ATI med surg post assessment.
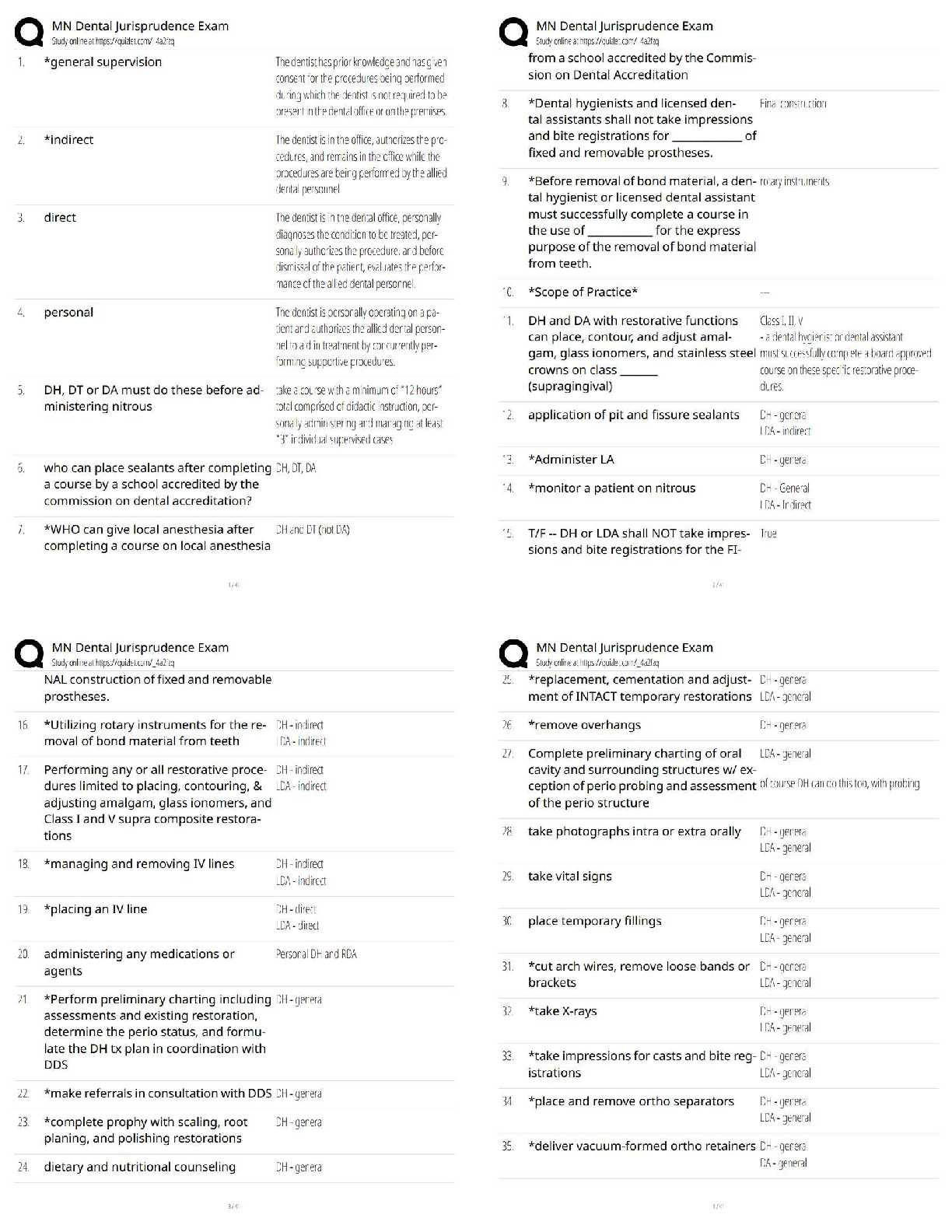
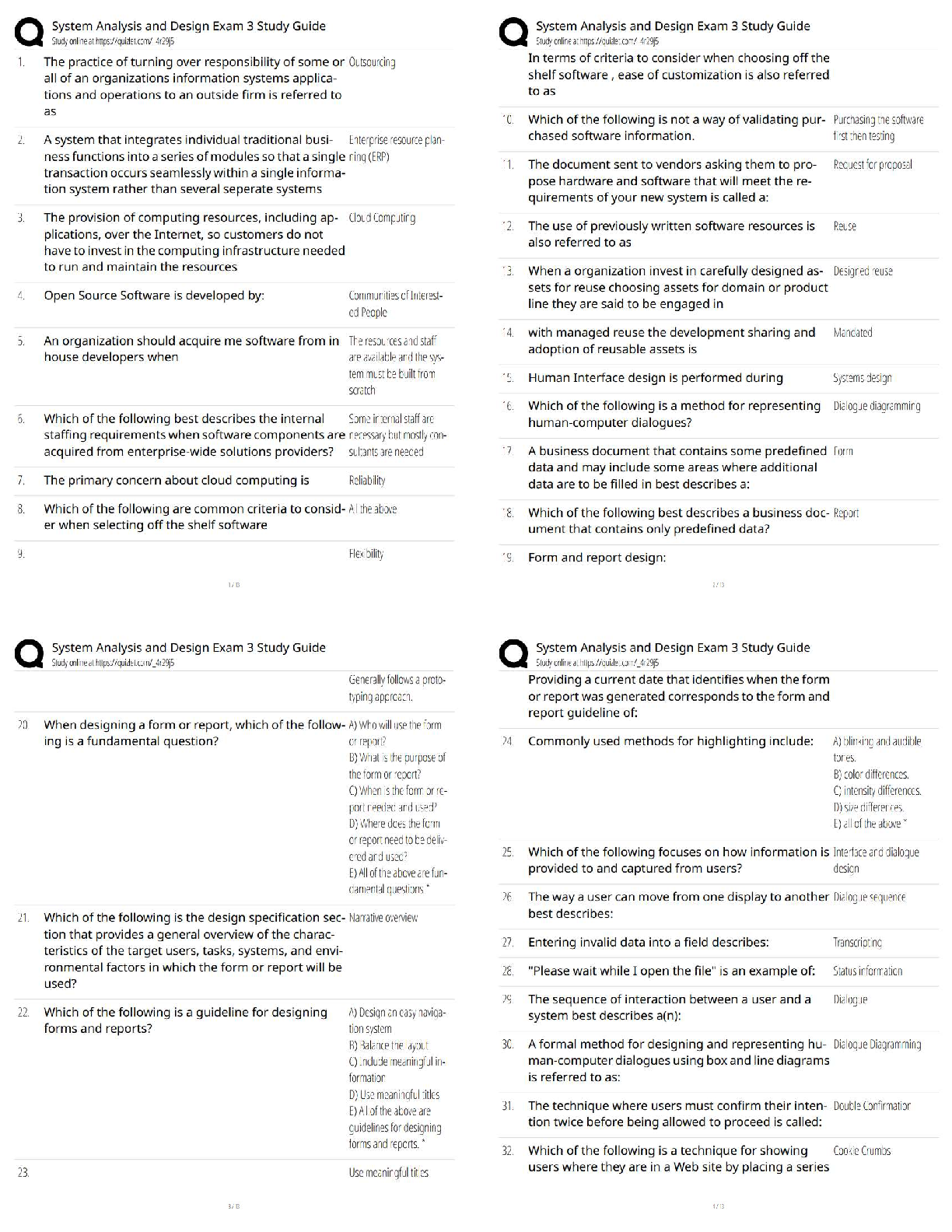
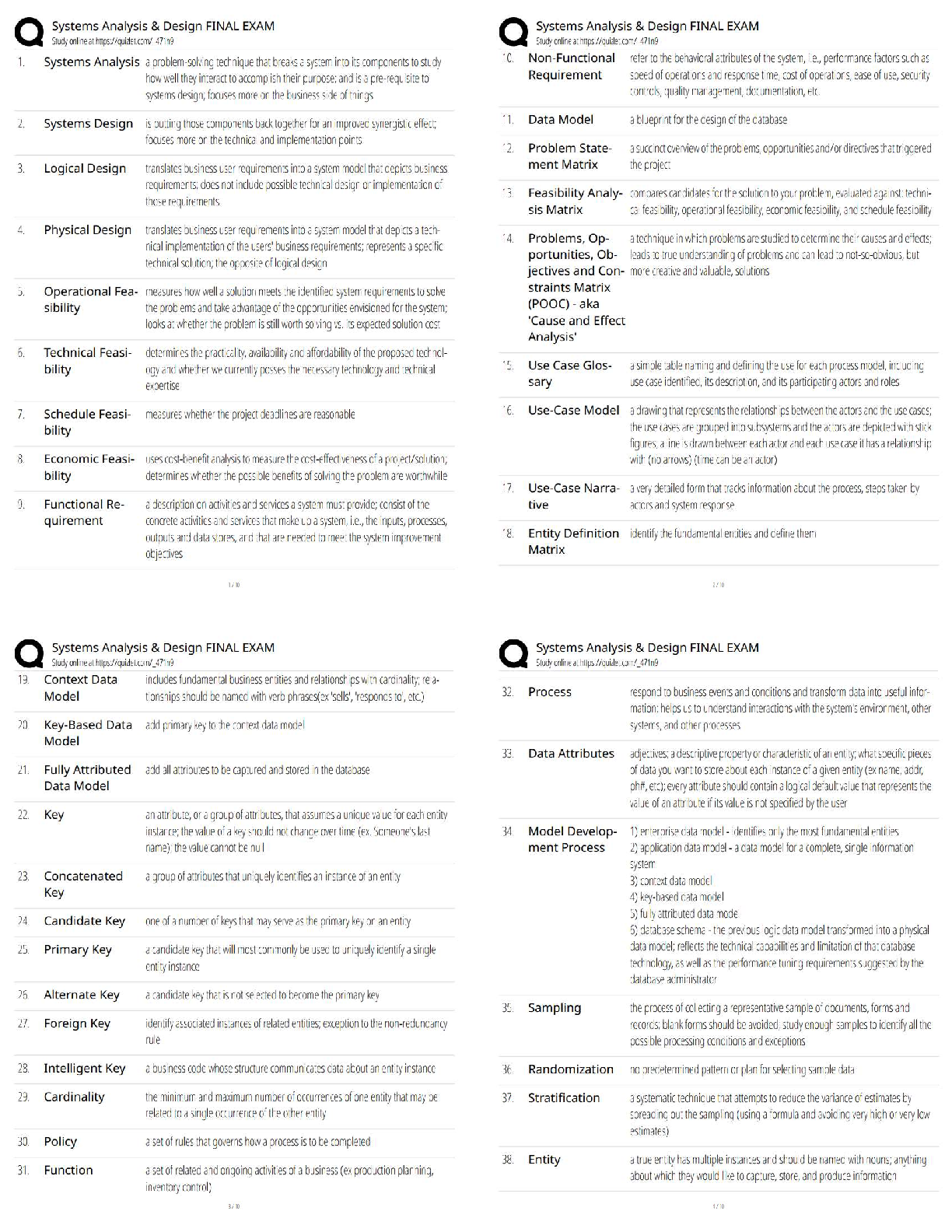
Hematologic Diagnostic Procedures: Bone Marrow Biopsy (RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 39, Active Learning Template - Diagnostic Procedure)
Bone biopsy takes a small sample of bone marrow removed by ne
...
ATI med surg post assessment.
Hematologic Diagnostic Procedures: Bone Marrow Biopsy (RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 39, Active Learning Template - Diagnostic Procedure)
Bone biopsy takes a small sample of bone marrow removed by needle aspiration for cytological (histological) examination
Performed with local anesthesia or conscious sedation.
Used to diagnose blood disorders (anemia, thrombocytopenia) or diseases of bone marrow (leukemia, infection) or stage lymphoma or other forms of cancer.
