DANB Radiology Exam
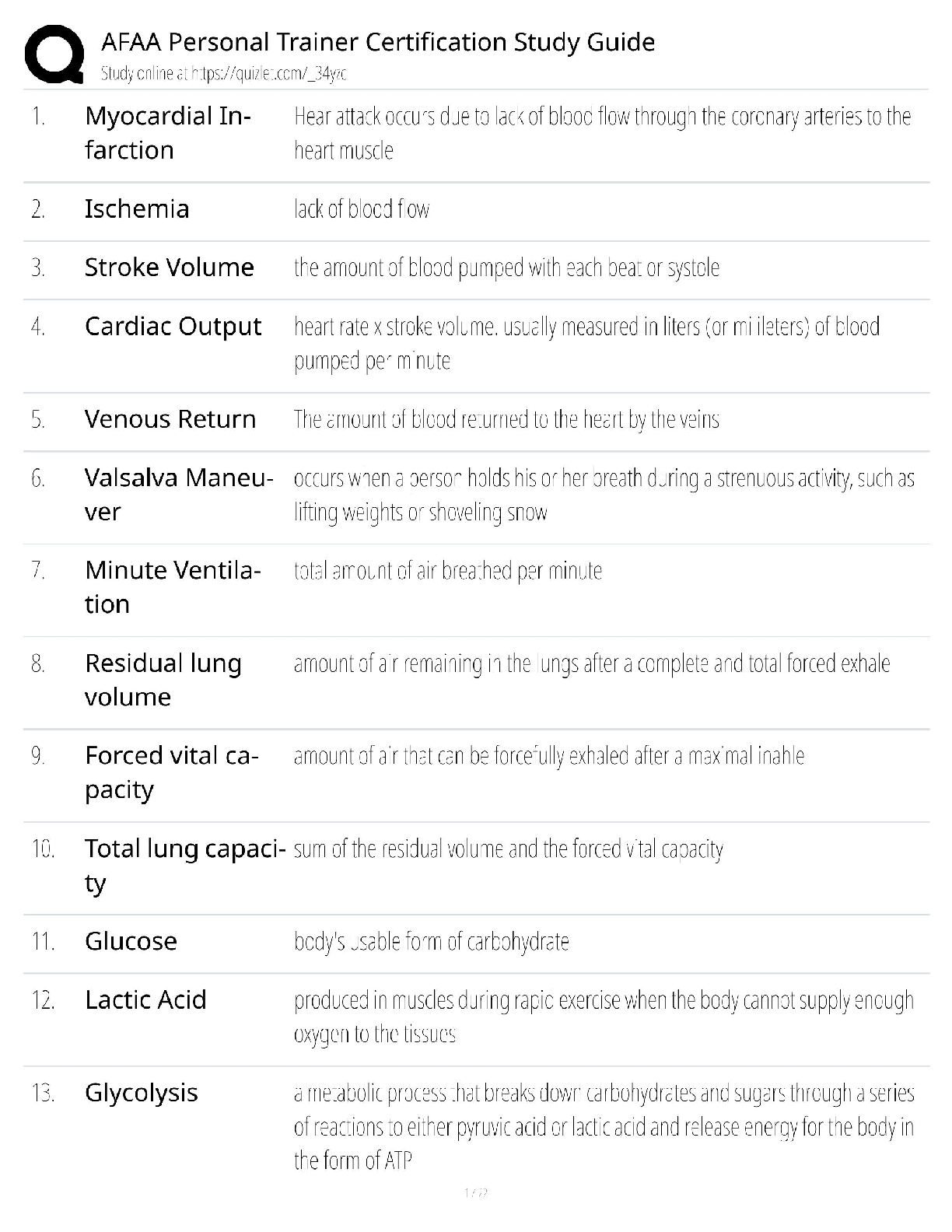
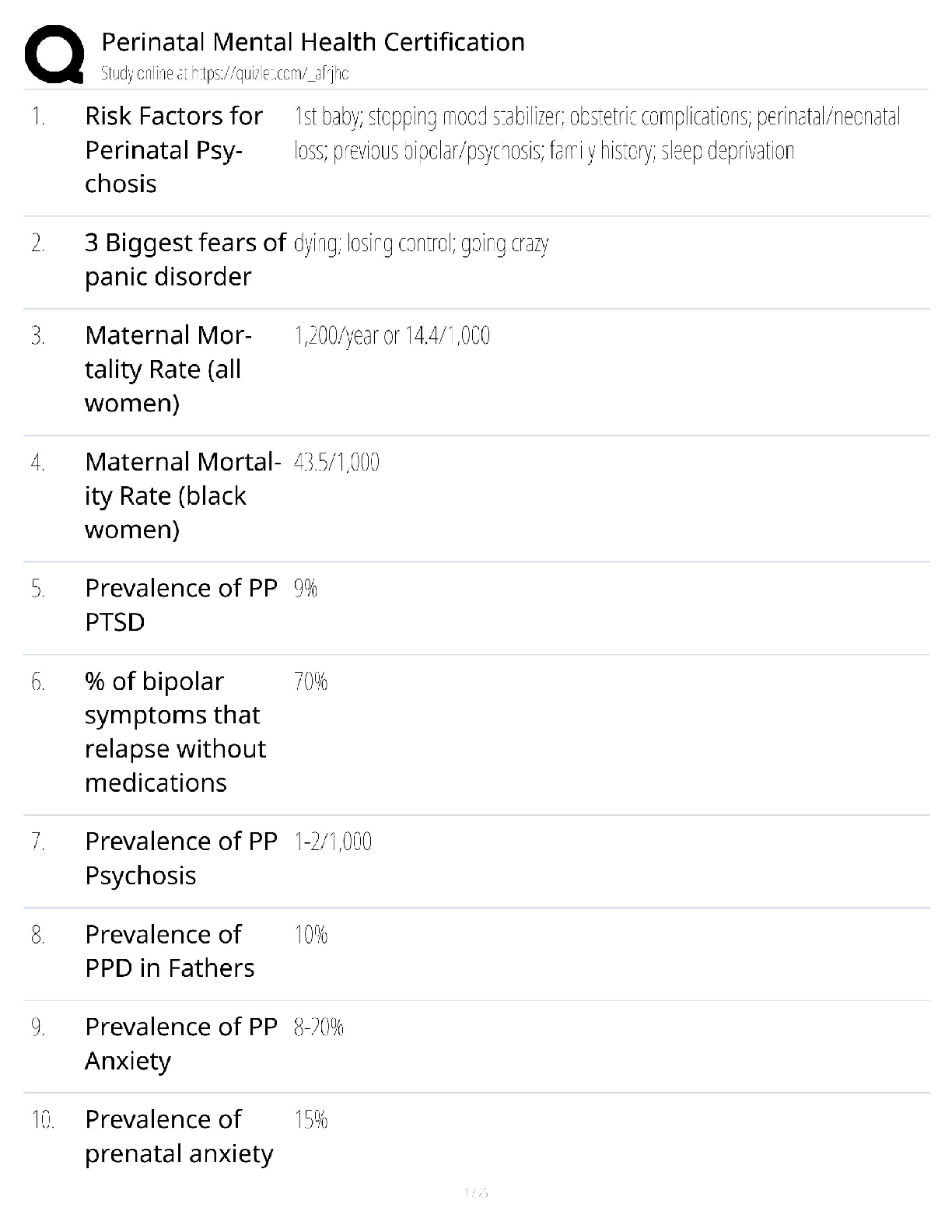
