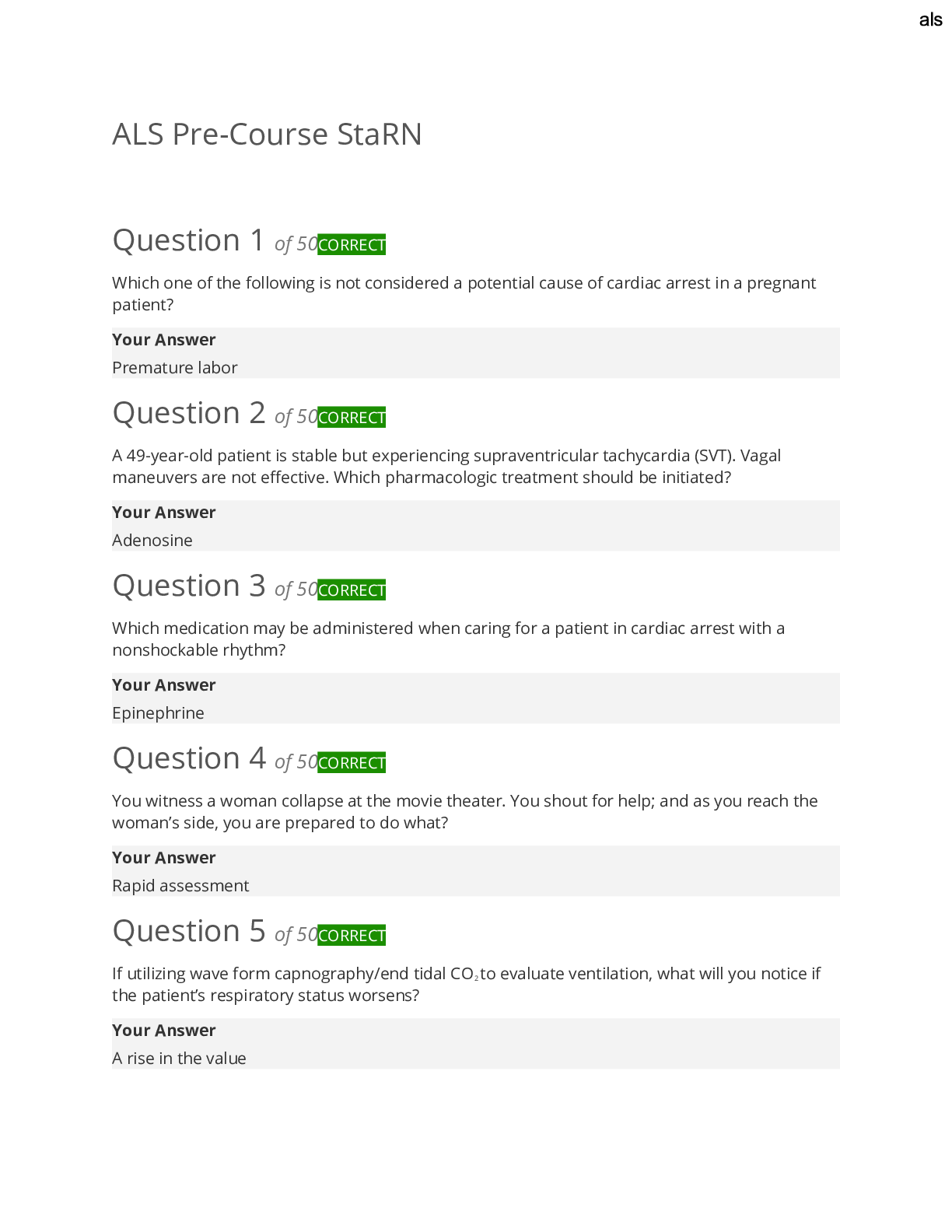
Key Competencies for Comp Professionals - ANSWER Financial Management, HR Management, Resource Management
Financial Management Competencies - ANSWER 1. funding
2. ROI of programs
3. budget for programs
4. cost ben
...
Key Competencies for Comp Professionals - ANSWER Financial Management, HR Management, Resource Management
Financial Management Competencies - ANSWER 1. funding
2. ROI of programs
3. budget for programs
4. cost benefit thinking
5. expendetures
6. Cost effective approaches
7. procurement & contracting
8. performance plans
HR Management Competencies - ANSWER 1. Assess current and future staffing needs based on goals and budget.
