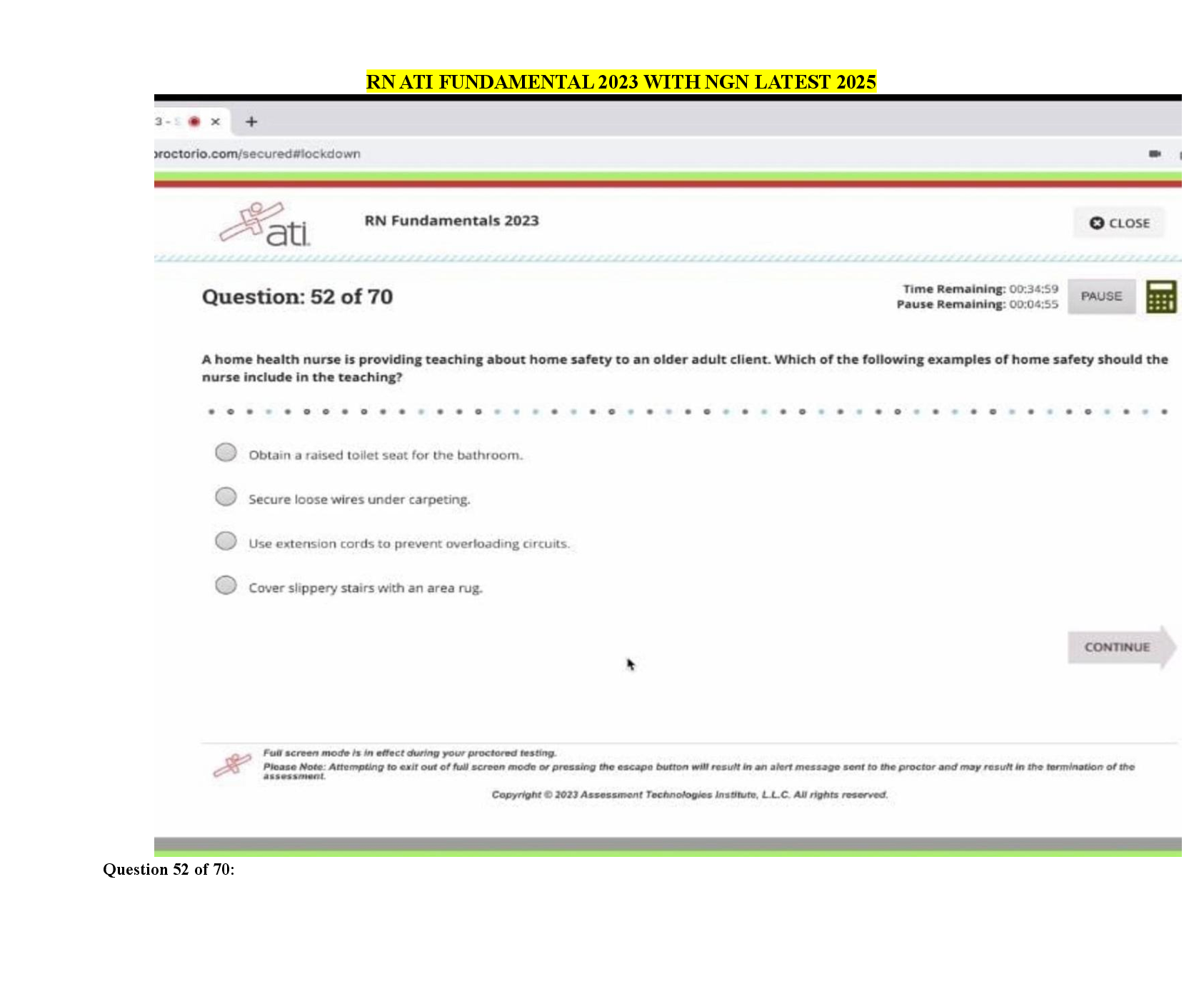
Social Sciences > EXAMs > PMP Exam Questions and Answers 2022 (All)
PMP Exam Questions and Answers 2022
Document Content and Description Below
Earned Value (EV) - ANSWER The measure of work performed expressed in terms of the budget authorized for that work. BAC x % Work Completed Planned Value (PV) - ANSWER The portion of the approved to ... tal cost estimate planned to be spent on an activity during a given period. Planned % Complete x BAC Actual Cost (AC) - ANSWER The realized cost incurred for the work performed on an activity during a specific time period. Budget at Completion (BAC) - ANSWER The sum of all budgets established for the work to be performed. Estimate to Complete (ETC) - ANSWER The expected cost to finish all the remaining project work. EAC - AC Estimate at Completion (EAC) - ANSWER The expected total cost of completing all work expressed as the sum of the actual cost to date and the estimate to complete. BAC / CPI Cost Performance Index (CPI) - ANSWER A measure of the cost efficiency of budgeted resources expressed as the ratio of earned value to actual cost. EV / AC Schedule Performance Index (SPI) - ANSWER A measure of schedule efficiency expressed as the ratio of earned value to planned value. EV / PV To-Complete Performance Index (TCPI) - ANSWER A measure of the cost performance that is required to be achieved with the remaining resources in order to meet a specified management goal, expressed as the ratio of the cost to finish the outstanding work to the remaining budget. (BAC - EV) / (BAC - AC) Cost Variance (CV) - ANSWER EV - AC Negative is over budget; positive is under budget Schedule Variance (SV) - ANSWER EV - PV Negative is behind schedule; positive is ahead of schedule Variance at Completion (VAC) - ANSWER A projection of the amount of budget deficit or surplus, expressed as the difference between the budget at completion and the estimate at completion. BAC - EAC Economic Value Added (EVA) - ANSWER Net operating profit after taxes minus (capital x cost of capital); a measure of the economic value of an investment or project Future Value (FV) - ANSWER the value of future cash flows discounted at the appropriate discount rate FV = PV(1+r)^n Return on Invested Capital (ROIC) - ANSWER Net income after tax / Invested Tax (smaller is better) Order of Magnitude Estimate - ANSWER A high-level estimate of the time and cost of a project based on the actual cost and duration of a similar project. -50% to +100% Conceptual Estimate - ANSWER a cost estimate based on very little design information and using gross unit pricing to determine the project cost. -30% to +50% Preliminary Estimate - ANSWER -20% to +30% estimate range Definitive Estimate - ANSWER -15% to +20% estimate range Control Estimate - ANSWER -10% to +15% estimate range Delphi Technique - ANSWER A decision-making technique in which group members do not meet face-to-face but respond in writing to questions posed by the group leader. Prevents biasing opinions and groupthink. Nominal Group Technique - ANSWER Brainstormed ideas are voted upon and sorted by priority Scope Baseline - ANSWER The approved version of a scope statement, work breakdown structure (WBS), and its associated WBS dictionary, that can be changed only through formal change control procedures and is used as a basis for comparison. Baseline - ANSWER The original plan plus all approved changes (scope, schedule, cost) Functional Organization - ANSWER Departmentalization around specialized activities such as production, marketing, and human resources. Projectized Organization - ANSWER Any organizational structure in which the project manager has full authority to assign priorities, apply resources, and direct the work of persons assigned to the project. Matrix Organization - ANSWER An organization in which specialists from different parts of the organization are brought together to work on specific projects but still remain part of a line-and-staff structure. Strong, Balanced, and Weak, where in strong PM has power. Project Scope Statement - ANSWER The description of the project scope, major deliverables, assumptions, and constraints. Includes product scope description, acceptance criteria and project exclusions. Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) - ANSWER A hierarchical decomposition of the total scope of work to be carried out by the project team to accomplish the project objectives and create the required deliverables. Lead - ANSWER Starting an activity prior to the finish of the preceding activity Lag - ANSWER Delaying the start of an activity after the finish of the preceding activity Analogous/Top-Down Estimating - ANSWER A technique for estimating the duration or cost of an activity or a project using historical data from a similar activity or project. Bottom-Up Estimating - ANSWER A method of estimating project duration or cost by aggregating the estimates of the lower-level components of the work breakdown structure (WBS). Parametric Estimating - ANSWER A cost-estimating technique that uses project characteristics (parameters) in a mathematical model to estimate project costs Three-Point Estimating - ANSWER A technique used to estimate cost or duration by applying an average or weighted average of optimistic, pessimistic, and most likely estimates when there is uncertainty with the individual activity estimates. (Pessimistic + (4xRealistic) + Optimistic) / 6 Standard Deviation Estimate - ANSWER (Pessimistic - Optimistic) / 6 Critical Path - ANSWER The path(s) of schedule activities where the delay of any one activity would delay the project finish; the path of highest risk Float/Slack - ANSWER The amount of time a schedule activity could be delated without impacting the finish date of the project Free Float - ANSWER The amount of time that a schedule activity can be delayed without delaying the early start date of any successor or violating a schedule constraint. Negative Float - ANSWER The situation of a schedule activity's early finish being after a subsequent activity's early start. Critical Path Method (CPM) - ANSWER a project-management tool that illustrates the relationships among all the activities involved in completing a project and identifies the sequence of activities likely to take the longest to complete Critical Chain Method - ANSWER A schedule method that allows the project team to place buffers on any project schedule path to account for limited resources and project uncertainties. Schedule Compression - ANSWER Techniques used to shorten the schedule duration without reducing the project scope (e.g., crashing). Resource Optimization Techniques - ANSWER Smoothing or leveling - adjusting resources to the level of resources available. Load balancing. Monte Carlo Analysis - ANSWER A risk quantification technique that simulates a model's outcome many times to provide a statistical distribution of the calculated results Life Cycle Costing (LCC) - ANSWER Looking at total cost of ownership from purchase (creation) through operations to disposal. Value Engineering - ANSWER An approach used to optimize project life cycle costs, save time, increase profits, improve quality, expand market share, solve problems, and/or use resources more effectively. Cost Baseline - ANSWER The approved version of the time-phased project budget, excluding any management reserves, which can be changed only through formal change control procedures and is used as a basis for comparison to actual results. Funding Limit Reconciliation - ANSWER The process of comparing the planned expenditure of project funds against any limits on the commitment of funds for the project to identify any variances between the funding limits and the planned expenditures. 