MATH 221 Week 2 Discussion Post # 2
Professor Ramanathan
Create a contingency table with two variables. Then pose two conditional probability questions for others to solve.
Here is an example: Other students can reply
...
MATH 221 Week 2 Discussion Post # 2
Professor Ramanathan
Create a contingency table with two variables. Then pose two conditional probability questions for others to solve.
Here is an example: Other students can reply with details on how to find the conditional probabilities.
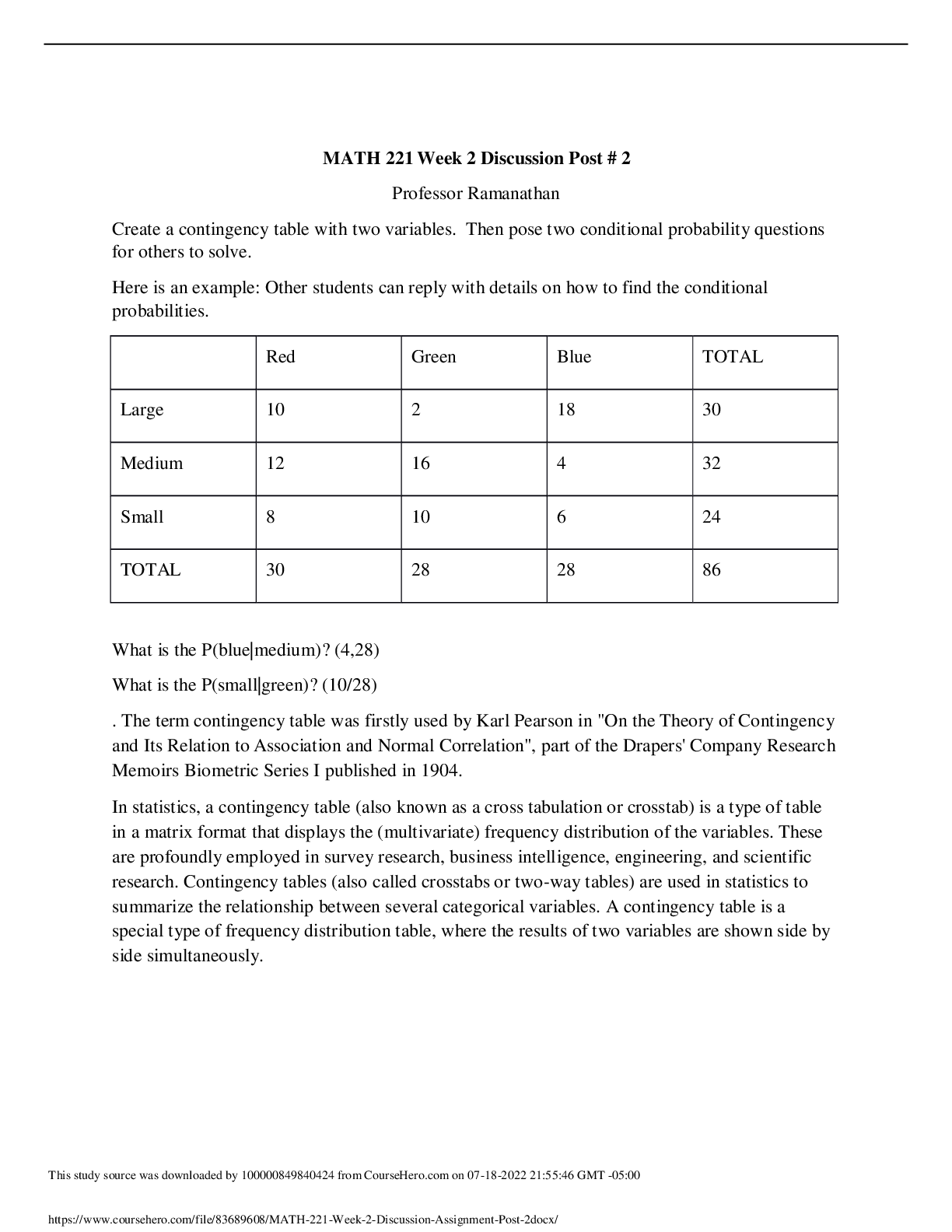
Red Green Blue TOTAL
Large 10 2 18 30
Medium 12 16 4 32
Small 8 10 6 24
TOTAL 30 28 28 86
What is the P(blue|medium)? (4,28) What is the P(small|green)? (10/28)
. The term contingency table was firstly used by Karl Pearson in "On the Theory of Contingency and Its Relation to Association and Normal Correlation", part of the Drapers' Company Research Memoirs Biometric Series I published in 1904.
In statistics, a contingency table (also known as a cross tabulation or crosstab) is a type of table in a matrix format that displays the (multivariate) frequency distribution of the variables. These are profoundly employed in survey research, business intelligence, engineering, and scientific research. Contingency tables (also called crosstabs or two-way tables) are used in statistics to summarize the relationship between several categorical variables. A contingency table is a special type of frequency distribution table, where the results of two variables are shown side by side simultaneously.
They deliver a straightforward depiction of the interrelation amid two variables and can assist in finding interactions between them
Common Question: Why do we subtract the probability of Male and blue eyes? The answer is that when we count up all the males and then we count up all the people with blue eyes, there is some overlap because some males have blue eyes. This means we counted them twice and so we have to subtract the extra count.
Therefore:
P(Blue eyes OR Male) = P(Blue eyes) + P( Male) – P(Blue eyes AND Male)
= 22/167 + 82/167 – 12/167 = (22 + 82 – 12) / 167 = 92/167 = .55 or 55%
References:
Wikipedia listing. “Contingency Tables”, Karl Pearson, F.R.S. (1904). Mathematical contributions to the theory of evolution. Dulau and Co.
Link to Reference: contingency table in statistics - Bing
Learn Math and Stats with Dr. G
A Shortcut is the Longest Distance Between Two Points
Link to Website: Using Contingency Tables for Probability and Dependence | Learn Math and Stats with Dr. G (mathandstatistics.com)
[Show More]