Teaching: teach client to report excessive bleeding and evidence of infection to provider
Teach client to check the biopsy site daily, keep the dressing clean, dry, and intact
If sutures in place, have client return in 7 days to have them removed
Esophageal Disorders: Dietary Selections for a Client Who Has a Hiatal Hernia (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RN QSEN - Patient-centered Care, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 48)
Avoid eating immediately prior to going to bed
Avoid foods and beverages that decrease LES pressure (fatty and fried foods, chocolate, coffee, peppermint, spicy foods, tomatoes, citrus fruits, and alcohol)
Musculoskeletal Trauma: Teaching Strategies to Prevent Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (RN QSEN - Safety , RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 71, Active Learning Template - Basic Concept)
Avoid repetitive flexion of wrist
Perform ROM
Have item under wrists while using computer to prevent prolonged flexion
Elevate hand above level of heart
Renal Calculi: Priority Intervention for a Client Who Has Renal Calculi (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 61)
Report laboratory and diagnostic findings to the provider
Strain all urine to check for passage of the calculus and save the calculus for laboratory analysis
Encourage client to increase oral intake to 3L/day unless contraindicated
Encourage ambulation to promote passage of the calculus
Administer IV fluids as prescribed
Urinary Elimination: Identifying Type of Urinary Incontinence (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RM FUND 9.0 Ch 44)
Stress: loss of small amounts of urine from increased abdominal pressure without bladder muscle contraction with laughing, sneezing or lifting
Urge: inability to stop urine flow long enough to reach the bathroom due to an overactive detrusor muscle with increased bladder pressure
Overflow: urinary retention from bladder overdistention and frequent loss of small amounts of urine due to obstruction of the urinary outlet or an impaired detrusor muscle
Reflex: involuntary loss of a moderate amount of urine usually without warning due to hyperreflexia of the detrusor muscle, usually from spinal cord dysfunction
Functional: loss of urine due to factors that interfere with responding to the need to urinate, such as cognitive, mobility and environmental barriers
Total: unpredictable involuntary loss of urine that generally does not respond to treatment
Rheumatoid Arthritis: Adverse Effects of NSAIDs (Active Learning Template - Medication, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 88)
NSAIDS -> provide analgesic, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory effects.
NSAIDs can cause considerable gastrointestinal (GI) distress
Nursing considerations:
Monitor for fluid retention, hypertension and renal dysfunction
Education:
Have client take with food or full glass of water or milk, if taken routinely an H2 receptor antagonist can also be prescribed
Instruct the client to observe for GI bleeding (coffee-ground emesis; dark, tarry stools).
Instruct the client to avoid alcohol, which can increase the risk of GI complications
Cancer Disorders: Positioning Following a Liver Biopsy (RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 92, RN QSEN - Safety , Active Learning Template - Diagnostic Procedure)
Position the client to the right side for 1 to 2 hr to ensure hemostasis
Cancer Disorders: Postoperative Teaching Following a Colectomy (Active Learning Template - Therapeutic Procedure, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 92)
Teach client regarding turning and deep breathing
Educate the client regarding the care of the incision, activity limits, and stony care, if applicable
Provide instructions regarding management of postoperative complications, including incontinence or sexual dysfunction (most likely to occur with AP resection)
Cushing's Disease/Syndrome: Expected Laboratory Values (RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 80, Active Learning Template - System Disorder)
Elevated plasma cortisol levels
Elevated ACTH levels
Hypokalemia
Hypocalcemia
Hypernatremia
Decreased lymphocytes
Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures for Female Reproductive Disorders: Client Teaching Following Colposcopy and Cervical Biopsy (Active Learning Template - Diagnostic Procedure, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 62, RN QSEN - Patient- centered Care)
Nursing Considerations:
Post-procedure care is the same as for a Pap test
Provide client with perineal pad and tissues
Instruct the client to rest for the first 24 hour after the procedure
Instruct the client to abstain from sexual intercourse and avoid using a douche, vaginal creams, or tampons until all discharge has stopped (usually about 2 weeks).
Instruct the client to avoid lifting heavy objects for approximately 2 weeks to allow time for the cervix to heal
Instruct the client to use analgesics as directed by the provider, but to avoid the use of aspirin because it can cause bleeding
Instruct the client to report excessive bleeding, fever, or foul-smelling drainage to the provider.