7 basic quality tools - ANSWER cause and effect diagrams flowcharts checksheets pareto diagrams histograms control charts scatter diagrams probability distribution - ANSWER Control Chart - ANSWER A graphic display of process data over time and against established control limits, which has a centerline that assists in detecting a trend of plotted values toward either control limit. run chart - ANSWER Pareto Diagram - ANSWER A histogram, ordered by frequency of occurrence, that shows how many results were generated by each identified cause. Ishikawa/Fishbone/Why-Why Diagram - ANSWER Helps establish cause-and-effect by identifying factors that contribute to outcomes or problems; the factors are categories as People, Machines, Methods, Measurements, Materials, and Environment and include intentional and unintentional consequences and influence quality performance. Total Quality Management (TQM) - ANSWER a management philosophy that focuses on satisfying customers through empowering employees to be an active part of continuous quality improvement Kaizen - ANSWER continuous improvement Just-in-time (JIT) - ANSWER An inventory-management approach in which supplies arrive just when needed for production or resale ISO 9000 - ANSWER Set of international standards on quality management and quality assurance, critical to international business Six Sigma Quality - ANSWER a quality measure that allows only 3.4 defects per million opportunities Three Sigma Quality - ANSWER 2,700 defects per million opportunities One Sigma Quality - ANSWER 317,000 defects per million opportunities mutually exclusive - ANSWER Events that cannot occur at the same time. Statistical Independence - ANSWER The absence of an association or covariation between two variables standard deviation - ANSWER a measure of variability that describes an average distance of every score from the mean Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs - ANSWER (level 1) Physiological Needs, (level 2) Safety and Security, (level 3) Relationships, Love and Affection, (level 4) Self Esteem, (level 5) Self Actualization. Meeting needs in one category does not motivate unless the lower level needs are already met. Herzberg's Motivation-Hygiene Theory - ANSWER A need theory that distinguishes between motivator needs (related to the nature of the work itself) and hygiene needs (related to the physical and psychological context in which the work is performed) and proposes that motivator needs must be met for motivation and job satisfaction to be high. McGregor's Theory - ANSWER Theory X - the assumption that employees dislike work, are lazy, avoid responsibility, and must be coerced to perform. Theory Y - the assumption that employees are creative, enjoy work, seek responsibility, and can exercise self-direction. Fiedler's Contingency Theory - ANSWER theory stating that leadership effectiveness is dependent on the characteristics of the leader and the characteristics of the situation McClelland's Theory of Needs - ANSWER a theory that states achievement, power, and affiliation are three important needs that help explain motivation Expectancy Theory - ANSWER the theory that people will be motivated to the extent to which they believe that their efforts will lead to good performance, that good performance will be rewarded, and that they will be offered attractive rewards Number of Communication Channels - ANSWER (n(n-1))/2 where n is the number of people involved Constructive Team Roles - ANSWER clarifiers, encouragers, information givers, information seekers, initiators, gate keepers, harmonizers, and summarizers Destructive Team Roles - ANSWER aggressors, blockers, dominators, devil's advocate, recognition seekers, topic jumpers, withdrawers Forms of Power - ANSWER reward expert (best) referent legitimate referent punishment (worst) Methods of Conflict Resolution - ANSWER 1. Avoiding or withdrawing 2. Accommodating or smoothing 3. Forcing the issue or competing 4. Negotiating or compromising 5. Problem solving Origins of Project Conflict - ANSWER Schedule, Priorities, Resources interpersonal skills - ANSWER Leading, Influencing, decision-making*, emotional intelligence* Communication Strategies - ANSWER Interactive, push, pull paralingual communication - ANSWER Vocal but not verbal - tone of voice, volume, pitch Opportunity Strategies - ANSWER Exploit (change something to ensure the opportunity occurs), Share (share with a third party, perhaps via a joint venture), Enhance (increase or decrease the probability and/or impact an alternate plan), Accept (live with it) Threat Strategies - ANSWER Avoid (change something so that the threat no longer exists), Transfer (shift the risk to a third party, perhaps via a contract), Mitigate (increase or decrease the probability and/or impact, an alternate plan), Accept (includes passive and active approaches) Stakeholder Analysis Grid - ANSWER Influence vs. Interest Firm-Fixed-Price Contract (FFP) - ANSWER A type of fixed price contract where the buyer pays the seller a set amount (as defined by the contract), regardless of the seller's costs. Fixed Price Incentive Fee Contract (FPIF) - ANSWER A type of contract where the buyer pays the seller a set amount (as defined by the contract), and the seller can earn an additional amount if the seller meets defined performance criteria. Cost Plus Fixed Fee Contract (CPFF) - ANSWER A type of cost-reimbursable contract where the buyer reimburses the seller for the seller's allowable costs (allowable costs are defined by the contract) plus a fixed amount of profit (fee). Cost Plus Incentive Fee Contract (CPIF) - ANSWER A type of cost-reimbursable contract where the buyer reimburses the seller for the seller's allowable costs (allowable costs are defined by the contract), and the seller earns its profit if it meets defined performance criteria. Time and Material Contract (T&M) - ANSWER a type of contract that is a hybrid arrangement containing aspects of both cost-reimbursable and fixed-price contracts. resemble cost-reimbursable type arrangements in that they have no definitive end, because the full value of the arrangement is not defined at the time of the award. thus these contracts can grow in contract value as if they were cost-reimbursable type arrangements. conversely, these arrangements can also resemble fixed-price arrangements. for example, the unit rates are preset by the buyer and seller, when both parties agree on the rates for the category of senior engineers Point of Total Assumption (PTA) - ANSWER ((Ceiling Price - Target Price)/Buyer's Share Ratio) + Target Cost The cost at which the contractor assumes total responsibility for each additional dollar of contract cost in a fixed price incentive fee contract Develop Project Charter - ANSWER Knowledge Area: Initiating Process Group: Integration Inputs: Business Documents, Agreements, EEF, OPA T&T: Expert Judgment, Data Gathering, Interpersonal/team skills, meetings Outputs: Project Charter, Assumption Log Identify Stakeholders - ANSWER Knowledge Area: Initiating Process Group: Stakeholder Inputs: Charter, business documents, PM Plan, Project documents, Agreements, EEF/OPA T&T: Expert Judgment, Data gathering, data analysis, Data representation, meetings Outputs: Stakeholder register, change requests, PM Plan updates, project documents updates Plan Scope Management - ANSWER Knowledge Area: Planning Process Group: Scope Inputs: Project charter, PM Plan, EEF/OPA T&T: Expert judgment, data analysis, meetings Outputs: Scope management plan, requirements management plan Collect Requirements - ANSWER Knowledge Area: Scope Process Group: Planning Inputs: Charter, PM plan, project/business documents, agreements, EEF/OPA T&T: Expert judgment, data gathering, data analysis, decision making, data representation, interpersonal team skills, context diagram, prototypes Outputs: requirements documentation, requirements traceability matrix Define Scope - ANSWER Knowledge Area: Planning Process Group: Scope Inputs: Project Charter, PM Plan, project documents, EEF/OPA T&T: Expert judgment, data analysis, decision making, interpersonal and team skills, product analysis Outputs: project scope statement, project documents updates Create WBS - ANSWER Knowledge Area: Planning Process Group: Scope Inputs: PM Plan, project documents, EEF/OPA T&T: Expert judgment, Decomposition Outputs: scope baseline, project documents updates [Show More]
Last updated: 3 years ago
Preview 1 out of 38 pages

Buy this document to get the full access instantly
Instant Download Access after purchase
Buy NowInstant download
We Accept:

Reviews( 0 )
$9.00
Can't find what you want? Try our AI powered Search
Document information
Connected school, study & course
About the document
Uploaded On
Aug 14, 2022
Number of pages
38
Written in
All
Additional information
This document has been written for:
Uploaded
Aug 14, 2022
Downloads
0
Views
37