CS 234 assignment 2-ALL ANSWERS 100% CORRECT
$ 8

NCLE Test Questions And Answers 2024
$ 17

Test Bank for Managing Human Resources 8th Edition By Luis Gomez-Mejia, David Balkin, Robert Cardy (Test Bank All Chapters, 100% Original Verified, A+ Grade)
$ 20

eBook [PDF] Procedures in Cosmetic Dermatology Series Chemical Peels 3rd Edition By Suzan Obagi
$ 30

CLG 0010 Exam 100% Scored_ Spring 2022
$ 10

CompTIA Network+ N10-008 All-in-One Exam Guide with Practice Questions
$ 36.5
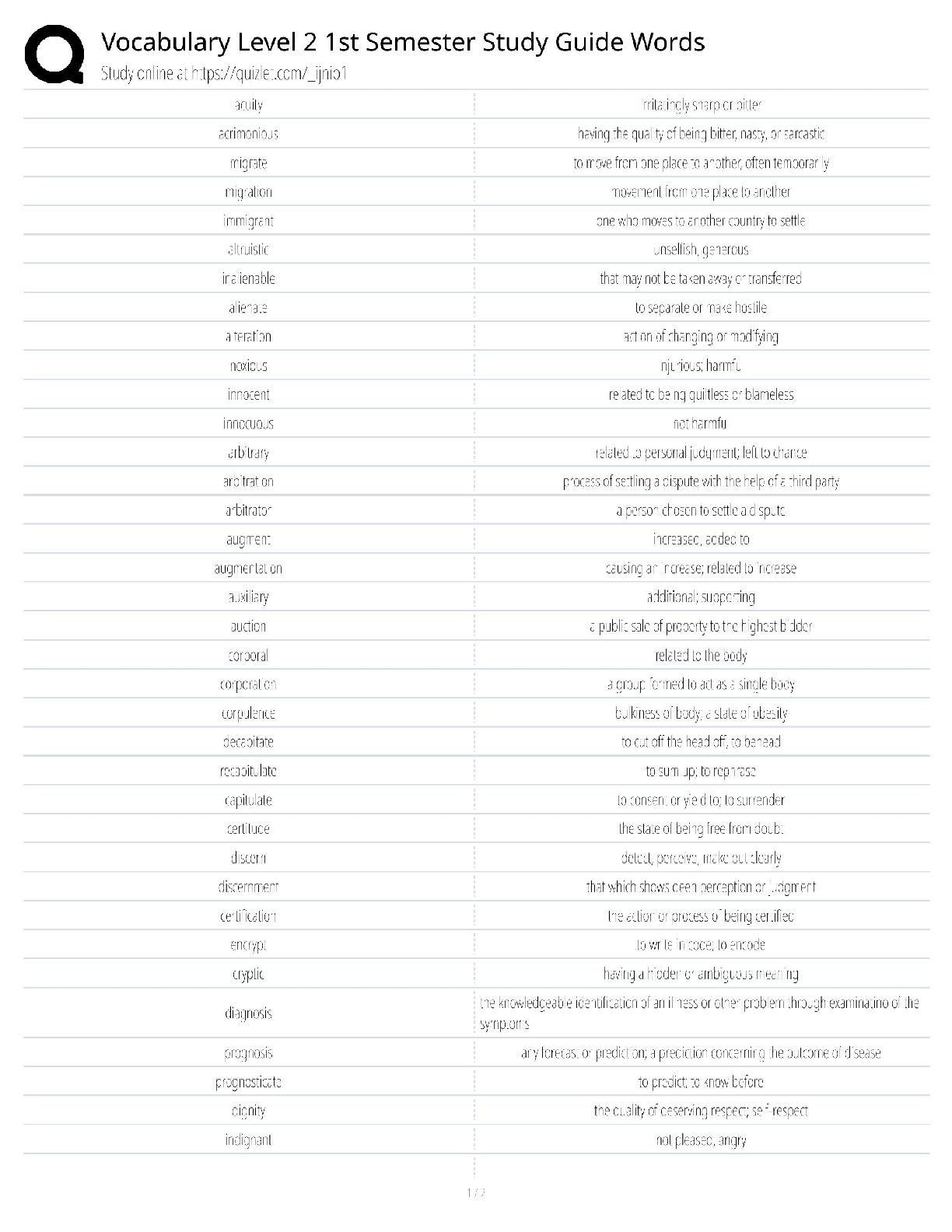
Vocabulary Level 2 / 1st Semester Study Guide Words / Test Bank & Flashcards / Score 100% 2025
$ 19

