A. You are using a thermistor with a resistance of 5000Ω at 25.0 °C and with
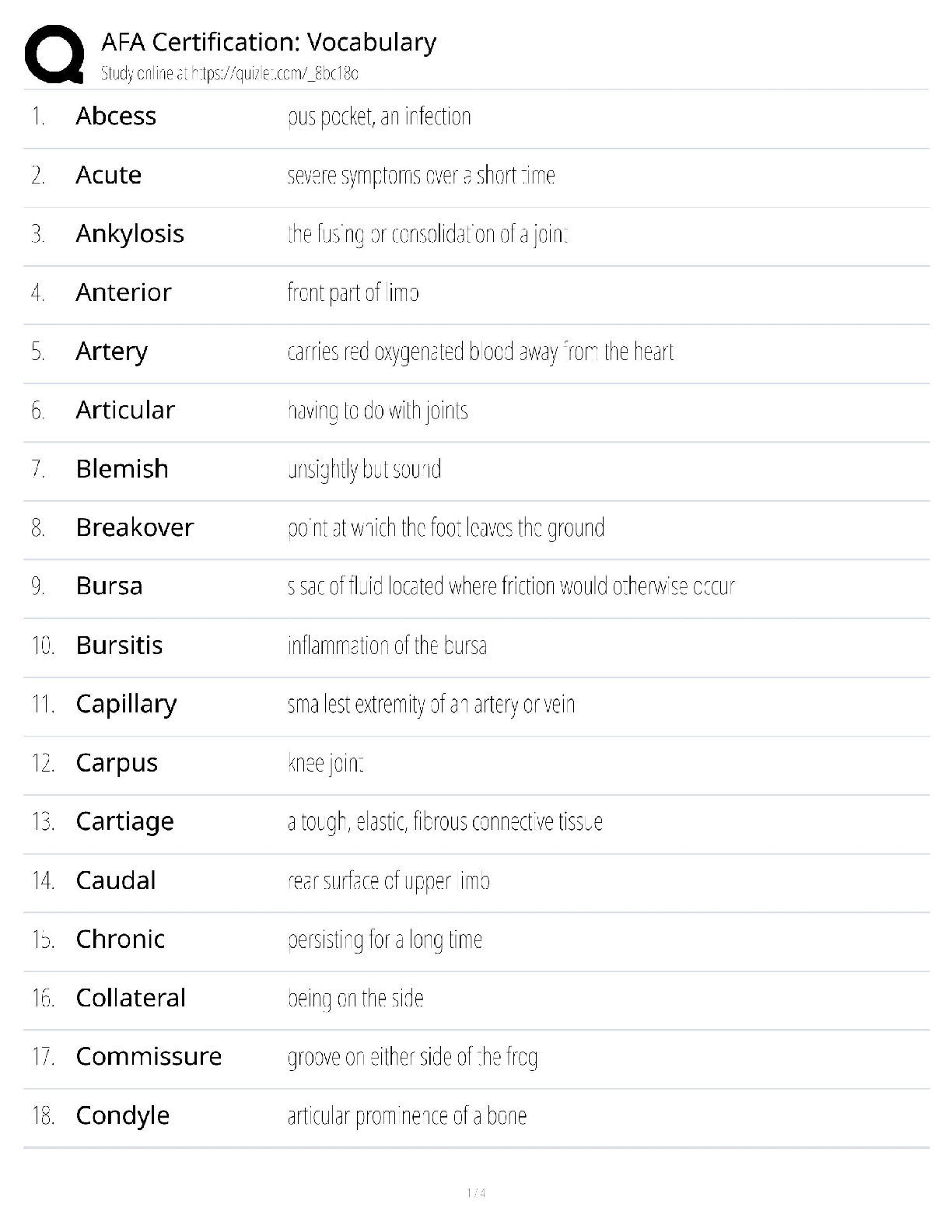
β = 3630. You measure a resistance of 921 ohms. What is the
temperature in °C?
B. You are deciding between using a thermistor or a class
...
A. You are using a thermistor with a resistance of 5000Ω at 25.0 °C and with
β = 3630. You measure a resistance of 921 ohms. What is the
temperature in °C?
B. You are deciding between using a thermistor or a class A RTD for
measuring the temperature of a critical circuit board of a smart phone near
25°C. The accuracy must be within 0.25°C throughout the range of
measurement. Neither speed of response nor component cost is an issue.
What type of sensor do you use and why? Find an example online of a
sensor that you could use for this application.
C. A 100-ohm Class A RTD probe is calibrated at three points for extra
precision, with a curve of RTD (T) = RTD0 ((1 + AT +BT2 + CT3(T -100))
where:
RTD (T) = the RTD element’s resistance in ohms at temperature T
RTD0 = the RTD element’s resistance in ohms at 0°C
T = the RTD element’s temperature in °C
A = 3.9083 x 10-3 /°C
B = -5.775 x 10-7 /°C2
C = 0 if T >= 0°C
IF RTD(T) = 116.01 ohms, what is T?
D. You are using a Type K thermocouple to measure the temperature of a
process that operates in the range of 1000°C to 1100°C. In particular, you
know that the thermoelectric voltage is 42.053 mV at 1020°C and 42.440
mV at 1030°C. Having no other data in between, and no way to look up
the data on thermocouple tables, what is a good approximation for the
thermoelectric voltage at 1027°C?
E. You are using a Type K thermocouple to measure the temperature of a
semiconductor etch process that operates in the range of 1000°C to
1100°C. The thermistor in your isothermal block (junctions J3 and J4)
measures a temperature of 20°C and your voltmeter measures 44.240 mV.
What is the temperature T1 of your process?
F. Suppose we include the lead resistance in the calculation of temperature
for a class A RTD. If R3 = 1000 ohms, Ra = 20 ohms, V0 = 1.75 ohms, and V
= 5 volts, what is the nominal temperature measured. Given the tolerances,
what is the highest temperature you could measure
[Show More]