Chamberlain College of Nursing NCLEX practice solved solution docs
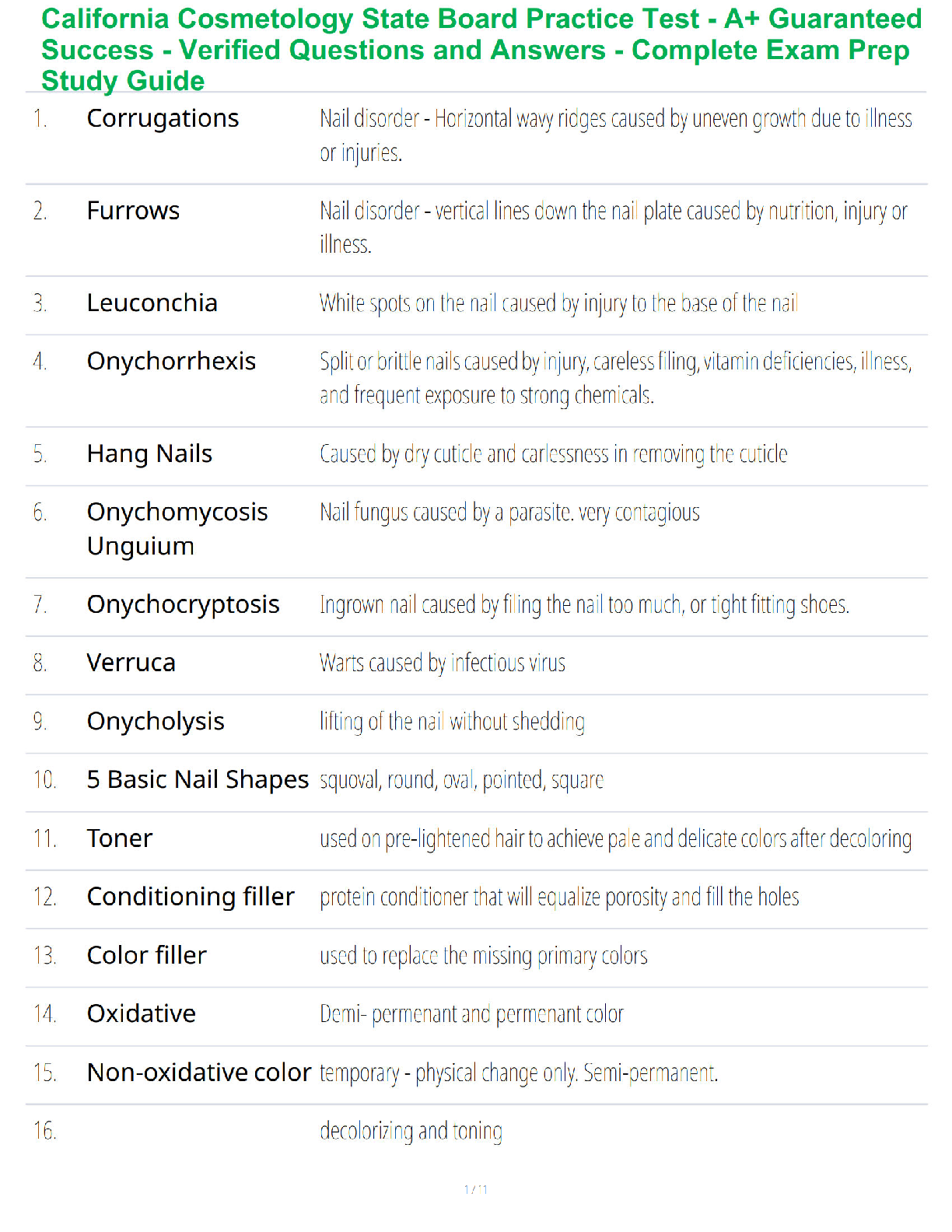
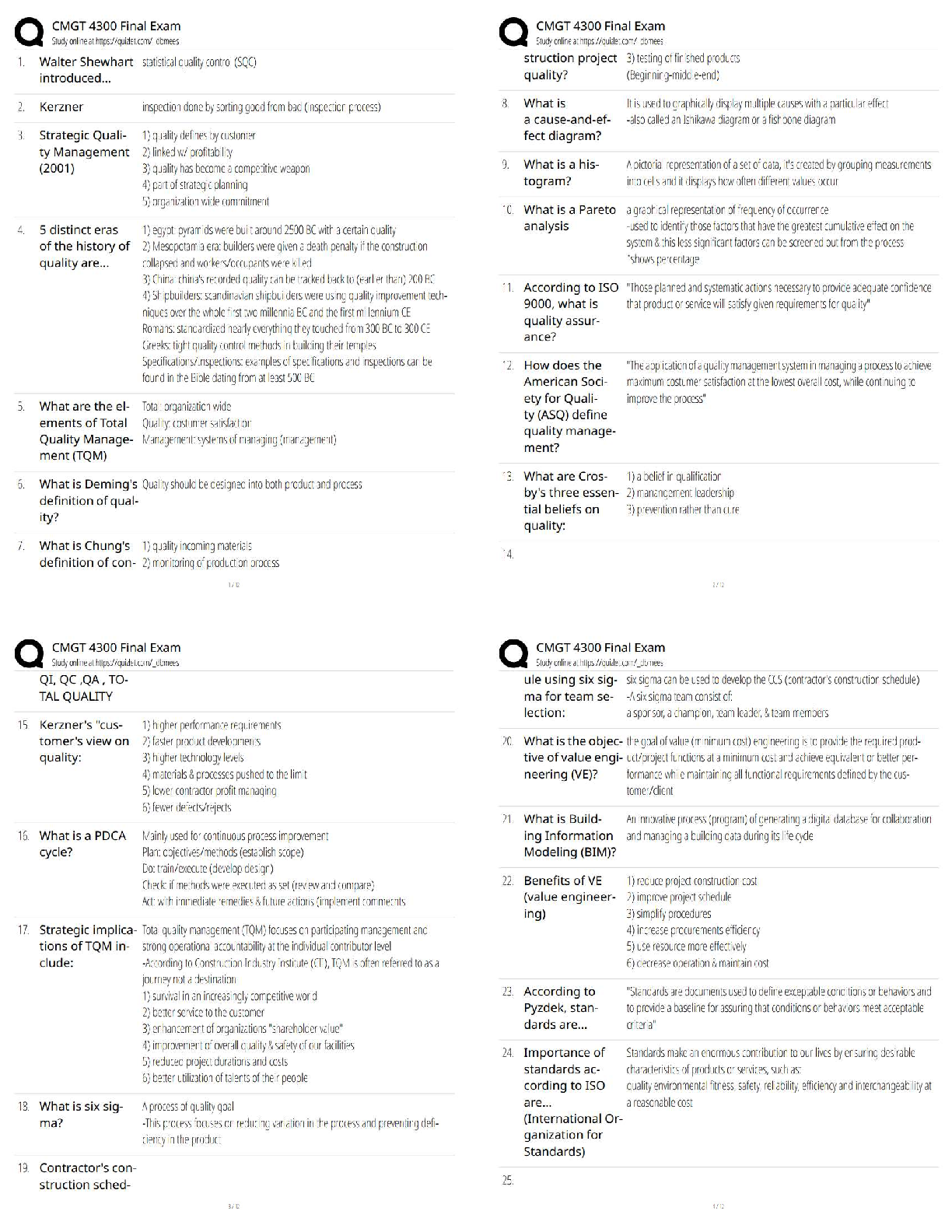
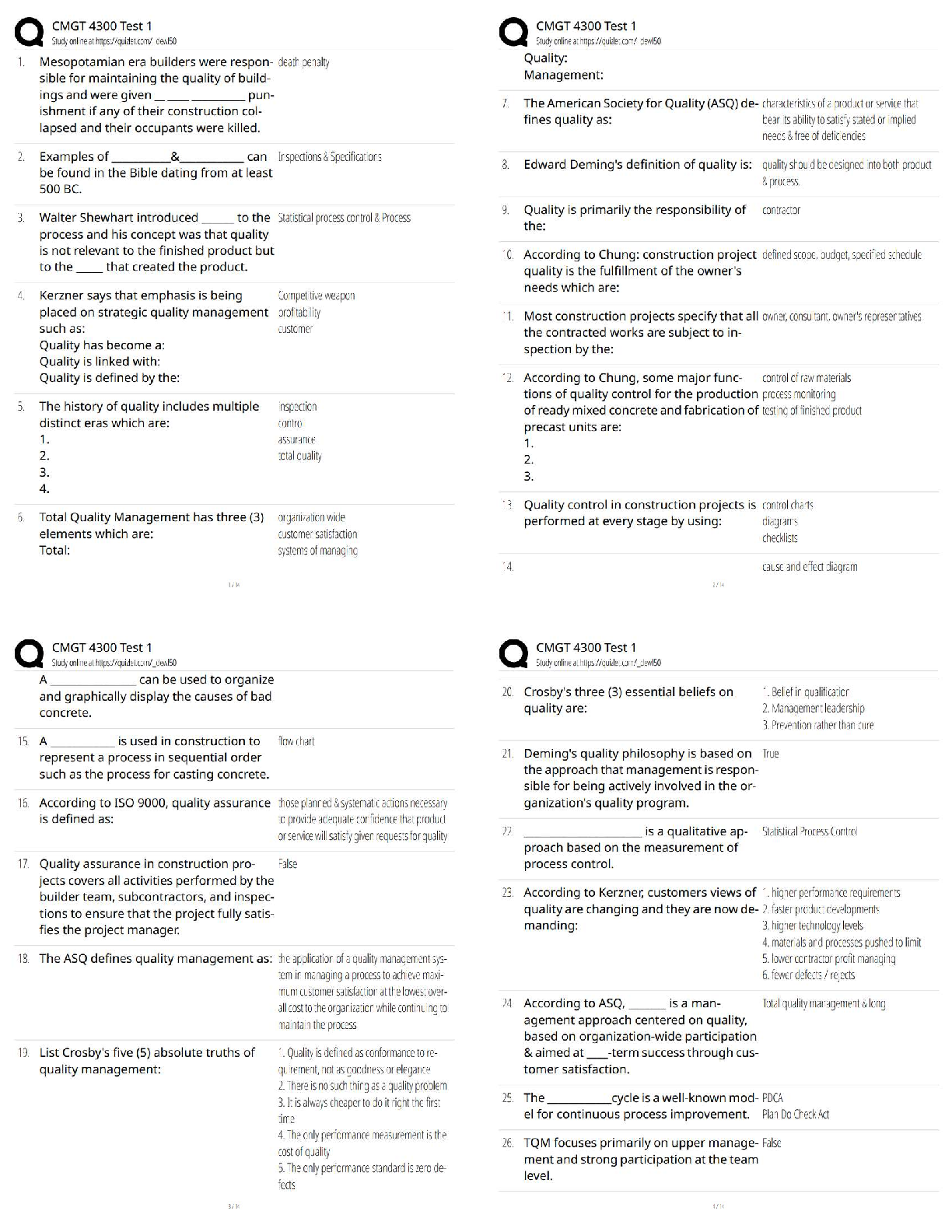
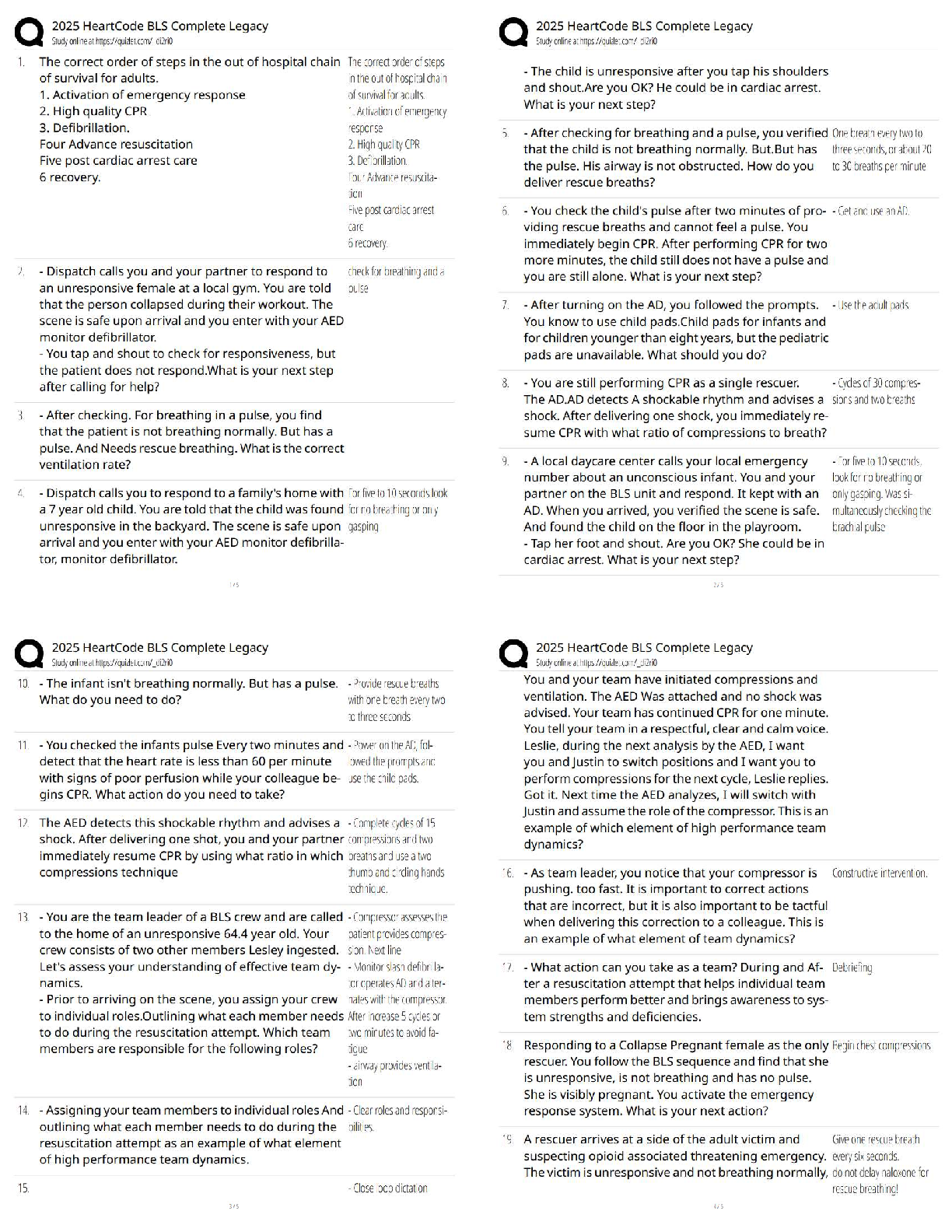
An RN is making assignments for client care to an LPN at the beginning of the shift. Which of the following assignments should the LPN question?
A. As
...
Chamberlain College of Nursing NCLEX practice solved solution docs
An RN is making assignments for client care to an LPN at the beginning of the shift. Which of the following assignments should the LPN question?
A. Assisting a client who is 24 hr postop to use an incentive spirometer
