a student demonstrates a need for further teaching?
17. A pregnant patient is in premature labor. Which class of drug will she be given?
Chapter 12: Muscarinic Agonists and Antagonists
18. A prescriber has ordered bethanechol [Urecholine] for a postoperative patient who has urinary retention. The nurse reviews the patient’s chart before giving the drug. Which part of the patient’s history would be a contraindication to using this drug?
19. Bethanechol [Urecholine] is used to treat urinary retention but is being investigated for use in which other condition?
20. An older adult patient who lives alone and is somewhat forgetful has an overactive bladder (OAB) and reports occasional constipation. The patient has tried behavioral therapy to treat the OAB without adequate results. Which treatment will the nurse anticipate for this patient?
21. A nurse is helping a nursing student who is administering a medication to a patient with myasthenia gravis. Which statement by the student indicates the need for further teaching?
22. A patient is experiencing toxic side effects from atropine, including delirium and hallucinations. Which medication will the nurse expect to administer?
23. A prescriber has ordered pilocarpine [Pilocar]. A nurse understands that the drug stimulates muscarinic receptors and would expect the drug to have which action?
24. A nurse is caring for a patient who has myasthenia gravis. The prescriber has ordered neostigmine [Prostigmin]. An important initial nursing action before administration of the medication includes assessing:
25. A patient who has myasthenia gravis will be taking neostigmine [Prostigmin]. What will the nurse emphasize when teaching this patient about the medication?
26. A patient who has esophageal cancer is experiencing dry mouth and the provider orders oral pilocarpine to treat this symptom. What will the nurse expect to teach this patient about this medication?
Chapter 13: Adrenergic Agonists
27. A nursing student asks the nurse about receptor specificity of adrenergic agonist medications. What will the nurse say?
28. A nurse is teaching parents how to use an Epi-Pen for their child, who has a peanut allergy. Which statement by the parents indicates understanding of the teaching?
29. A nursing student asks the nurse why epinephrine, and not other adrenergic agonists, is used to treat anaphylactic shock. What will the nurse tell the student?
30. Dopamine is administered to a patient who has been experiencing hypotensive episodes. Other than an increase in blood pressure, which indicator would the nurse use to evaluate a successful response?
31. A nursing student asks why albuterol, which is selective for beta2 receptors, causes an increased heart rate in some patients. How should the nurse respond?
32. Because they cause vasoconstriction, alpha1-adrenergic agonists are especially useful for:
33. A nurse is teaching a nursing student about the two classes of adrenergic agonist drugs. Which statement by the nursing student indicates understanding of the teaching?
34. A patient with asthma uses albuterol [Ventolin] for wheezing. The nurse assesses the patient and notes vital signs of HR, 96 beats/minute; RR, 18 breaths/minute; and BP, 116/78 mm Hg. The patient has clear breath sounds and hand tremors. What will the nurse do?
35. A nurse is administering intravenous dopamine [Intropin] to a patient in the intensive care unit. Which assessment finding would cause the most concern?
36. A patient is receiving dobutamine [Dobutrex] as a continuous infusion in the immediate postoperative period. The patient also is receiving a diuretic. What adverse drug reactions are possible in this patient?
Select all that apply.
37. A patient brought to the emergency department requires sutures. The prescriber orders a local anesthetic with epinephrine. The nurse understands that epinephrine is ordered to:
38. A patient is admitted to the intensive care unit for treatment of shock. The prescriber orders isoproterenol [Isuprel]. The nurse expects this drug to increase tissue perfusion in this patient by activating:
Chapter 14: Adrenergic Antagonists
39. A patient with pheochromocytoma is admitted for surgery. The surgeon has ordered an alpha- blocking agent to be given preoperatively. What does the nurse understand about this agent?
40. A patient with type 1 diabetes is taking NPH insulin, 30 units every day. A nurse notes that the patient is also taking metoprolol [Lopressor]. What education should the nurse provide to the patient?
41. A nurse is caring for a newborn 1 day after delivery. The infant’s mother used betaxolol during pregnancy. The nurse will expect to monitor this infant for which condition?
42. A patient with migraines is started on a beta blocker. The nurse explains the benefits of taking the medication for migraines. Which statement by the patient indicates an understanding of the medication’s effects?
43. A nurse is discussing phentolamine [OraVerse] with a nursing student. Which statement by the student indicates the need for further teaching?
44. The nurse assesses a patient who has been given phentolamine [OraVerse] to treat pheochromocytoma. The nurse notes a blood pressure of 76/52 mm Hg and a heart rate of 90 beats/minute. Which action by the nurse is correct?
45. Which are conditions that may be treated using beta blockers? Select all that apply.
46. Which are adverse effects of alpha blockade? Select all that apply.
47. The nurse is discussing home management with a patient who will begin taking an alpha- adrenergic antagonist for hypertension. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
48. A nurse is teaching nursing students about the use of alpha-adrenergic antagonists. Which statement by a student indicates the need for further teaching?
49. A patient taking a beta blocker complains of shortness of breath. The patient has respirations of 28 breaths/minute, a blood pressure of 162/90 mm Hg, and a pulse of 88 beats/minute. The nurse auscultates crackles in all lung fields. The nurse understands that these assessments are consistent with:
50. A male patient is being treated for benign prostatic hyperplasia and has stopped taking his alpha-adrenergic antagonist medication because of ejaculatory difficulties. Which medication does the nurse expect the provider to prescribe?
A patient is taking a beta-adrenergic antagonist medication for angina pectoris and asks the nurse how the drug works to relieve the discomfort associated with this condition. Which statement by the patient after the nurse’s teaching indicates understanding of the drug’s effects?
51. A nurse prepares to administer propranolol [Inderal] to a patient recovering from acute myocardial infarction. The patient’s heart rate is 52 beats/minute, and the rhythm is regular. What action should the nurse take next?
52. A patient will begin taking propranolol [Inderal] for hypertension. Which statement by the nurse is important when teaching this patient about the medication?
Chapter 15: Indirect-Acting Antiadrenergic Agents
53. A patient who has been taking clonidine [Catapres] for several weeks complains of drowsiness and constipation. What will the nurse do?
54. A prescriber has ordered methyldopa for a patient with hypertension. The nurse teaches the patient about drug actions, adverse effects, and the ongoing blood tests necessary with this drug. The nurse is correct to tell the patient what?
55. A prescriber has ordered clonidine [Catapres] for a patient who has hypertension. The nurse teaches the patient about side effects of this drug. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
56. A prescriber has ordered methyldopa for a female patient with hypertension. The nurse understands that which laboratory tests are important before beginning therapy with this drug? Select all that apply.
57. A nurse is teaching nursing students about the pharmacology of methyldopa. Which statement by a student indicates the need for further teaching?
58. A patient complains to the nurse that the clonidine [Catapres] recently prescribed for hypertension is causing drowsiness. Which response by the nurse to this concern is appropriate?
59. A prescriber orders clonidine [Kapvay] ER tablets for a 12-year-old child. The nurse understands that this drug is being given to treat which condition?
60. A patient with hypertension has a previous history of opioid dependence. Which medication would the nurse question?
61. Clonidine is approved for the treatment of which conditions? Select all that apply.
62. A prescriber orders transdermal clonidine [Catapres TTS] for a patient with hypertension. What will the nurse teach this patient?
63. A nurse is teaching a patient about a new prescription for reserpine [Serpasil] for hypertension. Which statement by the patient indicates the need for further teaching?
Chapter 16: Introduction to Central Nervous System Pharmacology
64. An infant who receives a drug that does not produce CNS side effects in adults exhibits drowsiness and sedation. The nurse understands that this is because of differences in which physiologic system in infants and adults?
65. Which monoamines act as neurotransmitters in the central nervous system? Select all that apply.
66. A patient asks a nurse to explain what drug tolerance means. The nurse responds by telling the patient that when tolerance occurs, it means the patient:
67. A group of nursing students asks a nurse to explain the blood-brain barrier. The nurse would be correct to say that the blood-brain barrier:
68. A nurse is teaching a group of students about how CNS drugs are developed. Which statement by a student indicates a need for further teaching?
69. A nurse is teaching a group of nursing students how the CNS adapts to psychotherapeutic medications. Which statement by a nursing student indicates a need for further teaching?
70. A psychiatric nurse is teaching a patient about an antidepressant medication. The nurse tells the patient that therapeutic effects may not occur for several weeks. The nurse understands that this is likely the result of:
71. Which are medical applications of central nervous system drugs? Select all that apply.
Chapter 17: Drugs for Parkinson's Disease
72. A nursing student wants to know how carbidopa can be effective for treating Parkinson disease if it prevents the conversion of levodopa to dopamine. The nurse explains that carbidopa:
73. A 25-year-old patient has been newly diagnosed with Parkinson disease, and the prescriber is considering using pramipexole [Mirapex]. Before beginning therapy with this drug, the nurse will ask the patient about:
74. A patient with Parkinson disease is taking levodopa/carbidopa [Sinemet] and reports occasional periods of loss of drug effect lasting from minutes to several hours. The nurse questions the patient further and discovers that these episodes occur at different times related to the medication administration. The nurse will contact the provider to discuss:
75. A nurse is discussing motor symptoms with a patient with Parkinson disease who has been taking levodopa/carbidopa [Sinemet] for 9 months and who is now having regular tics. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of this symptom?
