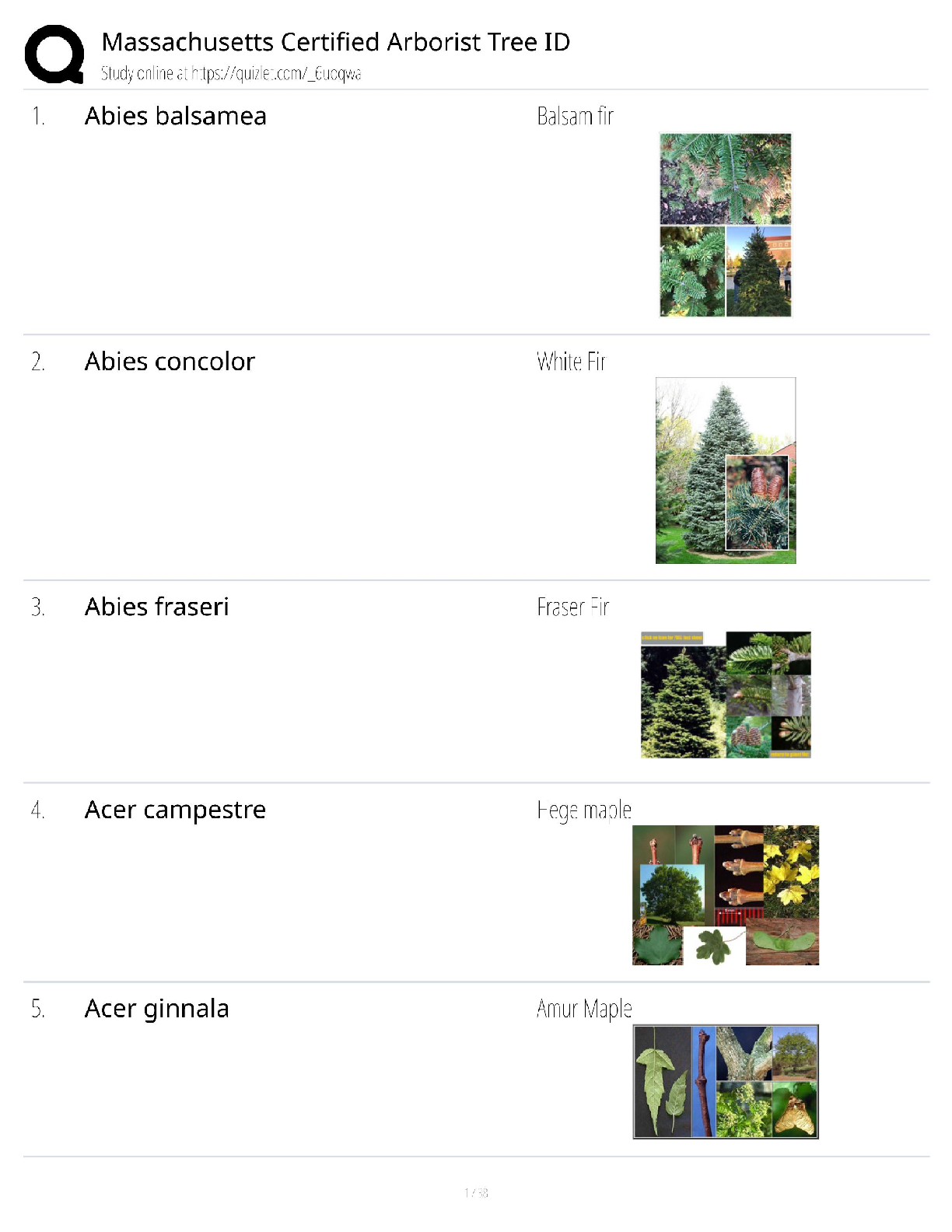
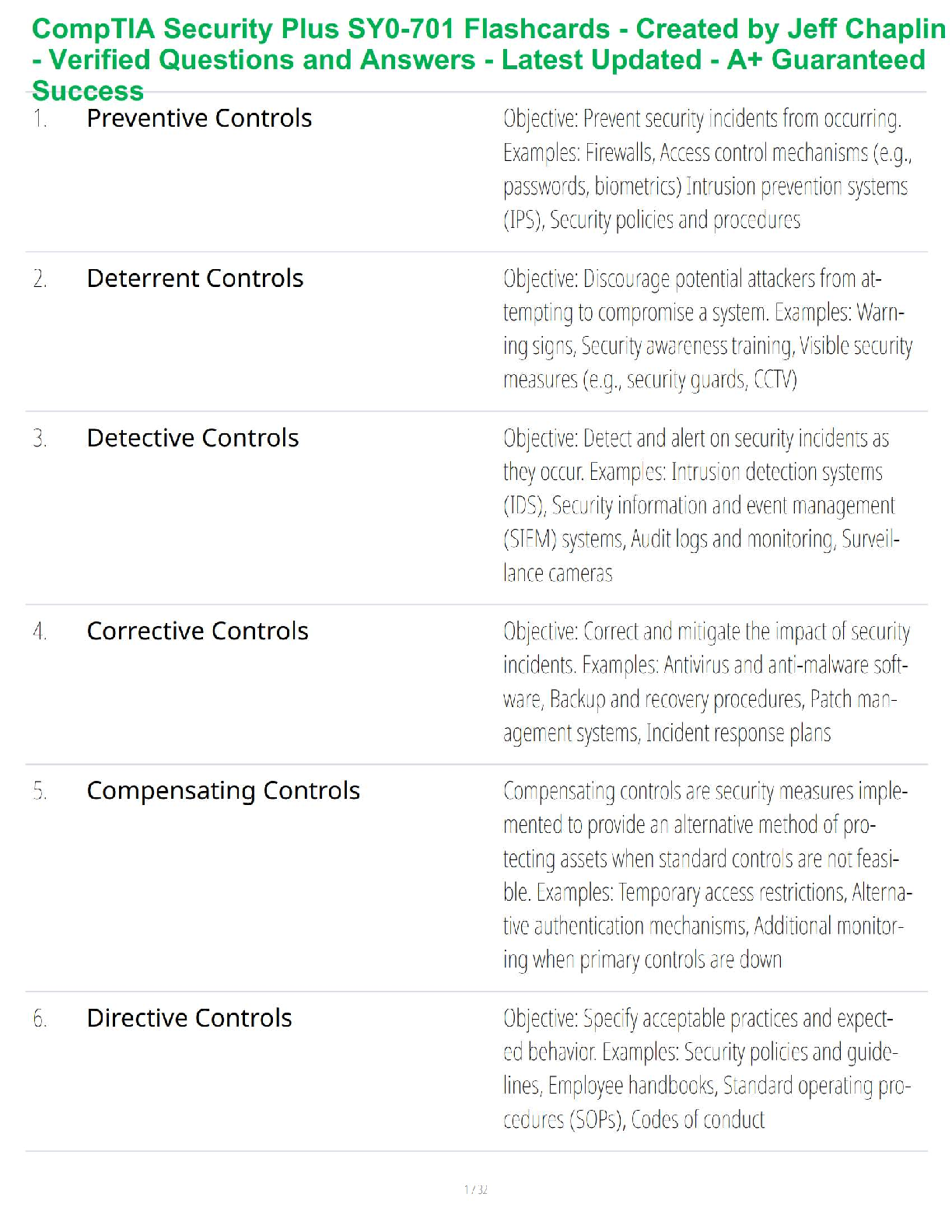
Scribe America Final Exam Study Guide
Latest 2022 Graded A+
What does ROS stand for? ✔✔Review of symptoms, head to toe checklist of symptoms
The HPI and ROS are considered what type of information? ✔✔Subjective
The p
...