B. Collecting a clean catch urine specimen from a client who was admitted on the previous shift
C. providing nasopharyngeal suctioning for a client who has pneumonia
D. Replacing the cartridge and tubing on a PCA pump
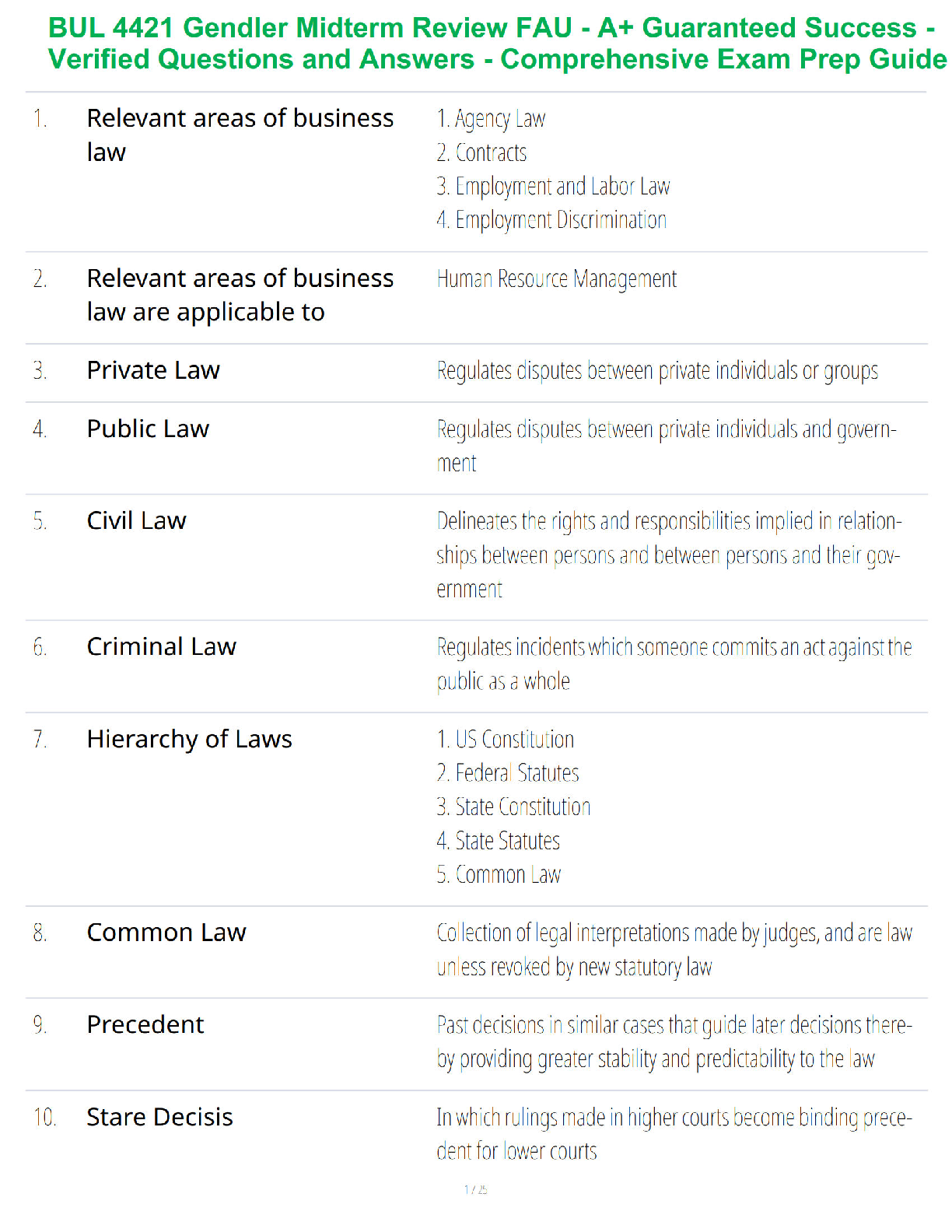
A nurse is preparing an inservice program about delegation. Which of the following elements should she identify when presenting the 5 rights of delegation. Select all:
A. Right client
B. Right supervision/evaluation
C. Right direction/communication
D. Right time
E. Right circumstances
A nurse offers pain meds to a client who is postop prior to ambulation. The nurse understands that this aspect of care delivery is an example of which of the following ethical principles?
