Microeconomics > EXAM > Questions and Answers > Rutgers University 373 421 Demand Price Analysis: First Exam Practice Questi (All)
Questions and Answers > Rutgers University 373 421 Demand Price Analysis: First Exam Practice Questions Demand & Price Analysis. Chapter 1-4
Document Content and Description Below
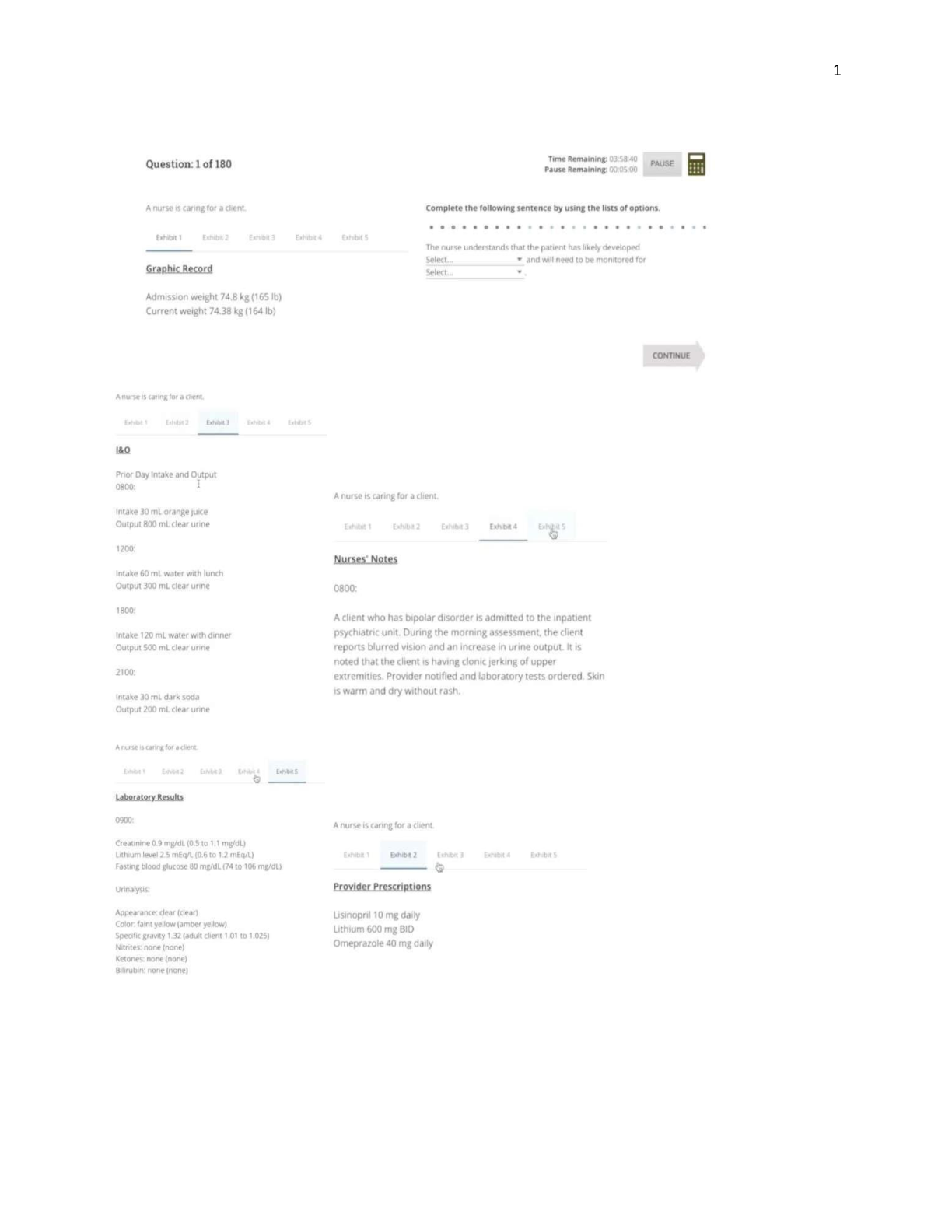
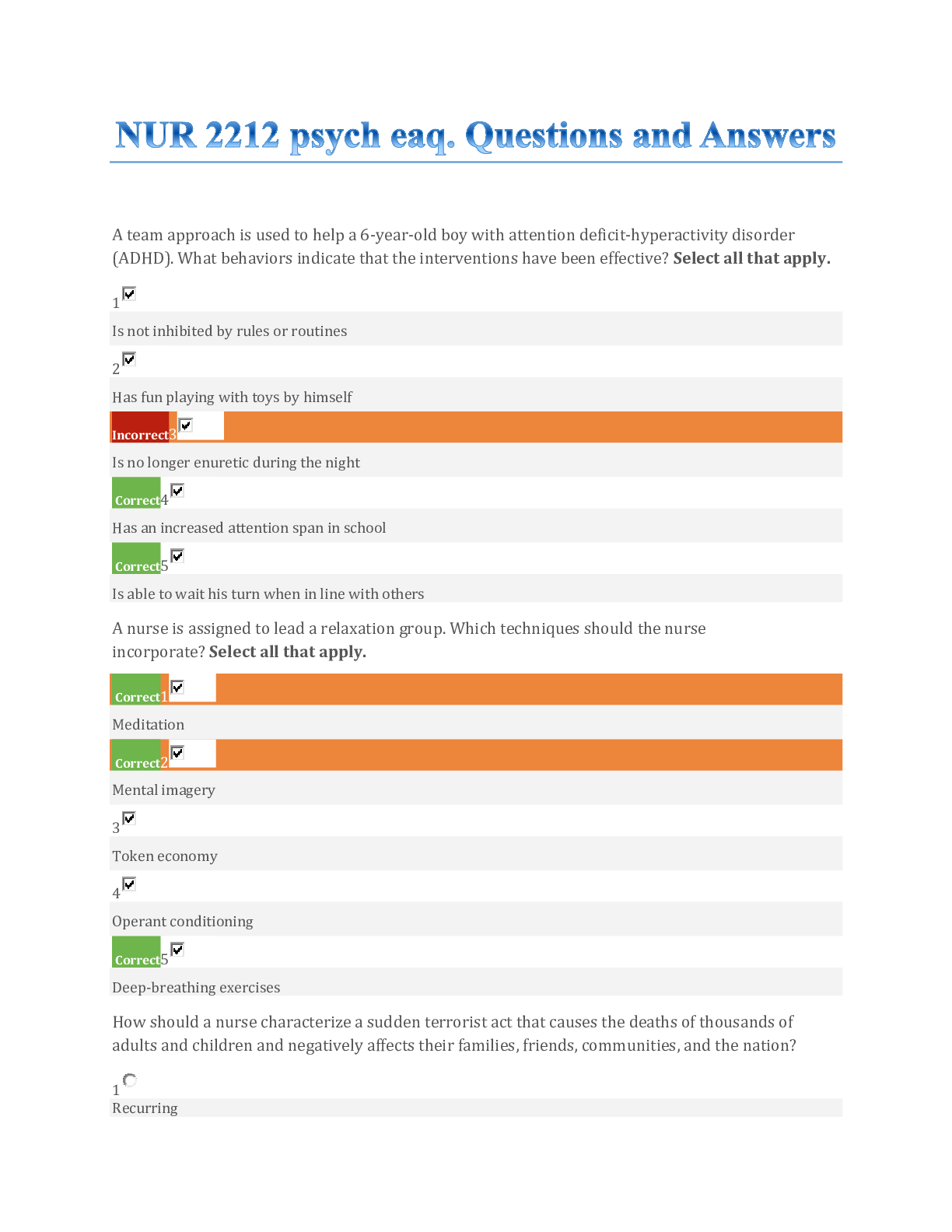
Rutgers University 373 421 First Exam Practice Questions Demand & Price Analysis 11:373:422 Chapter 1 ____ 1. Managerial economics uses ____________ to help managers solve problems. a. formal mo ... dels b. prescribed behavior c. quantitative methods d. microeconomic theory e. all of the above ____ 2. If the annual interest rate is i, the present value of $X to be received at the end of each of the next n years is: a. $X/i b. $X/(1 + i)n c. d. $X[(1 + i)n] / [ i(1 + i)n – 1] e. $X / [i(1 + i)n – 1] ____ 3. You’ve just won the $25 million lottery. You are going to receive a check for $1 million today and at the end of every year for the next 24 years. If the interest rate is 10 percent, the present value of your prize is: a. $8,984,744 b. $9,984,744 c. $12,984,744 d. $20,000,000 e. $25,000,000 ____ 4. In managerial economics, managers are assumed to maximize: a. current profits b. their take-home pay c. their employees’ welfare d. the value of their firm e. social welfare ____ 5. Economic profits may result from: a. innovation b. risk taking c. exploiting market inefficiencies d. all the above e. a and b 1 ____ 6. Managers may make decisions that are not consistent with the goals of stockholders. This is referred to as the _____ problem. a. principal–agent b. economic disincentive c. incentive–compromise d. efficiency–inefficiency e. equilibrium ____ 7. California imposes strict new regulations on the blending of gasoline that increase production costs. As a result, the: a. demand for gasoline will increase b. demand for gasoline will decrease c. supply of gasoline will increase d. supply of gasoline will decrease e. demand for and supply of gasoline will not change Figure 1 ____ 8. In Figure 1, the equilibrium price and quantity are: a. Pa and Qa b. Pb and Qb c. Pc and Qc d. Pa and Qc e. Pc and Qa 2 ____ 9. In Figure 1, there will be an excess supply at any price: a. above Pb b. below Pb c. other than Pb d. below Pa e. above Pc Ch1 Answer Section 3 Chapter 2 ____ 1. The demand curve’s usual slope implies that consumers: a. buy more as the price of a good is increased b. buy more as a good is advertised more c. buy more at higher average incomes d. buy less as the price of a good is increased e. have tastes that sometimes change ____ 2. A market demand curve is likely to shift to the right when: a. average income falls b. prices fall c. prices rise d. population increases e. new firms enter the market ____ 3. If the elasticity of per capita demand with respect to population is zero, then a 10 percent increase in the population will cause the quantity demanded to: a. increase by 25 percent b. decrease by 10 percent c. remain constant d. increase