76. A hospitalized patient with Parkinson disease who is receiving apomorphine to treat “off” episodes develops nausea and vomiting. The nurse will discuss the use of which medication with the patient’s provider?
77. A patient has been diagnosed with Parkinson disease (PD) and begins treatment with levodopa/carbidopa [Sinemet]. After several months of therapy, the patient reports no change in symptoms. The nurse will expect the provider to:
78. A nursing student wants to know why a patient who has been taking levodopa [Dopar] for years will now receive levodopa/carbidopa [Sinemet]. The nurse explains the reasons that levodopa as a single agent is no longer available. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further education?
79. A patient has taken levodopa [Dopar] for Parkinson disease for 2 weeks but reports no improvement in the symptoms. Which response by the nurse is correct?
80. A patient with Parkinson disease is taking levodopa/carbidopa [Sinemet]. The prescriber orders bromocriptine [Parlodel] to treat dyskinesias. The nurse notes that the patient is agitated, and the patient reports having frequent nightmares. The nurse will contact the provider to discuss:
81. A nurse is teaching a group of nurses about Parkinson medications. The nurse is correct to state that one side effect associated with pramipexole [Mirapex] that is less likely to occur with other dopamine agonists is:
Chapter 18: Drugs for Alzheimer's Disease
82. A nurse is caring for an older adult man who has Alzheimer disease (AD). The patient’s daughter wants to know if testing can be done to determine her risk for developing the disease. What will the nurse tell her?
83. A patient will begin taking a cholinesterase inhibitor for early Alzheimer disease. The nurse is teaching the patient’s spouse about the medication. Which statement by the spouse indicates a need for further teaching?
84. The spouse of a patient who is newly diagnosed with Alzheimer disease asks the nurse if medications will prevent the need for nursing home care. Which response by the nurse is correct?
85. A nurse is caring for an older adult patient who has Alzheimer disease. The patient is taking a cholinesterase inhibitor drug. Which side effects would concern the nurse?
86. An older adult patient with Alzheimer disease is admitted to the hospital. The patient’s spouse reports that the patient is often confused and gets lost walking to the store, which is three blocks from their home. That evening, the nurse observes the patient pacing the hall and screaming. What will the nurse do?
87. A nurse is preparing to administer memantine [Nemanda] to a patient and notes a slight elevation in the patient’s creatinine clearance level. What will the nurse expect the provider to order for this patient?
88. The spouse of a patient with Alzheimer disease asks a nurse for more information about the rivastigmine [Exelon] transdermal patch that is being used. Which statement by the spouse indicates a need for further explanation?
89. A patient is worried about the risk of developing Alzheimer disease, because both parents had the disease. The nurse will tell this patient that known risk factors include what?
Select all that apply.
90. A nurse is teaching a group of nursing students about the use of memantine [Namenda] for Alzheimer disease. Which statement by a student indicates understanding of the teaching?
91. An older adult patient has confusion, memory loss, and disorientation in familiar surroundings. The patient has been taking donepezil [Aricept] 10 mg once daily for 6 months. The patient’s symptoms have begun to worsen, and the patient’s spouse asks if the medication dose can be increased. What will the nurse tell the spouse?
Chapter 19: Drugs for Epilepsy
92. A nurse is assessing a patient who becomes motionless and seems to stare at the wall and then experiences about 60 seconds of lip smacking and hand wringing. What should the nurse do?
93. A nurse counsels a patient who is to begin taking phenytoin [Dilantin] for epilepsy. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
94. A nurse is caring for a patient who has been taking an antiepileptic drug for several weeks. The nurse asks the patient if the therapy is effective. The patient reports little change in seizure frequency. What will the nurse do?
95. A patient is to begin taking phenytoin [Dilantin] for seizures. The patient tells the nurse that she is taking oral contraceptives. What will the nurse tell the patient?
96. A patient with a form of epilepsy that may have spontaneous remission has been taking an AED for a year. The patient reports being seizure free for 6 months and asks the nurse when the drug can be discontinued. What will the nurse tell the patient?
97. A patient who has a seizure disorder is admitted to the hospital after an increase in seizure frequency, and the prescriber orders carbamazepine [Tegretol] 100 mg twice daily to be added to the patient’s medication regimen. The nurse reviewing the patient’s medical history notes that the patient is already taking lamotrigine [Lamictal] 375 mg twice daily. The nurse will contact the provider to discuss which action?
98. A patient who is taking oral contraceptives begins taking valproic acid [Depakote] for seizures. After a week of therapy with valproic acid, the patient tells the nurse that she is experiencing nausea. What will the nurse do?
99. A nurse is discussing partial versus generalized seizures with a group of nursing students. Which statement by a student indicates understanding of the teaching?
100. A nurse provides teaching for a patient with a newly diagnosed partial complex seizure disorder who is about to begin therapy with antiepileptic drugs (AEDs). Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
Chapter 20: Drugs for Muscle Spasm and Spasticity
101. A nurse is teaching the parent of a child with spastic quadriplegia about intrathecal baclofen [Lioresal]. Which statement by the parent indicates a need for further teaching?
102. A nurse is admitting a patient to the hospital. The patient reports taking oral baclofen [Lioresal] but stopped taking the drug the day before admission. The nurse would be correct to anticipate which adverse effects?
103. A patient with cerebral palsy has severe muscle spasticity and muscle weakness. The patient is unable to take anything by mouth. The nurse is correct to anticipate that which medication will be ordered for home therapy?
104. A patient has localized muscle spasms after an injury. The prescriber has ordered tizanidine [Zanaflex] to alleviate the spasms. When obtaining the patient’s health history, the nurse should be concerned about which possible reason for considering another drug?
105. A patient with multiple sclerosis needs pharmacologic treatment for spasticity to begin strengthening exercises to improve walking ability. The nurse anticipates that which medication will be ordered for spasticity?
106. A patient with cerebral palsy who has been receiving baclofen [Lioresal] via gastrostomy tube for 3 months is admitted to the hospital for evaluation of new-onset seizures. What may the nurse suspect to be the cause of these seizures?
107. Which drugs are used to treat spasticity? Select all that apply.
108. A patient who has a lower back injury exhibits muscle spasms. The provider orders cyclobenzaprine [Flexeril] 10 mg three times a day. What will the nurse include when teaching this patient about this drug?
109. Which patient should receive dantrolene [Dantrium] with caution?
110. A nurse is caring for a patient receiving intrathecal baclofen [Lioresal]. The patient is unresponsive. After asking a coworker to contact the provider, the nurse anticipates performing which intervention?
Chapter 34: Review of Hemodynamics
111. A nurse is teaching a nursing student how blood can return to the heart when pressure in the venous capillary beds is very low. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
112. A nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving a drug that causes constriction of arterioles. The nurse expects to observe which effect from this drug?
113. A patient with hypertension is admitted to the hospital. On admission the patient’s heart rate is 72 beats/minute, and the blood pressure is 140/95 mm Hg. After administering an
antihypertensive medication, the nurse notes a heart rate of 85 beats/minute and a blood pressure of 130/80 mm Hg. What does the nurse expect to occur?
114. A nurse is assessing a patient who has heart failure. The patient complains of shortness of breath, and the nurse auscultates crackles in both lungs. The nurse understands that these symptoms are the result of:
115. A patient is taking a drug that interferes with venous constriction. The nurse will tell the patient to:
116. A patient is taking a beta1-adrenergic drug to improve the stroke volume of the heart. The nurse caring for this patient knows that this drug acts by increasing:
117. A patient with a history of hypertension is admitted for a procedure. If the patient’s arterial pressure decreases, which clinical manifestation would the nurse expect to see?
Chapter 35: Diuretics
118. A patient is brought to the emergency department with shortness of breath, a respiratory rate of 30 breaths/minute, intercostal retractions, and frothy, pink sputum. The nurse caring for this patient will expect to administer which drug?
119. A patient has 2+ pitting edema of the lower extremities bilaterally. Auscultation of the lungs reveals crackles bilaterally, and the serum potassium level is 6 mEq/L. Which diuretic agent ordered by the prescriber should the nurse question?
120. A patient who is taking digoxin is admitted to the hospital for the treatment of congestive heart failure. The prescriber has ordered furosemide [Lasix]. The nurse notes an irregular heart rate of 86 beats/minute, a respiratory rate of 22 breaths/minute, and a blood pressure of 130/82 mm Hg. The nurse auscultates crackles in both lungs. Which laboratory value causes the nurse the most concern?
121. A patient who was in a motor vehicle accident sustained a severe head injury and is brought into the emergency department. The provider orders intravenous mannitol [Osmitrol]. The nurse knows that this is given to:
122. An older adult patient with congestive heart failure develops crackles in both lungs and pitting edema of all extremities. The physician orders hydrochlorothiazide [HydroDIURIL]. Before administering this medication, the nurse reviews the patient’s chart. Which laboratory value causes the nurse the most concern?
