NURS 6630 - WEEK 11 FINAL EXAM
User
Course NURS-6630N-11,Approaches to Treatment.2020 Spring Qtr 02/24-05/17-PT27
Test Week 11 Final Exam
Started 5/9/20 9:48 PM
Submitted 5/9/20 11:34 PM
Due Date 5/11/20 1:59 AM
...
NURS 6630 - WEEK 11 FINAL EXAM
User
Course NURS-6630N-11,Approaches to Treatment.2020 Spring Qtr 02/24-05/17-PT27
Test Week 11 Final Exam
Started 5/9/20 9:48 PM
Submitted 5/9/20 11:34 PM
Due Date 5/11/20 1:59 AM
Status Completed
Attempt Score 65 out of 75 points
Time Elapsed 1 hour, 46 minutes out of 2 hours
Results Displayed Submitted Answers
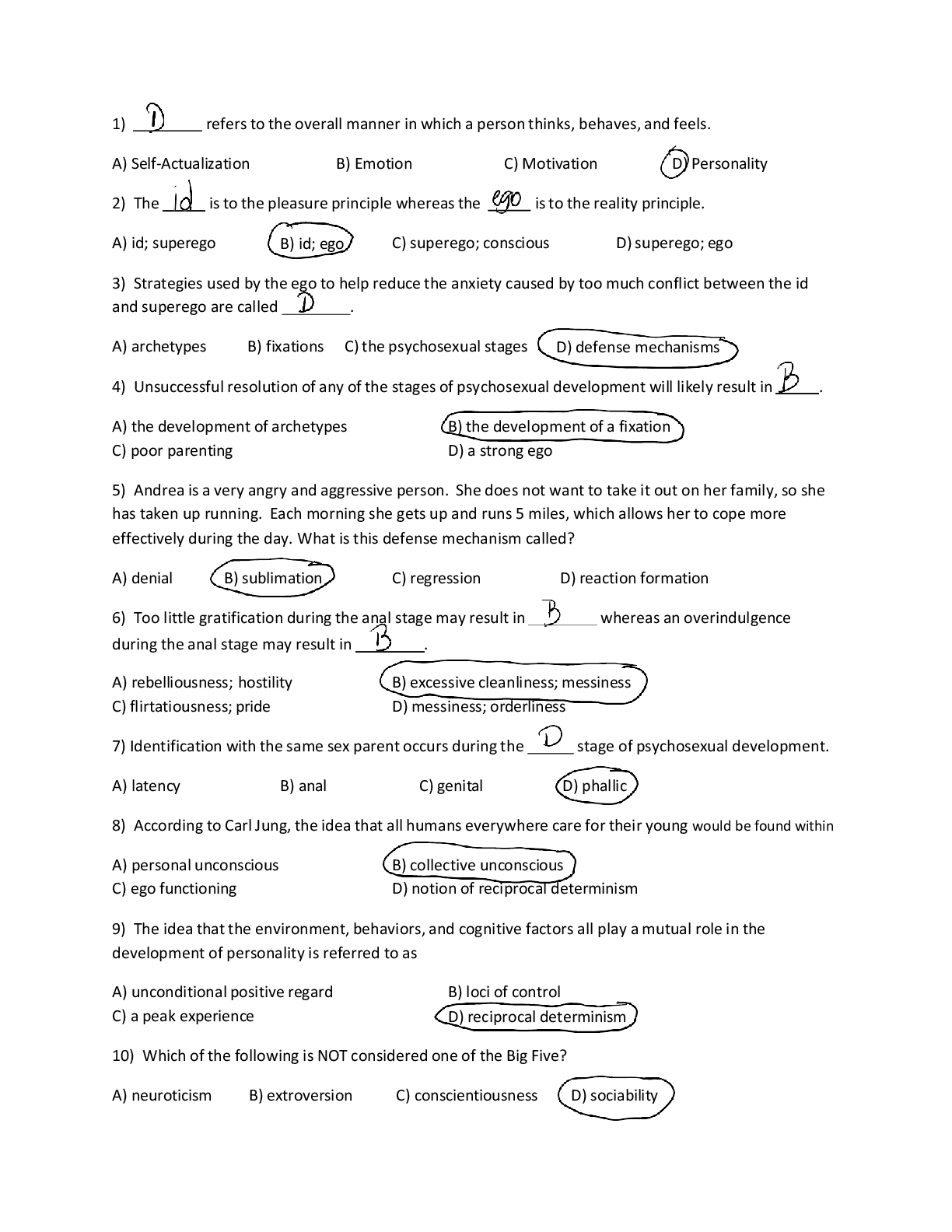
• Question 1
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is discussing dopamine D2 receptor occupancy and its association with aggressive behaviors in patients with the student. Why does the PMHNP prescribe a standard dose of atypical antipsychotics?
