Information Security and Assurance -
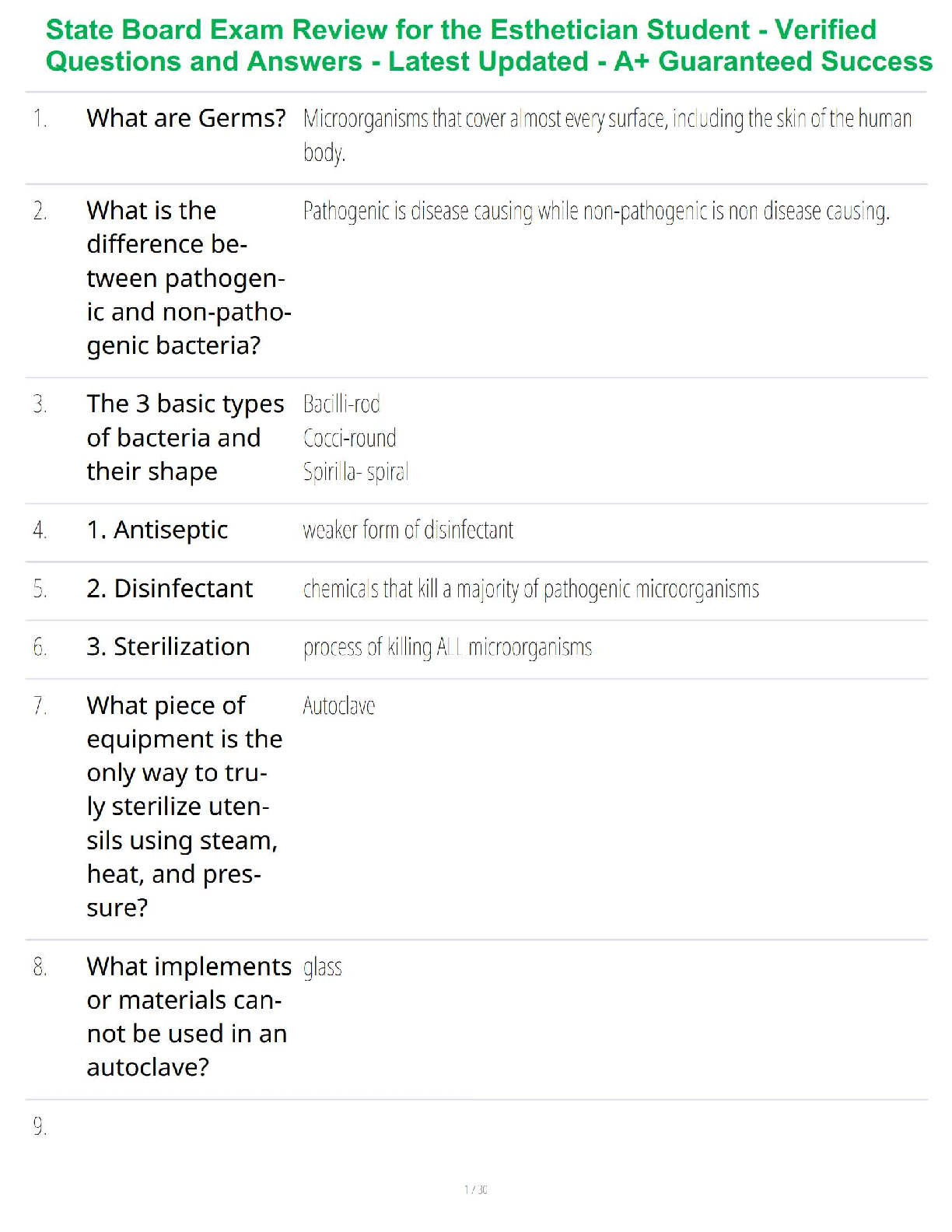
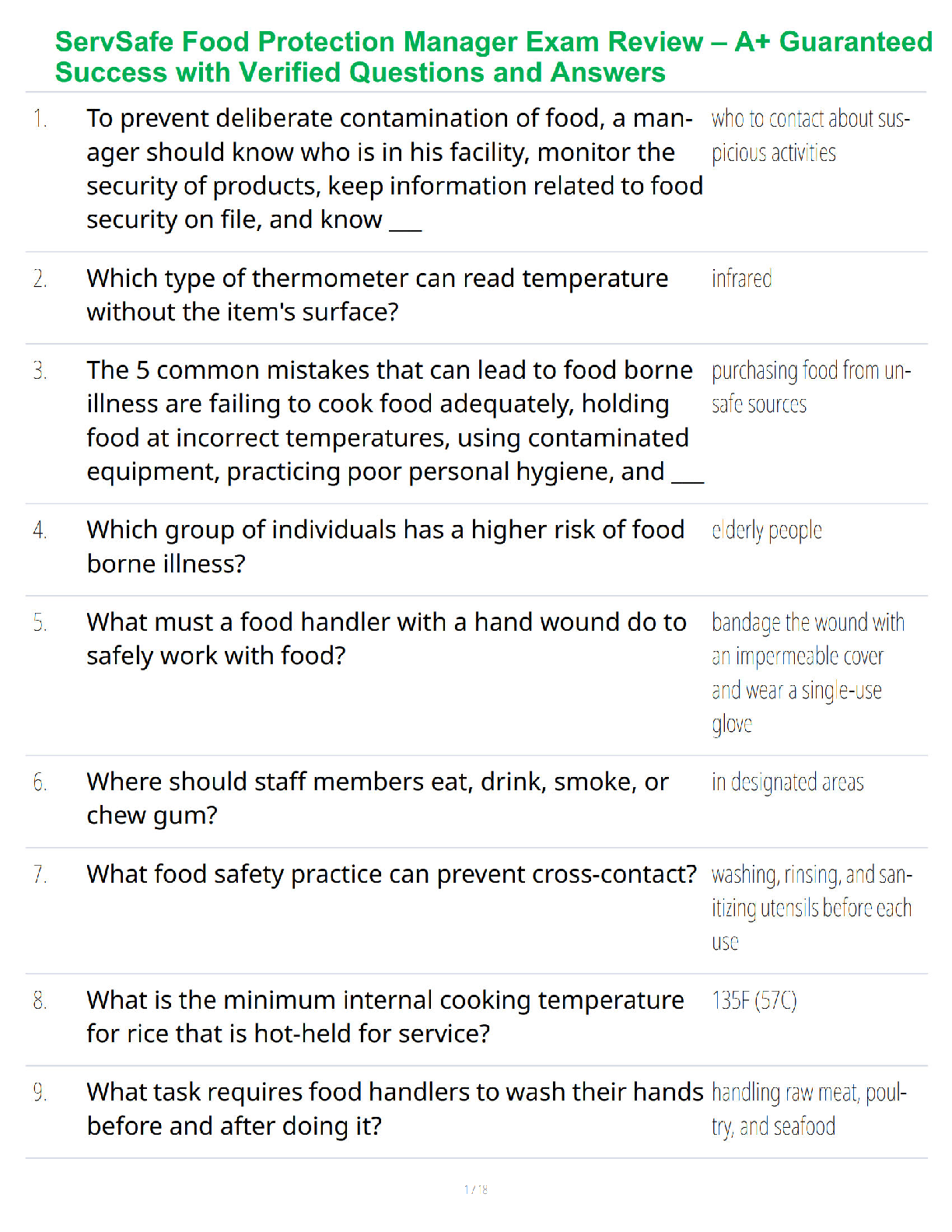
C725
People - - ✔✔Information security is primarily a discipline to manage the behavior of
_____.
A. Technology
B. People
C. Processes
D. Organizations
All of these - - ✔✔Care
...
Information Security and Assurance -
C725
People - - ✔✔Information security is primarily a discipline to manage the behavior of
_____.
A. Technology
B. People
C. Processes
D. Organizations
All of these - - ✔✔Careers in information security are booming because of which of the
following factors?
A. Threats of cyberterrorism
B. Government regulations
C. Growth of the Internet
D. All of these
Security policies and procedures
Explanation: Answer A is correct.
The Carnegie Melon Information Network Institute (INI) designed programs to carry out
multiple tasks including Information Security Policies. - - ✔✔A program for information
security should include which of the following elements?
A. Security policies and procedures
B. Intentional attacks only
C. Unintentional attacks only
D. None of these
D. All of these - - ✔✔The growing demand for InfoSec specialists is occurring
predominantly in which of the following types of organizations?
A. Government
B. Corporations
C. Not-for-profit foundations
D. All of these
Confidentiality - - ✔✔The concept of the measures used to ensure the protection of the
secrecy of data, objects, or resources.
B-Rate Safe Rating - - ✔✔A catchall safe rating for any box with a lock on it. This rating
describes the thickness of the steel used to make the lockbox. No actual testing is