Scribe America Final Exam Study Guide
Latest 2022 Graded A+
What does ROS stand for? ✔✔Review of symptoms, head to toe checklist of symptoms
The HPI and ROS are considered what type of information? ✔✔Subjective
The physical exam is what type of information? ✔✔Objective
If a physician told you a patients abdomen was nontender or the patients skin was plale, where
would you document this information ✔✔Physical Exam (PE)
What section focuses directly on the chief complaint? ✔✔HPI (History of present illness)
What are the 5 vital signs? ✔✔1. Heart rate (HR)
2. Respiratory rate (RR)
3. Blood pressure (BP)
4. Temperature (T)
5. Oxygen Saturation (SpO2)
Surgical Hx example ✔✔CABG (Coronary artery bypass graft)
Social Hx example ✔✔Smoker 1 ppd
Family Hx example ✔✔Brother diagnosed with CAD < 55 y/o
Removal of appendix ✔✔Appendectomy
Removal of gallbladder ✔✔Cholecystectomy
Removal of uterus ✔✔Hysterectomy
Removal of tonsils ✔✔Tonsillectomy
What are the 2 types of heart attacks and how are they diagnosed? ✔✔STEMI - EKG
Non-STEMI - Troponin
What are 3 cardiac risk factors? ✔✔HTN, HLD, Smoking, CAD, DM, FHx CAD < 55 y/o
Chest pain, dyspnea, cough and fever correlated to which DDx?
What study would be ordered? ✔✔PNA (Pneumonia)
CXR
What are 3 symptoms a patient with an Ischemic CVA would present with? ✔✔Unilateral
weakness/numbness, slurred speech, vision changes
What heart rhythm would a physician hear if the patient were in atrial fibrillation and how is the
disease diagnosed? ✔✔Irregularly irregular rhythm (A-Fib)
EKG
Name 2 risk factors to hemorrhagic CVA ✔✔Head Trauma, anticoagulants (blood thinner
medication), uncontrolled HTN
How is AMS different from a focal neurological deficit?
What is the major cause of AMS in the elderly? ✔✔AMS (confusion, lethargy,
unresponsiveness) affects the whole brain (drugs, EtOH) and FND (one sided
weakness/numbness, speech changes, vision changes) affects a small portion/localized of the
brain
AMS in elderly - UTI
Layman's term for GERD ✔✔Heartburn, Indigestion, Acid Reflux
Most common cause for seizures in children? ✔✔Fever
Which drug causes smooth muscle relaxation, causing vasodilation and increase blood supply to
heart muscle? ✔✔NTG (Nitroglycerin)
Describe the significance of an HPI ✔✔Explains patients CC and answers "Why did the patient
seek treatment?"
CC of a headache, name 5 elements of the HPI and provide an applicable example of each
element ✔✔Onset - 3 weeks ago
Timing - intermittent
Quality - pressure
Severity - 9/10
location - frontal/forehead
Modifying factors - worse with light, better after Excedrin
Context - does not take a blood thinner, no recent head injuries, Hx of similar HA
True or False:
Patients entire ED visit is based on their answers to the questions asked during the interview?
✔✔True
True or False:
Accurate chronology is not important in an HPI ✔✔False
What is the main different between HPI and ROS? ✔✔HPI - story of the CC
ROS - head-to-toe checklist of subjective Sx
True or False:
Symptoms listed in ROS can contradict the Sx discussed in the HPI ✔✔False
How would you document GPA for a patient who is currently pregnant, has been pregnant 4 time
in the past, and has one child at home? ✔✔G - 5
P - 1
A - 3
List 5 body systems found in the ROS and provide 2 symptoms for each system. ✔✔Skin -
Rashes, itching, redness
General - fever, chills, weight loss
Cardio - Chest pain,Palpitations
Pulmonary - shortness of breath, dyspnea, cough, wheezing
GI - abdominal pain, acid reflux
Neuro - headache, seizures, uni
[Show More]
.png)

.png)












.png)