123. A nurse preparing to administer morning medications notes that a patient with a history of hypertension has been prescribed spironolactone [Aldactone]. The nurse assesses the patient and notes dyspnea, bilateral crackles, and pitting edema in both feet. Which intervention is appropriate?
124. A patient is taking gentamicin [Garamycin] and furosemide [Lasix]. The nurse should counsel this patient to report which symptom?
125. A patient with hypertension is taking furosemide [Lasix] for congestive heart failure. The prescriber orders digoxin to help increase cardiac output. What other medication will the nurse expect to be ordered for this patient?
126. Besides having diuretic effects for patients with congestive heart failure, thiazides are also used to treat what?
Select all that apply.
127. A patient with chronic congestive heart failure has repeated hospitalizations in spite of ongoing treatment with hydrochlorothiazide [HydroDIURIL] and digoxin. The prescriber has ordered spironolactone [Aldactone] to be added to this patient’s drug regimen, and the nurse
provides education about this medication. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
Chapter 36: Drugs Acting on the Renin-Angiotensin-Aldosterone Systems
128. A patient who stops taking an ACE inhibitor because of its side effects will begin taking an angiotensin II receptor blocker (ARB) medication. Which side effect of ACE inhibitors will not occur with an ARB medication?
129. A patient who is taking furosemide [Lasix] and digoxin will begin taking captopril [Capoten]. The nurse is providing information about the drug. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
130. A female patient who is not taking any other medications is prescribed aliskiren [Tekturna], a direct renin inhibitor (DRI). The nurse reviews medication information with the patient. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
131. A nurse administers an ACE inhibitor to a patient who is taking the drug for the first time. What will the nurse do?
132. A provider has ordered captopril [Capoten] for a patient who has hypertension. The patient reports a history of swelling of the tongue and lips after taking enalapril [Vasotec] in the past. Which action by the nurse is correct?
133. A patient with hypertension is prescribed an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. The nurse reviewing this patient’s chart before administering the medication will be most concerned about which other disease process?
134. A patient who has been taking an antihypertensive medication for several years is recovering from a myocardial infarction. The prescriber changes the patient’s medication to an
ACE inhibitor. The patient asks the nurse why a new drug is necessary. What is the nurse’s response?
135. A female patient who begins taking spironolactone [Aldactone] as an adjunct to furosemide [Lasix] complains that her voice is deepening. What will the nurse do?
136. A prescriber orders ramipril [Altace] for an obese patient with type 2 diabetes mellitus who has developed hypertension. The nurse provides teaching before dismissing the patient home. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
137. A female patient taking an ACE inhibitor learns that she is pregnant. What will the nurse tell this patient?
138. A nurse is reviewing a patient’s medications before administration. Which drug-to-drug interactions will most concern the nurse in a patient with a history of heart failure and a potassium level of 5.5 mEq/L?
139. A patient begins taking an ACE inhibitor and complains of a dry cough. What does the nurse correctly tell the patient about this symptom?
Chapter 37: Calcium Channel Blockers
140. A nurse is caring for a patient who is receiving verapamil [Calan] for hypertension and digoxin [Lanoxin] for heart failure. The nurse will observe this patient for:
141. A nurse is teaching a patient who will begin taking verapamil [Calan] for hypertension about the drug’s side effects. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
142. A patient who took an overdose of verapamil has been treated with gastric lavage and a cathartic. The emergency department nurse assesses the patient and notes a heart rate of 50 beats/minute and a blood pressure of 90/50 mm Hg. The nurse will anticipate:
143. A nurse is preparing to assist a nursing student to administer intravenous verapamil to a patient who also receives a beta blocker. The nurse asks the nursing student to discuss the plan of care for this patient. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
144. A patient who has been taking verapamil [Calan] for hypertension complains of constipation. The patient will begin taking amlodipine [Norvasc] to avoid this side effect. The nurse provides teaching about the difference between the two drugs. Which statement by the patient indicates that further teaching is needed?
145. Which are therapeutic uses for verapamil? Select all that apply.
146. A patient begins taking nifedipine [Procardia], along with metoprolol, to treat hypertension. The nurse understands that metoprolol is used to:
Chapter 38: Vasodilators
147. Which medications are most likely to cause postural hypotension? Select all that apply.
148. The nurse is caring for a patient who is taking a vasodilator that dilates capacitance vessels. The nurse will expect which effect in this patient?
149. A nurse is obtaining a medication history on a newly admitted patient, who reports taking minoxidil for hypertension. Admission vital signs reveal a heart rate of 78 beats/minute and a blood pressure of 120/80 mm Hg. What is an important part of the initial assessment for this patient?
150. A female patient with essential hypertension is being treated with hydralazine 25 mg twice daily. The nurse assesses the patient and notes a heart rate of 96 beats/minute and a blood pressure of 110/72 mm Hg. The nurse will request an order to:
151. A nurse is administering a vasodilator that dilates resistance vessels. The nurse understands that this drug will have which effect on the patient?
152. A patient is taking a vasodilator that relaxes smooth muscles in veins. To help minimize drug side effects, the nurse caring for this patient will:
153. Which patients may receive hydralazine to treat hypertension? Select all that apply.
154. A nurse is caring for a patient who will begin taking hydralazine to treat hypertension. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the nurse’s teaching about this drug?
155. A nursing student asks a nurse why a patient in hypertensive crisis is receiving both intravenous sodium nitroprusside [Nitropress] and oral hydralazine. The nurse will explain that this is done to prevent:
156. A nurse is reviewing the phenomenon of reflex tachycardia with a group of nursing students. Which statement by a student indicates understanding of this phenomenon?
157. A patient is admitted with severe hypertensive crisis. The nurse will anticipate administering which medication?
Chapter 39: Drugs for Hypertension
158. A nurse has provided education for a patient newly diagnosed with hypertension who is just beginning therapy with antihypertensive medications. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
159. A hospitalized patient has a blood pressure of 145/96 mm Hg. The nurse caring for this patient notes that the blood pressure the day before was 132/98 mm Hg. The patient reports ambulatory blood pressure readings of 136/98 and 138/92 mm Hg. The patient has a history of a previous myocardial infarction and has adopted a lifestyle that includes the use of the DASH diet and regular exercise. What will the nurse do?
160. A patient has been taking chlorthalidone to treat hypertension. The patient’s prescriber has just ordered the addition of spironolactone to the patient’s drug regimen. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
161. A patient with hypertension will begin taking an alpha1 blocker. What will the nurse teach this patient?
162. A nurse checks a patient’s vital signs in the hospital and notes a blood pressure of 146/98 mm Hg. What will the nurse do?
163. A nursing student asks the nurse why multidrug therapy is often used to treat hypertension. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
164. A patient has three separate blood pressure (BP) readings of 120/100 mm Hg, 138/92 mm Hg, and 126/96 mm Hg. Which category describes this patient’s BP?
165. A patient has had blood pressures of 150/95 mm Hg and 148/90 mm Hg on two separate office visits. The patient reports a blood pressure of 145/92 mm Hg taken in an ambulatory setting. The patient’s diagnostic tests are all normal. The nurse will expect this patient’s provider to order:
166. The nurse is caring for a pregnant patient who is in labor. The woman reports having had mild preeclampsia with a previous pregnancy.The nurse notes that the woman has a blood pressure of 168/102 mm Hg. The nurse will contact the provider to request an order for which drug?
167. A patient with diabetes develops hypertension. The nurse will anticipate administering which type of medication to treat hypertension in this patient?
168. A patient who does not consume alcohol or nicotine products reports a strong family history of hypertension and cardiovascular disease. The patient has a blood pressure of 126/82 mm Hg and a normal weight and body mass index for height and age. The nurse will expect to teach this patient about:
169. A patient is taking clonidine for hypertension and reports having dry mouth and drowsiness. What will the nurse tell the patient?
170. Which two-drug regimen would be appropriate for a patient with hypertension who does not have other compelling conditions?
171. A patient takes an ACE inhibitor to treat hypertension and tells the nurse that she wants to become pregnant. She asks whether she should continue taking the medication while she is pregnant. What will the nurse tell her?
172. A 60-year-old African-American patient has a blood pressure of 120/80 mm Hg and reports a family history of hypertension. The patient has a body mass index of 22.3. The patient reports consuming alcohol occasionally. Which therapeutic lifestyle change will the nurse expect to teach this patient?
173. A patient with a recent onset of nephrosclerosis has been taking an ACE inhibitor and a thiazide diuretic. The patient’s initial blood pressure was 148/100 mm Hg. After 1 month of drug therapy, the patient’s blood pressure is 130/90 mm Hg. The nurse will contact the provider to discuss:
174. A patient with hypertension with a blood pressure of 168/110 mm Hg begins taking hydrochlorothiazide and verapamil. The patient returns to the clinic after 2 weeks of drug therapy, and the nurse notes a blood pressure of 140/85 mm Hg and a heart rate of 98 beats/minute. What will the nurse do?