• Question 2
1 out of 1 points
A patient is prescribed D-methylphenidate, 10-mg extended-release capsules. What should the PMHNP include when discussing the side effects with the patient?
• Question 3
1 out of 1 points
A patient on chronic opioids is currently on oxycodone ER (OxyContin). The PMHNP is consulted to treat underlying depression. Under which circumstance should the PMHNP order naloxone (NARCAN)?
• Question 4
1 out of 1 points
An adult patient presents with a history of substance-use disorder and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Which of the following treatment options is best for this patient?
• Question 5
0 out of 1 points
Molly is a 52-year-old female that has a diagnosis of fibromyalgia. She complains of fatigue and cognitive difficulties. Which medication is the PMHNP most likely to prescribe?
• Question 6
1 out of 1 points
Methylphenidate, amphetamine, and cocaine are alike because all three _____________________.
• Question 7
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is assessing a female patient who has been taking lamotrigine (Lamictal) for migraine prophylaxis. After discovering that the patient has reached the maximum dose of this medication, the PMHNP decides to change the patient’s medication to zonisamide (Zonegran). In addition to evaluating this patient’s day-to-day activities, what should the PMHNP ensure that this patient understands?
• Question 8
1 out of 1 points
Antihistamines may cause side effects such as blurred vision, constipation, memory problems, and dry mouth. This is due to the _______________ effects of antihistamines.
• Question 9
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP understands that slow-dose extended release stimulants are most appropriate for which patient with ADHD?
• Question 10
1 out of 1 points
A 14-year-old patient is prescribed Strattera and asks when the medicine should be taken. What does the PMHNP understand regarding the drug’s dosing profile?
• Question 11
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is assessing a 49-year-old male with a history of depression, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), alcoholism with malnutrition, diabetes mellitus type 2, and hypertension. His physical assessment is unremarkable with the exception of peripheral edema bilaterally to his lower extremities and a chief complaint of pain with numbness and tingling to each leg 5/10. The PMHNP starts this patient on a low dose of doxepin (Sinequan). What is the next action that must be taken by the PMHNP?
