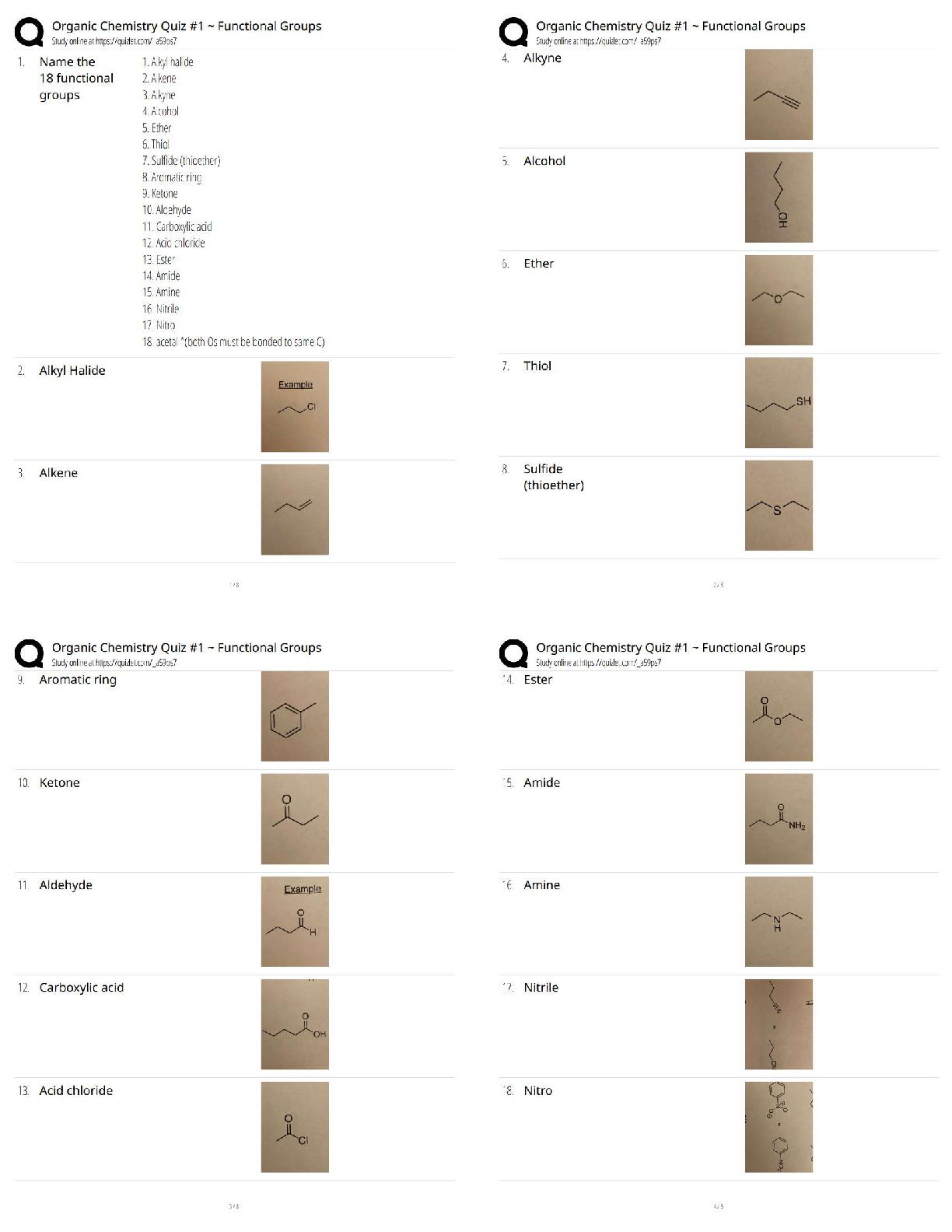
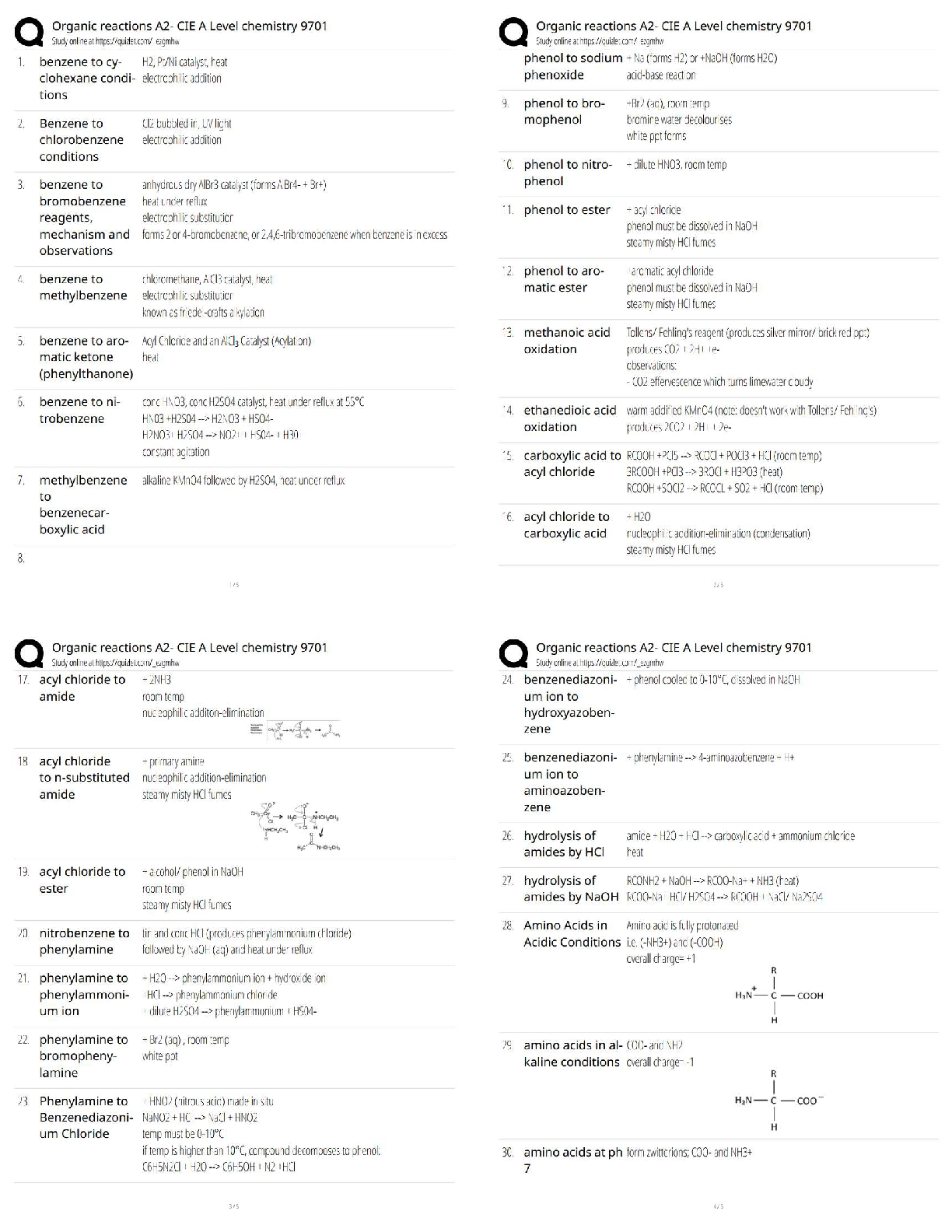
NCLEX UWorld
When do *advanced directives* go into effect? - ✔✔when person is *unable to speak for
him/herself* due to either:
1. *Mental Incapacity* - *coma *(GCS score ≤ 7)
2. *Aphasia*
(≠as soon as signed; direct
...