2. Ensure staff are selected, developed, appraised and rewarded
3. Take corrective action
4. Understand basic org design principles
Resource Management Competencies - ANSWER 1. Determine sources and collect data to facilitate decisions
2. Partner with internal staff and external consult/vendors
3. Use efficient and cost effective approaches to integrate technology
What sets apart top performers - ANSWER The ability to tie the key competencies together, distill key messages and make impactful decisions
Business acumen skills and behaviors - ANSWER 1. Mission, vision, values. Understanding the purpose of your organization, how it creates value, how it makes money
2. Business strategy. Understandings your customers competition and competitive advantage
3. Organizational culture. Understanding the culture and subcultures of the organization
4. HR strategy. Ability to speak about your area of expertise and collaborate with others
Business acumen for the comp professional - ANSWER Demonstrate influencing and negotiation skills, be an expert with data, navigate regulatory challenges
The importance of business acumen - ANSWER Contributions to organizational success, engaging with executive leadership, self improvement and career development
Contributions to organizational success - ANSWER Understand the financial and strategic context of your organization, influence the organizations bottom line and financial results
Engaging with executive leadership - ANSWER Represent the perspective of your area of expertise and articulate its role in business outcomes, align with the company's mission and financial priorities
Self-improvement and career development - ANSWER Better understand connections between you and wider org opportunities for cooperative value creation, understand business disciplines and what is critical to their success, Display confidence and decisiveness, be a better leader, inspire and excite others
Why organizations are in business - ANSWER Purpose is reflected in mission, vision, values, strategy, profit model
Mission - ANSWER The intention or purpose of the business, answers why are we in business?
Vision - ANSWER What organization wants for the future, who we are and where we are heading
Values - ANSWER Guiding principles and or beliefs, how we work and who we are. What kind of organization we want to create in pursuit of our vision
Strategy - ANSWER Goals directions to achieve goals and policies to support. How we are going to compete and achieve our mission and what makes us different
Profit model - ANSWER Plan for how organization generates revenue, why customers are willing to pay
Competitive strategy - ANSWER Broad framework of principles that guide day to day decisions affecting business.
Primary focus of competitive strategy - ANSWER Operational excellence, product/service leadership, customer intimacy
Operational excellence - ANSWER Price/cost-based strategy, combo of price, quality, dependability, ease of purchase, minimizing Waze, rewarding efficiency
Product/service leadership - ANSWER Innovation based strategy, product development, market exploitation, best products, better ideas, commercialize faster
Customer intimacy - ANSWER Solution-based strategy, creating results for customers by building bonds to build loyalty
Market position - ANSWER Star: high market share high growth potential, use cash, sustained growth, high profit
Question mark: low market share hi market growth, use cash ability to generate profit is unknown because low market share
Dog: Low market share low market growth, uses cash from other segments
Cash cow: hi market share low market growth, cash used to develop businesses and other segments, such as question mark's
Business life cycle - ANSWER Start up, growth, mature, decline
Start up lifecycle - ANSWER New, little to no policies, focus on obtaining capital, marketing products, initial sales, cash conservation
Growth life cycle - ANSWER Focus on growing sales, increasing the distribution and Efficiently produce products to meet demand, begin standardizing procedures policies
Mature business lifecycles - ANSWER Focus on maintaining marketshare, improving productivity, reduce costs, improvements to products are evolutionary, greater amounts of cash on hand
Decline business lifecycle - ANSWER Revenues are declining, decide to reinvest, create new, or maximize profits with current products
Linking business strategy and comp strategy - ANSWER Should be aligned with rewards strategy, HR strategy business strategy and comp strategy, comp is often large percentage of operating cost
Elements of comp plan directly influenced by org bsns strategy - ANSWER Investment in resources, fixed and variable comp, market competitive posture
Investment in resources - ANSWER Bottom line directly related to investing in HR resources including comp resources. Bottom line increases = more comp and HR resources. Willing to invest more If high return predicted
Fixed and variable comp - ANSWER The mix may be impacted by bottom line
Market competitive posture - ANSWER The bottom line determines position in the market. Market median or market upper quartile, lead, lag, lead lag