WGU C235 - Training and Development Learning Style Types 2. Verified, latest update.
$ 4

HESI A2 Entrance Exam 225 Questions with Verified Answers,100% CORRECT
$ 10.5

ATI MED SURG PROCTORED STUDY GUIDE 2021
$ 9

ITC 246 – CISCO 100-105 Exam | WGU | Verified Practice Exam & Answers for ICND1 Certification
$ 35

Chapter 33: Deterministic Effects of Radiation Test Bank
$ 18.5

eBook(EPUB)Fear Is a Choice Tackling Life's Challenges with Dignity, Faith, and Determination by James Conner, Tiffany Yecke Brooks
$ 29
.png)
WGU C235 Training and Development – Latest 2022 Already Passed
$ 8

UNIT 2 assignment.docx IS 3110 Unit 2 Assignment 1 PCI DSS and the Seven Domains 1.Id
$ 5

eBook [PDF] Modernist Waterscapes Water, Imagination and Materiality in the Works of Virginia Woolf 1st Edition By Marlene Dirschauer
$ 29

NURS 231 MODULE 4 EXAM GRADE A+ CORRECT
$ 18

PATHOPHYSIOLOGY CHPTR 23 Urologic Disorders - Davis Adv Assessments w/ Pre & Post
$ 8

RMI 2302 Final Exam Nyce | 45 Questions with 100% Correct Answers | Updated 2023
$ 7