175. A nurse is discussing how beta blockers work to decrease blood pressure with a nursing student. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
176. A 5-year-old patient seen in an outpatient clinic is noted to have hypertension on three separate visits. Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring confirms that the child has hypertension. As an initial intervention with the child’s parents, the nurse will expect to:
Chapter 40: Drugs for Heart Failure
177. A patient asks a nurse why he cannot use digoxin [Lanoxin] for his heart failure, because both of his parents used it for HF. The nurse will explain that digoxin is not the first-line therapy for which reason?
178. A patient has been taking digoxin [Lanoxin] 0.25 mg, and furosemide [Lasix] 40 mg, daily. Upon routine assessment by the nurse, the patient states, “I see yellow halos around the lights.” The nurse should perform which action based on this assessment?
179. A patient has heart failure and is taking an ACE inhibitor. The patient has developed fibrotic changes in the heart and vessels. The nurse expects the provider to order which medication to counter this development?
180. A patient with heart failure who has been taking an ACE inhibitor, a thiazide diuretic, and a beta blocker for several months comes to the clinic for evaluation. As part of the ongoing assessment of this patient, the nurse will expect the provider to evaluate:
181. A patient is taking enalapril [Vasotec]. The nurse understands that patients taking this type of drug for heart failure need to be monitored carefully for:
182. A patient is recovering from a myocardial infarction but does not have symptoms of heart failure. The nurse will expect to teach this patient about:
183. The potassium-sparing diuretic spironolactone [Aldactone] prolongs survival and improves heart failure symptoms by which mechanism?
184. An 88-year-old patient with heart failure has progressed to Stage D and is hospitalized for the third time in a month. The nurse will expect to discuss which topic with the patient’s family?
185. A patient with heart failure who has been given digoxin [Lanoxin] daily for a week complains of nausea. Before giving the next dose, the nurse will:
186. Which medications are included in first-line therapy for heart failure? Select all that apply.
187. A nurse prepares to administer a scheduled dose of digoxin. The nurse finds a new laboratory report showing a plasma digoxin level of 0.7 ng/mL. What action should the nurse take?
188. A patient with Stage C heart failure (HF) who has been taking an ACE inhibitor, a beta blocker, and a diuretic begins to have increased dyspnea, weight gain, and decreased urine output. The provider orders spironolactone [Aldactone]. The nurse will instruct the patient to:
189. Which are expected effects of cardiac glycosides? Select all that apply.
190. A nurse is preparing to administer digoxin [Lanoxin] to a patient. The patient’s heart rate is 62 beats/minute, and the blood pressure is 120/60 mm Hg. The last serum electrolyte value showed a potassium level of 5.2 mEq/L. What will the nurse do?
191. A patient is taking a thiazide diuretic for hypertension and quinidine to treat a dysrhythmia. The prescriber orders digoxin 0.125 mg to improve this patient’s cardiac output. The nurse should contact the provider to request:
192. A patient with chronic hypertension is admitted to the hospital. During the admission assessment, the nurse notes a heart rate of 96 beats/minute, a blood pressure of 150/90 mm Hg bibasilar crackles, 2+ pitting edema of the ankles, and distention of the jugular veins. The nurse will contact the provider to request an order for which medication?
193. A patient with heart failure who takes a thiazide diuretic and digoxin [Lanoxin] is admitted for shortness of breath. The patient’s heart rate is 66 beats/minute, and the blood pressure is 130/88 mm Hg. The serum potassium level is 3.8 mEq/L, and the digoxin level is 0.8 ng/mL. The nurse admitting this patient understands that the patient:
194. A patient newly diagnosed with heart failure is admitted to the hospital. The nurse notes a pulse of 90 beats/minute. The nurse will observe this patient closely for:
195. A patient with volume overload begins taking a thiazide diuretic. The nurse will tell the patient to expect which outcome when taking this drug?
196. A nurse is discussing heart failure with a group of nursing students. Which statement by a student reflects an understanding of how compensatory mechanisms can compound existing problems in patients with heart failure?
Chapter 41: Antidysrhythmic Drugs
197. A nurse is discussing adenosine with a nursing student. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
198. A patient will be taking amiodarone [Cordarone]. Which baseline tests are necessary before this medication is started?
Select all that apply.
199. A nurse is providing teaching to a patient who is admitted to the hospital for initiation of treatment with amiodarone [Cordarone] for atrial fibrillation that has been refractory to other medications. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
200. A patient is in the intensive care unit after a myocardial infarction. The nurse notes that the QT interval on this patient’s electrocardiogram has been elongating. The nurse is concerned that which cardiac dysrhythmia may occur?
201. A patient is taking digoxin [Lanoxin] and quinidine to treat sustained ventricular tachycardia. Before giving medications, the nurse reviews the patient’s electrocardiogram (ECG) and notes a QRS complex that has widened by 50% from the baseline ECG. What will the nurse do?
202. A nursing student asks a nurse how digoxin causes dysrhythmias. The nurse correctly states that digoxin:
203. A nurse is caring for a patient in the intensive care unit who is receiving intravenous lidocaine. The patient is drowsy and confused and reports numbness of the fingers and toes. Which standing order will the nurse initiate at this time?
204. A patient is taking digoxin [Lanoxin] and develops a dysrhythmia. The nurse reports this finding to the prescriber, who will most likely order what?
Select all that apply.
205. A prescriber has ordered propranolol [Inderal] for a patient with recurrent ventricular tachycardia. The nurse preparing to administer this drug will be concerned about what in the patient’s history?
206. A patient with atrial fibrillation is taking verapamil [Calan]. The patient has read about the drug on the Internet and wants to know why a drug that affects the rate of ventricular contraction is used to treat an abnormal atrial contraction. What will the nurse tell the patient?
207. A prescriber orders verapamil [Covera-HS] for a patient who is taking digoxin [Lanoxin] and warfarin. The nurse will expect the prescriber to the dose of .
208. A nurse provides teaching for a patient who will begin taking procainamide [Procanbid] for long-term suppression of a dysrhythmia. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
209. Which two classes of antidysrhythmic drugs have nearly identical cardiac effects?
210. A nurse is teaching a group of nursing students about antidysrhythmic medications. Which statement by a student indicates understanding of the teaching?
211. The nurse is teaching a group of nursing students about dofetilide [Tikosyn] to treat dysrhythmias. Which statement by a student indicates understanding of the teaching?
212. A prescriber is considering prescribing the amiodarone derivative dronedarone [Multaq] for a patient with atrial flutter. The nurse should be concerned about which of the following?
213. A nurse is teaching a patient who is about to undergo direct-current (DC) cardioversion to treat atrial flutter. The patient has been taking verapamil and warfarin for 6 months. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
214. The nurse educator is providing patient education about the Cardiac Arrhythmia Suppression Trial (CAST). The nurse correctly explains that the trial demonstrated what effect from the pharmacologic suppression of dysrhythmias?
215. A nurse is teaching a class on dysrhythmias and associated therapy. The nurse asks the class, “Which cardiac dysrhythmia would result in the lowest cardiac output, and what treatment would be effective?” The class best demonstrates understanding by responding that
results in the lowest cardiac output, and treatment includes .
216. A patient with diabetes develops ventricular tachycardia and is in the hospital for evaluation of this condition. The nurse reviews the history and learns that the patient takes mexiletine [Mexitil] for pain caused by peripheral neuropathy. What should the nurse do?
Chapter 42: Prophylaxis of Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease: Drugs That Help Normalize Cholesterol and Triglyceride Levels
217. Which is a possible benefit of taking fish-oil supplements?
218. A nurse is providing discharge teaching instructions for a patient taking cholestyramine [Questran]. Which statement made by the patient demonstrates a need for further teaching?
219. A patient who recently started therapy with an HMG-COA reductase inhibitor asks the nurse, “How long will it take until I see an effect on my LDL cholesterol?” The nurse gives which correct answer?
220. A patient with a history of elevated triglycerides and LDL cholesterol begins taking nicotinic acid [Niacin]. The patient reports uncomfortable flushing of the face, neck, and ears when taking the drug. What will the nurse advise the patient?
221. A nurse is reviewing a patient’s medications and realizes that gemfibrozil [Lopid] and warfarin [Coumadin] are to be administered concomitantly. Which effect will the nurse anticipate in this patient?
222. Lovastatin [Mevacor] is prescribed for a patient for the first time. The nurse should provide the patient with which instruction?
223. While giving discharge instructions to a patient who will be taking cholestyramine [Questran], the nurse wants to assess the patient’s understanding of the treatment. Which statement made by the patient best demonstrates a need for additional teaching?
224. A postmenopausal woman will begin taking atorvastatin [Lipitor] to treat hypercholesterolemia. The woman reports a history of osteopenia with a family risk of osteoporosis. What will the nurse include when teaching this patient?
225. A nurse is instructing a patient receiving a cholesterol-lowering agent. Which information should the nurse include in the patient education?
226. A patient has begun taking an HMG-COA reductase inhibitor. Which statement about this class of drugs made by the nurse during patient education would be inappropriate?
227. Which plasma lipoprotein level is most concerning when considering the risk of coronary atherosclerosis?
228. A patient taking gemfibrozil [Lopid] and rosuvastatin [Crestor] concurrently begins to complain of muscle aches, fatigue, and weakness. What should the nurse monitor?