by 10 percent e. decrease by 25 percent ____ 4. As we move down a linear demand curve, demand becomes: a. more elastic b. less elastic at first and then more elastic c. steeper d. more elastic at first and then less elastic e. less elastic ____ 5. The demand for personal computers has been estimated to be Q = 500,000 – 700P + 200I – 500S. Assume that per capita income I is $13,000 and the average price of software S is $400. When the price of personal computers is P = $3,000, the price elasticity of demand is: a. –2.625 b. –7.0 c. –1.0 d. –21.0 e. –4.25 ____ 6. The demand for fashion watches is Q = 9 – 0.7P + 2I. Assume that per capita income I is $13. When the price of fashion watches is P = $30, the price elasticity of demand is: a. –0.66 b. –1.0 c. –2.0 d. –0.5 4 e. –1.5 ____ 7. The demand for space heaters is Q = 250 – P + 2COOL, where COOL is the absolute value of the difference between the average overnight low temperature and 40°F. Assume that the average overnight low this month is 40°F. When the price of space heaters is P = $50, the price elasticity of demand is: a. –1.38 b. –13.8 c. –0.138 d. –1.50 e. –0.25 ____ 8. The demand for office chairs in thousands is Q = 80 – P2. At a price of $4, the price elasticity of demand is: a. –0.5 b. –8.0 c. –2.0 d. –4.0 e. –0.25 ____ 9. The formula for the arc price elasticity can be written (where ∆Q denotes the change in Q) as: a. b. c. d. e. none of the above ____ 10. If price is $25 when the price elasticity of demand is –0.5, then marginal revenue must be: a. $50 b. –$25 c. $12.50 d. $37.50 e. $25 ____ 11. If the marginal cost of seating a theatergoer is $5 and the elasticity of demand is –4, the profitmaximizing price is: a. $3.33 b. $5.00 c. $10.00 d. $13.33 e. $6.67 5 ____ 12. The demand for fax machines in thousands of units has been estimated to be Q = 1,000 – 1.5P + 5L, where P is the price of the machines and L is the average cost of a 10-minute midday call from Los Angeles to New York. At a fax machine price of $400 and a phone call cost of $10, the price elasticity of demand for fax machines is: a. –4.0 b. –2.50 c. –0.61 d. –0.25 e. –1.33 ____ 13. The formula for the point price elasticity can be written as: a. b. c. d. e. none of the above ____ 14. The demand for cable television hookups is Q = 100 – 10P1/2 + 2I–1, where P is price and I is per capita income. Cable TV is a(n): a. normal good b. natural monopoly c. inferior good d. substitute good e. complement good ____ 15. Makers of disposable diapers must advertise 5 percent more to offset completely the 2 percent decline in sales due to heightened environmental concern. The advertising elasticity of demand is: a. 4.0 b. 0.4 c. 2.5 d. 0.25 e. 0.20 ch2 Answer Section 7 Chapter 3 ____ 1. Indifference curves describe: a. various consumer income levels b. alternative market prices for goods and services c. the quantities of a good or service that people are willing and able to buy at alternative prices d. producer production levels at alternative market prices e. consumer preferences ____ 2. The marginal rate