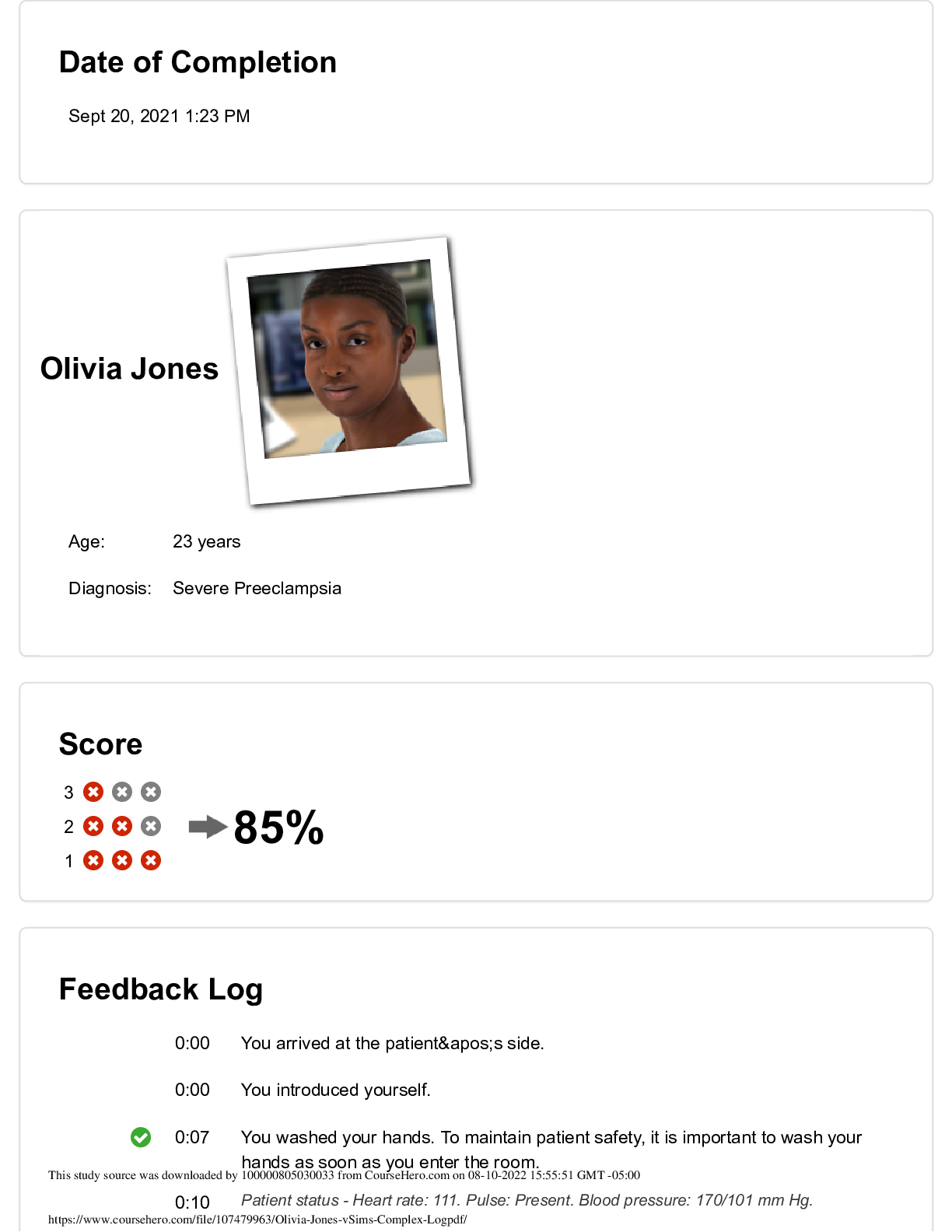
Wall Street Prep
Debt and Fixed Income Crash Course
I. Intro
a. Demand comes from governments (lots of expenditure, when you have
deficit start borrowing), corporations, and households
b. Fixed income securities:
...
Wall Street Prep
Debt and Fixed Income Crash Course
I. Intro
a. Demand comes from governments (lots of expenditure, when you have
deficit start borrowing), corporations, and households
b. Fixed income securities: financial instruments that require borrower pay a
pre-determined amount to the holder of the security in exchange for capital
upfront
i. Refers to debt with fixed or variable debt (changes in LIBOR!), other
instruments
c. Debt is a significantly larger component of the capital markets than equity
i. Equity is silo-ed for corporations, but governments + households have
debt too
d. Types of debt:
i. Bonds: actively traded financial instruments,
1. used by governments primarily
ii. Loans: lender holds loan that’s not tradeable (unless securitized, ie.
MBS)
1. Used by households mostly
iii. Corporations do both
e. Geographical breakdown: U.S. has heavy weight toward issuing corporate
bonds
i. U.S. dominates debt market, accounts for 40% of global debt, EM has
14%
II. Bond basics (math)
a. Types of bonds
i. Bullet bond: conventional/vanilla bond, typical structure where bond
pays out incremental interest payments and principal return at the end
then you basically do
trial and error to find ‘y’ or use Excel’s =RATE() function
1. =RATE(# periods, coupon rate * FV, -PV, FV)
2. =PV(target rate, # periods, couon rate * FV, FV)
3. reinvestment assumption: assumes that the interest payments
you receive will be reinvested coupons at the yield, assumes
every single cash flow is reinvested at the y the model spits out
4. used in corporate and longer term government bonds
ii. Zero-coupon bond: bond that pays no coupon, but price at end
embeds interest payments ,
1. Used in short term government bonds, ie. T-Bill, money market
instruments
iii. Annuity bond: commingles interest and principal to create even
payments every period –
1.
2. FV=0, coupon rate=0
3. Also assumes reinvestments at the yield of annuity payments
4. Used in mortgages and insurance and retirement products
iv. Notes: bonds with shorter maturities usually, depending on type f note
This study source was downloaded by 100000831777157 from CourseHero.com on 07-16-2022 00:04:38 GMT -05:00
https://www.coursehero.com/file/99286907/Wall-Street-Prep-Fixed-Income-and-Debtdocx/
1. ie. corporate bonds with 20 year can be a note, but U
[Show More]








.png)
.png)