ATI NUTRIATION RETAKE EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 300 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 14

Respiratory Therapy CRT Exam Questions
$ 10

issa_sports_nutrition_final_exam.docx.pdf
$ 7

ServSafe Manager Exam. All Questions and answers. Rated A+. Latest update
$ 9

ATI Nutrition Final Exam Questions & Answers-VERIFIED 100% CORRECT
$ 12

Pro Tools 101 V12 Test Questions
$ 10.5
.png)
SAFe 5 Scrum Master Exam Study Guide Questions and Answers Already Passed
$ 13

Wreb Jurisprudence Exam
$ 10

X-ray Certification Practice
$ 10

ProPrac Test 2
$ 10

ATI NUTRIATION RETAKE EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 300 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 14

HLT 230 Nutrition assignment 2022/2023 with complete solution
$ 8

TEST BANK for Medical Emergencies Essentials for the Dental Professional, 2nd Edition
$ 19.5
C787 Module 5 Study Guide.
$ 12

WREB Study: Local Anesthesia & NO Questions
$ 10
-MODULE 1 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS.png)
BIOD 121 (Portage)-MODULE 1 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 7

ATI NUTRIATION RETAKE EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 300 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 14

ATI NUTRIATION RETAKE EXAM QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS 300 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
$ 14

Procore Superintendent Certification
$ 10

PSG 211 Fina
$ 10

PSG Boards Exam Study Guide
$ 10

Pro Tools 101 Certification
$ 10

PSG Fall Exam 3
$ 10

Vett 116 - Final Study Guide
$ 10

BIOD 121 FINAL EXAM GRADED A+
$ 8

PSG 2411 FINAL EXAM SET
$ 10

SERE 100.2 Level A SERE Education and Training in Support of the Code of Conduct (FOUO) (4 hrs.) Military Pre Test
$ 10

RAD Midterm 1 TCDHA
$ 10

Proprac Exam 1
$ 10

VETT 236 All Quizzes
$ 10

Procore Final Exam
$ 9
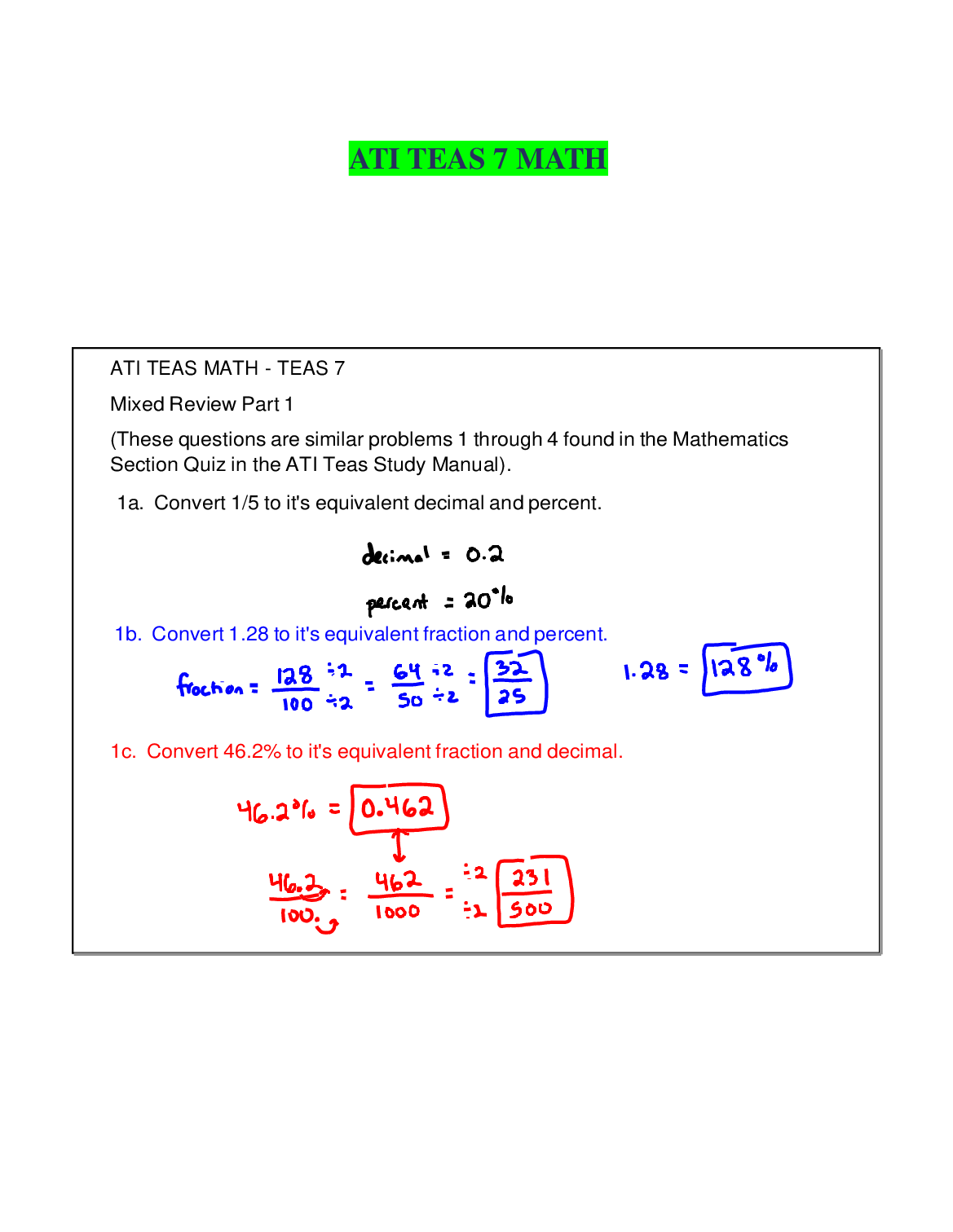
ATI TEAS MATH - TEAS 7 Mixed Review Part 1
$ 7.5

WELL Practice Exams
$ 10

C787 Unit 2 Module Study Guide
$ 11

NCP TUTORIAL QUESTIONS | 58 Questions with 100% Correct Answers
$ 10

RRT Test Questions & Answers









.png)
.png)