of substitution: a. remains constant as the consumer moves around an indifference curve b. is constant if the goods are perfect complements c. decreases as the consumer moves down a typical indifference curve d. cannot be defined if the goods are perfect substitutes e. none of the above ____ 3. Suppose Al is currently consuming five movies and two concerts per month. If his utility function is given by U = 15MC, where M represents the number of movies seen and C represents the number of concerts attended, Al’s total utility is equal to: a. 10 b. 15 c. 30 d. 75 e. 150 ____ 4. A budget constraint: a. must be convex to the origin if consumers prefer more to less b. will be upward-sloping if consumers consider one good a “bad” c. must be downward-sloping if both goods have positive prices d. will be concave to the origin if the consumer’s budget is fixed e. will always have slope equal to –1 ____ | 5. Consider the budget constraints below. These constraints represent the market baskets that Edith can afford to buy at alternative:8 a. prices of good X b. levels of income c. prices of good Y d. preferences over goods X and Y e. prices of goods X and Y ____ 6. Consider the budget constraint below. Dennis spends all his money on sweaters and sweatshirts. If the price of sweaters is $15, what is the price of sweatshirts? a. $5 b. $7 c. $15 d. $21 9 e. none of the above ____ 7. A consumer’s budget constraint changes slope whenever: a. the consumer buys a different combination of goods b. relative prices change c. the consumer’s income increases d. an indifference curve is tangent to it e. absolute prices change ____ 8. Don consumes bagels and cream cheese. He likes to place 2 ounces of cream cheese on each bagel, no more, no less. In this case, Don’s indifference curves for bagels and cream cheese will be: a. straight lines with slopes equal to –2 b. L-shaped, or right angles c. upward-sloping d. horizontal lines e. vertical lines ____ 9. Tom spends all his monthly income on pretzels and potato chips. Currently, he is maximizing his utility; the marginal utility of pretzels is 150 and the marginal utility of potato chips is 125. If pretzels cost $6 per box, how much do potato chips cost? a. $2 b. $3 c. $4 d. $5 e. $6 ____ 10. Assume that the utility function of wine for a certain consumer is given by TU = 96Q – 3Q2. If wine is free, to maximize utility, the amount the consumer should consume is: a. 6 bottles of wine b. 16 bottles of wine c. 90 bottles of wine d. 93 bottles of wine e. unknown; there is insufficient information to determine this ____ 11. The table below describes Ben’s preferences over cake and ice cream. The utility from consumption of one good is independent of the consumption of the other. The price of cake is $10 per unit and the price of ice cream is $4 per unit. Units | MU | MU Consumed | Cake | Ice Cream1 80 20 2 60 19 3 40 18 4 20 17 5 0 16 If Ben has $50 to spend, the optimal combination of these goods is: a. 4 units of cake and 1 unit of ice cream 10 b. 3 units of cake and 5 units of ice cream c. 3 units of