Why do orgs use financial reports - ANSWER Standardize data across companies and industries, promote consistency of financial communication, provide information to Key constituents(leaders, managers, shareholders, lenders, govt)
Types of financial reports - ANSWER Annual report - shows 12 mos result, called the school year, sometimes matches calendar year sometimes not. Quarterly report - shows basic financial results for three months. Compares to previous year same quarter and cumulative comparables, not as detailed
Types of financial statements - ANSWER Balance sheet, income statement, cash flow statement
Balance sheet - ANSWER Statement of financial position as specific date, list whats owned, what's owed, equity of entity. Shows book value of company, represents financial health
Income statement - ANSWER Covers a period of time, shows revenues earned, expenses incurred. Shows profitability
Cash flow statement - ANSWER Explains change during period in cash and cash equivalents, comprehensive view of the company's financial situation
Sources of capital - ANSWER Profit - money that comes from sales. Equity - money that investors pay to own a share of business. Debt - money that is borrowed usually in loans or notes
Profit measures - ANSWER Revenue, gross profit, EBIT, EBITDA, net income, EPS, growth and margin
Revenue - ANSWER Volume x price, The top line on a starting point of an orgs income
Gross profit - ANSWER Revenue-cost of goods sold, how much the Org earns from each unit
EBIT - ANSWER Gross profit minus expenses, earnings before interest and taxes, also called operating profit, how much the Org earns before financing the business
EBITDA - ANSWER EBIT+depreciation+amortization, same as EBIT but adds annual charge from previous captl investments, often largest non-cash expense, indicative of real cash generated by business
Net income - ANSWER EBIT-interest-taxes, Earnings available to equity owners after paying debt and taxes
EPS - ANSWER Net income/common shares outstanding, earnings per-share
Growth and margin - ANSWER Growth rates look at how fast org is growing. Margins at how much organization earns per dollar of revenue, how efficiently operating leverage is.
Market metrics - ANSWER Measure potential gap between shareholder and management expectations for feature, include market ratios and multiples
Price to earnings ratio - ANSWER Stock price/net earnings per-share
Price to EBIT/EBITDA Ratio - ANSWER Stock price/EBIT or EBITDA per share
Price to revenue ratio - ANSWER Stock price/net sales per share
Market to book - ANSWER Stock price/book value per share
TSR(total shareholder return) - ANSWER Measures the total return shareholders have earned on their investment
Uses of financial data and metrics - ANSWER Working capital efficiency, return on capital.
Working capital efficiency - ANSWER How quickly org converts short-term capital to cash
Accounts receivable turnover/days receivable, inventory turnover/days inventory, payable turnover/days outstanding
Return on capital - ANSWER How effectively org is investing capital.
Return on equity = net earnings/shareholder equity, return on assets = net earnings/total assets, return on capital/invested capital = net operating profit after taxes/invested capital, economic value added = net operating profit after taxes minus (capital times cost of capital)
Time value of money - ANSWER Present value will increase to a future value with the inclusion of time and interest rate
Money in the past/money today/money in the future - ANSWER Money in hand today is worth more than money promised at sometime in the future because it can be invested with interest and grow overtime
Future value - ANSWER Looks at current holdings and determines how much investment will grow overtime
Present value - ANSWER Looks at desired value in future and determines how much needs to be invested today to realize that amount
Accrual accounting - ANSWER Most common accounting practice of companies, revenues and expenses are recorded when they occur regardless of cash flow
Accrued revenue - ANSWER When company ships order it is recorded as sale even though payment is not received until future
Accrued expenses - ANSWER Payday Jan 8 is for prior two weeks, accrued cost for two weeks are recorded in prior years income statement including base salary and related benefits
Evaluating the organizations financial state - ANSWER Businesses evaluate to make decisions on expected return, occurs in annual budgeting and long-range planning
Forecasting - ANSWER Determining what the future holds based on historical data and External factors
Questions to ask when making forecast - ANSWER What will our workforce needs be, how will pension liability change, how fast will markets grow or shrink, can we gain market share, can we increase pricing, how much money do we need, are prices stable
Forecasting profit questions - ANSWER How much profit are we earning for each dollar of revenue, how much profit are we earning compared to peers
Growth forecasting questions - ANSWER How fast are we growing by measuring revenue, fixed and variable cost, profits, division or productline.
Investment forecasting questions - ANSWER Where do we have to invest to generate profit, what is our maintenance capital expenditure, what is our investment capital expenditure.