229. A nurse is reviewing the medications of a patient with diabetes before discharge. The nurse realizes that the patient will be going home on colesevelam, a bile acid sequestrant, and insulin. What patient education should the nurse provide in the discharge teaching for this patient?
230. A patient is being started on nicotinic acid [Niaspan] to reduce triglyceride levels. The nurse is providing patient education and should include teaching about which adverse effects? Select all that apply.
231. A patient who is taking simvastatin [Zocor] develops an infection and the provider orders azithromycin [Zithromax] to treat the infection. The nurse should be concerned if the patient complains of:
232. A patient will begin taking atorvastatin [Lipitor] to treat elevated LDL levels. The patient asks the nurse what to do to minimize the risk of myositis associated with taking this drug. What will the nurse counsel this patient?
233. An Asian patient will begin taking rosuvastatin [Crestor] to treat hypercholesterolemia. What will the nurse include when teaching this patient about this medication?
234. A nurse is providing patient education about colesevelam [Welchol], a bile acid sequestrant. Which statement made by the patient demonstrates a need for further teaching?
Chapter 43: Drugs for Angina Pectoris
235. A patient who takes nitroglycerin to treat stable angina reports having erectile dysfunction and states that he plans to ask his primary provider for a prescription for tadalafil [Cialis]. What will the nurse tell this patient?
236. A patient with angina who uses sublingual nitroglycerin tells the nurse that the episodes are increasing in frequency and usually occur when the patient walks the dog. The patient
reports needing almost daily doses of nitroglycerin and states that one tablet usually provides complete relief. What will the nurse do?
237. A patient who has begun using transdermal nitroglycerin for angina reports occasional periods of tachycardia. The nurse will expect the prescriber to order:
238. A patient who has renal impairment will begin taking ranolazine [Ranexa] as an adjunct to nitroglycerin to treat angina. What will the nurse include when teaching this patient?
239. A nurse provides teaching to a patient with angina who also has type 2 diabetes mellitus, asthma, and hypertension. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
240. A patient is taking a calcium channel blocker (CCB) for stable angina. The patient’s spouse asks how calcium channel blockers relieve pain. The nurse will explain that CCBs:
241. A nurse is discussing the difference between stable and variant angina with a group of nursing students. Which statement by a student indicates the need for further teaching?
242. A patient with variant angina wants to know why a beta blocker cannot be used to treat the angina. Which response by the nurse is correct?
243. A nursing student asks a nurse how beta blockers increase the oxygen supply to the heart in the treatment of anginal pain. The nurse tells the student that beta blockers:
244. A patient with asthma and depression develops stable angina. In addition to organic nitrites, which other medications will be used to treat this condition?
Select all that apply.
245. A hospitalized patient complains of acute chest pain. The nurse administers a 0.3-mg sublingual nitroglycerin tablet, but the patient continues to complain of pain. Vital signs remain stable. What is the nurse’s next step?
246. A patient with stable exertional angina has been receiving a beta blocker. Before giving the drug, the nurse notes a resting heart rate of 55 beats/minute. Which is an appropriate nursing action?
247. A nursing student is helping to care for a patient who takes verapamil for stable angina. The nurse asks the student to explain the purpose of verapamil in the treatment of this patient. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
248. A patient with angina who is taking ranolazine [Ranexa] has developed a respiratory infection and a dysrhythmia. The provider has ordered azithromycin [Zithromax] for the infection and amlodipine for the dysrhythmia. A nursing student caring for this patient tells the nurse that the patient’s heart rate is 70 beats/minute, and the blood pressure is 128/80 mm Hg. The nurse asks the student to discuss the plan for this patient’s care. Which action is correct?
249. A patient with new-onset exertional angina has taken three nitroglycerin sublingual tablets at 5-minute intervals, but the pain has intensified. The nurse notes that the patient has a heart rate of 76 beats/minute and a blood pressure of 120/82 mm Hg. The electrocardiogram is normal. The patient’s lips and nail beds are pink, and there is no respiratory distress. The nurse will anticipate providing:
250. A nurse is providing teaching for a patient with stable angina who will begin taking nitroglycerin. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
251. A patient asks a nurse how nitroglycerin works to relieve anginal pain. The nurse correctly states, “Nitroglycerin:
Chapter 44: Anticoagulant, Antiplatelet, and Thrombolytic Drugs
252. A patient has been receiving heparin while in the hospital to treat deep vein thromboses and will be discharged home with a prescription for enoxaparin [Lovenox]. The nurse provides teaching for the nursing student who asks about the advantages of enoxaparin over heparin. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
253. A patient is receiving heparin postoperatively to prevent deep vein thrombosis. The nurse notes that the patient has a blood pressure of 90/50 mm Hg and a heart rate of 98 beats/minute. The patient’s most recent aPTT is greater than 90 seconds. The patient reports lumbar pain. The nurse will request an order for:
254. A nursing student who is preparing to care for a postoperative patient with deep vein thrombosis asks the nurse why the patient must take heparin rather than warfarin. Which response by the nurse is correct?
255. A postoperative patient reports pain in the left lower extremity. The nurse notes swelling in the lower leg, which feels warm to the touch. The nurse will anticipate giving which medication?
256. A patient who is taking warfarin [Coumadin] has just vomited blood. The nurse notifies the provider, who orders laboratory work revealing a PT of 42 seconds and an INR of 3.5. The nurse will expect to administer:
257. A patient is admitted to the emergency department with chest pain. An electrocardiogram shows changes consistent with an evolving myocardial infarction. The patient’s cardiac enzymes are pending. The nurse caring for this patient will expect to:
258. A patient who takes warfarin for atrial fibrillation undergoes hip replacement surgery. On the second postoperative day, the nurse assesses the patient and notes an oxygen saturation of 83%, pleuritic chest pain, shortness of breath, and hemoptysis. The nurse will contact the provider to report possible and request an order for .
259. A patient with atrial fibrillation is receiving warfarin [Coumadin]. The nurse notes that the patient’s INR is 2.7. Before giving the next dose of warfarin, the nurse will notify the provider and:
260. A postoperative patient will begin anticoagulant therapy with rivaroxaban [Xarelto] after knee replacement surgery. The nurse performs a history and learns that the patient is taking erythromycin. The patient’s creatinine clearance is 50 mL/minute. The nurse will:
261. A patient who is taking clopidogrel [Plavix] calls the nurse to report black, tarry stools and coffee-ground emesis. The nurse will tell the patient to:
262. A patient has been taking warfarin [Coumadin] for atrial fibrillation. The provider has ordered dabigatran etexilate [Pradaxa] to replace the warfarin. The nurse teaches the patient about the change in drug regimen. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
263. A 50-year-old female patient asks a nurse about taking aspirin to prevent heart disease. The patient does not have a history of myocardial infarction. Her cholesterol and blood pressure are normal, and she does not smoke. What will the nurse tell the patient?
264. A patient who takes warfarin [Coumadin] is brought to the emergency department after accidentally taking too much warfarin. The patient’s heart rate is 78 beats/minute and the blood pressure is 120/80 mm Hg. A dipstick urinalysis is normal. The patient does not have any obvious hematoma or petechiae and does not complain of pain. The nurse will anticipate an order for:
265. A nurse caring for a patient receiving heparin therapy notes that the patient has a heart rate of 98 beats/minute and a blood pressure of 110/72 mm Hg. The patient’s fingertips are purplish in color. A stat CBC shows a platelet count of less than 100,000 mm3. The nurse will:
266. A patient will begin taking dabigatran etexilate [Pradaxa] to prevent stroke. The nurse will include which statement when teaching this patient?
267. A patient is admitted to the hospital with unstable angina and will undergo a percutaneous coronary intervention. Which drug regimen will the nurse expect to administer to prevent thrombosis in this patient?
268. A patient who has taken warfarin [Coumadin] for a year begins taking carbamazepine. The nurse will anticipate an order to:
269. A nurse has just received an order for tenecteplase [TNKase] for a patient experiencing an acute myocardial infarction. The nurse should administer this drug:
Chapter 46: Drugs for Diabetes Mellitus
270. The nurse working on a high-acuity medical-surgical unit is prioritizing care for four patients who were just admitted. Which patient should the nurse assess first?
271. A patient with type 1 diabetes recently became pregnant. The nurse plans a blood glucose testing schedule for her. What is the recommended monitoring schedule?
272. Which statement is correct about the contrast between acarbose and miglitol?
273. A nurse is educating the staff nurses about ketoacidosis. To evaluate the group’s understanding, the nurse asks, “Which sign or symptom would not be consistent with ketoacidosis?” The group gives which correct answer?
274. The nurse assesses a newly diagnosed patient for short-term complications of diabetes. What does this assessment include?
275. A patient with type 1 diabetes is eating breakfast at 7:30 AM. Blood sugars are on a sliding scale and are ordered before a meal and at bedtime. The patient’s blood sugar level is 317 mg/dL. Which formulation of insulin should the nurse prepare to administer?
276. A patient with type 1 diabetes who takes insulin reports taking propranolol for hypertension. Why is the nurse concerned?