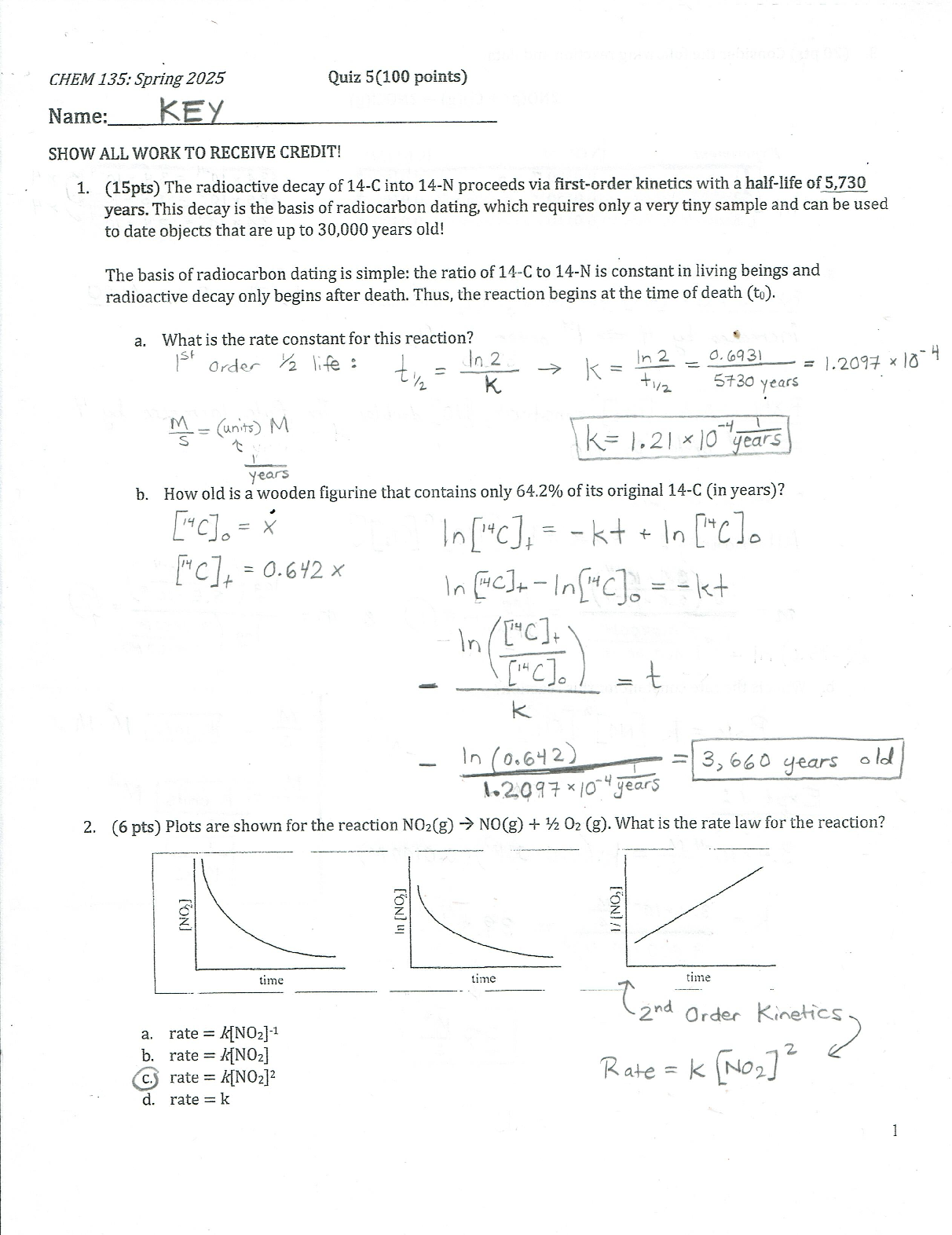
• Question 12
1 out of 1 points
Which statement best describes a pharmacological approach to treating patients for impulsive aggression?
• Question 13
1 out of 1 points
A PMHNP supervisor is discussing with a nursing student how stimulants and noradrenergic agents assist with ADHD symptoms. What is the appropriate response?
• Question 14
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is caring for a patient with chronic insomnia who would benefit from taking hypnotics. The PMHNP wants to prescribe the patient a drug with an ultra-short half-life (1–3 hours). Which drug will the PMHNP prescribe?
• Question 15
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP understands that varenicline (CHANTIX) is an effective way to assist patients with smoking cessation. Why is this medication effective for these patients?
• Question 16
1 out of 1 points
Kevin is an adolescent who has been diagnosed with kleptomania. His parents are interested in seeking pharmacological treatment. What does the PMHNP tell the parents regarding his treatment options?
• Question 17
1 out of 1 points
A 43-year-old male patient is seeking clarification about treating attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in adults and how it differs from treating children, since his son is on medication to treat ADHD. The PMHNP conveys a major difference is which of the following?