NCLEX UWorld
When do *advanced directives* go into effect? - ✔✔when person is *unable to speak for
him/herself* due to either:
1. *Mental Incapacity* - *coma *(GCS score ≤ 7)
2. *Aphasia*
(≠as soon as signed; directives can always be changed later by person)
SBAR Communication Framekwork Components - ✔✔1. *S* = Situation - what *prompted* the
communication (eg *what* changes occurred)
2. *B* = Background - *pertinent information, relevant history, vital signs*
3. *A* = Assessment - nurse's assessment of the situation (*when* & *what changes* occurred)
4. *R* = Recommendation - *request* for *prescription* or *action* from HCP
Appropriate order of actions when client found on floor - ✔✔1. *Assessment* of *physiological
stability* (ABCs)
2. *Assessment* of *injuries*
3. *Moving client*
4. *Notifications*
5. *Documentation*
Conditions of being *ineligible to leave AMA* - ✔✔1 *danger to self or others*
2. *lack of consciousness*
3. *Altered consciousness*
4. *Mental illness*
5. Being under *chemical influence*
6. *Court decision*
Effective handoff communication components - ✔✔Nurse should:
1. Provide *identifying information* (eg client's name and room number)
2. Note *care priorities* and upcoming or outstanding tasks (eg time to replace medication
infusion bag, need to perform delayed wound care and cause of delay)
3. Provide *exact, pertinent information* (eg medication dose, time, measurable outcomes)
4. Include *multidisciplinary plans* (eg radiology examinations, family meetings, physical
therapy)
5. Relay significant client changes in a clear manner
*Risk factors* for *cervical cancer* - ✔✔1. Infection with high-risk HPV strains
2. History of sexually transmitted diseases
3. Early onset of sexual activity
4. Multiple or high-risk sexual partners
5. Immunosuppression
6. Oral contraceptive use
7. Low SES
8. Tobacco use
what medications interact with grapefruit? - ✔✔1. *calcium channel blockers* (diltiazem,
nifedipine, verapamil, etc)
2. *statins*
3. *SSRIs*
Risk associated with *stent placement* using the *femoral approach* - ✔✔*retroperitoneal
hemorrhage*
what are early signs of bleeding into the retroperitoneal space? - ✔✔hypotension, back pain,
flank ecchymosis (grey turner sign), hematoma formation, diminshed distal pulses
what is the grey-turner sign and what is it a sign of? - ✔✔bruising of the flanks and
retroperitoneal hemorrhage and is a bluish color
what are some physical signs of peripheral arterial disease? - ✔✔intermittent calf muscle pain?,
rest pain, hair loss, decreased peripheral pulses, cool, dry, shiny skin, thick brittle nails,
gangrene, ulcers (all of these are in the extremities)
transplanted hearts are expected to be - ✔✔tachycardic like 90-110
what is the priority intervention for pain with sickle cell crisis and why? - ✔✔administer IV
fluids to reduce blood viscosity and restore perfusion to areas affected by vasoocclusion
what is the purpose of continuous bladder irrigation? - ✔✔it is perscribed after TURP to prevent
obstruction of urine outflow by removing clotted blood from the bladder
what is the nurses care of monitoring CBI? - ✔✔monitor quality of drainage, titrate the inflow
rate, and manurally irrigating as needed
characteristics of a basilar skull fracture - ✔✔periorbital hematomas (raccoon eyes), csf fluid
rhinorrhea, and battle sign (behind the ear bruising)
immediate client care for basilar skull fracture - ✔✔cervical spime immobilization, close
neurologic monitoring, and support of ABCs
vomiting with intake may mean - ✔✔viral or bacterial infection
tympanosomty tubes are placed for - ✔✔recurrent otis medias
nurse actions during a seizure - ✔✔assist them to lie down is standing/sitting, put them on side
for patent airway, loosen tight clothing, give oxygen as needed, remove objects from immediate
area, document time and duration of seizure (for tests are done later to see which type of seizure
and maybe what exacerates it)
never put anything in mouth or restrain them since musclec ontractions can occur during a
seizure
what are some early symptoms of ICP? - ✔✔altered LOC, headache, abnormal reathing, rise in
bp, slow pulse, vomiting
client who has a TIA is often placed on - ✔✔prophylactic antithrombotic treatment like aspirin
or clopidogrel
glascow coma scale ranges from - ✔✔3-15; 3 being worst 15 being best condition (8 or below in
a coma)
what are the 3 components? - ✔✔eye opening
motor response
verbal response
what is a primary component in TPN? - ✔✔*glucose,* so the nurse should be monitoring blood
glucose and be assessing for signs of hyperglycemia
when a client is on TPN, the nurse must assess for hyperglycemia why? - ✔✔bc a primary
component is glucose. therefore the nurse must be assessing to see if the client is getting too
much glucose (hoerglycemia). and with a large urinary output like 4800, this could indicate
symptoms of hyperglycemia
signs of hyperglycemia - ✔✔- polydipsia,
- polyuria,
- restless,
- confused,
- bg over 200,
- fatigue,
- headache
- blurred vision
- kussmaul resp
Interventions to resolve TPN-associated hyperglycemia - ✔✔- reduce amount of carbohydrate in
TPN solution
- slow down infusion rate
- administer subcutaneous insulin
what is the goal for mass casualty events? - ✔✔do the greatest good for the greatest number of
people
keep in mind that disaster triage ranks the l
[Show More]







.png)




.png)

.png)