performed to gain this rating.
C-Rate Safe Rating - - ✔✔This safe rating is defined as a variably thick steel box with a
1-inch-thick door and a lock. No tests are conducted to provide this rating, either.
UL TL-15 Safe Rating - - ✔✔Safes with an Underwriters Laboratory rating that have
passed standardized tests as defined in Underwriters Laboratory Standard 687 using
tools and an expert group of safe-testing engineers. The safe rating label requires that
the safe be constructed of 1-inch solid steel or equivalent. The label means that the safe
has been tested for a net working time of 15 minutes using "common hand tools, drills,
punches hammers, and pressure applying devices." Net working time means that when
the tool comes off the safe, the clock stops. Engineers exercise more than 50 different
types of attacks that have proven effective for safecracking.
UL TL-30 Safe Rating - - ✔✔This Underwriters Laboratory rating testing is essentially
the same as the TL-15 testing, except for the net working time. Testers get 30 minutes
and a few more tools to help them gain access. Testing engineers usually have a safe's
manufacturing blueprints and can disassemble the safe before the test begins to see
how it works.
B. Disclosure
Explanation:
Confidentiality models are primarily intended to ensure that no unauthorized access to
information is permitted and that accidental disclosure of sensitive information is not
possible. - - ✔✔Related to information security, confidentiality is the opposite of which
of the following?