• Question 18
1 out of 1 points
A 75-year-old male patient diagnosed with Alzheimer’s disease presents with agitation and aggressive behavior. The PMHNP determines which of the following to be the best treatment option?
• Question 19
1 out of 1 points
Brandon is a non-compliant patient that presents to the clinic asking for help with his alcohol dependence. The PMHNP evaluates the patient and determines a long-acting injection that blocks the mu-receptors would be the best treatment option for Brandon. Which medication should the PMHNP prescribe?
• Question 20
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP has been asked to provide an in-service training to include attention to the use of antipsychotics to treat Alzheimer’s. What does the PMHNP convey to staff?
• Question 21
1 out of 1 points
A patient’s daughter calls your office with concerns that her mother is having significant gastrointestinal side effects. You review the patient’s chart and realize she is having side effects from donepezil (ARICEPT). What is the mechanism of the gastrointestinal disturbances?
• Question 22
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is assessing a patient who has expressed suicidal intent and is now stating that he is hearing voices and sees people chasing him. The PMHNP identifies these symptoms to be associated with which of the following?
• Question 23
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is attempting to treat a patient’s chronic insomnia and wishes to start with an initial prescription that has a half-life of approximately 1–2 hours. What is the most appropriate prescription for the PMHNP to make?
• Question 24
1 out of 1 points
The parents of a 7-year-old patient with ADHD are concerned about the effects of stimulants on their child. The parents prefer to start pharmacological treatment with a non-stimulant. Which medication will the PMHNP will most likely prescribe?
• Question 25
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is caring for a patient who experiences too much overstimulation and anxiety during daytime hours. The patient agrees to a pharmacological treatment but states, “I don’t want to feel sedated or drowsy from the medicine.” Which decision made by the PMHNP demonstrates proper knowledge of this patient’s symptoms and appropriate treatment options?
• Question 26
0 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is treating a patient with depression and fibromyalgia. The PMHNP chooses to prescribe a treatment that may help treat the patient's fibromyalgia and depressive symptoms. Which medication is the PMHNP likely to choose?
• Question 27
0 out of 1 points
Jordan is diagnosed with obsessive compulsive disorder. He has been trialed on several different SSRIs and is currently on high dose sertraline. He reports an inability to carry out responsibilities because of an obsession with handwashing. Which is the best treatment option for Jordan?
• Question 28
1 out of 1 points
A patient with chronic back pain has been prescribed a serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (SNRI). How does the PMHNP describe the action of SNRIs on the inhibition of pain to the patient?
• Question 29
1 out of 1 points
Parents of a 12-year-old boy want to consider attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) medication for their son. Which medication would the PMHNP start?
• Question 30
1 out of 1 points
A patient with irritable bowel syndrome reports chronic stomach pain. The PMHNP wants to prescribe the patient an agent that will cause irrelevant nociceptive inputs from the pain to be ignored and no longer perceived as painful. Which drug will the PMHNP prescribe?
• Question 31
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is evaluating a 30-year-old female patient who states that she notices pain and a drastic change in mood before the start of her menstrual cycle. The patient states that she has tried diet and lifestyle changes but nothing has worked. What will the PMHNP most likely do?
• Question 32
1 out of 1 points
Mr. Peterson is meeting with the PMHNP to discuss healthier dietary habits. With a BMI of 33, Mr. Peterson is obese and needs to modify his food intake. “Sometimes I think I’m addicted to food the way some people are addicted to drugs,” he says. Which statement best describes the neurobiological parallels between food and drug addiction?
• Question 33
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP prescribes an obese patient phentermine (Adipex-p)/topiramate ER (Topamax) (Qsymia), Why is topiramate (Topamax) often prescribed with phentermine (Adipex-P)?
• Question 34
1 out of 1 points
Alcohol enhances inhibition at ____________ synapses and reduces excitation at ______________ synapses.
• Question 35
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP wants to use a symptom-based approach to treating a patient with fibromyalgia. How does the PMHNP go about treating this patient?