A. Fidelity
B. Autonomy
C. Justice
D. Beneficience
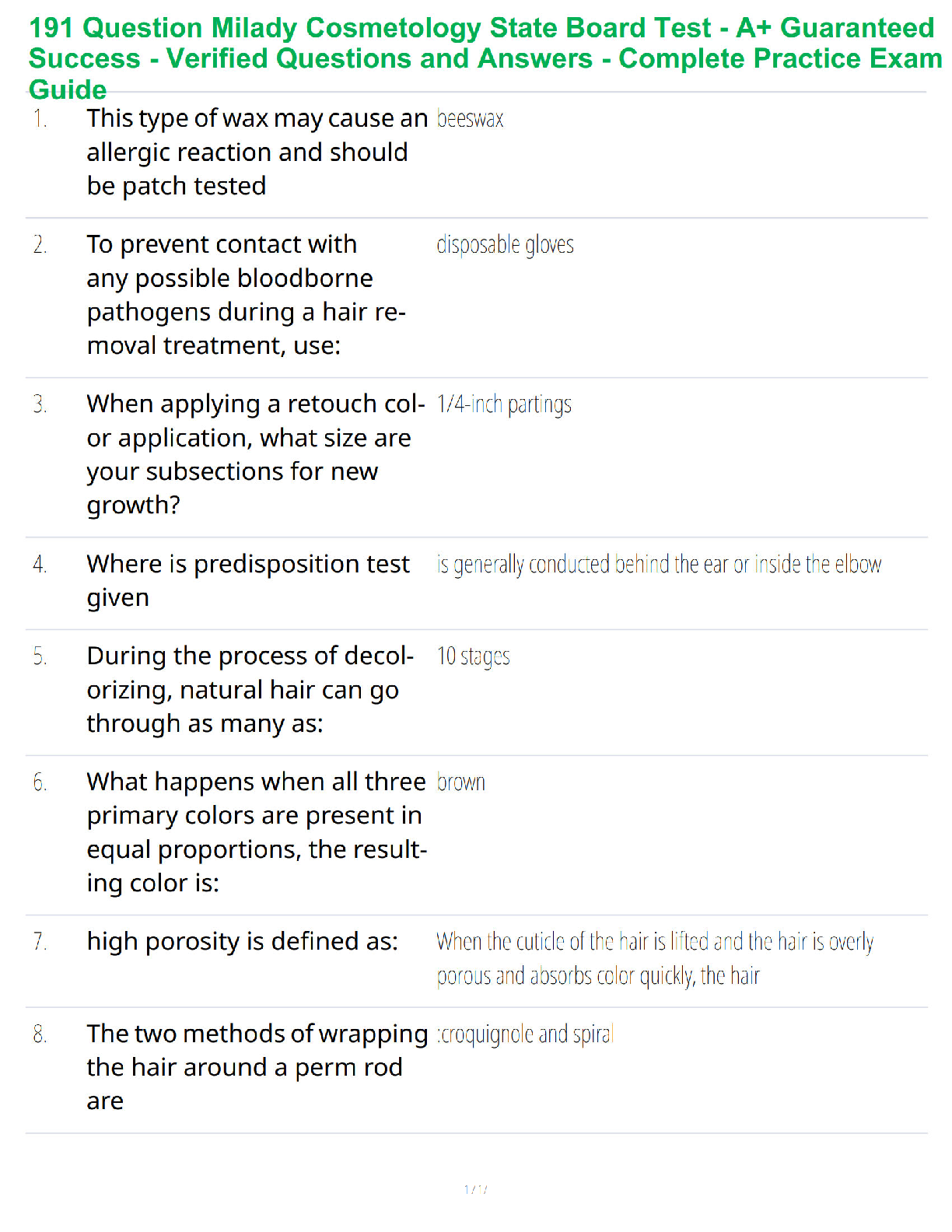
An RN is making assignments for client care to an LPN at the beginning of the shift. Which of the following assignments should the LPN question?
A. Assisting a client who is 24 hr postop to use an incentive spirometer
B. Collecting a clean catch urine specimen from a client who was admitted on the previous shift
C. providing nasopharyngeal suctioning for a client who has pneumonia
D. Replacing the cartridge and tubing on a PCA pump
A four-month-old infant is admitted to the pediatric intensive care unit
with a temperature of 105°F (40.5 °C). The infant is irritable, and the nurse
observes nuchal rigidity. Which assessment finding would indicate an
increase in intracranial pressure?
1. Positive Babinski.
2. High-pitched cry.
3. Bulging posterior fontanelle.
4. Pinpoint pupils.
A client is receiving total parenteral nutrition (TPN). To determine the
client's tolerance of this treatment, the nurse should assess for which of the
following?
1. A significant increase in pulse rate.
2. A decrease in diastolic blood pressure.
3. Temperature in excess of 98.6°F (37°C).
4. Urine output of at least 30 cc per hour.
The client is exhibiting symptoms of myxedema. The nursing
assessment should reveal
1. increased pulse rate.
2. decreased temperature.
3. fine tremors.
4. increased radioactive iodine uptake level.
2
A nonstress test is scheduled for a client at 34-weeks gestation who
developed hypertension, periorbital edema, and proteinuria. Which of the
following nursing actions should be included in the care plan in order to
BEST prepare the client for the diagnostic test?
1. Start an intravenous line for an oxytocin infusion.
2. Obtain a signed consent prior to the procedure.
3. Instruct client to push a button when she feels fetal movement.
4. Attach a spiral electrode to the fetal head.
3
Which of the following nursing interventions is MOST important for a
45-year-old woman with rheumatoid arthritis?
1. Provide support to flexed joints with pillows and pads.
2. Position her on her abdomen several times a day.
3. Massage the inflamed joints with creams and oils.
4. Assist her with heat application and ROM exercises.
the nurse is caring for a young adult admitted to the hospital with a
severe head injury. The nurse should position the patient
1. with his neck in a midline position and the head of the bed elevated 30°.
2. side-lying with his head extended and the bed flat.
3. in high Fowler's position with his head maintained in a neutral position.
4. in semi-Fowler's position with his head turned to the side.
The nurse is teaching a 40-year-old man diagnosed with a lower motor
neuron disorder to perform intermittent self-catheterization at home. The
nurse should instruct the client to
1. use a new sterile catheter each time he performs a catheterization.
2. perform the Valsalva maneuver(holding breath and bearing down) before doing the catheterization.
3. perform the catheterization procedure every 8 hours.
4. limit his fluid intake to reduce the number of times a catheterization is needed.
A client is being discharged with sublingual nitroglycerin (Nitrostat).
The client should be cautioned by the nurse to
1. take the medication five minutes after the pain has started.
2. stop taking the medication if a stinging sensation is absent.
3. take the medication on an empty stomach.
4. avoid abrupt changes in posture.
A 38-year-old woman is returned to her room after a subtotal
thyroidectomy for treatment of hyperthyroidism. Which of the following, if
found by the nurse at the patient's bedside, is nonessential?
1. Potassium chloride for IV administration.
2. Calcium gluconate for IV administration.
3. Tracheostomy set-up.
4. Suction equipment.
A nurse recognizes that an initial positive outcome of treatment for a
victim of sexual abuse by one parent would be that the client
1. acknowledges willing participation in an incestuous relationship.
2. reestablishes a trusting relationship with his/her other parent.
3. verbalizes that s/he is not responsible for the sexual abuse.
4. describes feelings of anxiety when speaking about sexual abuse.
An adolescent client is ordered to take tetracycline HCL (Achromycin)
250 mg PO bid. Which of the following instructions should be given to this
client by the nurse?
1. "Take the medication on a full stomach, or with a glass of milk."
2. "Wear sunscreen and a hat when outdoors."
3. "Continue taking the medication until you feel better."
4. "Avoid the use of soaps or detergents for two weeks."
After a client develops left-sided hemiparesis from a cerebral vascular
accident (CVA), there is a decrease in muscle tone. Which of the following
nursing diagnoses would be a priority to include in his care plan?
1. Alteration in mobility related to paralysis.
2. Alteration in skin integrity related to decrease in tissue oxygenation.
3. Alteration in skin integrity related to immobility.
4. Alteration in communication related to decrease in thought processes
history of oliguria, hypertension, and peripheral edema. Current lab values are: BUN -25, K+ -4.0 mEq/L. Which nutrient should berestricted in the client's diet?
1. Protein.
2. Fats.
3. Carbohydrates.
4. Magnesium
An extremely agitated client is receiving haloperidol (Haldol) IM every30 minutes while in the psychiatric emergency room. The MOST importantnursing intervention is to
1. monitor vital signs, especially blood pressure, every 30 minutes.
2. remain at the client's side to provide reassurance.
3. tell the client the name of the medication and its effects.
4. monitor the anticholinergic effects of the medication.
The nurse is caring for clients in the skilled nursing facility. Which of the
following clients require the nurse's IMMEDIATE attention?
1. A client admitted for a cerebral vascular accident (CVA) whose prescription for
warfarin (Coumadin) expired two days ago.
2. A client in pain who was receiving morphine in an acute care institution and was
transferred with a prescription for acetaminophen with codeine.
3. A client who has dysuria and foul-smelling, cloudy, dark amber urine.
4. An immunosuppressed client who has not received an influenza immunization.
The nurse is observing care given to a client experiencing severe topanic levels of anxiety. The nurse would intervene in which of the followingsituations?