cake and 1 unit of ice cream d. 5 units of cake e. none of the above ____ 12. Consider the indifference map below. The price of Y is $5. Two points on a demand curve for good X are: a. (8, $5) and (10, $5) b. (3, $10) and (5, $20) c. (3, $20) and (8, $5) d. (3, $20) and (5, $10) e. none of the above ____ 13. Betty is investing in the stock market. She is choosing among a variety of stocks; each stock has an expected return and a level of risk attached. Betty likes higher returns and she likes risk. If we were to draw indifference curves for Betty over risk and expected return, they would be: a. L-shaped b. linear c. upward-sloping d. downward-sloping e. vertical lines ____ 14. Consumer surplus is important to firms because: a. it represents value consumers receive that they do not pay for b. market prices must incorporate consumer surplus c. they must pay taxes based on the level of consumer surplus d. if firms can capture it, they can increase their profitability e. a and d 11 The diagram below represents the demand for trips to a local swimming pool during the summer. Please use it to answer the following questions. ____ 15. If the price of a day of swimming is $5 per person, consumer surplus will be: a. $0 b. $1,500 c. $11,250 d. $20,000 e. none of the above ch3 Answer Section 12 Chapter 4 ____ 1. A production function is a table, a graph, or an equation showing the: a. least-cost method of producing output b. optimal combination of inputs c. maximum output that can be achieved from specified levels of inputs d. combinations of inputs that can be produced with equal costs e. optimal production technology that a firm should employ ____ 2. The average product of labor is defined as the: a. change in output divided by the change in labor input usage b. change in labor input usage divided by the change in output c. output divided by the labor input usage d. labor input usage divided by the output level e. output divided by the marginal product of labor ____ 3. The average product of labor can be illustrated geometrically as the: a. slope of the total product curve with respect to labor b. slope of the total product curve with respect to capital c. slope of a chord from the origin out to the total product curve at the specified level of labor d. inverse of the slope of a chord from the origin out to the total product curve at the specified level of labor e. slope of the total product curve with respect to labor divided by the slope of the total product curve with respect to capital ____ 4. In the table below, the average product of labor at L = 3 is: a. 5 b. 8 c. 0.2 d. 2 e. 3 ____ 5. In the table below, the marginal product of labor at L = 4 is: 13 a. 7 b. 11 c. 17 d. 16 e. 6 ____ 6. Whenever marginal product is positive and declining with increasing use of an input: a. total product is declining as input use increases b. average product is declining as input use increases c. marginal product is greater than average product d. marginal product is less than average product e. total product is increasing at a decreasing rate as