• Question 36
1 out of 1 points
Daniel is a 33 year old patient with ADHD and multiple comorbidities: mood disorder, alcohol abuse, ADHD, and nicotine dependence. Which comorbidity should be treated first?
• Question 37
1 out of 1 points
A 63-year-old patient presents with the following symptoms. The PMHNP determines which set of symptoms warrant prescribing a medication? Select the answer that is matched with an appropriate treatment.
• Question 38
0 out of 1 points
The PMHNP evaluates a patient presenting with symptoms of dementia. Before the PMHNP considers treatment options, the patient must be assessed for other possible causes of dementia. Which of the following answers addresses both possible other causes of dementia and a rational treatment option for Dementia?
• Question 39
1 out of 1 points
A young patient is prescribed Vyvanse. During the follow-up appointment, which comment made by the patient makes the PMHNP think that the dosing is being done incorrectly?
• Question 40
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP wants to prescribe Mr. Barber a mood stabilizer that will target aggressive and impulsive symptoms by decreasing dopaminergic neurotransmission. Which mood stabilizer will the PMHNP select?
• Question 41
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is attempting to treat a patient’s chronic pain by having the agent bind the open channel conformation of VSCCs to block those channels with a “use-dependent” form of inhibition. Which agent will the PMHNP most likely select?
• Question 42
1 out of 1 points
An opioid-naive patient is taking MS Contin (morphine sulfate) to treat his pain that is secondary to cancer. Under what circumstances would the PMHNP order naloxone (Narcan) IM/SQ?
• Question 43
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is caring for a patient with chronic insomnia who is worried about pharmacological treatment because the patient does not want to experience dependence. Which pharmacological treatment approach will the PMHNP likely select for this patient for a limited duration, while searching and correcting the underlying pathology associated with the insomnia?
• Question 44
1 out of 1 points
Naltrexone (Revia), an opioid antagonist, is a medication that is used for which of the following conditions?
• Question 45
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP prescribes gabapentin (Neurontin) for a patient’s chronic pain. How does the PMHNP anticipate the drug to work?
• Question 46
1 out of 1 points
A nursing students asks the PMHNP the difference between impulsivity and compulsivity. Which of the following responses is correct?
• Question 47
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP understands that bupropion (Wellbutrin) is an effective way to assist patients with smoking cessation. Why is this medication effective for these patients?
• Question 48
0 out of 1 points
All drugs that lead to addiction increase __________________in the ventral striatum, which is also called the _______________.
• Question 49
1 out of 1 points
A patient with a new diagnosis of diabetic peripheral neuropathy is switched from sertraline (ZOLOFT) to duloxetine (CYMBALTA). The patient asks why they are switching treatment. What is the best response?
• Question 50
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is teaching a patient with a sleep disorder about taking diphenhydramine (Benadryl). The patient is concerned about the side effects of the drug. What can the PMHNP teach the patient about this treatment approach?
• Question 51
1 out of 1 points
A patient is being prescribed bupropion and is concerned about the side effects. What will the PMHNP tell the patient regarding bupropion?
• Question 52
1 out of 1 points
An 8-year-old patient presents with severe hyperactivity, described as “ants in his pants.” Based on self-report from the patient, his parents, and his teacher; attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is suspected. What medication is the PMNHP most likely to prescribe?
• Question 53
1 out of 1 points
Which medication is an irreversible inhibitor of aldehyde dehydrogenase that creates a negative and aversive response following ingestion of alcohol?
• Question 54
1 out of 1 points
Which of these characteristics does NOT meet the criteria for probably Alzheimer's dementia?
• Question 55
1 out of 1 points
Which of the following anticonvulsants increases serotonergic neurotransmission and GABAergic transmission, while decreasing glutamatergic neurotransmission?
• Question 56
1 out of 1 points
A 26-year-old female patient with nicotine dependence and a history of anxiety presents with symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Based on the assessment, what does the PMHNP consider?