1. The staff maintains a calm manner when interacting with the client.
2. The staff attends to client's physical needs as necessary.
3. The staff helps the client identify thoughts or feelings that occurred prior to the
onset of the anxiety.
4. The staff assesses the client's need for medication or seclusion if other
interventions have failed to reduce anxiety.
A 69-year-old client is undergoing his second exchange of intermittent
peritoneal dialysis (IPD). Which of the following would require an
intervention by the nurse?
1. The client complains of pain during the inflow of the dialysate.
2. The client complains of constipation.
3. The dialysate outflow is cloudy.
4. There is blood-tinged fluid around the intra-abdominal catheter.
The clinic nurse is performing diet teaching with a 67-year-old client
with acute gout. The nurse should teach the client to limit his intake of
1. red meat and shellfish.
2. cottage cheese and ice cream.
3. fruit juices and milk.
4. fresh fruits and uncooked vegetables.
A client is scheduled for a left lower lobectomy. The physician has
ordered diazepam (Valium) 2 mg IM for anxiety. The nurse would determine
that the medication is appropriate if the client displays which of the
following symptoms?
1. Agitation and decreased level of consciousness.
2. Lethargy and decreased respiratory rate.
3. Restlessness and increased heart rate.
4. Hostility and increased blood pressure.
A 59-year-old woman with bipolar disorder is receiving haloperidol
(Haldol) 2 mg PO tid. She tells the nurse, "Milk is coming out of my
breasts." Which of the following responses by the nurse is BEST?
1. "You are seeing things that aren't real."
2. "Why don't we go make some fudge."
3. "You are experiencing a side effect of Haldol."
4. "I'll contact your physician to change your medication."
The physician orders ranitidine hydrochloride (Zantac) 150 mg PO qd for
a client. The nurse should advise the client the BEST time to take this
medication is
1. before breakfast.
2. with dinner.
3. with food.
4. at hs.
. If a client develops cor pulmonale (right-sided heart failure), the nurse
would expect to observe
1. increasing respiratory difficulty seen with exertion.
2. cough productive of a large amount of thick, yellow mucus.
3. peripheral edema and anorexia.
4. twitching of extremities.
The nurse is performing triage on a group of clients in the emergency
department. Which of the following clients should the nurse see FIRST?
1. A 12-year-old oozing blood from a laceration of the left thumb due to cut on a
rusty metal can.
2. A 19-year-old with a fever of 103.8°F (39.8°C) who is able to identify her sister
but not the place
and time.
3. A 49-year-old with a compound fracture of the right leg who is complaining of
severe pain.
4. A 65-year-old with a flushed face, dry mucous membranes, and a blood sugar of
470 mg/dL.
The nurse in the outpatient clinic teaches a client with a sprained right
ankle to walk with a cane. What behavior, if demonstrated by the client,
would indicate that teaching was effective?
1. The client advances the cane 18 inches in front of her foot with each step.
2. The client holds the cane in her left hand.
3. The client advances her right leg, then her left leg, and then the cane.
4. The client holds the cane with her elbow flexed 60°.
A client returns to his room following a myelogram. The nursing care
plan should include which of the following?
1. Encourage oral fluid intake.
2. Maintain the prone position for 12 hours.
3. Encourage the client to ambulate after the procedure.
4. Evaluate the client's distal pulses on the affected side.
The nurse is caring for a patient following an appendectomy. The patient
takes a deep breath, coughs, and then winces in pain. Which of the
following statements, if made by the nurse to the patient, is BEST?
1. "Take three deep breaths, hold your incision, and then cough."
2. "That was good. Do that again and soon it won't hurt as much."
3. "It won't hurt as much if you hold your incision when you cough."
4. "Take another deep breath, hold it, and then cough deeply
A young woman is transferred to a psychiatric crisis unit with a
diagnosis of a dissociative disorder. The nurse knows which of the following
comments by the client is MOST indicative of this disorder?
1. "I keep having recurring nightmares."
2. "I have a headache and my stomach has bothered me for a week."
3. "I always check the door locks three times before I leave home."
4. "I don't know who I am and I don't know where I live."
A 23-year-old man is admitted with a subdural hematoma and cerebral
edema after a motorcycle accident. Which of the following symptoms should
the nurse expect to see INITIALLY?
1. Unequal and dilated pupils.
2. Decerebrate posturing.
3. Grand mal seizures.
4. Decreased level of consciousness.
An elderly client is returned to her room after an open reduction and
internal fixation of the left femoral head after a fracture. It is MOST
important for the nursing care plan to include that the client
1. eat a high-protein, low-residue diet.
2. lie on her unoperated side.
3. exercise her arms and legs.
4. cough and deep breathe.
Which of the following is a correctly stated nursing diagnosis for a client
with abruptio placentae?
1. Infection related to obstetrical trauma.
2. Potential for fetal injury related to abruptio placentae.
3. Potential alteration in tissue perfusion related to depletion of fibrinogen.
4. Fluid volume deficit related to bleeding.
An 8-year-old client is returned to the recovery room after a
bronchoscopy. The nurse should position the client
1. in semi-Fowler's position.
2. prone, with the head turned to the side.
3. with the head of the bed elevated 45° and the neck extended.
4. supine, with the head in the midline position
Which of the following assessment findings would indicate to the nurse
the need for more sedation in a client who is withdrawing from alcohol
dependence?
1. Steadily increasing vital signs.
2. Mild tremors and irritability.
3. Decreased respirations and disorientation.
4. Stomach distress and inability to sleep.
The home care nurse is instructing a client recently diagnosed with
tuberculosis. It is MOST important for the nurse to include which of the
following as a part of the teaching plan?
1. During the first two weeks of treatment, the client should cover his mouth and
nose when he coughs or sneezes.
2. It is necessary for the client to wear a mask at all times to prevent transmission of
the disease.
3. The family should support the client to help reduce feeling of low self-esteem and
isolation.
4. The client will be required to take prescribed medication for a duration of 6-9
months.
The nurse's INITIAL priority when managing a physically assaultiveclient is to
1. restrict the client to the room.
2. place the client under one-to-one supervision.
3. restore the client's self-control and prevent further loss of control.
4. clear the immediate area of other clients to prevent harm.
A client with newly diagnosed type I diabetes mellitus is being seen bythe home health nurse. The physician orders include: 1,200-calorie ADAdiet, 15 units of NPH insulin before breakfast, and check blood sugar qid.When the nurse visits the client at 5 PM, the nurse observes the manperforming a blood sugar analysis. The result is 50 mg/dL. The nurse wouldexpect the client to be
1. confused with cold, clammy skin and a pulse of 110.
2. lethargic with hot, dry skin and rapid, deep respirations.
3. alert and cooperative with a BP of 130/80 and respirations of 12.
4. short of breath, with distended neck veins and a bounding pulse of 96.
The nurse is supervising the staff providing care for an 18-month-oldhospitalized with hepatitis A. The nurse determines that the staff's care isappropriate if which of the following is observed?
1. The child is placed in a private room.
2. The staff removes a toy from the child's bed and takes it to the nurse's station.
3. The staff offers the child french fries and a vanilla milkshake for a midafternoon
snack.
4. The staff uses standard precautions.
When using restraints for an agitated/aggressive patient, which of the
following statements should NOT influence the nurse's actions during this
intervention?
1. The restraints/seclusion policies set forth by the institution.
2. The patient's competence.
3. The patient's voluntary/involuntary status.
4. The patient's nursing care plan.
The nurse is caring for an 80-year-old client with Parkinson's disease.
Which of the following nursing goals is MOST realistic and appropriate in
planning care for this client?
1. Return the client to usual activities of daily living.
2. Maintain optimal function within the client's limitations.
3. Prepare the client for a peaceful and dignified death.
4. Arrest progression of the disease process in the client.
A client with a peptic ulcer had a partial gastrectomy and vagotomy(Billroth I). In planning the discharge teaching, the client should becautioned by the nurse about which of the following?
1. Sit up for at least 30 minutes after eating.
2. Avoid fluids between meals.
3. Increase the intake of high-carbohydrate foods.
4. Avoid eating large meals that are high in simple sugars and liquids.
A nurse is caring for a 37-year-old woman with metastatic ovariancancer admitted for nausea and vomiting. The physician orders totalparenteral nutrition (TPN), a nutritional consult, and diet recall. Which ofthe following is the BEST indication that the patient's nutritional status hasimproved after 4 days?
1. The patient eats most of the food served to her.
2. The patient has gained 1 pound since admission.
3. The patient's albumin level is 4.0mg/dL.
4. The patient's hemoglobin is 8.5g/dL.
A 23-year-old woman at 32-weeks gestation is seen in the outpatientclinic. Which of the following findings, if assessed by the nurse, wouldindicate a possible complication?
1. The client's urine test is positive for glucose and acetone.
2. The client has 1+ pedal edema in both feet at the end of the day.
3. The client complains of an increase in vaginal discharge.
4. The client says she feels pressure against her diaphragm when the baby moves.
After abdominal surgery, a client has a nasogastric tube attached to lowsuctioning. The client becomes nauseated, and the nurse observes adecrease in the flow of gastric secretions. Which of the following nursinginterventions would be MOST appropriate?
1. Irrigate the nasogastric tube with distilled water.
2. Aspirate the gastric contents with a syringe.
3. Administer an antiemetic medicine.
4. Insert a new nasogastric tube.
After sustaining a closed head injury and numerous lacerations and
abrasions to the face and neck, a five-year-old child is admitted to the
emergency room. The client is unconscious and has minimal response to
noxious stimuli. Which of the following assessments, if observed by the
nurse three hours after admission, should be reported to the physician?