A. Closure
B. Disclosure
C. Disaster
D. Disposal
D. All of these
Explanation:
Integrity models keep data pure and trustworthy by protecting system data from
intentional or accidental changes. - - ✔✔Integrity models have which of the three goals:
A. Prevent unauthorized users from making modifications to data or programs
B. Prevent authorized users from making improper or unauthorized modifications
C. Maintain internal and external consistency of data and programs
D. All of these
D. All of these
Explanation:
Availability models keep data and resources available for authorized use, especially
during emergencies or disasters. - - ✔✔Information security professionals usually
address which of these three common challenges to availability:
A. Denial of service (DoS) due to intentional attacks or because of undiscovered flaws
in implementation (for example, a program written by a programmer who is unaware of
a flaw that could crash the program if a certain unexpected input is encountered)
B. Loss of information system capabilities because of natural disasters (fires, floods,
storms, or earthquakes) or human actions (bombs or strikes)
C. Equipment failures during normal use.
D. All of these
A. Confidentiality, integrity, and availability
Explanation:
These goals form the confidentiality, integrity, availability (CIA) triad, the basis of all
security programs. - - ✔✔Which of the following represents the three goals of
information security?
A. Confidentiality, integrity, and availability
B. Prevention, detection, and response
C. People controls, process controls, and technology controls
D. Network security, PC security, and mainframe security
business case
Explanation:
A business case is often made to justify the start of a new project, especially a project
related to security. - - ✔✔Usually a documented argument or stated position in order to
define a need to make a decision or take some form of action.
top-down approach - - ✔✔A type of security management planning where upper, or
senior, management is responsible for initiating and defining policies for the
organization.
bottom-up approach - - ✔✔A type of security management planning where IT staff
makes security decisions directly without input from senior management. This approach
is rarely used in organizations and is considered problematic in the IT industry.
Strategic Plan - - ✔✔This security plan is a long-term plan that is fairly stable. It defines
the organization's security purpose. It also helps to understand security function and
align it to the goals, mission, and objectives of the organization. It's useful for about five
years if it is maintained and updated annually. This plan also serves as the planning
horizon. Long-term goals and visions for the future are discussed this plan. This
plan should include a risk assessment.
Tactical Plan - - ✔✔This security plan is a midterm plan developed to provide more
details on accomplishing the goals set forth in the strategic plan or can be crafted ad
hoc based upon unpredicted events. This plan is typically useful for about a year and
often prescribes and schedules the tasks necessary to accomplish organizational goals.
Some examples of these plans are project plans, acquisition plans, hiring plans, budget
plans, maintenance plans, support plans, and system development plans.
Operational Plan - - ✔✔This security plan is a short-term, highly detailed plan based on
the strategic and tactical plans. It is valid or useful only for a short time. These plans
must be updated often (such as monthly or quarterly) to retain compliance with tactical
plans. These plans spell out how to accomplish the various goals of the organization.
They include resource allotments, budgetary requirements, staffing assignments,
scheduling, and step-by-step or implementation procedures. These plans include details
on how the implementation processes are in compliance with the organization's security
policy. Examples of these plans are training plans, system deployment plans, and
product design plans.
Data classification - - ✔✔Also called classification, the primary means by which data is
protected based on its need for secrecy, sensitivity, or confidentiality. It is the process of
organizing items, objects, subjects, and so on into groups, categories, or collections
with similarities.
Five levels of government/military classification - - ✔✔Top secret, Secret, Confidential,
Sensitive but unclassified, Unclassified.
Top Secret - - ✔✔The highest level of government/military data classification. The
unauthorized disclosure of top-secret data will have drastic effects and cause grave
damage to national security. This data is compartmentalized on a need-to-know basis
such that a user could have this clearance and have access to no data until the user
has a need to know.
Secret - - ✔✔This level of government/military data classification is used for data of a
restricted nature. The unauthorized disclosure of data classified as secret will have
significant effects and cause critical damage to national security.
Confidential - - ✔✔This level of government/military data classification is used for data
of a sensitive, proprietary, or highly valuable nature. The unauthorized disclosure of
data with this classification level will have noticeable effects and cause serious damage
to national security. This classification is used for all data between secret and sensitive
but unclassified classifications.
Sensitive But Unclassified (SBU) - - ✔✔This level of government/military data
classification is used for data that is for internal use or for office use only (FOUO). Often
this data classification is used to protect information that could violate the privacy rights
of individuals. This is not technically a classification label; instead, it is a marking or
label used to indicate use or management.
Unclassified - - ✔✔This level of government/military data classification is used for data
that is neither sensitive nor classified. The disclosure of this type of data does not
compromise confidentiality or cause any noticeable damage. This is not technically a
classification label; instead, it is a marking or label used to indicate use or management.
U.S. Can Stop Terrorism.
Top Secret
Secret
Confidential
Sensitive But unclassified
Unclassified - - ✔✔The easy way to remember the names of the five levels of the
government or military data classification scheme,
Four common or possible business classification levels - - ✔✔Confidential
Private
Sensitive
Public
[Show More]
.png)