277. A nurse provides dietary counseling for a patient newly diagnosed with type 1 diabetes. Which instruction should be included?
278. A patient with type 1 diabetes reports mixing NPH and regular insulin to allow for one injection. What should the nurse tell the patient?
279. Which statement is accurate about the long-term complications of diabetes?
280. An elderly patient who has type 2 diabetes has a history of severe hypoglycemia. The patient’s spouse asks the nurse what the optimal A1c level is for the patient. Which is correct?
281. An adolescent patient recently attended a health fair and had a serum glucose test. The patient telephones the nurse and says, “My level was 125 mg/dL. Does that mean I have diabetes?” What is the nurse’s most accurate response?
282. A patient who has type 2 diabetes will begin taking glipizide [Glucotrol]. Which statement by the patient is concerning to the nurse?
283. What is the most reliable measure for assessing diabetes control over the preceding 3- month period?
284. Insulin glargine is prescribed for a hospitalized patient who has diabetes. When will the nurse expect to administer this drug?
Chapter 47: Drugs for Thyroid Disorders
285. A patient with hypothyroidism begins taking PO levothyroxine [Synthroid]. The nurse assesses the patient at the beginning of the shift and notes a heart rate of 62 beats/minute and a temperature of 97.2°F. The patient is lethargic and difficult to arouse. The nurse will contact the provider to request an order for which drug?
286. A patient has been taking levothyroxine for several years and reports that “for the past 2 weeks, the drug does not seem to work as well as before.” What will the nurse do?
287. A nurse is teaching a patient who will begin taking methimazole [Tapazole] for Graves disease about the medication. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
288. A patient is admitted to the hospital and will begin taking levothyroxine [Synthroid]. The nurse learns that the patient also takes warfarin [Coumadin]. The nurse will notify the provider to discuss the dose.
289. The nurse prepares a patient with Graves disease for radioactive iodine (131I) therapy. Which statement made by the patient best demonstrates understanding of 131I therapy?
290. A nurse caring for a patient notes that the patient has a temperature of 104°F and a heart rate of 110 beats/minute. The patient’s skin is warm and moist, and the patient complains that the room is too warm. The patient appears nervous and has protuberant eyes. The nurse will contact the provider to discuss:
291. The nurse is caring for a pregnant patient recently diagnosed with hypothyroidism. The patient tells the nurse she does not want to take medications while she is pregnant. What will the nurse explain to this patient?
292. A patient has a free T4 level of 0.6 ng/dL and a free T3 level of 220 pg/dL. The patient asks the nurse what these laboratory values mean. How will the nurse respond?
293. An older adult patient is diagnosed with hypothyroidism. The initial free T4 level is 0.5 mg/dL, and the TSH level is 8 microunits/mL. The prescriber orders levothyroxine [Levothroid] 100 μg/day PO. What will the nurse do?
294. A patient in her twenties with Graves disease who takes methimazole [Tapazole] tells a nurse that she is trying to conceive and asks about disease management during pregnancy. What will the nurse tell her?
295. A nurse is teaching a patient who has been diagnosed with hypothyroidism about levothyroxine [Synthroid]. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
296. A 1-year-old child with cretinism has been receiving 8 mcg/kg/day of levothyroxine [Synthroid]. The child comes to the clinic for a well-child checkup. The nurse will expect the provider to:
297. A nurse obtaining an admission history on an adult patient notes that the patient has a heart rate of 62 beats/minute, a blood pressure of 105/62 mm Hg, and a temperature of 96.2°F. The patient appears pale and complains of always feeling cold and tired. The nurse will contact the provider to discuss tests for which condition?
298. A patient arrives in the emergency department with a heart rate of 128 beats/minute and a temperature of 105°F. The patient’s skin feels hot and moist. The free T4 level is 4 ng/dL, the free T3 level is 685 pg/dL, and the TSH level is 0.1 microunits/mL. The nurse caring for this patient will expect to administer:
Chapter 57: Drug Therapy of Rheumatoid Arthritis
299. A patient about to begin therapy with etanercept has a positive tuberculin skin test. A chest radiograph is negative. The nurse will expect this patient to:
300. A child who has juvenile idiopathic arthritis and who has been taking methotrexate [Rheumatrex] will begin a course of abatacept [Orencia]. What will the nurse include when teaching the child’s family about this drug?
301. A patient will begin taking hydroxychloroquine [Plaquenil] for rheumatoid arthritis. The patient is currently taking high-dose NSAIDs and methotrexate. What will the nurse teach the patient?
302. A patient will begin taking etanercept [Enbrel] for severe rheumatoid arthritis. The patient has been taking methotrexate [Rheumatrex]. The patient asks if the etanercept is stronger than the methotrexate. The nurse will tell the patient that etanercept methotrexate.
303. A patient with rheumatoid arthritis is taking leflunomide [Arava] and an oral contraceptive.
She tells the nurse she would like to get pregnant. What will the nurse tell her?
304. A patient is beginning therapy with oral methotrexate [Rheumatrex] for rheumatoid arthritis. The nurse will teach this patient about the importance of:
305. A nurse is discussing the administration of an intravenous infusion of rituximab (Rituxan) with a nursing student. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further education about the care of a patient receiving this drug?
306. A patient who has been diagnosed with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) for 1 month and has generalized symptoms is taking high-dose nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and an oral glucocorticoid. The provider has ordered methotrexate [Rheumatrex]. The patient asks the nurse why methotrexate is necessary since pain and swelling have been well controlled with the other medications. The nurse will tell the patient that:
Chapter 58: Drug Therapy of Gout
307. A patient who has gout will begin taking febuxostat [Uloric] and colchicine. What will the nurse include when teaching this patient about this drug regimen?
308. A patient with chronic gout is admitted to the hospital for treatment for an infection. The patient is receiving allopurinol and ampicillin. The nurse is preparing to administer medications and notes that the patient has a temperature of 101° F and a rash. What will the nurse do?
309. A patient with chronic gout has an acute gouty episode and is admitted to the hospital. The patient has been taking nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for several months. The prescriber plans to begin therapy with probenecid. What will the nurse do?
310. A patient is being treated with warfarin [Coumadin] to prevent thrombus. The patient develops hyperuricemia, and the provider orders allopurinol [Zyloprim]. The nurse will contact the provider to discuss the dose.
311. A patient who will begin taking colchicine for gout reports taking nonsteroidal anti- inflammatory drugs, simvastatin, amoxicillin, and digoxin. What will the nurse do?
312. A patient who is hospitalized for an acute gout attack has received several doses of hourly oral colchicine but still reports moderate to severe pain. As the nurse prepares to administer the next dose, the patient begins vomiting. What will the nurse do?
313. A patient with gout who has increasingly frequent acute gouty attacks will begin receiving allopurinol [Zyloprim] and colchicine. The nurse will include which statement when teaching the patient about this drug regimen?
314. A patient has had three gouty flare-ups in the past year. Which drug class will the nurse expect the provider to order for this patient?
315. A patient is admitted for treatment of gout that has been refractory to treatment with allopurinol and probenecid. The patient is taking colchicine, and the prescriber orders pegloticase [Krystexxa]. Before administering this drug, the nurse will expect to:
Chapter 59: Drugs Affecting Calcium Levels and Bone Mineralization
316. A nurse provides teaching for a woman who will begin taking supplemental calcium.
Which statement by the woman indicates understanding of the teaching?
317. A nurse is preparing to administer IV calcium chloride to a patient with a low serum calcium level. Which drug on the patient’s medication record, administered concurrently, would require additional patient monitoring by the nurse?
318. A nurse is providing teaching for a patient with osteoporosis who has just switched from alendronate [Fosamax] to zoledronate [Reclast]. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
319. A patient with severe glucocorticoid-induced osteoporosis will start therapy with teriparatide [Forteo]. What will the nurse expect to administer?
320. A nurse is discussing the role of vitamin D in calcium regulation with a nursing student.
Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
321. A postmenopausal patient develops osteoporosis. The patient asks the nurse about medications to treat this condition. The nurse learns that the patient has a family history of breast cancer. The nurse will suggest discussing which medication with the provider?
322. A patient has severe Paget disease of the bone. The patient asks the nurse what can be done to alleviate the pain. The nurse will suggest that the patient discuss the use of which medication with the provider?
323. A patient with metastatic cancer has had several fractures secondary to bone metastases.
The provider orders denosumab [Xgeva]. What will the nurse teach this patient?
324. A patient taking risedronate IR [Actonel] for osteoporosis reports experiencing diarrhea and headaches. What will the nurse tell this patient?
325. A 55-year-old female patient asks a nurse about calcium supplements. The nurse learns that the patient consumes two servings of dairy products each day. The patient’s serum calcium level is 9.5 mg/dL. The serum vitamin D level is 18 ng/mL. The nurse will recommend adding
daily and IU of vitamin D3 each day.
326. A patient who has developed postmenopausal osteoporosis will begin taking alendronate [Fosamax]. The nurse will teach this patient to take the drug:
327. A patient is taking alendronate [Fosamax] to treat Paget disease. The patient asks the nurse why calcium supplements are necessary. The nurse will tell the patient that calcium supplements are necessary to:
328. A patient who takes teriparatide [Forteo] administers it subcutaneously with a prefilled pen injector. The patient asks why she must use a new pen every 28 days when there are doses left in the syringe. Which is the correct response by the nurse?