1. The client has slight edema of the eyelids.
2. There is clear fluid draining from the client's right ear.
3. There is some bleeding from the child's lacerations.
4. The client withdraws in response to painful stimuli.
The nurse is caring for a manic client in the seclusion room, and it is
time for lunch. It is MOST appropriate for the nurse to take which of the
following actions?
1. Take the client to the dining room with 1:1 supervision.
2. Inform the client he may go to the dining room when he controls his behavior.
3. Hold the meal until the client is able to come out of seclusion.
4. Serve the meal to the client in the seclusion room.
A client is given morphine 6 mg IV push for postoperative pain.
Following administration of this drug, the nurse observes the following:
pulse 68, respirations 8, BP 100/68, client sleeping quietly. Which of the
following nursing actions is MOST appropriate?
1. Allow the client to sleep undisturbed.
2. Administer oxygen via facemask or nasal prongs.
3. Administer naloxone (Narcan).
4. Place epinephrine 1:1,000 at the bedside.
What type of infectious diseases are required to be reported to the health department?
- severe cases of Staphylococcus aureus infections including methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA)
A nurse is caring for a client who has tuberculosis. Which of the following actions should the nurse take? SATA
a) Place the client in a negative pressure room
b) wear gloves when assisting the client with oral care
c) limit each visitor to 2 hr increments
d) wear a surgical mask when providing care
e) Use antimicrobial sanitizer for hand hygiene
A charge nurse is discussing the responsibility of nurses carig for clients who have C. difficile. Which of the following information should the nurse include in the teaching?
a) Assign the client to a room with a negative air-flow system
b) Use alcohol-based hand sanitizer when leaving the clients room
c) clean contaminated surfaces in the clients room with a phenol solution
d) have family members wear a gown and gloves when visiting
A nurse is caring for a client receiving IV fluids. During a routine check, the nurse determines that the client has developed phlebitis and removes the IV catheter. Which of the following actions should the nurse take next?
a) place a warm compress over the IV site
b) record the findings in the client's chart
c) notify the client's primary care provider
d) prepare to insert a new IV catheter
A nurse is implementing a plan of care for a client who is at risk for falls. Which of the following is an appropriate nursing action?
a) implement a regular toileting schedule
b) encourage the client to wear athletic socks when ambulating
c) place all 4 bed rails in the upright position
d) require a family member to remain at the bedside
Which of the following techniques should the nurse use when performing nasotracheal suctioning for a client?
a) insert the suction catheter while the client is swallowing
b) apply intermittent suction when withdrawing the catheter
c) place the catheter in a location that is clean and dry for later use
d) hold the suction catheter with the clean, non-dominant hand
A nurse is caring for a client following an acute myocardial infarction. The client is concerned that providing self-care will be difficult due to extreme fatigue. Which of the following strategies should the nurse implement to promote the client's independence?
a) request an occupational therapy consult to determine the need for assistive devices
b) assign assistive personnel to perform self-care tasks for client
c) instruct the client to focus on gradually resuming self-care tasks
d) ask the client if a family member is available to assist with his care
A nurse is reviewing the medical records of a client who has a pressure ulcer. Which of the following is an expected finding?
a) serum albumin level of 3 g/dL
b) HDL level of 90 mg/dL
c) Norton scale score of 18
d) Braden scale score of 20
A nurse is caring for a client who needs a 24-hr urine collection initiated. Which of the following client statements indicates an understanding of the procedure?
a) "I had a bowel movement, but I was able to save the urine"
b) "I have a specimen in the bathroom from about 30 minutes ago"
c) "I flushed what I urinated at 7 am and have saved the rest since"
d) "I drink a lot, so I will fill up the bottle and complete the test quickly"
A nurse is caring for a client who has an NG tube that is to be irrigated every 8 hr. Which of the following should be used to irrigate the tube in order to maintain fluid and electrolyte balance?
a) tap water
b) sterile water
c) 0.9% sodium chloride
d) 0.45% sodium chloride
A nurse is reinforcing teaching regarding the use of a cane to a client who has left-leg weakness. Which of the following should the nurse include in the teaching?
a) use the cane on the weak side of the body
b) advance the cane and the strong leg simultaneously
c) maintain two points of support on the floor
d) advance the cane 30 to 45 cm (12-18 in) with each step
Which of the following should indicate to a nurse the need to suction a client's tracheostomy?
a) irritability
b) hypotension
c) flushing
d) bradycardia
A nurse is caring for a client who has a prescription for wound irrigation. Which of the following actions should the nurse take?
a) wear sterile gloves when removing the old dressing
b) warm the irrigation solution to 40.5C (105F)
c) cleanse the wound from the center outwards
d) use a 20 mL syringe to irrigate the wound
providing teaching about a clear liquid diet. Which of the following should the nurse instruct the client to avoid?
a) lemon-lime sports drinks
b) ginger ale
c) black coffee
d) orange sherbet
A nurse is caring for a client who is having difficulty voiding following the removal in an indwelling urinary catheter. Which of the following interventions should the nurse take?
a) assess for bladder distention after 6 hr
b) encourage the client to use a bed pan in the supine position
c) restrict the clients intake of oral fluids
d) pour warm water over the clients perineum
When caring for the client diagnosed with delirium, which condition is the most important for the nurse to investigate?
1. Cancer of any kind.
2. Impaired hearing.
3. Prescription drug intoxication.
4. Heart failure.
Which of the following is essential when caring for a client who is experiencing delirium?
1. Controlling behavioral symptoms with low-dose psychotropics.
2. Identifying the underlying causative condition or illness.
3. Manipulating the environment to increase orientation.
4. Decreasing or discontinuing all previously prescribed medications.
Which of the following is a realistic short-term goal to be accomplished in 2 to 3 days for a client with delirium?
1. Explain the experience of having delirium.
2. Resume a normal sleep-wake cycle.
3. Regain orientation to time and place.
4. Establish normal bowel and bladder function.
A client diagnosed with dementia wanders the halls of the locked nursing unit during the day. To ensure the client's safety while walking in the halls, the nurse should do which of the following?
1. Administer PRN haloperidol (Haldol) to decrease the need to walk.
2. Assess the client's gait for steadiness.
3. Restrain the client in a geriatric chair.
4. Administer PRN lorazepam (Ativan) to provide sedation.
During a home visit to an elderly client with mild dementia, the client's daughter reports that she has one major problem with her mother. She says, "She sleeps most of the day and is up most of the night. I can't get a decent night's sleep anymore." Which suggestions should the nurse make to the daughter? Select all that apply.
1. Ask the client's physician for a strong sleep medicine.
2. Establish a set routine for rising, hygiene, meals, short rest periods, and bedtime.
3. Engage the client in simple, brief exercises or a short walk when she gets drowsy during the day.
4. Promote relaxation before bedtime with a warm bath or relaxing music.
5. Have the daughter encourage the use of caffeinated beverages during the day to keep her mother awake.
The physician orders risperidone (Risperdal) for a client with Alzheimer's disease. The nurse anticipates administering this medication to help decrease which of the following behaviors?
1. Sleep disturbances.
2. Concomitant depression.
3. Agitation and assaultiveness.
4. Confusion and withdrawal.
The nurse is making a home visit with a client diagnosed with Alzheimer's disease. The client recently started on lorazepam (Ativan) due to increased anxiety. The nurse is cautioning the family about the use of lorazepam (Ativan). The nurse should instruct the family to report which of the following significant side effects to the health care provider?
1. Paradoxical excitement.
2. Headache.
3. Slowing of reflexes.
4. Fatigue.
When providing family education for those who have a relative with Alzheimer's disease about minimizing stress, which of the following suggestions is most relevant?
1. Allow the client to go to bed four to five times during the day.
2. Test the cognitive functioning of the client several times a day.
3. Provide reality orientation even if the memory loss is severe.
4. Maintain consistency in environment, routine, and caregivers
A nurse is providing discharge instructions to a client who has a prescription for the use of oxygen in
his home. Which of the following should the nurse teach the client about using oxygen safely in his
home? (Select all that apply.)
A. Family members who smoke must be at least 10 ft from the client when oxygen is in use.
B. Nail polish should not be used near a client who is receiving oxygen.
C. A "No Smoking" sign should be placed on the front door.
D. Cotton bedding and clothing should be replaced with items made from wool.
E. A fire extinguisher should be readily available in the home.
When performing nasotracheal suctioning what technique should be used?
Sterile asepsis bc the trachea is considered sterile and prevents infections
A nurse educator is presenting a module on basic first aid for newly licensed home health nurses. The nurse educator evaluates the teaching as effective when the newly licensed nurse states the client who has heat stroke will have which of the following?