IICRC - Carpet Cleaning Technician - Knowledge Test Guide 2024
$ 13

CRCR CERTIFICATION EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS (2023) (VERIFIED ANSWERS BY EXPERT)
$ 10

Test Bank for Microeconomics 8th Edition David Colander
$ 20
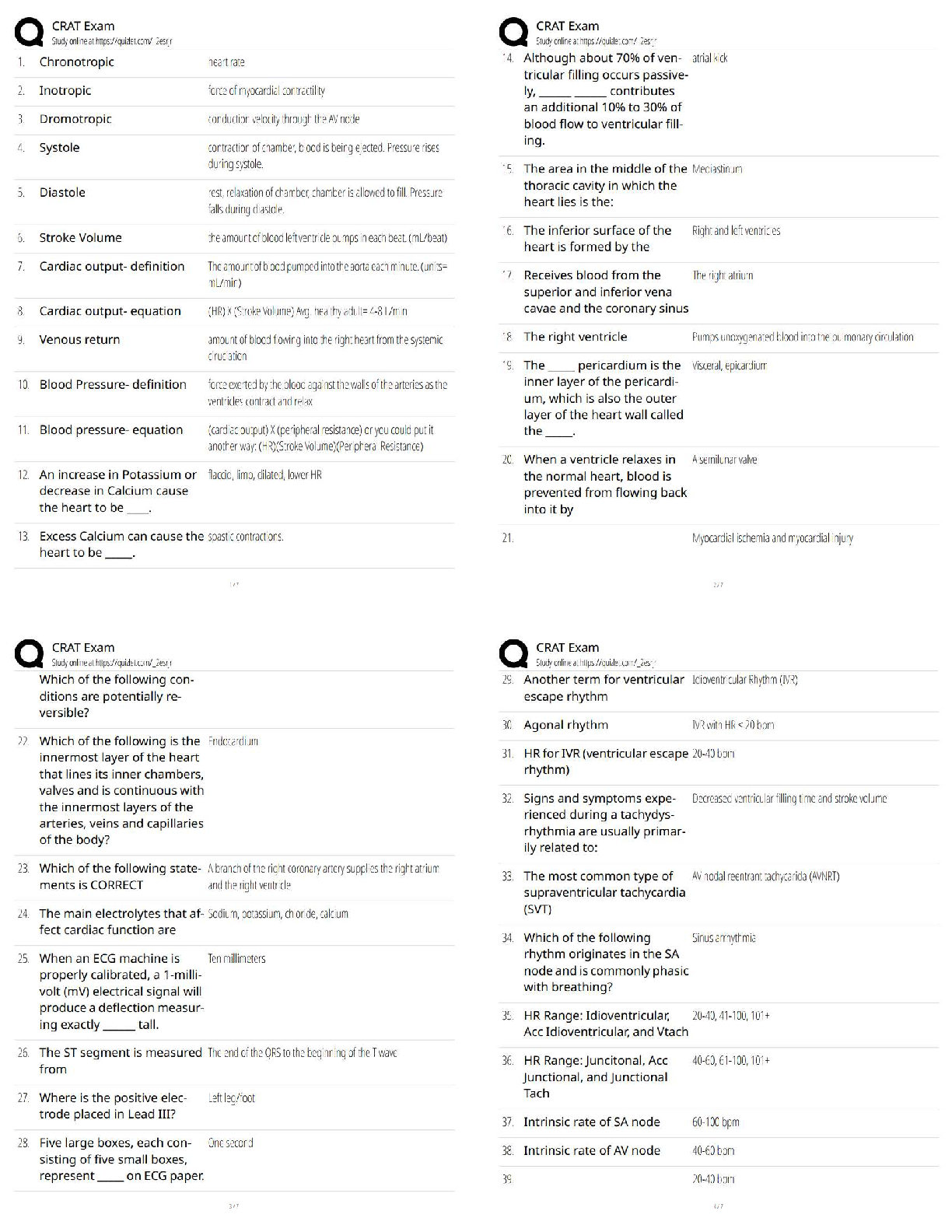
CRAT Exam / Score 100% / New Version / 2025 Update / Full Study Guide & Test Bank
$ 11
NR 507 WEEK 4 Midterm Exam Questions and Answers
$ 30

NR 603 Week 3 Case Discussion: Cardiovascular{100%}(LATEST UPDATE)
$ 12

Classical Greek H444/01: Unseen translation Advanced GCE Question Paper
$ 6.5

eBook [PDF] Music in Theory and Practice (Volume 2) 10th Edition By Bruce Benward, Marilyn Saker
$ 30

Com 204 Exam 1 Questions and complete Answers
$ 8

Maternal Child Nursing Unit 1 Practice Questions / 2025 Update / Score 100% Exam Prep & Test Bank
$ 11

The Science of Nutrition, 5th edition By Janice Thompson, Melinda Manore, Linda A Vaughan (Solutions Manual)
$ 25

NR 661 REFLECTION ON THE DOCTOR OF NURSING PRACTICE (DNP)
$ 12

PENN FOSTER EXAM QUESTIONS
$ 8
 COMPLETE STUDY GUIDE LATEST 2021.png)
VATI PREDICTOR (GREENLIGHT) COMPLETE STUDY GUIDE LATEST 2021
$ 8

Pharmacology for Nurses A Pathophysiologic Approach, 6th Edition by Michael Adams, Norman Holland TEST BANK
$ 23

HRMT 413 Midterm Exam (100% Correct, Graded A)
$ 13

North Carolina State University ST 350 ST 350 Homework #2 This Excel file Flight Performance US Airports shows the flight data for a recent month at most US airports. Variables included are City, State, AirportCode, Airport, Flights, Delayed, Cancelled, Diverted, Ontime, and Ontime Percentage. Use Excel to make a histogram of the variable Ontime Percentage. Read the comments below for assistance.
$ 6

vSIM CLINICAL PACKET FOR STUDENTS
$ 10

NURS 6521 Final Exam Version 1-7| 2022/23
$ 29

GCU 322 Map Quiz 13 - Questions and Answers