input use increases ____ 7. Whenever average product is declining with increases in input usage: a. marginal product is less than average product b. total product is declining with increases in input c. total product is increasing with increases in input d. marginal product is greater than average product e. total product is at a maximum ____ 8. The optimal combination of two inputs, K and L, can be characterized by: a. PKMPK = PLMPL b. MPK = MPL c. PLMPK = PKMPL d. MPK /MPL = PL /PK e. none of the above ____ 9. Output is produced according to Q = 4LK, where L is the quantity of labor input and K is the quantity of capital input. If the price of K is $10 and the price of L is $5, then the cost minimizing combination of K and L capable of producing 32 units of output is: a. L = 8 and K = 1 b. L = 4 and K = 2 c. L = 2 and K = 2 d. L = 2 and K = 4 e. L = 1 and K = 8 14 ____ 10. Happiness can be produced with wine and roses according to Q = W1/2R1/4, where W is bottles of wine and R is bouquets of roses obtained per month. If wine costs $20 per bottle and roses cost $60 per dozen, the happiness-maximizing combination of wine and roses costing $360 in total is: a. W = 18 bottles, R = 0 bouquets b. W = 15 bottles, R = 1 bouquets c. W = 12 bottles, R = 2 bouquets d. W = 9 bottles, R = 3 bouquets e. W = 6 bottles, R = 4 bouquets ____ 11. If labor is on the vertical axis and capital is on the horizontal axis, the slope of an isocost line is given by: a. -PL /PK b. -PK /PL c. -PKPL d. -MPL /MPK e. -MPK /MPL ____ 12. Increasing returns to scale: a. occur only where marginal returns are increasing b. cannot occur if all inputs have diminishing returns c. imply imperfect capital market returns d. result from just-in-time production e. are consistent with diminishing marginal returns by all inputs ____ 13. If output is produced according to Q = (KL)3/4, then this production process exhibits: a. increasing returns to scale b. decreasing returns to scale c. first increasing and then decreasing returns to scale d. constant returns to scale e. first decreasing and then increasing returns to scale ____ 14. Output elasticity can be defined as the: a. percentage change in output divided by the (equal) percentage change in all inputs b. change in output divided by the change in all inputs c. change in inputs divided by the change in output d. change in output divided by the change in one input e. percentage change in output divided by the (average) percentage change in all inputs ____ 15. Hedge Fun is a landscaping firm that specializes in topiary. Last year, the firm had 60 employees and served 120 customers. This year, it had 70 employees and served 140 customers. What is the marginal product of labor? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 e. none of the above 15 ch4 Answer Section [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 16 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 06, 2022
Number of pages
16
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 06, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
73