A. Hypotension
B. Bradycardia
C. Clammy skin
D. Bradypnea
What position is good to use for a patient who is at high risk for a pressure ulcer
30 degree lateral position is recommended for clients at risk for pressure ulcers
health promotion (injury prevention-suffocation): infant (birth-1 yr)
-avoid plastic bags
-keep balloons out of reach
-ensure crib mattress fits snugly
-ensure crib slats are no more than 6 cm (2.4 in) apart
-remove crib mobiles and gyms by 4-5 months
-do not use pillows in crib
-place infant on back for sleep
-keep toys with small parts out of reach
-remove drawstrings from jackets and other clothing
hypotension is classified with a reading below normal;
systolic < 90 mm Hg; can be a result of fluid depletion, heart failure, or vasodilation
What temperature should pork be cooked at
160 degrees
What is the safest way to thaw out frozen foods
In the refrigerator
What are the precautions for vancomycin resistant enterococcus
Standard precautions including hand washing and gloving should be followed
What does a newborns poop look like
If your baby is exclusively breastfed, her poop will be yellow or slightly green and have a mushy or creamy consistency
What should be avoided during pregnancy
Do not take vitamin A supplements, or any supplements containing vitamin A (retinol), as too much could harm your baby
What is the most appropriate method for contraception for an adolescent
IUD or implant
What medications can be taken to help with smoking cessation
Bupropion hydrochloride is a medicine for depression, but it also helps people quit smoking. Brand names include Zyban®, Wellbutrin®, Wellbutrin SR® and Wellbutrin XL® but this medication is also available as a generic. Varenicline (chantix)
Signs for meningococcemia
Vomiting, febrile, petechial rash
(unstable)
Levothyroxine effects
Used to restore client's metabolic rate
* Toxic effects = heat intolerance, Tachycardia, Weight loss, Hypertension
Multiple Sclerosis Patient
Mitoxantrone SE's Mitoxantrone IV every 3 months (chemo drug)
* Report Sore Throat
(greatest risk for client is severe infection due to myelosuppression from mitoxantrone)
* Vomiting = causes dehydration
* Hair Loss = emotional distress
* Amenorrhea = emotional distress
Malnourished COPD patients
(1) Limit liquid intake at meal times
(2) Consume foods w/ protein (like eggs)
(3) Maintain an upright position (High Fowler's position) to promote ventilation
(4) Use milk instead of water when making soup
What should the nurse do when one member of a support group expresses anger repeatedly?
Focus more on the group members who have a positive outlook
(Speak to group member privately to uncover source of anger)
What immunizations are CONTRAINDICATED for pregnant women + which SHOULD be given?
Contraindicated = Herpes Zoster + Varicella + MMR (measles, mumps, rubella)
Should give = TDaP (Tetanus, Diphtheria, Pertussis)
Long term effects of NSAIDS (Ibuprofen)
Gastric Ulcerations, perforations, hemorrhage, hypertension
Alcohol Use Manifestations of Withdrawal
Body burns 0.5 oz of alcohol per hour
* Withdrawal appears within 4-12 hours
* Irritability + Tremors + Anxiety
* Nausea + Vomiting + HA
* Diaphoresis
* Sleep Disturbances
* TACHYCARDIA + HTN
Use Benzodiazepines = tx
Diazepam (Valium), lorazepam (Ativan), and chlordiazepoxide (Librium)
Case Management nursing involves:
*Decreasing cost by improving client outcomes
* Providing education to optimize health participation
* Advocating for services + client's rights
What therapy will be useful for patients with bipolar?
Electroconvulsive therapy for the patient who is suicidal or rapid cycling who HAS taken Lithium and has proven ineffective. Used to subdue manic behavior.
What kind of medications are indicated for abstinence maintenance of alcohol?
Disulfiram (Antabuse), Naltrexone (Vivitrol), Acamprosate (Campral)
Teaching points for naltrexone (Vivitrol)?
Take with meals to supress GI distress. Monthly IM injections should be suggested for patients who have difficulty to adhering to the medication regimen.
A nurse is caring for a client who underwent a subtotal gastrectomy. To manage dumping syndrome, the nurse should advise the client to:
a) restrict fluid intake to 1 qt (1,000 ml)/day.
b) drink liquids only between meals.
c) don't drink liquids 2 hours before meals.
d) drink liquids only with meals.
A patient who has undergone colostomy surgery is experiencing constipation. Which of the following interventions should a nurse consider for such a patient?
a) Instruct the patient to keep a record of food intake
b) Instruct the patient to avoid prune or apple juice
c) Suggest fluid intake of at least 2 L per day
d) Assist the patient regarding the correct diet or to minimize food intake
A client is admitted with a diagnosis of acute appendicitis. When assessing the abdomen, the nurse would expect to find rebound tenderness at which location?
a) Left lower quadrant
b) Left upper quadrant
c) Right upper quadrant
d) Right lower quadrant
Patients diagnosed with esophageal varices are at risk for hemorrhagic shock. Which of the following is a sign of potential hypovolemia?
a) Hypotension
b) Bradycardia
c) Warm moist skin
d) Polyuria
The nurse is assessing a client with a bleeding gastric ulcer. When examining the client's stool, which of the following characteristics would the nurse be most likely to find?
a) Green color and texture
b) Black and tarry appearance
c) Clay-like quality
d) Bright red blood in stool
After teaching a group of students about the various organs of the upper gastrointestinal tract and possible disorders, the instructor determines that the teaching was successful when the students identify which of the following structures as possibly being affected?
a) Large intestine
b) Ileum
c) Stomach
d) Liver
A nurse is caring for a client with active upper GI bleeding. What is the appropriate diet for this client during the first 24 hours after admission?
a) Skim milk
b) Nothing by mouth
c) Regular diet
d) Clear liquids
what are normal creatinine levels?
0.8-1.4 mg/dL
what are normal BUN levels?
8-25 mg/dL
What are total serum protein values (normals)
6-8 g/dL
Describe pre-albumin
this is the best tool for evaluating nutrition. it has a half-life of 2 days which is much shorter than albumin so it is much more accurate. (albumin's half-life is 2-3 weeks)
what is normal pre-albumin values?17-40 mg/dL
what are normal serum levels of magnesium ?
1.5-2.5 mEq/L (less than 1.5 is considered hypomagnesemia)
what is a normal potassium serum level?
3.5-5.0 mEq/L (less than 3.5 is considered hypokalemia)
what are good sources of folic acid?
Excellent sources of folate include romaine lettuce, spinach, asparagus, turnip greens, mustard greens, calf's liver, parsley, collard greens, broccoli, cauliflower, beets, chicken liver and lentils.
Sources of potassium
beans, spinach, potatoes, dried apricots, acorn squash, yogurt, salmon, avocados, mushrooms and bananas
what is important about the diet of someone taking ACE inhibitors?
can result in high potassium levels. Limit potassium intake (beans, spinach, potatoes, dried apricots, acorn squash, yogurt, salmon, avocados, mushrooms and bananas)
what is a normal hematocrit level in a female?
37-48% (male is 42-52%)
What are normal Hgb values (female)?
12-16 g/dL (male 13-17)
what are normal values for WBCs?
4500-11,000 / uL
what foods should you avoid if you have diverticulitis?
avoid hard-to-digest foods such as nuts, corn, popcorn, and seeds, for fear that these foods would get stuck in the diverticula and lead to inflammation. (Eat foods high in fiber)
When taking MAOI's, limit your consumption of
thyramine--it can cause elevated BP. This is found in "aged" products such as aged cheeses (swiss), cured meats (pepperoni/salomi), sauerkraut, soy sauce...Examples of MAOI's are: Isocarboxazid (Marplan), Phenelzine (Nardil), Selogilive, Emsam, Eldepryl, Zelapar...
At what age does bone loss begin with osteoporotis
what are normal Calcium levels?
at age 35 (women)
8.6-10 mg/dL
A positive Chvosteks sign is found in a patient. The nurse would anticipate IV administration of
calcium gluconate (because hypocalcemia causes Chvostek's sign)
What are the S/S of lithium toxicity?
(depakote for bipolar disorder)
fine hand tremors, mild GI upset, slurred speech and muscle weakness
a client should receive a dose of flumazenil ( romazicon) to treat symptoms of
benzodiazepine overdose
a nurse is reinforcing teaching to a client who is prescribed diazepam tor anxiety of the following statement indicated the client understand the teaching
I will tell my doctor before I stop taking the medication
a nurse is reinforcing teaching to a client who is starting amitriptyline ( Elavil) for treatment of depression which of the following should the nurse include
1. change position slowly to minimize dizziness
2. chewing sugarless gum to prevent dry mouth
a client who is start taking lithium carbonate month ago tell the nurse she has just begun taking multiply daily doses of ibuprofen ( motrin) for tension headache. should the client avoid ibuprofen. why or why not ?
what , if any is the appropriate action for the nurse to take NSAIDS such as ibuprofen increase the renal reabsorption of lithium carbonate , possibly leading to lithium carbonate toxicity . therefor this client would avoid NSAIDS . the nurse should notify the provider of client headache and ibuprofen us
a client has prescription for valproic ( Depakote) which of the following laboratory value should the nurse anticipate monitor for the client taking this medication
thrombocytes, amylase count and liver function test
Alcohol withdrawal: Librium
Heroin withdrawal: methadone
Nicotine withdrawal: buproprion (welbrutin)
Alcholabsitence: disulfiram (Antabuse)
Opiod overdose: naloxone
a client who has parkinson's disease is prescribed levodopa/carbidopa ( sinemet) and pramipexole ( Mirapex) for which of the following should the nurse monitor this client
orthostatic hypotension
a nurse is preparing to care for a client in the surgical unit who will be receiving lorazapam( ativan IV) . for what adverse effect should the nurse monitor this client
the nurse should monitor the client respiratory depression
a client has a new prescription for spironilactone( aldactone ) which of the following laboratory value should the nurse recognized as a reason to withhold the morning dose of the medication and notify the provider
serum potassium 5.2
Which of these manifestations, if reported by a client who is 10-weeks-pregnant, supports the diagnosis of ruptured tubal pregnancy.
a. Sharp unilateral abdominal pain.
b. Uncontrollable vomiting.
c. Marked abdominal distention.
d. Profuse vaginal bleeding.
A client has the following order for regular insulin (Humulin R) on a sliding scale:
Blood sugar 150-180 mg: Give 2 units regular insulin
Blood sugar 181-200 mg: Give 4 units regular insulin
Blood sugar 201-220 mg: Give 6 units of regular insulin
Blood sugar above 220 mg: Call MD
At 11 A.M., a nurse obtains a finger stick glucose of 198 mg. The only syringe is a three milliliter one. Regular insulin is available as 100 units per milliliter. How many milliliters should the nurse administer?
a. 0.04
b. 0.4
c. 4
d. 40
Which of these nursing diagnosis is the priority for a client who is one-hour postoperative after extensive abdominal surgery?
a. Risk for impaired physical mobility.
b. Risk for deficient fluid volume.
c. Risk for ineffective airway clearance.
d. Risk for infection.