• Question 57
1 out of 1 points
What will the PMHNP most likely prescribe to a patient with psychotic aggression who needs to manage the top-down cortical control and the excessive drive from striatal hyperactivity?
• Question 58
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is assessing a patient who will be receiving phentermine (Adipex-P)/topiramate (Topamax) (Qsymia). Which of the following conditions/diseases will require further evaluation before this medication can be prescribed?
• Question 59
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is caring for a patient with fibromyalgia. Which second-line treatment does the PMHNP select that may be effective for managing this patient’s pain?
• Question 60
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is selecting a medication treatment option for a patient who is exhibiting psychotic behaviors with poor impulse control and aggression. Of the available treatments, which can help temper some of the adverse effects or symptoms that are normally caused by D2 antagonism?
• Question 61
1 out of 1 points
An elderly woman with a history of Alzheimer’s disease, coronary artery disease, and myocardial infarction had a fall at home 3 months ago that resulted in her receiving an open reduction internal fixation. While assessing this patient, the PMHNP is made aware that the patient continues to experience mild to moderate pain. What is the PMHNP most likely to do?
• Question 62
1 out of 1 points
A patient calls the clinic to ask about an over-the-counter sleep aid. What is the best response?
• Question 63
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is caring for a patient on risperidone (Risperdal). Which action made by the PMHNP exhibits proper care for this patient?
• Question 64
0 out of 1 points
A patient you have been evaluating was admitted to the hospital with some abnormal lab work. Hematology/oncology was consulted and diagnoses the patient with aplastic anemia and agranulocytosis. Which medication was likely the culprit?
• Question 65
1 out of 1 points
An 18-year-old female with a history of frequent headaches and a mood disorder is prescribed topiramate (Topamax), 25 mg by mouth daily. The PMHNP understands that this medication is effective in treating which condition(s) in this patient?
• Question 66
0 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is assessing a patient who presents with elevated levels of brain amyloid as noted by positron emission tomography (PET). What other factors will the PMHNP consider before prescribing medication for this patient, and what medication would the PMHNP want to avoid given these other factors?
• Question 67
1 out of 1 points
An 80-year-old female patient diagnosed with Stage II Alzheimer’s has a history of irritable bowel syndrome. Which cholinergic drug may be the best choice for treatment given the patient’s gastrointestinal problems?
• Question 68
1 out of 1 points
The novel neurotransmitter adenosine is responsible for the sleep-wake cycle by increasing throughout the day and diminishing during night. Which of the follow is an antagonist of adenosine?
• Question 69
1 out of 1 points
A patient with hypersexual disorder is being assessed for possible pharmacologic treatment. Why does the PMHNP prescribe an antiandrogen for this patient?
• Question 70
1 out of 1 points
The PMHNP is providing a workshop for pediatric nurses, and a question is posed about noradrenergic agents to treat ADHD. Which of the following noradrenergic agents have norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NRI) properties that can treat ADHD?
• Question 71
0 out of 1 points
The parents of a 10 year old girl diagnosed with ADHD ask if the PMHNP can prescribe something to help their daughter’s ADHD that is not a stimulant. Which of the following responses is correct?
• Question 72
1 out of 1 points
A patient with chronic insomnia asks the PMHNP if they can first try an over-the-counter (OTC) medication before one that needs to be prescribed to help the patient sleep. Which is the best response by the PMHNP?
• Question 73
1 out of 1 points
Antipsychotics are doses at a level that blocks ________% of D2 receptors.
• Question 74
0 out of 1 points
Sandra complains of constipation after being on quetiapine (SEROQUEL) for several weeks. Constipation is likely caused by the binding of quetiapine (SEROQUEL) to which receptor?
• Question 75
0 out of 1 points
A patient presents with psychotic aggression. Which treatment option is best for a patient presenting with psychotic aggression due to impaired top-down cortical control and excessive drive from striatal hyperactivity?
• Question 76
0 out of 0 points
When completing this exam, did you comply with Walden University’s Code of Conduct including the expectations for academic integrity?
[Show More]