Integumentary Diagnostic Procedures: Identifying Fungal Infections (Active Learning Template - Diagnostic Procedure, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 73)
Requires a sufficient quantity of scales collected using a wooden tongue depressor and placing the specimen in a clean container to be sent to the laboratory
If a fungal culture is needed because of inconclusive results due to a deeper fungal infection, a punch biopsy is performed
Specimens must be properly labeled and delivered to the laboratory promptly for appropriate storage and analysis
Osteoarthritis and Low-Back Pain: Expected Assessment Findings for a Herniated Lumbar Disk (RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 72, Active Learning Template - System Disorder)
Expected findings:
dull or sharp low back pain
Pain aggravated by coughing, sneezing or straining
Muscle spasms, cramping and stiffness
Pain in the buttock
Sciatic nerve compression causes severe pain when leg is straightened and held up
Numbness/tingling of the leg (paresthesia); burning or stabbing pain in the leg or foot
Report chills/fever, bowel or bladder incontinence, progression of decreased ability to move, and paresthesias to the provider promptly (can indicate a more serious condition)
Herniated disk which can cause sciatic nerve involvement with burning or stabbing pain into one leg or foot
Peripheral Vascular Diseases: Risk Factors for Deep-Vein Thrombosis (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 35)
Associated with Virchow's triad (hypercoagulability, impaired blood flow, damage to blood vessels)
- hip surgery, total-knee replacement, open prostate surgery
- heart failure
- immobility
- pregnancy
- oral contraceptives
- active cancer
Pituitary Disorders: Caring for a Client Following a Hypophysectomy (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 77)
- The nurse should monitor the drainage to the mustache dressing
- Monitor for bleeding
- Monitor nasal drainage a possible cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) leak. Assess drainage for presence of glucose or a halo sign (yellow on the edge and clear in the middle), which can indicate CSF. Notify the provider is this occurs
- Protect the client from developing an infection by using good hand hygiene and making sure the client avoid contact with those who have infections. Use caution to prevent a fracture by providing assistance getting out of bed and raising side rails
- Assess neurologic status every hour for the first 24 hr then every 4 hr
- Administer glucocorticoids to prevent an abrupt drop in cortisol level
- Administer stool softeners to prevent straining
Addison's Disease and Acute Adrenal Insufficiency (Addisonian Crisis): Manifestations of Addisonian Crisis (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 81)
Drop in adrenocorticoid level
Severe hypotension
Hyponatremia
Hyperkalemia
Hypoglycemia
Hypercalcemia
Weight loss
Craving for salt
Hyperpigmentation
Weakness and fatigue
Nausea and vomiting
Abdominal pain
Constipation or diarrhea
Coagulation Disorders: Laboratory Values Associated with Heparin-Induced Thrombocytopenia (RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 42, Active Learning Template - System Disorder)
Decreased platelet levels
Other s/s: redness, pain, warmth and swelling of lower extremities, excessive bleeding, tachycardia, hypotension, diaphoresis, oliguria, decreased LOC
Kidney Transplant: Indications of Transplant Rejection (Active Learning Template - System Disorder, RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 58)
Hyperacute: within 48 hr
cause: small blood clots form in transplanted kidney that block vessels and lead to massive cellular destruction, irreversible
s/s: fever, hypertension, pain at transplant site
treatment: immediate removal of the donor kidney
Acute: occurs 1 week - 2 years after surgery
cause: vasculitis in the donor kidney and cellular destruction begins with inflammation that can cause lysis of the donor kidney
s/s: oliguria, anuria, low-grade fever, hypertension, tenderness over the transplanted kidney, lethargy, azotemia, and fluid retention
treatment: involves increased doses of immunosuppressive meds
Chronic: occurs gradually over months to years
cause: blood vessel injury from overgrowth of smooth muscles of the blood vessels causing fibrotic tissue to replace normal tissue resulting in a nonfunctioning donor kidney
s/s: gradual return of azotemia, fluid retention, electrolyte imbalance, fatigue
treatment: conservative (monitor kidney status, continue immunosuppressive therapy) until dialysis is required
Multiple Sclerosis: Teaching Client About Visual Changes (RM AMS RN 10.0 Chp 10, Active Learning Template - System Disorder)
Patient may be double (diplopia)
Teach scanning techniques.
Instruct client to visually can his environment by moving his head from side to side
........................Continued
[Show More]












.png)