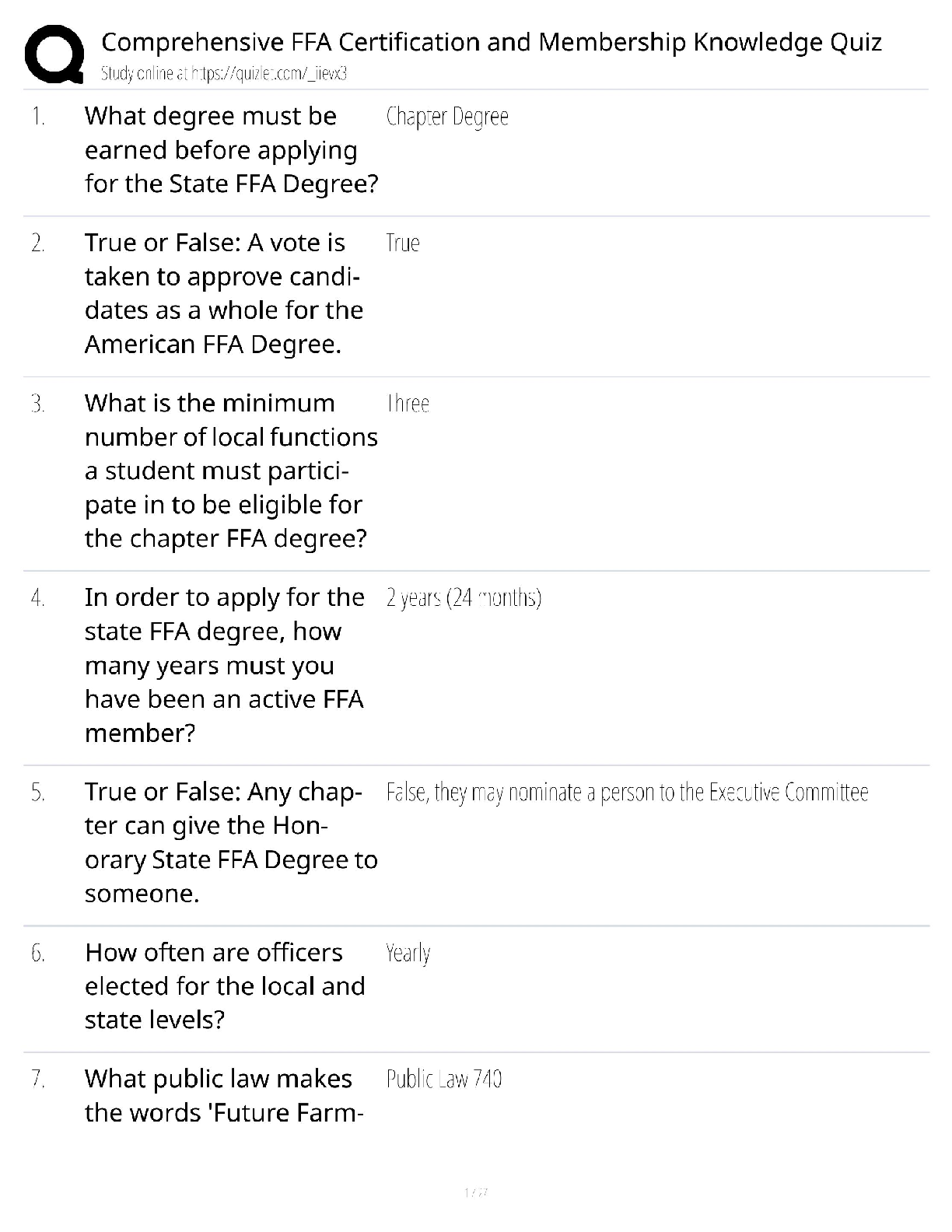
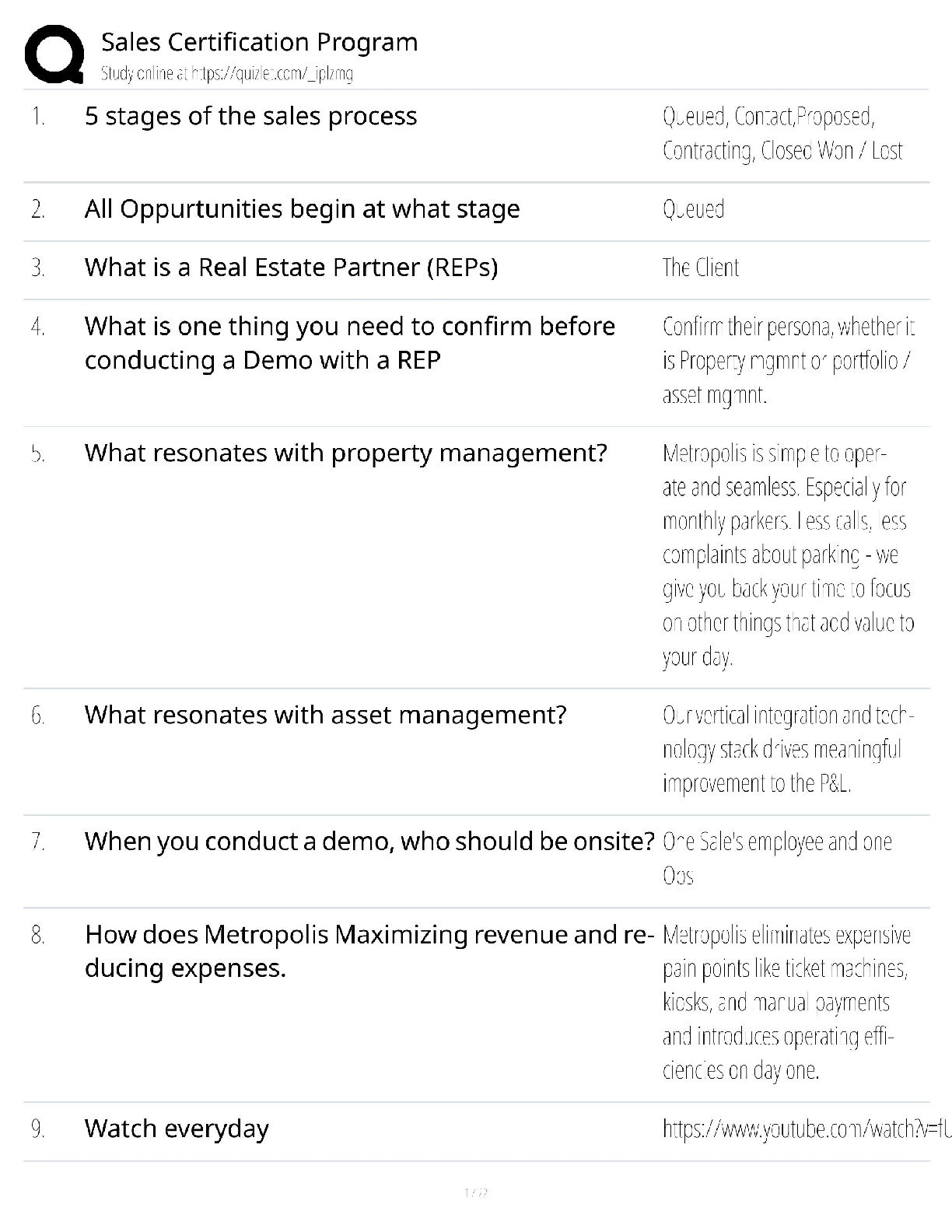
What is the base of dental film composed of? - ✔✔blue tinted polyester acetate
What is the emulsion composed of? - ✔✔gelatin and silver halide crystals
What determines the speed of dental films? -
...