Business analytics - ANSWER Refers to skills, technologies, applications, practices of exploration an investigation of business performance to drive planning
Strategic analysis - ANSWER Evaluating the industry and market economics, understanding business and competitive strength and weaknesses, determining possible future changes
Evaluating the industry and market economics - ANSWER What is state of industry now, is it expected to change
Understanding business and it's competitive strengths and weaknesses - ANSWER What is competitive position relative to other industry participants, what are your competitive advantages, disadvantages
Determining possible future changes - ANSWER How is industry expected to change, what are we doing to improve our competitive position
Data analysis gaps - ANSWER Identify missing data plan to address gaps, recognize when not using data effectively
Data analysis trends - ANSWER Identify trends and key messages emerging overtime, review budget requests over 2 to 3 years, key issues and messages
Key performance indicators - ANSWER Cost analysis, cost leverage, operating profit, marginal cost
Cost analysis - ANSWER Fixed cost - do not vary; staff, audit fees, maintenance, rent
Variable costs - vary for each dollar of revenue, sales low equals costs low, sales high equals production cost high, wages of production staff, sales comp, Raw materials, shipping
Cost leverage - ANSWER If org grows revenue faster than costs profit growth will accelerate. Find a balance in order to maximize profit
Operating profit - ANSWER Profits accelerate as sell more for same fixed cost, better when costs do not increase at the same rate as sales
Marginal cost - ANSWER If revenue accelerate faster than costs then cost per unit sold will decrease as you produce and sell more
Other performance metrics - ANSWER Financials - revenues, earnings. Needed to measure financial success, too much focus can overshadow other critical factors.
Customers - includes market share, customer satisfaction and loyalty poor performance can equal decline even if financial state strong
Internal processes - productivity, quality, deadlines. Tell how business is running a line process, reduce duplication, improve productivity
Innovation and learning - employee satisfaction/engagement, turnover, employee value proposition. Employee training and development industries where employees are primary resource
Budgeting - ANSWER Amount of revenue to be generated, cost to generate, other expenses including debt
Qualitative data - ANSWER The people, talk to key stakeholders and employees to get concerns of workforce
Quantitative data - ANSWER The numbers
Multiple perspectives - ANSWER Understanding of other functional areas, looking at business problems. Healthy tension creating a check and balance feel identify areas of conflict, leverage ability to communicate
Operating departments - ANSWER Narrow view of comp. Want to spend to attract, retain and motivate. May think comp is the problem or change to comp plan is solution
HR - ANSWER All business problems are ultimately HR problems. Need to spend a certain amount to attract retain and motivate, need comp programs to complement strategies
Legal - ANSWER Direct tie to comp. Follow local regional and national laws and regulations
Finance - ANSWER Wants to see spending allocated wisely to increase margins and Max probability with focus on variable costs over fixed costs
Investor - ANSWER Wants to see long-term success and viability and growth. Want to see money spent wisely
Effective communication - ANSWER Comp uses many technical terms. Understand your audience. Prepare to Taylor communication
Collaborate - ANSWER Contribute to Org goals, identify key influencers, decision-makers; consider how to help them achieve objectives, give consideration to partnerships with finance
Contribute to organizational goals - ANSWER Easy to get caught in comp silo, business acumen helps with big picture and how comp should contribute to larger goals
Identify key influencers and decision-makers - ANSWER Where does the power lie, who do employees listen to, who will be the opponents, how do you address concerns
How to help achieve objectives of decision-makers - ANSWER Build alliances
Special consideration to partnerships with finance - ANSWER Need data from finance to support numbers. Collaboration should be continuous channel for cultivating data sources
Connecting with other business units - ANSWER Keep up to date on org challenges, work on key initiatives, discover challenges of line managers, identify and develop proactive measures
Employee connections - ANSWER Understand needs of emplotees in diff units and ar diff levels, know who you can turn to for help
Individual contributors - ANSWER Communication position = me, focus on own comp, how do you pay decisions affect them, primary communication around major program changes
Managers - ANSWER Communication position: me and my staff. How levels are set, guidance and setting and adjusting staff pay, guidance in communicating pay related issues
Executives - ANSWER Communication position: me, my staff, the organization. Managing pay for large groups, understanding broad program objectives
Presenting to executives - ANSWER Articulate the problem, provide relevant facts and data, recommend a solution
[Show More]