329. A patient reports experiencing weakness, fatigue, nausea, vomiting, constipation, and nocturia. Total serum calcium is 10.5 mg/dL. A dipstick urinalysis shows a positive result for protein. When questioned, the patient reports taking vitamin D and calcium supplements. The nurse will counsel the patient to:
330. A postmenopausal patient is at high risk for developing osteoporosis. The patient’s prescriber orders raloxifene [Evista], and the nurse provides teaching about this drug. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
331. A nurse is providing education to a patient who will begin taking alendronate [Fosamax].
Which complication should the patient be instructed to report immediately?
Chapter 60: Drugs for Asthma and Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
332. A patient with asthma is admitted to an emergency department with a respiratory rate of 22 breaths/minute, a prolonged expiratory phase, tight wheezes, and an oxygen saturation of 90% on room air. The patient reports using fluticasone [Flovent HFA] 110 μg twice daily and has used 2 puffs of albuterol [Proventil HFA], 90 mcg/puff, every 4 hours for 2 days. The nurse will expect to administer which drug?
333. A patient with stable COPD is prescribed a bronchodilator medication. Which type of bronchodilator is preferred for this patient?
334. A patient with COPD is prescribed tiotropium [Spiriva]. After the initial dose, the patient reports only mild relief within 30 minutes. What will the nurse tell the patient?
335. A patient with asthma comes to a clinic for treatment of an asthma exacerbation. The patient’s medication history lists an inhaled glucocorticoid, montelukast [Singulair], and a SABA as needed via MDI. The nurse assesses the patient and notes a respiratory rate of 18 breaths/minute, a heart rate of 96 beats/minute, and an oxygen saturation of 95%. The nurse auscultates mild expiratory wheezes and equal breath sounds bilaterally. What will the nurse do?
336. A parent asks a nurse about growth suppression resulting from the use of an inhaled glucocorticoid in children. What will the nurse tell the parent?
337. A patient who uses an inhaled glucocorticoid for chronic asthma calls the nurse to report hoarseness. What will the nurse do?
338. A young adult woman will begin using an inhaled glucocorticoid to treat asthma. The nurse will teach this patient about the importance of which action?
339. A 7-year-old child with asthma uses a daily inhaled glucocorticoid and an albuterol MDI as needed. The provider has added montelukast [Singulair] to the child’s regimen. Which statement by the child’s parent indicates understanding of this medication?
340. A child is receiving a combination albuterol/ipratropium [DuoNeb] inhalation treatment.
The patient complains of a dry mouth and sore throat. What will the nurse do?
341. A patient with stable COPD receives prescriptions for an inhaled glucocorticoid and an inhaled beta2-adrenergic agonist. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of this medication regimen?
342. A patient with severe, chronic COPD uses an inhaled LABA/glucocorticoid but continues to have frequent exacerbation of symptoms. The nurse will contact the provider to discuss:
343. Which medication should be used for asthma patients as part of step 1 management?
344. A nurse is teaching a group of nursing students about the different formulations of beta2- adrenergic agonist medications. Which statement by a student indicates understanding of the teaching?
345. A nurse and a nursing student are reviewing the care of a 30-kg patient who will receive intravenous aminophylline. Which statement by the student indicates an understanding of the administration of this medication?
346. A patient with persistent, frequent asthma exacerbations asks a nurse about a long-acting beta2-agonist medication. What will the nurse tell this patient?
347. A patient who has been newly diagnosed with asthma is referred to an asthma clinic. The patient reports daily symptoms requiring short-acting beta2-agonist treatments for relief. The patient has used oral glucocorticoids three times in the past 3 months and reports awakening at night with symptoms about once a week. The patient’s forced expiratory volume in 1 second (FEV1) is 75% of predicted values. The nurse will expect this patient to be started on which regimen?
348. A patient has just received a prescription for fluticasone/salmeterol [Advair Diskus]. What will the nurse include as part of the teaching for this patient about the use of this device?
349. A patient with asthma will be using a metered-dose inhaler (MDI) for delivery of an inhaled medication. The provider has ordered 2 puffs to be given twice daily. It is important for the nurse to teach this patient that:
350. A patient who takes oral theophylline [Theochron] twice daily for chronic stable asthma develops an infection and will take ciprofloxacin. The nurse will contact the provider to discuss:
Chapter 61: Drugs for Allergic Rhinitis, Cough, and Colds
351. A patient who has seasonal allergies in the spring and fall asks the nurse about oral antihistamines. Which response by the nurse is correct?
352. A patient admitted to the hospital has been using phenylephrine nasal spray [Neo- Synephrine], 2 sprays every 4 hours, for a week. The patient complains that the medication is not working, because the nasal congestion has increased. What will the nurse do?
353. A nurse provides teaching to a patient with allergic rhinitis who will begin using an intranasal glucocorticoid. Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching?
354. A patient with allergic rhinitis is taking a compound product of loratadine/pseudoephedrine [Claritin-D] every 12 hours. The patient complains of insomnia. The nurse notes that the patient is restless and anxious. The patient’s heart rate is 90 beats/minute, and the blood pressure is 130/85 mm Hg. The nurse will contact the provider to:
355. A child who has perennial allergic rhinitis has been using an intranasal glucocorticoid. The provider has ordered montelukast [Singulair] to replace the glucocorticoid because the child has frequent nosebleeds. When teaching this child’s parents about montelukast, the nurse will include which statement?
356. A patient who has a viral upper respiratory infection reports having a runny nose and a cough that prevents sleep and asks the nurse to recommend an over-the-counter medication. Which medication will the nurse recommend?
357. A child with seasonal rhinitis has used budesonide [Rhinocort Aqua] for several years. The parents are concerned that the child’s rate of growth has slowed. What will the nurse do?
358. A parent asks a nurse to recommend an intranasal decongestant for a 6-year-old child.
Which response by the nurse is correct?
359. A 7-year-old child has a cough, runny nose, congestion, and fever, and the parents ask the nurse to recommend an over-the-counter product. Which response by the nurse is correct?
360. Which medication used for asthma has off-label uses to treat allergic rhinitis?
361. A patient with a cough has been advised to use guaifenesin. The patient asks the nurse to explain the purpose of the drug. The nurse will explain that guaifenesin:
362. A parent asks a nurse about giving diphenhydramine [Benadryl] to a child to relieve cold symptoms. Which response by the nurse is correct?
363. A patient asks the nurse what type of medications would be most effective for treating seasonal and perennial rhinitis. Which response by the nurse is correct?
364. What is ipratropium bromide [Atrovent]?
Chapter 62: Drugs for Peptic Ulcer Disease
365. A patient stops taking a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) after 6 weeks of therapy for treatment of peptic ulcer disease. The patient reports symptoms of dyspepsia to the nurse. The nurse will tell this patient to:
366. When metronidazole [Flagyl] is a component of the H. pylori treatment regimen, the patient must be instructed to do what?
367. A patient is diagnosed with Zollinger-Ellison syndrome. Which medication does the nurse expect the provider to order for this patient?
368. A patient who has gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) receives a prescription for a proton pump inhibitor (PPI) medication. What will the nurse include when teaching the patient about this drug?
369. An older adult patient with severe gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) has had only minimal relief using a histamine2-receptor antagonist (H2RA). The patient is to begin taking omeprazole [Prilosec]. What will the nurse teach this patient?
370. A patient admitted to the hospital has a history of peptic ulcer disease. The patient takes ranitidine [Zantac] and sucralfate [Carafate]. The patient tells the nurse that discomfort is usually controlled but that symptoms occasionally flare up. What will the nurse do?
371. The nurse is providing education to a patient who has been prescribed both an antacid and cimetidine [Tagamet]. Which instruction should the nurse give the patient about taking the medications?
372. A patient is diagnosed with peptic ulcer disease. The patient is otherwise healthy. The nurse learns that the patient does not smoke and that he drinks 1 or 2 glasses of wine with meals each week. The nurse anticipates that the provider will prescribe which drugs?
373. A nursing student is caring for a patient who is taking sucralfate [Carafate] and ciprofloxacin [Cipro] to treat peptic ulcer disease. The student asks the nurse about the pharmacokinetics of sucralfate. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
374. A 30-year-old male patient will begin a three-drug regimen to treat peptic ulcer disease. The regimen will consist of bismuth subsalicylate, tetracycline, and cimetidine [Tagamet]. The nurse will include which information when teaching this patient about this drug regimen?
375. A patient who takes nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) for arthritis asks a nurse what can be done to prevent ulcers. The nurse will recommend asking the provider about using which medication?