DANB Radiology Exam
What is the base of dental film composed of? - ✔✔blue tinted polyester acetate
What is the emulsion composed of? - ✔✔gelatin and silver halide crystals
What determines the speed of dental films? - ✔✔size of crystals, thickness of emulsion,
radiosensitive dyes
What is the purpose of the lead foil? - ✔✔absorb scatter radiation and prevent fogging
What Film speed is faster and reduces radiation exposure to patient? - ✔✔F- Speed
What size film is used for PA's on small children - ✔✔#0
what size film is used for Bite-wings on adults when only one film is taken on each side - ✔✔#3
size film used for anterior PA's for patients with narrow arches - ✔✔#1
size film used for PA's on adults - ✔✔#2
size film used for BW on adults - ✔✔#2
size film used for occlusals on adults - ✔✔#4
What is the purpose of the embossed dot - ✔✔to determine film orientation, to help aid in
mounting radiographs in anatomical order
What is the latent image - ✔✔invisible image (remains like this until film is processed)
What happens in the developer - ✔✔reduces the exposed silver halide crystals to black metallic
silver. converts latent image into visible image
What happens in the fixer - ✔✔removes the undeveloped silver halide crystals, hardens the
emulsion
how long does film stay in the developer - ✔✔5 min
what is the optimum processing temp. - ✔✔68 degrees F
when can the films be exposed to white light - ✔✔after 2-3 min of fixing if needed
what causes film fogging - ✔✔-old or contaminated processing solutions
-exposure to chemical fumes
-faulty safelight
-scatter radiation
what would cause a film to be too light - ✔✔-underexposure
-underdevelopment
-depleted developer solution
-excessive fixation (takes all crystals off)
what would cause a film to be too dark - ✔✔-overexposure
-overdevelopment
-developer is too strong
-not enough fixation
-exposure to white light
-improper safelighting
What causes a HERRINGBONE effect - ✔✔film placed backwards during exposure
what would happen to a film that is placed in the fixer prior to development - ✔✔blank or clear
(takes all of the crystals off)
what is reticulation - ✔✔cracking of the emulsion caused by excessive temp difference between
solutions
how far from the work surface must the safelight be mounted - ✔✔4 feet
The difference between direct and indirect digial imaging. - ✔✔direct - directly obtaining a
digital image by exposing intraoral sensor to x-rays to provide an image that can be viewed on a
computer
indirect - photostimuable phosphor plate sensor technology, obtaining a digital image in which
an exposed phosphor plate is placed into a scanner and then converted into a digital image
what film is used to diagnose interproximal decay - ✔✔Bite-Wing
what projection would you take for a patient complaining of pain in the lower left molar area -
✔✔left molar Periapical
what is the purpose of a panoramic - ✔✔image the entire dentition, surrounding alveolar bone,
sinuses, and the TMJ, examine large area of face and jaws, locate impacted teeth, retain root tips,
evaluate trauma, lesions, and diseases, and assess growth and development
what causes foreshortening - ✔✔excessive vertical angulation
what causes elongation - ✔✔insufficient vertical angulation
what causes overlapping - ✔✔incorrect horrizontal angulation
what causes conecut - ✔✔not centered on sensor
what causes clear film - ✔✔no exposure, or fixer before developer
what causes missing apices - ✔✔insufficient vertical angulation
what mounting method is the used as if you are looking straight at the patient, and the patients
right is on your left - ✔✔Labial
how do you differentiate between max and mand molar when mounting - ✔✔- max molars have
3 roots, mand have 2 roots
what mounting method is the used as if you are inside the patients mouth looking out, and the
patients right is on your right - ✔✔Lingual
Phosphor Storage Plates are what type of digital imaging? Direct or Indirect - ✔✔indirect digital
imaging
In the paralleling technique how should the film be placed in relation to the tooth? - ✔✔parallel
to the long axis of the tooth
In the paralleling technique, how should the central beam be directed - ✔✔perpendicular to the
tooth and film
what periapical technique offers the best diagnostic quality? - ✔✔paralleling
what is penumbra - ✔✔shadow around the tooth
how does packet placement differ between bisecting and paralleling - ✔✔-bisecting - packet is as
close to tooth as possible, but not parallel
-parallel - packet is parallel to tooth, further away
proper patient positiong for paralleling - ✔✔doesn't matter
how far should the operator stand from the source of radiation - ✔✔6 ft
[Show More]

.png)


.png)


.png)