Which of these assessments is the priority for a client who sustained second-degree burns of the face and neck?
a. Respiratory status.
b. Renal function.
c. Level of pain.
d. Signs of infection.
A nurse should place a child who is two hours post-tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy in which of these positions?
a. Supine, flat.
b. Orthopneic.
c. Trendelenberg.
d. Side-lying.
When caring for a client who has hepatitis B, a nurse should wear:
a. gloves when administering oral medications to the client.
b. a gown when changing the client's position.
c. gloves when removing the intravenous cannula.
d. a gown when emptying the client's used bath water.
Which of these outcome criteria is appropriate for a client who has a nursing diagnosis of ineffective airway clearance?
a. Absence of wheezing throughout the lung fields.
b. Clear lung sounds on auscultation.
c. Pulse oximetry level of 80%.
d. Frequent coughing throughout the day.
A doctor prescribes liquid oral iron medication for a 4-year-old child. Which of these questions should a nurse ask the child's mother to determine if the medication is being administered correctly?
a. "Are you using a straw to administer the medicine?"
b. "Has your child been urinating more frequently?"
c. "Have you increased your child's milk intake each day?"
d. "Is there a change in the color of your child's skin?"
Which of these assessment findings, if present in a 4-month-old infant who has severe diarrhea, should a nurse recognize as suggestive that the infant is dehydrated?
a. Bulging anterior fontanel.
b. Pulse rate of 120/minute.
c. Decreased urine output.
d. Cyanosis of the mucus membrane.
Which of these instructions should be included in the teaching plan for the parents of a 10-month-old infant who is admitted to the hospital for failure to thrive?
a. Advise the mother to make sure the infant drinks the entire bottle at each feeding.
b. Encourage the mother to feed the infant slowly in a quiet environment.
c. Teach the mother to position the infant on the abdomen following feedings.
d. Instruct the mother to play actively with the infant during bottle feedings.
When a newborn is 48 hours old, a nurse notes that the child is jaundiced. The nurse should recognize which of these conditions as a probable cause of the newborn's jaundice?
a. Dehydration.
b. Liver immaturity.
c. ABO incompatibility.
d. Gallbladder immaturity.
Adverse effect of verapamil: avoid grapefruit juice
Interaction of diuretics and ACE inhibitors (Sartan): excessive reduction in bp and symptomatic hypotension or hyperkalemia
What can prevent MI, stroke, or death in high-risk patients
Ramipril
What to monitor for when taking enoxaparin (lovenox)
Hyperkalemia
Cases of headache, hemorrhagic anemia, eosinophilia, alopecia, hepatocellular and cholestatic liver injury reported
Adverse effects of ferrous sulfate
constipation;
upset stomach;
black or dark-colored stools; or.
temporary staining of the teeth.
Baclofen (Lioresal) therapeutic outcome:
Decrease the frequency and severity of muscle spasms (MS).
Identifying manifestations of transient ischemic attacks
symptoms r/t afffected area. Rapid onset of weakness, numbness, aphasia, visual field cuts. 1-2 clusters before stroke.
The nurse caring for a child in Buck's skin traction will keep the:
Child pulled up in bed
Where should the cath bag be placed when urinary catheterization
Make sure the catheter bag/system is at a level below the client's bladder to avoid reflux.
What are the signs and symptoms of fluid volume deficit
loss of total body Na. Causes include vomiting, excessive sweating, diarrhea, burns, diuretic use, and kidney failure. Clinical features include diminished skin turgor, dry mucous membranes, tachycardia, and orthostatic hypotension.
What is the nursing action for dehiscence
Cover with a sterile towel moistened with sterile saline; Have patient flex knees slightly and put in Fowler's .
Which of these instructions should a nurse include in the teaching plan for a client who had removal of a cataract in the left eye?
a. "Forcefully cough and take deep breaths every two hours to keep your airway clear."
b. "Perform the prescribed eye exercises each day to strengthen your eye muscles."
c. "Rinse your eyes with saline each morning to prevent postoperative infection."
d. "Take the prescribed stool softener to avoid increasing intraocular pressure."
A client vomits during a continuous nasogastric tube feeding. A nurse should stop the feeding and take which of these actions?
a. Suction the nasogastric tube.
b. Flush the tube with 30 mL of sterile water.
c. Remove the nasogastric tube.
d. Check the residual volume.
Which of these manifestations should a nurse expect to observe in a 3-month-old infant who is diagnosed with dehydration?
a. Hyperreflexia.
b. Tachycardia.
c. Bradypnea.
d. Agitation.
When assessing a client's risk of developing nosocomial infection, a nurse plans to determine potential entry portals, which include:
a. the urinary meatus.
b. vomitus.
c. contaminated water.
d. sexual intercourse.
Which of these measures should a nurse include when planning care for a school-aged child during a sickle cell crisis episode?
a. Monitoring for signs of bleeding.
b. Providing pain relief.
c. Administering cool sponge baths to reduce fevers.
d. Offering a high calorie diet.
Which of these instructions should a nurse include in the plan of care for a 32-week gestation client who had an amniocentesis today?
a. "Drink at least six glasses of fluids during the next six hours after the test."
b. "Call the clinic if you experience any abdominal cramps."
c. "Don't be concerned if you have some vaginal spotting in the next 12 hours."
d. "When you get home, stay on bed-rest for the next 48 hours."
A client has been admitted with acute pancreatitis. Which of these laboratory test results supports this diagnosis?
a. Elevated serum potassium level.
b. Elevated serum amylase level.
c. Elevated serum sodium level.
d. Elevated serum creatinine level.
Which of these manifestations, if assessed in a client who is two-hours postoperative after abdominal surgery, should a nurse report immediately?
a. Vomiting and a pulse rate of 106/minute.
b. Respiratory rate of 12/minute and urine dribbling.
c. Blood pressure of 100/60 mm Hg and wound discomfort.
d. Urine output of 100 mL/hr and flushed
An elderly client is at increased risk of developing drug toxicity to prescribed medications due to declining hepatic and renal functioning. Which of these strategies should a nurse plan to decrease this risk?
a. Increasing the time interval between medication doses.
b. Limiting the client's oral fluid intake.
c. Administering the medications with meals.
d. Encouraging the client to void every three to four hours.
A client has persistent paranoid delusions that the food on the unit is poisoned. Which of these measures should a nurse include in the client's care plan?
a. Explaining that staff does not poison clients.
b. Focusing on how the hospital staff helps clients.
c. Allowing the client to eat food from sealed containers.
d. Telling the client that not eating the food that is served will result in privilege restrictions.
Thrombophlebitis is a complication that may result due to surgery. Which of these actions should a nurse take in the operating room to prevent this complication from occurring?
a. Gatch the knee of the bed.
b. Administer anticoagulants preoperatively.
c. Apply sequential compression devices.
d. Maintain the legs in a dependent position.
Which of these manifestations, if reported by a client who is 10-weeks-pregnant, supports the diagnosis of ruptured tubal pregnancy.
a. Sharp unilateral abdominal pain.
b. Uncontrollable vomiting.
c. Marked abdominal distention.
d. Profuse vaginal bleeding
Which of these assignments, if made by a nurse to a nursing assistant, indicates that the nurse needs additional instructions regarding the principles of delegation?
a. "Please bathe the client in room 12, and then bring the client to the dining room for breakfast by 9 A.M."
b. "Please bathe the client in room 10, administer a back rub, and then evaluate if the back rub eased the client's discomfort."
c. "Please measure the intake and output for the client's in rooms 8. 9. and 10, and record each on the intake/output sheets by 2 P.M."
d. "Please toilet the clients in rooms 11, 12, and 13 mid-morning and after lunch."
An elderly client who is receiving a blood transfusion develops a rapid bounding pulse and an elevated blood pressure. Which of these actions should a nurse take?
a. Add a 5% dextrose solution to the line.
b. Raise the head of the bed.
c. Stop the transfusion.
d. Measure the client's temperature.
Which of these interventions should plan for a child who is receiving chelation therapy for lead poisoning?
a. Keeping an accurate record of intake and output.
b. Instituting measures to prevent skeletal fractures.
c. Maintaining isolation precautions.
d. Maintaining strict bed rest.
When determining the duration of a uterine contraction, a nurse should measure the contraction from the:
a. beginning of one contraction to the end of that contraction.
b. end of one contraction to the beginning of the next contraction.
c. beginning of one contraction to the beginning of the next contraction.
d. strongest point of one contraction to the strongest point of the next contraction.
A nurse should recognize which of these signs is a probably sign of pregnancy?
a. Frequency of urination.
b. Positive pregnancy test.
c. Nausea in the morning.
d. Abdominal distention.
A client diagnosed with type 1 diabetes mellitus has a glycosylated hemoglobin A1c of 4.2%. A nurse should interpret this to mean that the client has:
a. had a period of sustained hyperglycemia.
b. been non-compliant with home management.
c. been in relatively good diabetic control.
d. eaten a high carbohydrate snack just prior to testing.
A nurse is caring for a client with burns and in reverse isolation. Which measures should the nurse include?
a. Wearing disposable gloves when chaging the dressings.
b. Having the client wear goggles when staff is in the room.
c. Wearing a gown, mask, and gloves when providing care to the client.
d. Disposing of the client's soiled laundry in a red bag.