376. A patient newly diagnosed with PUD reports taking low-dose aspirin (ASA) for prevention of cardiovascular disease. The nurse learns that the patient drinks 2 to 3 cups of coffee each day and has a glass of wine with dinner 3 or 4 nights per week. The patient eats three meals a day. The nurse will counsel this patient to:
Chapter 63: Laxatives
377. A patient is admitted with lower abdominal pain and nausea. The nurse performing the initial assessment notes that the patient’s abdomen is distended and firm, and hypoactive bowel sounds are present. The patient has not had a stool for 3 days. The nurse will contact the provider, who will:
378. A patient reports taking an oral bisacodyl laxative [Dulcolax] for several years. The provider has suggested discontinuing the laxative, but the patient is unsure how to do this. The nurse will tell the patient to:
379. A patient with renal disease is scheduled for a colonoscopy. Before the procedure, the nurse will anticipate administering:
380. The parent of a child with cerebral palsy reports that the child has pebble-like stools most of the time and seems uncomfortable if several days have passed between stools. The nurse will suggest that the parent discuss which medication with the child’s provider?
381. A patient will undergo a colonoscopy, and the provider has ordered sodium phosphate as a bowel cleanser before the procedure. The nurse reviews the patient’s chart and notes that the patient’s creatinine clearance and blood urea nitrogen are both elevated. What will the nurse do?
382. The nurse is caring for an older adult patient after a right hip open reduction internal fixation (ORIF). The patient is taking an opioid every 6 hours as needed for pain. The nurse discusses obtaining an order from the prescriber for which medication?
383. A nurse is taking a history on a clinic patient who reports being constipated. Upon further questioning, the nurse learns that the patient’s last stool was 4 days ago, that it was of normal, soft consistency, and that the patient defecated without straining. The patient’s abdomen is not distended, and bowel sounds are present. The patient reports usually having a stool every 1 to 2 days. What will the nurse do?
384. A nurse receives an order to administer castor oil to a patient. Which action by the nurse is correct?
385. Which condition would cause the nurse to withhold a PRN order for magnesium hydroxide?
386. A patient has been taking senna [Senokot] for several days, and the nurse notes that the urine is yellowish-brown. What does the nurse know about this symptom?
387. A patient with a history of chronic alcohol abuse has been admitted to the unit with cirrhosis. Upon review of the patient’s laboratory test results, the nurse notes that the patient’s ammonia level is elevated at 218 μg/dL. What medication should the nurse prepare to administer?
388. A patient’s provider has recommended a bulk-forming laxative for occasional constipation.
Which statement by the patient indicates understanding of the teaching about this agent?
389. A patient has been taking psyllium [Metamucil] two to three times daily for several days.
The patient complains of stomach pain but has not had a stool. What will the nurse do?
390. A 6-year-old child has frequent constipation. The nurse provides teaching after the parent asks the nurse why the provider recommended using laxatives only when needed. Which statement by the parent indicates a need for further teaching?
Chapter 64: Other Gastrointestinal Drugs
391. A patient with gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is to begin taking oral metoclopramide [Reglan]. The patient asks the nurse about the medication. Which response by the nurse is correct?
392. A nursing student is discussing with a nurse the plan of care for a patient about to undergo a third round of chemotherapy with cisplatin. Which statement by the nursing student about the treatment of CINV is correct?
393. A patient is taking bismuth subsalicylate [Pepto-Bismol] to prevent diarrhea. The nurse performing an assessment notes that the patient’s tongue is black. What will the nurse do?
394. A nurse is providing education to a patient with ulcerative colitis who is being treated with sulfasalazine [Azulfidine]. Which statement by the patient best demonstrates understanding of the action of sulfasalazine?
395. A nurse is providing teaching to a nursing student about to care for a woman with irritable bowel syndrome with diarrhea (IBS-D) who is receiving alosetron [Lotronex]. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
396. A nurse caring for a patient who is undergoing a third round of chemotherapy is preparing to administer ondansetron [Zofran] 30 minutes before initiation of the chemotherapy. The patient tells the nurse that the ondansetron did not work as well the last time as it had the first time. What will the nurse do?
397. A patient with Crohn disease will begin receiving an initial infusion of infliximab [Remicade]. The nurse explains how this drug works to treat this disease. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
398. A pregnant patient who is taking ondansetron [Zofran] for morning sickness tells the nurse she is experiencing headache and dizziness. What will the nurse tell her?
399. A nurse explains to a nursing student why opioid antidiarrheal medications are classified as drugs with little or no abuse potential. Which statement by the student indicates a need for further teaching?
400. A nurse is caring for a patient with cancer who has been undergoing chemotherapy. The patient has oral mucositis as a result of the chemotherapy, and the provider has ordered palifermin [Kepivance]. Which is an appropriate nursing action when giving this drug?
401. A patient is being treated for chemotherapy-induced nausea and vomiting (CINV) with ondansetron [Zofran] and dexamethasone. The patient reports getting relief during and immediately after chemotherapy but has significant nausea and vomiting several days after each chemotherapy treatment. What will the nurse do?
402. A patient who is in her first trimester of pregnancy asks the nurse to recommend nonpharmaceutical therapies for morning sickness. What will the nurse suggest?
403. A nurse is discussing the use of immunosuppressants for the treatment of inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) with a group of nursing students. Which statement by a student indicates understanding of the teaching?
404. A patient is receiving intravenous promethazine [Phenergan] 25 mg for postoperative nausea and vomiting. What is an important nursing action when giving this drug?
405. A patient who has traveler’s diarrhea asks the nurse about using loperamide to stop the symptoms. What will the nurse tell the patient about this drug?
406. A patient is preparing to travel to perform missionary work in a region with poor drinking water. The provider gives the patient a prescription for ciprofloxacin [Cipro] to take on the trip. What will the nurse instruct this patient to do?
407. A patient who experiences motion sickness is about to go on a cruise. The prescriber orders transdermal scopolamine [Transderm Scop]. The patient asks the nurse why an oral agent is not ordered. The nurse will explain that the transdermal preparation:
408. A nurse is admitting a patient to the hospital who reports having recurrent, crampy abdominal pain followed by diarrhea. The patient tells the nurse that the diarrhea usually relieves the pain and that these symptoms have occurred daily for the past 6 months. The patient undergoes a colonoscopy, for which the findings are normal. The nurse will plan to teach this patient to:
Chapter 78: Antiviral Agents I: Drugs for Non-HIV Viral Infections
409. A patient with HIV and mucocutaneous HSV is being treated with foscarnet after failing treatment with acyclovir. After 2 weeks, the patient’s dose is increased to 90 mg/kg over 2 hours from 40 mg/kg over 1 hour. The patient reports numbness in the extremities and perioral tingling. What will the nurse do?
410. A nurse is teaching a group of nursing students about influenza prevention. Which statement by a student indicates understanding of the teaching?
411. A patient has a positive test for hepatitis C and is admitted to the hospital. The admission laboratory tests reveal a normal ALT, and a liver biopsy is negative for hepatic fibrosis and inflammation. The nurse will prepare this patient for:
412. A patient with HIV contracts herpes simplex virus (HSV), and the prescriber orders acyclovir [Zovirax] 400 mg PO twice daily for 10 days. After 7 days of therapy, the patient reports having an increased number of lesions. The nurse will expect the provider to:
413. A nursing student asks a nurse why pegylated interferon alpha is used instead of regular interferon for a patient with hepatitis C. The nurse will tell the student that pegylated interferon:
414. A patient has a positive test for influenza type A and tells the nurse that symptoms began 5 days before being tested. The prescriber has ordered oseltamivir [Tamiflu]. The nurse will tell the patient that oseltamivir:
415. A patient who is pregnant has a history of recurrent genital herpesvirus (HSV). The patient asks the nurse what will be done to suppress an outbreak when she is near term. The nurse will tell the patient that:
416. A nurse provides teaching for a patient with cytomegalovirus (CMV) retinitis who will receive the ganciclovir ocular implant [Vitrasert]. Which statement by the patient indicates a need for further teaching?
417. A patient has lamivudine-resistant hepatitis B and has been taking entecavir [Baraclude] for 2 years. The patient asks the nurse why the provider has recommended taking the drug for another year. What will the nurse tell the patient?
418. The nurse is caring for a patient receiving intravenous acyclovir [Zovirax]. To prevent nephrotoxicity associated with intravenous acyclovir, the nurse will:
419. A patient comes to the clinic and receives valacyclovir [Valtrex] for a herpes-zoster virus.
The nurse instructs the patient to take the medication:
420. An immunocompromised child is exposed to chickenpox and the provider orders valacyclovir [Valtrex] to be given orally three times daily. The nurse will contact the provider to change this order for which reason?
421. A male patient with hepatitis C will begin triple drug therapy with pegylated interferon alpha 2a [Pegasys], ribavirin [Ribasphere], and boceprevir [Victrelis]. The patient tells the nurse that his wife is pregnant. What will the nurse tell him?
422. A female patient who has hepatitis C is being treated with pegylated interferon alpha and ribavirin [Ribasphere]. It will be important for the nurse to teach this patient that:
423. A patient with hepatitis B begins treatment with adefovir [Hepsera] and asks the nurse how long the drug therapy will last. The nurse will tell the patient that the medication will need to be taken for:
[Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 104 pages
Buy Now
Instant download

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$40.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
174
0
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Nov 14, 2020
Number of pages
104
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Nov 14, 2020
Downloads
0
Views
174