Question 1. (TCOs 1, 2) Determine whether the following passage is an argument.
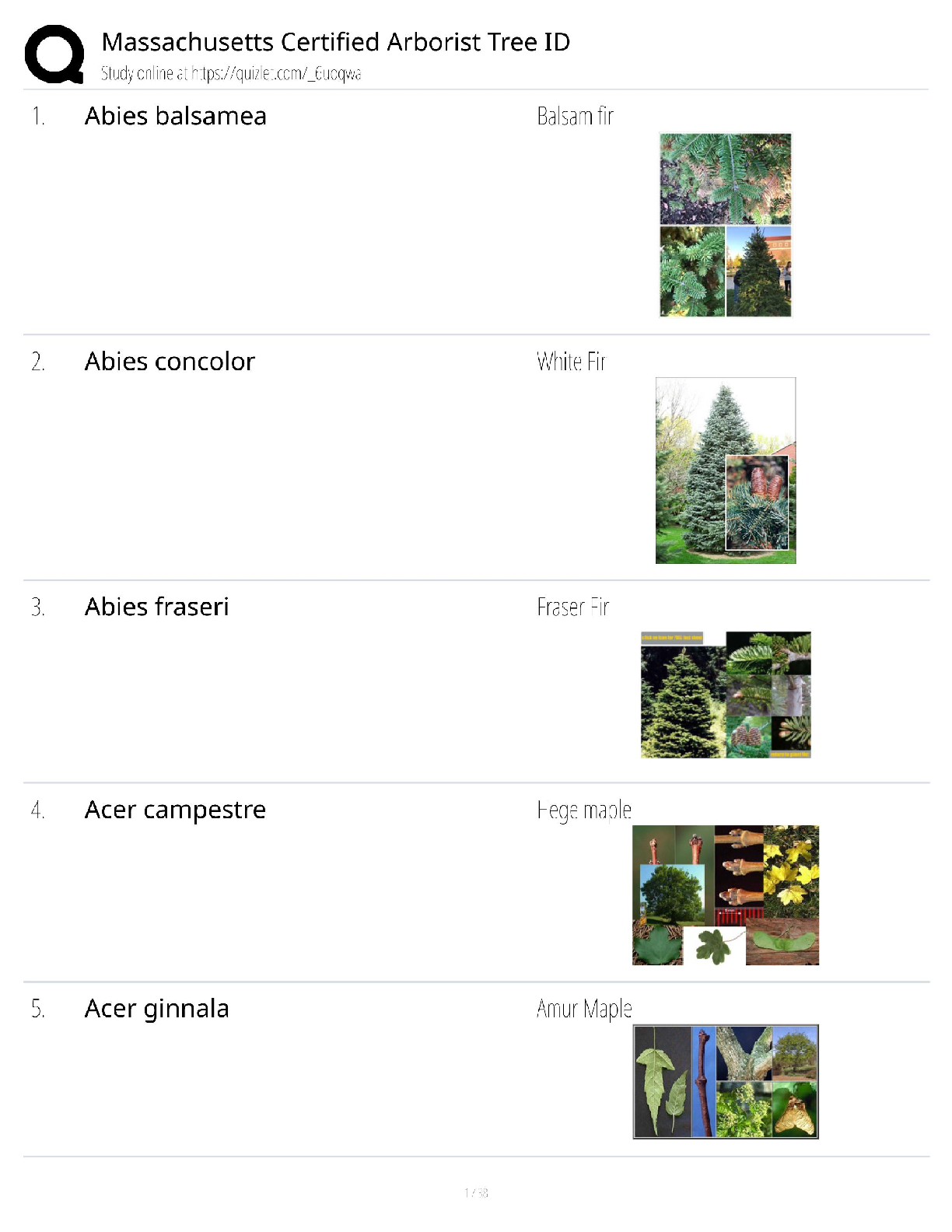
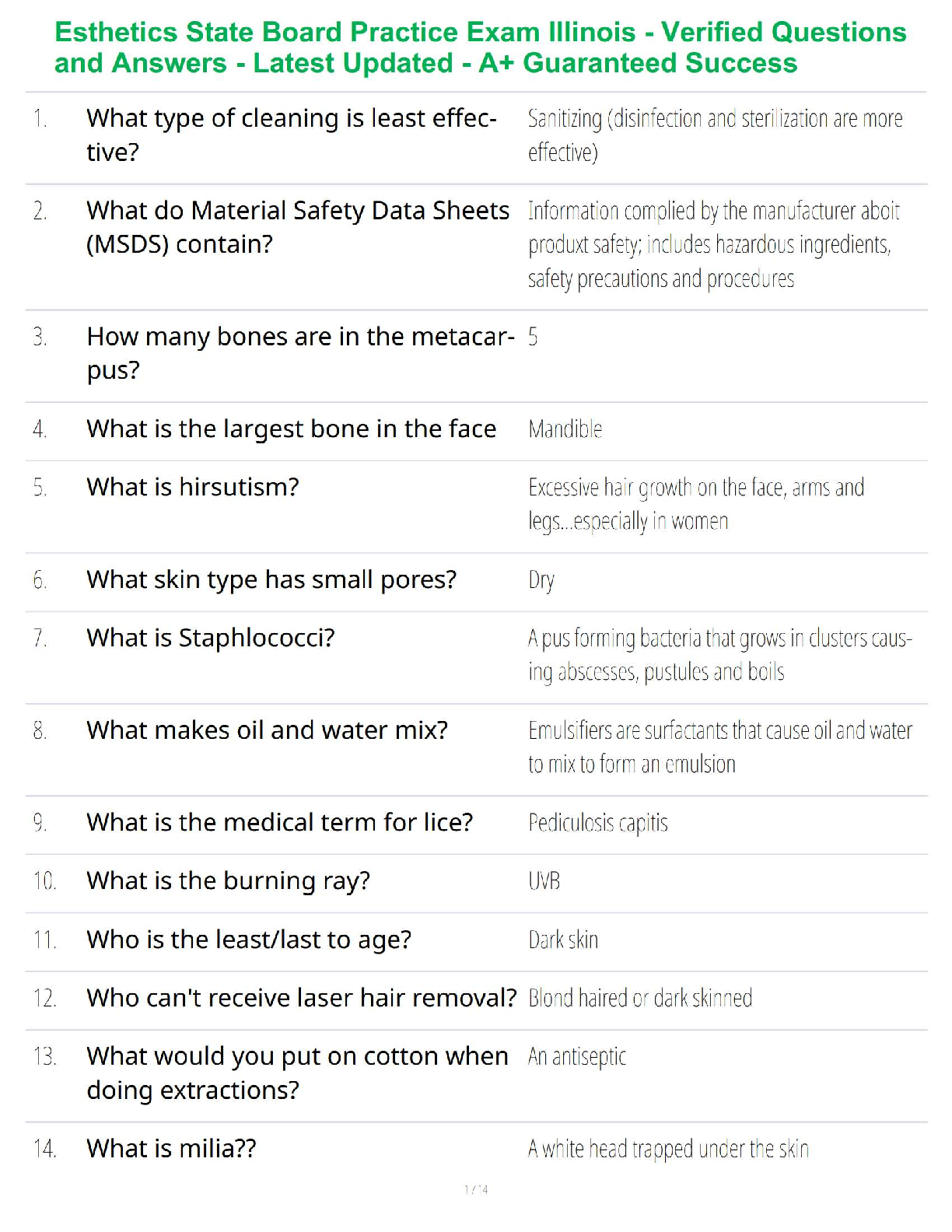
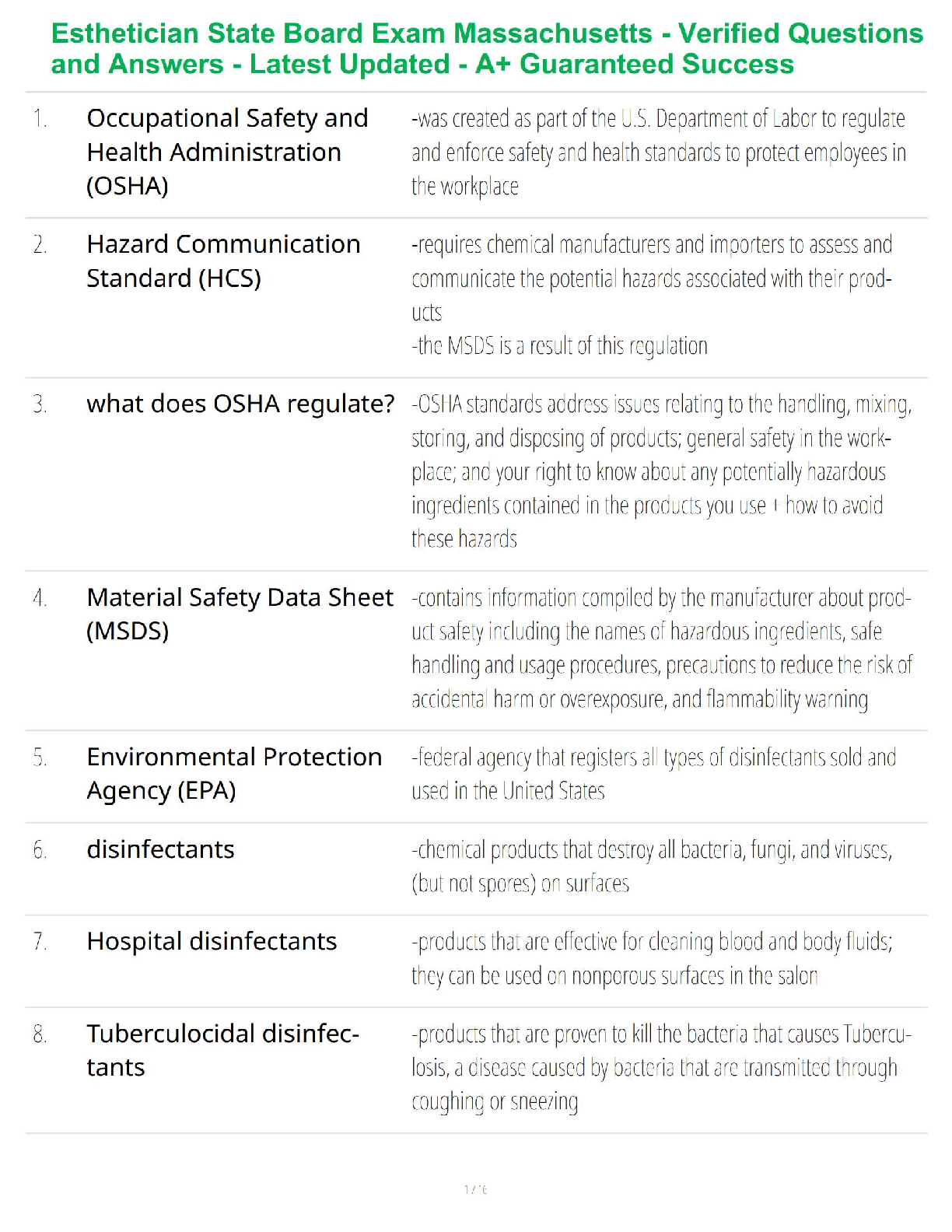
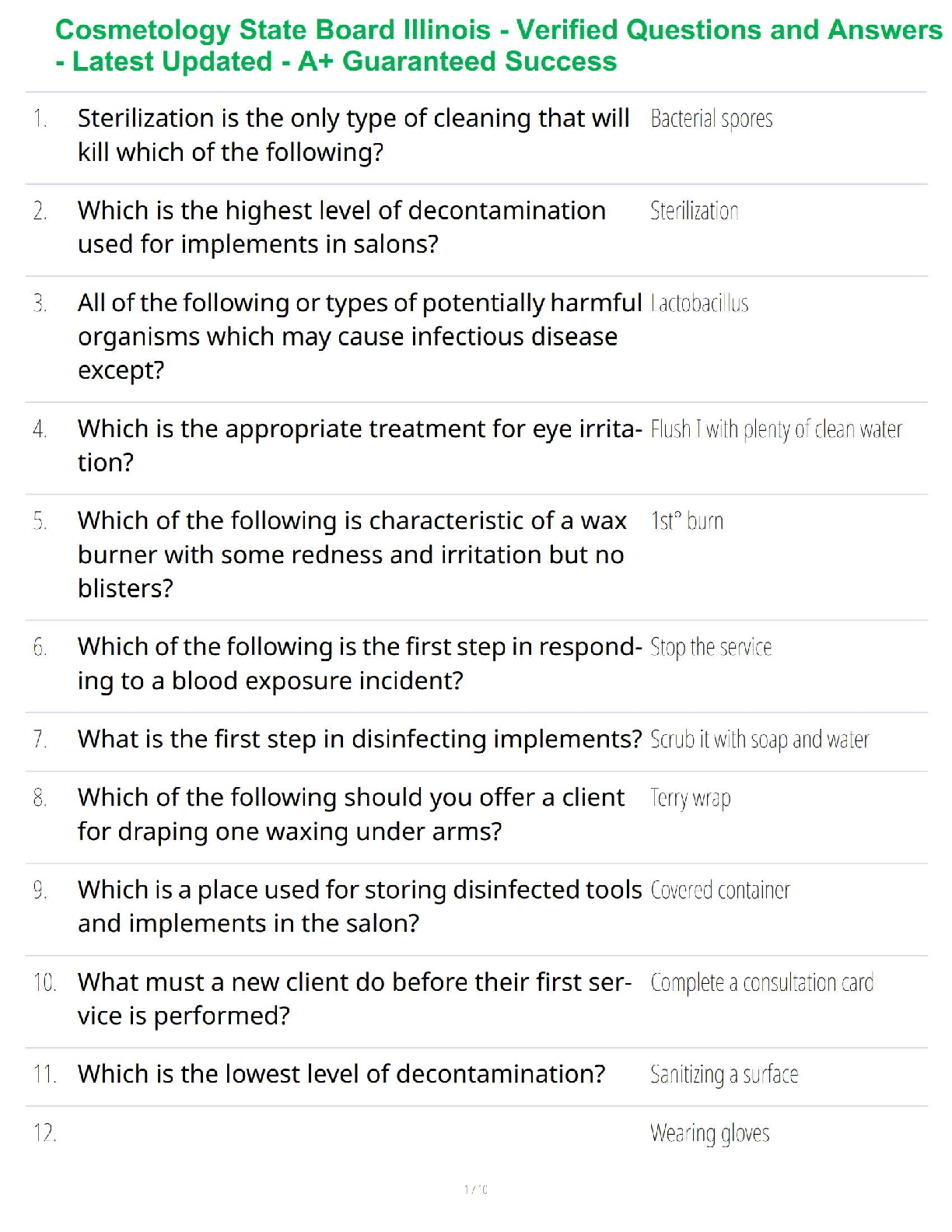
Mark is the newest member of the requisitions department. The requisitions department oversees
the purchasing of all goods, services, & ca
...
Question 1. (TCOs 1, 2) Determine whether the following passage is an argument.
Mark is the newest member of the requisitions department. The requisitions department oversees
the purchasing of all goods, services, & capital equipment for the entire company. (Pt : 5)
Argument
Not an argument because there are no claims or only one claim
Not an argument because none of the claims offers a reason for the other
Not an argument because the reasons explain rather than prove the other claims
Question 2. (TCOs 1, 2) Determine whether the following passage is an argument.