A nurse charts on all assigned clients at 2:00 P.M. The nurse then remembers something that happened at 9:00 A.M. to a client who was not charted. Which of these actions should the nurse take?
a. Include the 9:00 A.M. scenario in the shift report.
b. Enter the scenario after the original 2:00 P.M. charting and mark it as a "late entry".
c. Put the information in the margin and indicate the accurate time placement by drawing an arrow.
d. Draw a line through the previous charting with "error" and then re-record everything, including the new information.
While giving a bath to a client, a nurse notices that the client's back appear reddened. Which of these interpretations and additional assessments should the nurse make?
a. The client's skin is sensitive to touch; lightly rub the client's chest area.
b. The client has decreased circulation; palpate the peripheral pulses.
c. The client is showing signs of pressure; press on the skin and observe for a return of color.
d. The client is allergic to the soap; check the extremities for discoloration.
A newborn is placed under fluorescent light as part of the treatment for physiologic jaundice. During the duration of the newborn's treatment, a nurse should:
a. cover the newborn's closed eyes with patches.
b. measure the newborn's pulse and respirations every two hours.
c. keep the newborn under the light at all times, even during the feedings.
d. notify the physician if the newborns stools become greenish yellow.
Which of these symptoms should a nurse expect to assess in a client who develops hypoglycemia?
a. Fruity breath odor.
b. Polyuria.
c. Diaphoresis.
d. Flushed skin
A nurse should assess a child who has diabetes mellitus (type 1) for symptoms of hyperglycemia, which include:
a. flushed skin and thirst.
b. irritability and hunger.
c. sweating and jitteriness.
d. lethargy and tremors.
Which of these techniques should a nurse use to assess for correct placement of a nasogastric tube prior to administering a feeding?
a. Aspirate 10 mL contents and measure the pH.
b. Slowly inject 50 mL of saline and observe for resistance.
c. Inject 20 mL of water and listen for gurgling sounds.
d. Observe for bubbles after submerging the end of the tube in a cup of water.
A client has shortness of breath when lying down and usually assumes an upright or sitting position in order to breathe more comfortably. A nurse should document this observation as:
a. dyspnea.
b. bradypnea.
c. orthopnea.
d. apnea.
Which of these instructions should a nurse give to a client when collecting a sputum specimen?
a. "Take a deep breath, then cough and spit into this container."
b. "Gargle with antiseptic mouthwash before you spit into this container.
c. "Spit whatever sputum you have in your mouth into this container."
d. "Drink some fluids to loosen your secretions and the spit
A client who is receiving radiation therapy has a nursing diagnosis of imbalanced nutrition: less than body requirements related to diminished taste perception and nausea. Which of these additional nursing diagnoses should a nurse consider for the client?
a. Risk for aspiration.
b. Ineffective protection.
c. Risk for deficient fluid volume.
d. Altered tissue perfusion.
A young healthy adult, who has been exercising in hot weather, has fatigue, loss of appetite, and lightheadedness. Which of these assessments should a nurse make?
a. Determine the client's preferred diet.
b. Measure the client's body temperature.
c. Auscultate the lungs.
d. Ascertain the client's typical sleep pattern.
Which of these nursing measures is the priority for a child who has hemophilia and who sustains a leg injury?
a. Ensuring adequate hydration for the child.
b. Soaking the child's injured leg in warm water.
c. Administering the missing factor VIII to the child.
d. Transfusing one unit of whole blood to the child.
Which of these outcomes should a nurse focus on for a client who had a bronchoscopy two hours ago?
a. Preventing hemorrhage.
b. Preventing pneumonia.
c. Preventing aspiration.
d. Preventing dehydration.
A client who had a coronary artery bypass graft four days ago suddenly develops sinus tachycardia and reports shortness of breath and dizziness. Which of these interpretations and actions should a nurse take?
a. This is an expected occurrence following bypass surgery; continue to monitor the client.
b. This indicates normalization of the blood pressure; hold all anti-hypertensive medications.
c. This may be an early sign of heart failure; notify the physician.
d. This indicates hypoxia; administeroxygen at 5/L per minute.
Which of the statements if made by a client who is take furosemide (Lasix), supports a nursing diagnosis of knowledge deficit?
a. "This medication will increase the amount and frequency of my urination."
b. "This medication must be taken, even on days when I fell well."
c. "I will need to add more salt to my diet because this medication will increase its excretion."
d. "I should change my position slowly to avoid dizziness related to this medication."
Which of these statements, if made by a client who has chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, indicates improvement?
a. "I hope to attend my grandson's graduation next month."
b. "I can now walk one more block than I could last month."
c. "I take several quick breaths when I begin to cough."
d. "I do my breathing exercises in the evening after I eat dinner."
An 8-month-old infant is admitted to the hospital because of failure to thrive. Which of these actions should a nurse plan?
a. Limit the parents' interactions with the infant.
b. Consistently assign the care of the infant to the same staff.
c. Rotate assignments so that all staff can evaluate the infant.
d. Limit the infant's activity until the cause of the problem is identified.
A nurse should explain to a primigravida that urine tests will be done at each prenatal visit throughout the pregnancy to measure:
a. specific gravity and pregnancy hormones.
b. culture and white blood cell count.
c. glucose and protein.
d. bacteria and red blood cell count.
Which of these manifestations should a nurse expect to observe in a client who is diagnosed with paranoid schizophrenia?
a. Regression.
b. Suspiciousness.
c. Catatonia.
d. Hyperactivity.
Which of these changes in the assessment data of a child who has congestive heart failure should a nurse recognize as indicative of a therapeutic response to prescribed medication therapy?
a. Increased weight.
b. Increased urine output.
c. Increased respiratory rate.
d. Increased heart size.
A client who has a history of asthma develops an acute asthma attack. Which of these questions should a nurse ask when assessing the etiology of this attack?
a. "Have you eaten any new foods recently?"
b. "How many hours did you sleep last night?"
c. "Are you exercising every day?"
d. "Have you reduced your fluid intake recently?"
A nurse in a prenatal clinic performs Leopold's maneuvers on a client who is 8-months-pregnant primarily to:
a. turn the fetus in the uterus.
b. ease the fetus into the true pelvis.
c. assessment of the location of the placenta.
d. determine the fetal presentation.
A child is brought to the clinical for serum lead screening because of ingestion of lead-based paint. Which of these manifestations, if present in the child, would indicate early signs of lead toxicity?
a. Convulsive seizures.
b. Behavior changes.
c. Bleeding tendencies.
d. Low-grade fever.
Which of these recommendations should a nurse make when teaching a client who is to start taking oral prednisone (Deltasone)?
a. "Take this medicine at bedtime, on an empty stomach."
b. "Take this medicine with a hot beverage in the evening."
c. "Take this medicine in the morning, one hour before breakfast."
d. "Take this medicine in the morning with food or milk."
Which of these actions should a nurse take prior to initiating prescribed antibiotic therapy for a client who has a urinary tract infection?
a. Measure the body temperature.
b. Cleanse the perineum.
c. Weigh the client.
d. Obtain a urine culture specimen.
When caring for a client who is receiving oxygen therapy via nasal cannula, a nurse should instruct the client:
a. to inhale through the mouth.
b. to breathe through the nose.
c. to hold the catheter when coughing.
d. to take quick, shallow breaths.
Each of these clients has impaired mobility related to knee surgery. Which client should a nurse assess first?
a. A 20-year-old who has a sports-related injury.
b. A 37-year-old who reports limited mobility.
c. A 59-year-old who has a history of hypertension.
d. A 70-year-old who has bilateral cataracts
A nurse plans to assess a client's recent memory. Which of these questions should the nurse include?
a. "Who is your closest friend?"
b. "What was the name of the school you attended?"
c. "What day were you admitted to the unit?"
d. "What did you have for breakfast?"
Which of these actions, if taken by a nurse who is transferring a client from the bed to the chair, is correct?
a. The bed is raised to a comfortable working height for the nurse.
b. The wheelchair is placed perpendicular to the bed.
c. The nurse stands behind the client during the transfer.
d. The nurse supports the client in an upright standing position for a few moments.
A nurse should assist a pregnant client who is in the first trimester to achieve the developmental task of this stage of pregnancy, which is:
a. accepting the fact that she is pregnant.
b. accepting the fact that the fetus is a separate being.
c. accepting that she will soon deliver the child.
d. accepting that her body image has changed.
When interacting with a client who is paranoid, a nurse should:
a. use touch to place the client at ease.
b. maintain a caring facial expression.
c. stand close to the client.
d. maintain a professional attitude towards the client.
Which of these tasks is appropriate for a nurse to delegate to a nursing assistant in an acute care unit?
a. Feeding a client who was admitted with a stroke yesterday.
b. Ambulating a client who was admitted with a myocardial infarction yesterday.
c. Measure the blood pressure of a client who was admitted with an asthma attack yesterday.
d. Suctioning the tracheostomy that was performed on a client yesterday.
Which of these techniques should a nurse plan to use with a client who is delusional?
a. Explore the delusion so the client will know it is false.
b. Explain clearly why the client's belief is incorrect.
c. Focus on reality-based topics.
d. Avoid speaking with the client when he/she is delusional.
Which of the following manifestations should a nurse recognize as suggestive of right-sided heart failure?
a. Cool extremities and frothy sputum.
b. Jugular vein distention and pedal edema.
c. Orthopnea and frequent cough at night.
d. Weight loss and lower calf pains.
Which of these statements, if made by a nursing student prior to a sterile dressing change, is correct?
a. "I understand that if objects touch other objects on the sterile field they are considered contaminated."
b. "I understand that sterile objects that are below my waist are considered contaminated."
c. "I understand that all objects in the sterile field must be dry."
d. "I understand that contaminated objects can be used if rinsed with an antimicrobial solution."
[Show More]



 answers.png)