Either you are planning to vote in the fall election or you donât really want to improve the
politics of the local community. (Pt : 5)
Argument
Not an argument because there are no claims or only one claim
Not an argument because none of the claims offers a reason for the other
Not an argument because the reasons explain rather than prove the other claims
Question 3. (TCOs 2, 3) Choose the best answer.
Donât drive over the speed limit. Itâs against the law. You donât want a speeding ticket.
Which of the following claims represents the conclusion of this argument? (Pt : 5)
Driving over the speed limit is against the law.
You donât want a speeding ticket.
You should not drive over the speed limit.
Question 4. (TCOs 2, 3) Choose the best answer.
Healthy. Delicious. Drink Ovaltine!
Which of the following claims represents the implied conclusion of this argument? (Pt : 5)
Ovaltine is healthy.
Ovaltine is delicious
You should drink Ovaltine.
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 06-05-2022 05:28:32 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/45835992/PHIL-347N-Week-8-Final-Examdocx/
None; this is not an argument.
Question 5. (TCOs 3, 4) Identify the kind of argument.
Since all Ford Mustangs are automobiles, & not all Ford Mustangs are red, some automobiles
are not red. (Pt : 5)
Causal argument
Categorical argument
Inductive generalization
Analogical argument
Question 6. (TCOs 3, 4) Identify the kind of argument.
Using a lemon when cooking is like using a lime. Given that limes can be added to bl& foods to
give them some zest, lemons, too, will give zest to bl& foods. (Pt : 5)
Analogical argument
Categorical argument
Truth-functional argument
Causal argument
Question 7. (TCO 3, 4) Identify the kind of argument.
Learning to think critically is like learning to play the piano. Given that you have to practice a
lot to be good at playing the piano, you must practice a lot to be a critical thinker. (Pt : 5)
Causal argument
Truth-functional argument
Inductive generalization
Analogical argument
Question 8. (TCOs 2, 3, 5) Relate to the proper terminology.
What evaluative language should you use for analogical arguments? (Pt : 5)
This study source was downloaded by 100000831988016 from CourseHero.com on 06-05-2022 05:28:32 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/45835992/PHIL-347N-Week-8-Final-Examdocx/
Valid/invalid; cogent/uncogent
Valid/invalid; sound/unsound
Strong/weak; cogent/uncogent
Strong/weak; sound/unsound
Question 9. (TCOs 2, 3, 5) Relate to the proper terminology.
What evaluative language should you use for truth-functional arguments? (Pt : 5)
Valid/invalid; cogent/uncogent
Valid/invalid; sound/unsound
Strong/weak; cogent/uncogent
Strong/weak; sound/unsound
Question 10. (TCO 4) Select the answ
[Show More]














.png)